LEC 7.1: Health & Wellness
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Health
Traditionally defined as presence or absence of disease
Clients have different meanings of this
Nightingale
Who defined health as the state of well-being and using every power the individual possesses to fullest extent?
WHO
Who defined health with a more holistic view, state of complete physical, mental, social, well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity?
Individual lives are affected by everything, including climate, food, shelter, family and friends.
Talcott Parsons
Who conceptualized health as the ability to maintain normal roles?
US President Commission on Health Needs of the Nation
Who stated that health isn’t a condition, it is an adjustment and it is not a state but a process?
American Nurses Association (ANA)
Who stated that health and illness are human experiences and presence of illness doesn’t preclude health nor does does optimal health preclude illness?
Wellness
State of well-being that includes daily decision making, stress management, exercise, and the whole being of an individual
Anspaugh
Who proposed the 7 Components of Wellness?
Environmental
Occupational
Intellectual
Physical
Social
Emotional
Spiritual
What are the 7 Components of Wellness (Anspaugh)?
Environmental
One of the 7 Components of Wellness
Creating healthy and sustainable ___
Occupational
One of the 7 Components of Wellness
Finding satisfaction with job, work-life balance
Intellectual
One of the 7 Components of Wellness
Engaging in life-long learning and critical thinking
Physical
One of the 7 Components of Wellness
Maintaining a healthy body
Social
One of the 7 Components of Wellness
Building and maintaining positive relationships
Emotional
One of the 7 Components of Wellness
Coping mechanisms
Spiritual
One of the 7 Components of Wellness
Finding the meaning of life; mindfulness
Clinical Model
Role Performance Model
Adaptive Model
Eudaimonistic
Agent-Host Environmental/Ecological Model
Health Illness Scale
Dunns High Level Wellness Grid
Illness Wellness Continuum
What are the 8 Models of Health & Wellness?
Clinical Model
One of the 8 Models of Health & Wellness
People are viewed as physiological systems with relationship functions, and health is identified by absence of signs and symptoms of disease or injury
Role Performance Model
One of the 8 Models of Health & Wellness
Health defined in terms of the individual’s ability to fulfill societal roles that are to be performed in their work
People that can fulfill their roles are healthy even if they have clinical illness
Example: Even if a man has migraine and still goes to work, he is considered healthy under this model.
Adaptive Model
One of the 8 Models of Health & Wellness
Health is a creative process
Disease is the failure in adaptation — maladaptation
Extreme good health is flexible adaptation to the environment and interaction with environment to maximum advantage
Eudaimonistic
One of the 8 Models of Health & Wellness
Incorporates comprehensive view of health
Health is conditioned actualization of realization of an individual’s potential
Related to Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Agent-Host Environment/Ecologic Model
One of the 8 Models of Health & Wellness
Only in community health
Used in predicting illness rather than in promoting wellness
Composed of 3 Interactive Elements: Agent, Host, Environment
Agent
Host
Environment
What are the 3 interactive elements of the Agent Host Environment/Ecologic Model?
Agent
One of the 3 interactive elements of the Agent Host Environment/Ecologic Model
Any environmental factor or stressor (biological, chemical, mechanical, physical, and psychosocial) presence that can lead to illness/disease
Host
One of the 3 interactive elements of the Agent Host Environment/Ecologic Model
Person who may/may not be at risk of acquiring a disease
Reaction influenced by family history, environment
Environment
One of the 3 interactive elements of the Agent Host Environment/Ecologic Model
All factors external to host that may/may not predispose the person to the development of disease
Health Illness Scales
One of the 8 Models of Health & Wellness
Used to measure persons perceived level of wellness
Health and disease can be viewed as opposite ends of a health continuum
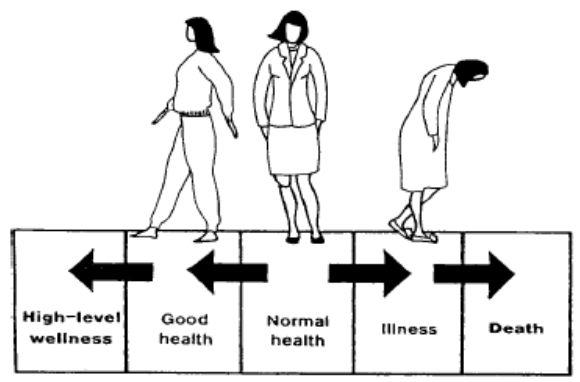
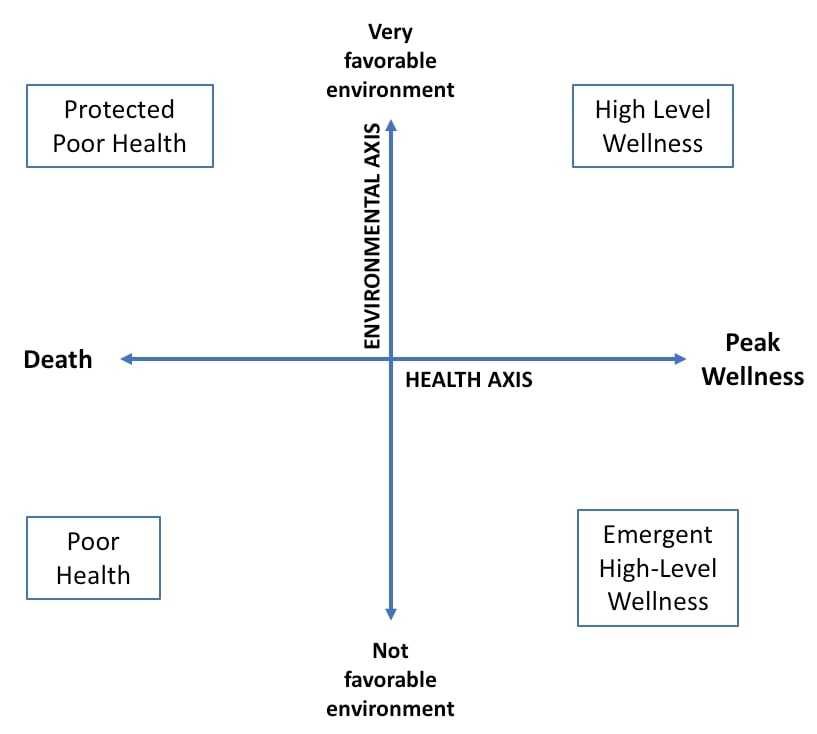
Dunn’s High Level Wellness Grid
One of the 8 Models of Health & Wellness
Health axis and an environmental axis intersect
Grid demonstrates the interaction of the environment with the illness-wellness continuum
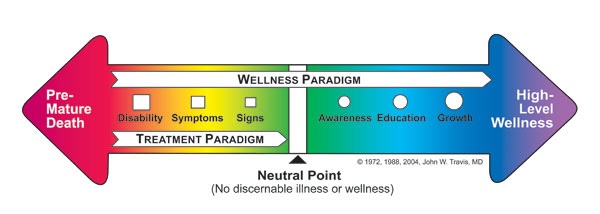
Illness Wellness Continuum
One of the 8 Models of Health & Wellness
Movement to the (right) side of the central point indicates increased levels of health
Achieved via health knowledge, disease prevention, health promotion, and positive attitude
Internal Variables
External Variables
Family or Cultural Beliefs
Social Support Networks
What are the 4 Variables Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors?
Internal Variables
One of the 4 Variables Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors
Biological, psychological, cognitive dimensions
Cannot be changed but can be influenced for health promotion and illness prevention
Biological
Psychological
Cognitive
What are the 3 components of Internal Variables (a Variable Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors)?
Biological
One of the 3 components of Internal Variables (a Variable Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors)
Genetic makeup, sex, age, developmental level
Example: Research has shown that those with African heritage are more prone to sickle cell disease and stomach ulcers.
Psychological
One of the 3 components of Internal Variables (a Variable Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors)
Mind-body interactions, self concept
Cognitive
One of the 3 components of Internal Variables (a Variable Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors)
Lifestyle choices, spiritual, religious beliefs
External Variables
One of the 4 Variables Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors
Includes Environment and Standards of Living
Environment
Standards of Living
What are the 2 Components of External Variables (a Variable Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors)?
Environment
One of the 2 components of External Variables (a Variable Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors)
People becoming increasingly aware how environment…
Geographical location and environment affects health
Example: Due to weather, cough is prevalent in the Philippines.
Standards of Living
One of the 2 components of External Variables (a Variable Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors)
Occupation, income, and education related to health, morbidity, mortality
Example: A wage earner prefers to spend salary on things for their family rather than on regular health check-ups.
Family & Cultural Beliefs
One of the 4 Variables Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors
Passes customs to offspring
Example: A man who was abused as a child is more likely to abuse his own children due to his experience of trauma.
Social Support Networks
One of the 4 Variables Informing Health Status, Beliefs, and Behaviors
Family, friends, lovers, job satisfaction
Individuals with inadequate support networks may become increasingly ill before getting checked
Health Locus of Control
Rosenstock & Becker’s Health Belief Model
What are the 2 Health Belief Models?
Health Locus of Control
One of the 2 Health Belief Models
Determines whether a client’s belief in health status is under their own or others’ control (Internal or external)
Internal Locus of Control
Component of Health Locus of Control (one of the Health Belief Models)
Self determined; more likely to make initiative for own life
External Locus of Control
Component of Health Locus of Control (one of the Health Belief Models)
Controlled by outside factors
May doubt changing behavior will do any good
Rosenstock & Becker’s Health Belief Model
One of the 2 Health Belief Models
Health-related action depends on the simultaneous occurrence of the following 3 factors:
Sufficient motivation to make health issues be viewed as important
Belief one is vulnerable to a serious health problem and its consequences
Relief that following a particular health recommendation would be beneficial
Health Adherence/Conformance
Individuals behavior coincides with medical or health behavior
Following the total therapeutic plan
Nurses must ensure client performs activities, understand instructions, and values planned outcomes