A&P Nervous System Lecture Test Guide
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
the brain and spinal cord.
What are the main components which make up the central nervous system?
neuron.
The basic unit of the nervous system is called the ...
excitability.
The ability of the neuron to respond to a stimulus is ...
Afferent neurons
what type of neurons carry sensory signals from the body to the central nervous system.
efferent neurons
why type of neurons transmit motor signals from the central nervous system to the body.
properties of the neuron
excitability, conductivity, integration, and the ability to communicate through synapses are all.
neurotransmitters
dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) are examples of
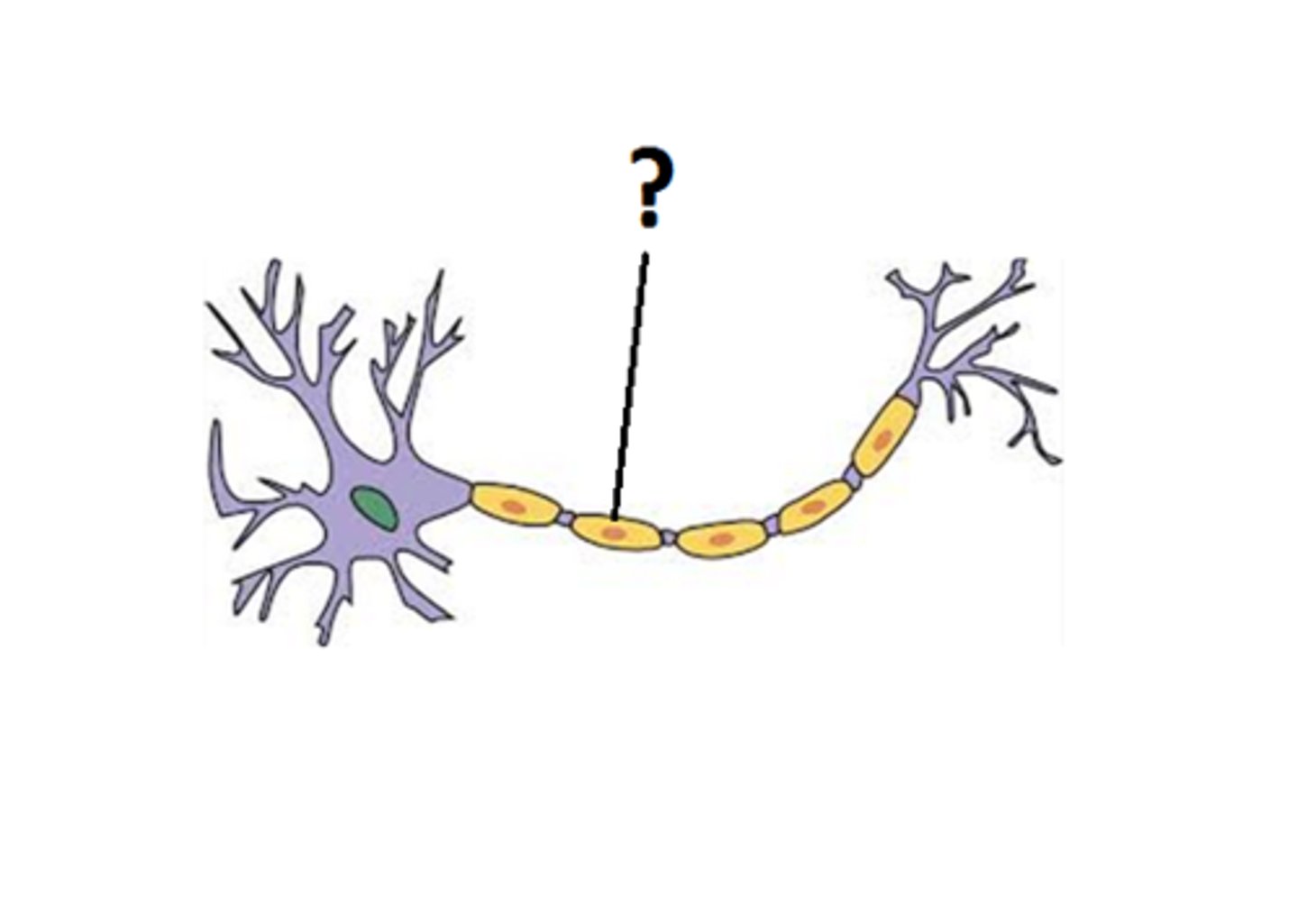
myelin sheath
insulate axons and increase the speed of nerve impulse conduction.
action potential
The wave of depolarization that spreads along the neuron is also called an...
neurotubules
involved in intracellular transport
involved in intracellular transport
Nissl bodies
involved in protein synthesis and are primarily composed of rough endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes.
synaptic boutons
The bulging ends of the axon terminal are called...
dendrites
extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them toward the cell body.
axons
long projections of neurons that transmit electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles.
nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath that facilitate rapid conduction of nerve impulses through saltatory conduction.
IPSP decreases the likelihood of a neuron firing and EPSP increases the likelihood of a neuron firing.
What is the difference between IPSP and EPSP?
sympathetic and parasympathetic
What is the autonomic nervous system made up of?
oligodendrocytes
glial cells in the central nervous system that produce myelin, which insulates axons.
astrocytes
support and maintain the blood-brain barrier, provide nutrients to neurons, and regulate ion concentrations.
microglia
act as the immune cells of the central nervous system, removing debris and dead neurons.
Schwann cells
responsible for producing myelin in the peripheral nervous system and aiding in the repair of damaged nerves.
ependymal cells
line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord, producing and circulating cerebrospinal fluid.
control, coordination, and integration
Major functions of the nervous system include
Central Nervous System (CNS)
the control center for the entire nervous system is
the brain
primary center for regulating and
coordinating body activities. (THE COMPUTER)
spinal cord
center of reflex action containing the
conducting paths to and from the brain.
brain and spinal cord
the Central Nervous System is made up of the
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
convey impulses to and
from the brain (cranial nerves) or spinal cord (spinal
nerves).
afferent and efferent divisions
The peripheral nervous system is made up of:
Afferent (sensory) division
sensory neurons conduct information toward the C.N.S.
Efferent (motor) division
motor neurons conduct information away from the C.N.S.
somatic and autonomic nervous systems
the efferent (motor) division consists of
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
consists of efferent neurons that conduct impulses from the C.N.S. to skeletal muscles, and is under conscious control.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
consists of efferent neurons that conduct impulses from the C.N.S. to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. Usually not under conscious control.
sympathetic and parasympathetic
the autonomic nervous system is subdivided into
Sympathetic Nervous System
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Parasympathetic Nervous System
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
Neuroglial Cells
support and protect the nervous system. includes astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglia
Astrocytes
most numerous, star shaped bodies, that play a major role in the transfer of materials to and from circulation (so-called blood brain barrier). Attaches neurons to their blood vessels.
Oligodendrocytes
functions in myelination of the C.N.S.
Ependymal Cells
cellular layer of epithelial cells that line the ventricles of the C.N.S., modified to produce cerebrospinal fluid; therefore, are also cells of choroid plexus.
Microglia
small phagocytic cells derived from connective tissue. They play a role in the destruction of dead tissue and defense against microorganisms.
Neurons
structural and functional units of the nervous system. they conduct action potentials. 3 major structures include the cell body, dendrites, and axon
cell body
central portion containing the nucleus, nucleolus, and other
organelles.
Nissl Bodies
condensations of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) which form dark staining bodies. They contain RNA and protein, and functions in protein synthesis.
Neurofibrils
slender rod-like structures composed of microtubules and fibrils; they play a role in cell support and release of neurotransmitters.
Dendrites
highly branched, short cell processes which conduct action potentials toward the cell body, (they contain Nissl bodies).
Axon
one long cell process which conducts action potentials away from the cell body (they do not contain Nissl bodies).
Myelin Sheath
white, fatty covering of axons produced by Schwann Cells in the P.N.S.; insulates and protects the axons.
Schwann Cells
produce myelin in the P.N.S.
Oligodendrocytes (neuroglia)
produce myelin in the C.N.S
Nodes of Ranvier
unmyelinated segments of an axon where nerve impulses are produced.
Neurolemma
outermost membrane, the cell membrane of a neuron's Schwann cell. It covers the myelin sheath.
Synapse
where end fibers of the axon of one cell body meet the end fibers of the dendrite of another. Junction between two neurons.
Motor, Sensory, and Interneurons
Functional (Physiological) Classification -
according to the direction in which the impulse is traveling.
Multipolar, Bipolar, and Unipolar
Structural (Anatomical) Classification -
according to the number of processes extending from the cell body.
Motor (Efferent) Neurons
transmit impulses from the C.N.S. to the effected site.
Sensory (Afferent) Neurons
transmit impulses from the effected site to the C.N.S.
Interneurons (Associate Neurons)
found in the C.N.S. and connect sensory neurons to motor neurons.
Multipolar Neurons
most common type have several dendrites and one axon extending from the cell body (ex. - motor neurons).
Bipolar Neurons
have two processes, one dendrite and one axon extending from the cell body; relay information concerning special senses.
Unipolar Neurons
dendrite and axonal process are continuous and both come off the cell body. Sensory neurons are usually amoung these
Exteroceptors
Located near surface, provide information about the external environment such as touch, temperature, hearing, vision, smell, etc.
Interoceptors
Provide information about the internal environment, located in the digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, and reproductive systems; detect deep pressure and pain.
Proprioceptors
Provide information about the position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints.
Nerve Impulse
Depends on polarization and depolarization of the neuronal membrane.
Membrane Potentials
Indicated by the difference between the amount of ion concentration outside the plasma membrane.
Polarization
Potassium (K+) ions are highly concentrated inside the cell, and sodium (Na+) ions are highly concentrated outside the cell.
Depolarization
Allows for transport of Na+ across the cell membrane and into the cell, and K+ outside of the cell; mechanism is called the 'sodium-potassium pump.'
Repolarization
Return of ions to the polarized state.
Action Potential
Initiated after depolarization has taken place; it is the principal way in which neurons communicate.
Refractory Period
When a nerve receives a second stimulus at such a close interval that no response will occur; the nerve must have sufficient time to recover from the initial stimulus.
All or None Response
If a stimulus is strong enough to initiate an action potential, the impulse will travel along a neuron until its transmission is complete.
White Matter
Group of myelinated nerve fibers and associated neuroglia.
Gray Matter
Contains cell bodies and unmyelinated nerve fibers.
Nerve
A group of nerve cells (neurons) located outside the C.N.S.
Tracts
A group of nerve cells (neurons) located inside the C.N.S.
Ascending Tracts
Conduct sensory impulses up the spinal cord to the brain.
Descending Tracts
Conduct motor impulses down the spinal cord.
Ganglion
A collection of neuron cell bodies located in the P.N.S. (that is, outside the C.N.S.).
Nucleus
A collection of neuron cell bodies located inside the C.N.S.
Horns
Areas of grey matter located in the spinal cord.
Posterior (Dorsal) Gray Horns
Contains sensory nuclei.
Anterior (Ventral) Gray Horns
Contains motor nuclei.
Spinal Cord
An ovoid column of nervous tissue about 18 inches long, extending from the medulla oblongata to the 2nd lumbar vertebrae.
Cervical Enlargement
Nerves arising from this region are associated with the upper extremities.
Lumbar Enlargement
Nerves arising from this region are associated with the lower extremities.
Cauda Equina
After the terminal portion of the spinal cord; composed of the roots of spinal nerves below the first lumbar vertebrae.
Denticulate Ligaments
Extensions of the pia mater to dura mater; prevent lateral movement of the cord.
Protection of the CNS
Purpose of the bony cranium & vertebral column, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid.
Meninges
Membranes surrounding the CNS and function in protection.
Dura Mater
A tough outer layer which is fused to the periosteum of the cranial bones and vertebrae; ends at S2.
Epidural Space
Between skull and vertebrae and the dura mater; contains a protective padding of adipose tissue.
Subdural Space
Narrow space that separates the dura mater from the arachnoid meninge.
Arachnoid
The second or middle membrane; very delicate and sends webs down to the pia mater; ends at S2.
Subarachnoid Space
Separates the arachnoid layer from the inner meninge; filled with CSF.
Pia Mater
The innermost meningeal membrane; very thin and delicate, tightly attached to the surface of the brain and spinal cord; ends at L1 ½.
Meningitis
Inflammation of the meninges, generally due to bacteria or virus.
Reflex Arc
A neural pathway between the point of stimulation (receptor) to the brain or spinal cord and to the responding organ (effector).
Components of a Reflex Arc
Receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, effector.