Infectious and Non Infectious Disorders of the Lacrimal Gland and Nasolacrimal Duct
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
main lacrimal glands
at temporal fossa of frontal bone
2 divisions separated by the levator aponeurosis
orbital
palpebral
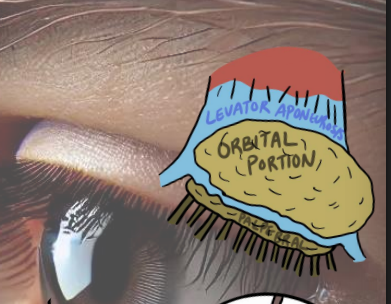
what part of tear film do the main and aaccespry la rimal glands make
aq layer
tubuloacinar exocrine gland secretion
merocrine —> product undergoes exocytosis out of cell
(meibomian are holocrine secretion)
MALT does what
plasma cells wi galnd secrete immunoglobulins
IgA (highest amount) and IgG antibodies
blood supply to lacrimal gland
suplied by laacrimal artery
drained by superior ophthalmic vein
sensory nerve supply to lacrimal gland
CN 5
autonomics of lacrimal gland innervation
parasympathetics of CN 7 —> Facial —> Stimulates lacrimation
sympathetic —> inhibits lacrimation
what are the parts of the nasolacrimal drainage system
lacrimal lake
puncta (upper and lower)
canaliculus (upper and lower)
lacrimal sac
nasolacrimal duct
Valve of Hasner
Inferior Nasal Meatus
what does the Valve of Hasner do
prevent backflow
nerve supply to nasolacrimal drainage system
motor CN 7 —> orbicularis oculi contributes to nasal lacrimal pump mech
how are the canaliculi and sac when the eyes are open
they are expanded
creates - pressure that draws tears in
in closed eye state (by orbicularis) what happens w nasolacrimal system
pars lacrimalis
creates + pressure that forces tears into nasolacrimal duct
pretarsal orbicularis
compresses canaliculi and closes off puncta
NO REGUGITATION OF TEARS
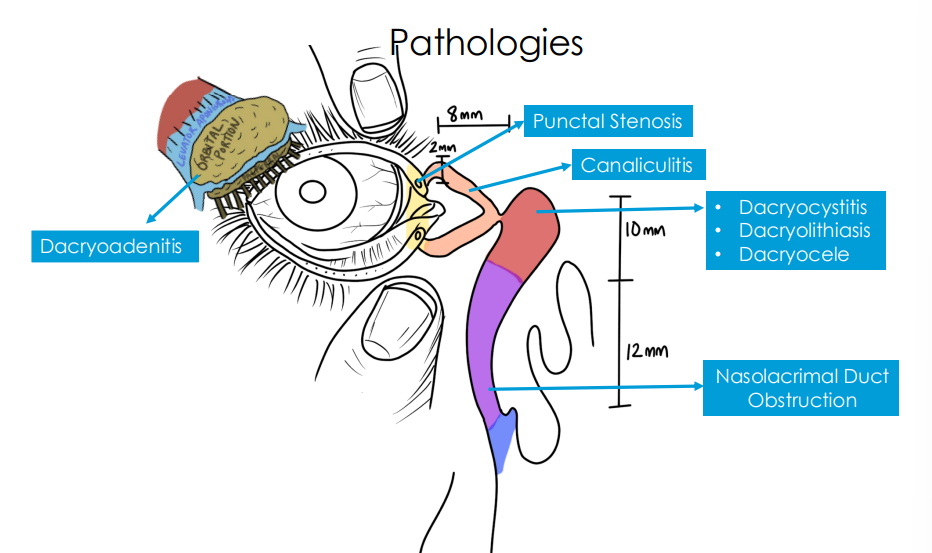
where are the pathoogies
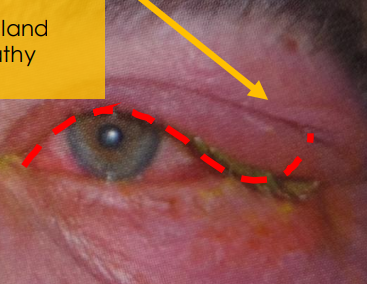
dacryoadenitis (acute) signs
superior temporal eyelid redness
tender and warm to touch
S shaped
unilateral > bilateral
onset it sudden
preauricular lymphadenopathy
symptoms of dacryoadenitis (acute)
upper eyelid is swollen on one side
swollen
pufy
painful to touch
past few days
fever and flu symptoms
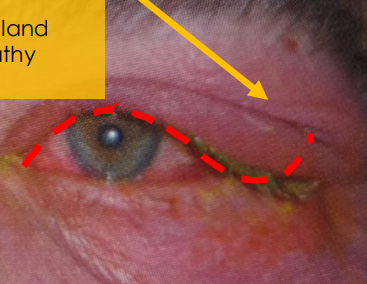
cause of acute dacryoadenities
inflammation of the main lacrimal gland secondary to systemic infection
most likely- viral: Epstein - Barr Virus, herpes zoster, mumps, influenza, adenovirus
bacterial- rare: Staph aureues , Streptococcus pneumonia, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (could be more chronic)
epi of acute dacryoadenities
rare
viral> bacteria
more ocmmon in kids and YA
exam of acute dacryoadenitis
ensure no orbital involvement
check for proptosis, mobility restrictions, (+) RAPD
examine palpebral portion of lacrimal gland for enlargement
findings to look out for
lab test for dacryoadenitis
culture discharge
complete blodo count
imaging for dacryoadenitis
refer for CT if (+) proptosis, EOM restriction, (+) RAPD
SUSPECT ORBITAL CELLULITIS
treating viral Acute Dacryoadenitis
Epstein-Barr, Mumps, Influenza, Adenovirus
observation
palliative therapy - warm compresses BID
self limiting in 4-6 weeks
Herpes Zoster Virus (rash)
treat as so
whats the difference btw viral and bacterial Acute Dacryoadenitis
viral - no pirulent discharge (discharge is watery)
bacterial has pirulent discharge
treating bacterial Acute Dacryoadenitis thats Staphylococcus and Streptococcus:
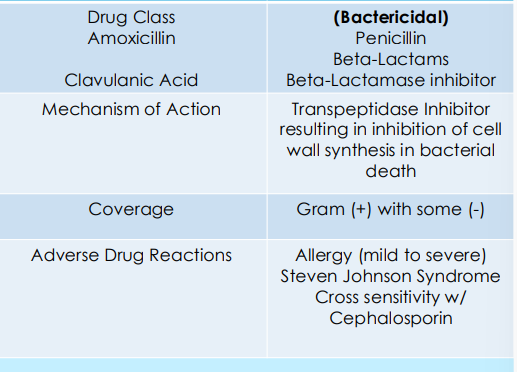
Augmentin 500mg/125mg TID PO
or
Augmentin 875 mg/125 mg BID PO
f/u every day
if no response after 24 horus —> need IV antibiotics (refer)
treating Acute Dacryoadenitis caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
IV antibiotic needed (Refer)
augmentin drug facts
Dacryoadenitis (Chronic) signs
• Superotemporal eyelid swelling and tenderness
• S-shaped edema
• Possible globe displacement and/or ocular motility restriction
• Bilateral > Unilateral
• Enlarged lacrimal glands
• Onset is gradual
symptoms of Dacryoadenitis (Chronic)
“I have chronic upper eyelid swelling of both side, it’s been like this for months. It’s not painful, but I have occasional discomfort and redness.”
Dacryoadenitis (Chronic) cause
nflammation of the main lacrimal gland secondary to inflammatory/autoimmune, or idiopathic origin.
Inflammatory/Auto-immune:
• Thyroid eye disease
• Sarcoidosis •
Sjogren syndrome
• Crohn’s Disease
• IgG4-related disease
• Granulomatosis with polyangiitis •
Rheumatoid Arthritis
DACRYOADENITIS IS CAUSED BY THESE DISEASES
Idiopathic: Idiopathic orbital inflammation/ orbital pseudotumor → diagnosis of exclusion
epi of Dacryoadenitis (Chronic)
• More common than acute infectious dacryoadenitis but overall, uncommon
• Females>Male (due to autoimmune component)
chronic dacruoadenitis eval
Exam:
• Ensure no orbital involvement, check for proptosis, motility restrictions
• Examine palpebral portion of lacrimal gland for enlargement
• Lab Tests: See Management •
Imaging:
• Orbital CT or MRI
• Chest X-ray or CT (if suspecting Sarcoidosis)
• Lacrimal gland biopsy if diagnosis uncertain
• Refer to Oculoplastics
defining features osf lacrimal gland malifnancy
• Gradual onset
no symptoms
palpable hard mass
possible proptosis & double vision with orbital involvement
1. Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
2. Metastasis from other cancers (Breast cancer most common)
3. Lymphoma
• Imaging essential for diagnosis
orbital cellulitis defining features
proptosis
double vision
pain
eyelid dermoid cyst defing features
congenital
firm
non tender
slow growing
unilateral
treating/managing chronic dacryoadenitis - 1 st step
determine cause
serum lab work
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE), Serum Lysozyme→ Sarcoidosis
Thyroid Panel→ Thyroid eye disease
SS-A, SS-B Antibodies → Sjogren Syndrome
HLA-B27→Crohn’s Disease
Rheumatoid Factor→ Rheumatoid A
rthritis Serum IgG4→IgG4 related disease (IgG4-RD)
cANCA→ Granulomatosis Polyangiitis
punctal stenosis
narrowing or occlusion of puncta
<0.3 mm
cause of punctal stenosis
Congenital
• Agenesis, Microphthalmia, congenital stenosis
Acquired Stenosis
• Idiopathic
• Inflammatory → Chronic blepharitis, dry eye
• Mechanical → Lid malposition, trauma, tumors
• Infectious → HSV, Trachoma (Chlamydia)
• Iatrogenic → Surgical, Chronic topical medication use
epi of punctal stenosis
females
idiopathic: aging
pathophys of acquired puncatal stenosis
In acquired stenosis: Irritants draining through puncta causes chronic inflammation leading to gradual fibrotic changes (scar formation over puncta)
clinical presentation of punctal stenosis
Symptoms: Excessive Tearing, Ocular irritation
Signs: Increased tear prism, unable to probe puncta
treatment of puncal stenosis
Punctal dilation
Punctoplasty
canaliculitis signs
red and swelling of puncta and adjacent tisue
pouting punctum
• Mucopurulent discharge from punctum
• Concretions from punctum
• Secondary conjunctivitis
symptoms of canaliculitis
“I have some tenderness around the corner of my eye. There’s also lots of tearing and redness of that area. It’s been this way for awhile, and I noticed worsening gradually.”
canaliculitis cause
Inflammation of the canaliculus resulting in recurrent conjunctivitis.
Infection:
• Bacterial: Actinomyces israelii* (Gram + anaerobe rod) —> ISREAL HAS LONG CANALS
• Fungal: Candida albicans, Aspergillus
• Viral: Herpes simplex or zoster
Retained Foreign body or punctal plug
epi of canaliculitis
uncommon accounts for <4% of lacrimal disease
females
middle aged
evaluation for canaliculitis
Careful slit lamp exam
• Compression of medial punctum to observe discharge and concretions (sulfur granules → actinomyces culprit)
• Lab test: Culture and Gram stain
• Imaging: Dacryocystography
dacryocysitis discriming features
Inflammation of the lacrimal sac • Painful swelling and redness below nasal canthus with no involvement of puncta or canalicular area
dacryolithiasis definig features
Formation of dacryoliths or lacrimal stones within lacrimal sac • Distended lacrimal sac, firm medial canthal mass, no involvement of puncta or canalicular area
dacryocystocele defining features
Ballooning of the lacrimal sac secondary to congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) • Bluish cystic bump below nasal canthus occurring in infants
canaliculitis treatment
warm compresses BID to QID (usually doesnt help)
remove obstructing concretion or punctal pluf thru canaliculotomy
if suspecting bacterial infection (Actinomyces Israelli
Canalicular irrigation with antibiotic solution (Penicillin G 100,000 U/mL) + Oral Penicillin V 500mg QID x 7 days. Follow up: 1-2 week
Dacryocystitis signs
Swelling and redness below the medial canthal tendon
• Lacrimal sac tenderness on palpation
• Expression of discharge
• Fistula or cyst formation
Dacryocystitis symptoms
corner of eye is very painful!!!
swollen and red
tearing and crusting
happend over last few days
Dacryocystitis Etiology cause
inflammation of the lacrimal sac
acute dacryocystitis cause
Bacterial infection • Streptococcus pneumoniae (Gram +) • Staphylococcus (Gram +) • Pseudomonas (Gram -) • Haemophilus influenzae (Gram -) → In children
dacryocystitis chronic cause
Secondary to Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction (NLDO)
epi of dacryocystitis
Right after birth for congenital form
• >40 yo for acquired form
• Females>males
eval for dacryocystitis
• Careful slit lamp exam
• Digital massage of lacrimal sac
• Lab test: Culture and Gram stain punctal discharge
• Do NOT probe with acute infection —> would just spread it
canaliculitis discriminating features
milder pain
chronic presentaion
pouting punctum
treating acute dacryocystitis
warm compresses 2 or 4 times a day w gentle massage
NO FEVER AND MALAISE
Oral Antibiotics
• Augmentin 500mg/125mg TID x 10 days
If Penicillin allergy: • Bactrim DS 800mg/160mg BID x 10 days
IF FEVER AND MALAISE
refer
whats the f/u for acute dacryocystitis
daily until reprovement
they may need IV antibiotics
chronic dacryocystitis treatment
treat underlying nasolacirmral duct obstruction
what can crhonic dacryocystitis lead to
dacryolithiasis
dacryolithiasis cause
Formation of dacryoliths or lacrimal stones within lacrimal sac from chronic dacryocystitis and nasolacrimal duct obstruction.
• Clumping of lacrimal sac epithelial cells with protein and debris forming a calcified cast within lacrimal sac
• Often incidental finding during dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR)
clinical presentation of dacryolithiasis
Symptoms: Excessive and intermittent tearing or asymptomatic
Signs: Distended lacrimal sac, firm medial canthal mass
treatment of dacrylithiasis
removed during Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR)
dacryocele (mucocele) sign
Cystic mass inferior to medial canthus
• Bluish discoloration of skin
• Mucopurulent discharge
• Matting of lashes
symptoms of Dacryocele (mucocele)
”My infant has this blue colored bump on the corner of his eye(s). He has some discharge and crusting when he wakes up.”
cause of dacryocele
Ballooning of the lacrimal sac secondary to congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO)
pathophys of dacyocele
Trapping of mucus or amniotic fluid in nasolacrimal sac causing distention of the sac which can close off the common canaliculu
epi of dacryocele
Occur in utero or during early neonatal period
• Females>Males
• Occur in 30% infants with congenital NLDO
• Most often unilateral but 30% can be bilateral
• ~50% develop acute dacryocystitis (infection)
congenital NLDO —> can cuase
if left untreated then you can get acute dacryocystitis
evaluation of dacryocele
Exam:
• Digital massage to express mucus
• Evaluate for signs of infection (fever, malaise, purulent discharge) •
Imaging: Endoscopic nasal examination
dermoid cysts definign feature
Congenital benign tumor
• Occurs nasally if frontomaxillary suture is affected
• Well delineated, mobile, skin colored cyst located above nasal canthal tendon
nasofrontal encephalocele differentials
we aren’t talkin ab it
Congenital incomplete closure o neural tube causing herniation of brain tissue
• Typically located above nasal canthal tendon
• May have neurological complications
pretty obvious
orbital rhabdomyoscarcoma defining things
Rapidly progressive rare childhood soft tissue cancer, not present at birth
• Rapidly developing proptosis and globe displacement, and nose bleeds
treating dacryocele if theres an infection
acute dacryocystitis
Hospital admission for observation and treatment with IV antibiotics.
dacryocele wo infection
unilateral
conservative management
digital massage
bilateral
prompt sx to prevent airway obstruction
Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction (NLDO) signs
• Chronic, typically unilateral
• Watery eyes, eyelash crusting
• Medial lower eyelid redness (secondary to excessive dabbing with tissue)
Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction (NLDO) symptoms
”I have constant watering of one eye that I’m always wiping away. It’s been on going. There’s no pain, it’s just bothersome.
redness on old ppl could be from excessive dabbing
congenital NLDO cause
Present since birth most often due to imperforate membrane over the valve of Hasner at nasal end of duct.
primary acquired LNDO cause
Involutional stenosis of the nasolacrimal duct due age-related narrowing of the bony lacrimal canal.
Secondary Acquired NLDO (SANDO) cause
Stenosis of nasolacrimal apparatus secondary to:
Infection→ Bacterial, viral, fungal
Inflammation → Granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Sarcoidosis
Neoplasm→ Primary tumor
Trauma→ Naso-orbital-ethmoidal fractures
Mechanical→ Foreign bodies such as dacryoliths
epi of congenital NLDO
premature birth or with Down Syndrome
bilateral in 1/3 of cases
eval of congenital LNDO
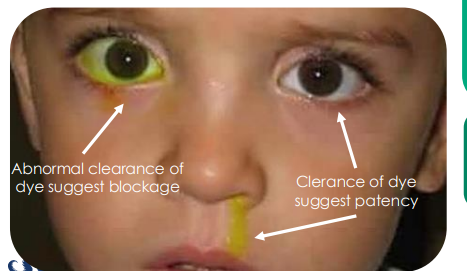
fluorescein dye disappearance test
yellow in eye = abnormal so blocked drain
yellow in snot = clearance of dye if godo
trichiasis defining features
normal lacrimal drainage
tearing is due to reflex tearing
congenital glaucoma defining features
increased IOP
cloudy cornea
buphlatlmos (large yes)
photophobia
bacterial conjunctivitis defining features
thick and purulent discharge
red eyes
congenital NLDO conservative management
Crigler Maneuver 2-3 x a day
gentle massage over lacrimal duct area
just og down nose basically
surgical managemetn fro congenital NLDO
IF Symptoms persisting > 6 months
1. Probing
2. Balloon Dacryoplasty
• Passage of an inflatable balloon catheter to dilate blocked duct
primary acquired NLDO patho phys
Diameter of lacrimal duct tends to narrow further with age, osteoporotic, and hormonal changes along with built up of sloughed off epithelial cell debris within the ducts leading to obstruction.
epi of primary acquired NLDO
females
females have smaller diameter of lacrimal ducts
eval for acquired NLDO
In Office:
• Fluorescein dye disappearance test
• Jone 1 & 2
• Lacrimal probing
• Dilation and Irrigation
Imaging:
• Dacryocystography, Dacryoscintigraphy, CT, MRI
viral conjunctivitis defining features
acute
bilateral
follicular conjunctivitis
watery discharge
fluorescein dye disappearance test
Checks for presence/ absence of adequate lacrimal outflow
– Especially useful for unilateral tearing
• Step 1: Instill NaFl onto conjunctival fornices
• Step 2: Observe tear film w/ Cobalt filter
• Step 3: Observe after 5 min for asymmetry of dye clearance between eyes.
Jones 1 TESt (Primary Dye test)
• Goal: Checks for lacrimal outflow under normal physiological conditions
• Step 1: Instill NaFl onto conjunctival fornices
• Step 2: @ 2-5 min mark; attempt to recover NaFl from inferior nasal meatus w/ cotton tip
trying to recover dye
swab up the nose
(+) recover y = no blockage
(-) recovery = functional deficit or mechanical block
Jones 2 Test
Goal: Determine if blockage is functional vs. anatomical
• Usually performed after (-) Jones 1 Test
• Step 1: Same up to Jones 1 Test
• Step 2: Lacrimal irrigation w/ cannula
• Step 3: Attempt to recover NaFl from inferior nasal meatus
flush saline thru
(+) recovery = functional deficit
(-) recovery = some kind of mechanical obstruction
lacrimal probing
• Goal: Help determine site of obstruction
• Step 1: Instillation of topical anesthesia
• Step 2: Probe passed through punctum
• Step 3: Feel for “stop” or resistance
hard stop = nasal bridge = blockage is more distal past canaliculus
soft stop = osbtruction at level of canaliculus or sac
dilation and irrigation test
(can forgo previous probing)
• Goal: Determine level of lacrimal drainage system occlusion
• Step 1: Instill topical anesthetic
• Step 2: Lower punctum is dilated (checks for punctal stenosis)
• Step 3: Irrigating cannula placed through canalicular system and saline is injected
usually on inferior bc its easir
normal result of dilation and irrigation
they test it
Dilation and irrigation cannula resistance w no fluid irrigation (they dont tate it)
total canalicular obstruction
fluid irrigation out of opposite canaliculus
blockage of common canalilculus
they dont taste it adn a lot of mucous comes thru opposite puncta
complete NLDO