Electrical circuits & Electrical safety
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What do power supplies do in a circuit?
They provide current to the circuit.
Power Supplies
Cells
What are resistors used for?
To control current in a circuit.
Resistors
Components that limit or control current flow.
What do ammeters measure?
Electric current.
Ammeter
Device connected in series to measure current.
Voltmeter
Device connected in parallel to measure potential difference.
What do switches do in a circuit?
Open or close the circuit to control current flow.
Switch
A device that opens or closes a circuit.
Motor
A device that rotates when current passes through it.
Lamp
A device that emits light when current flows.
Heater
A device that transfers thermal energy when current flows.

Bell
A device that emits sound when current flows.

Relay
A device using a small current to switch on a larger current in another circuit.
Transformer
Device that steps up or steps down voltage and current.
What does a fuse do?
Protects components by melting when current is too high.
Fuse
A safety component that melts to break a circuit when current is excessive.
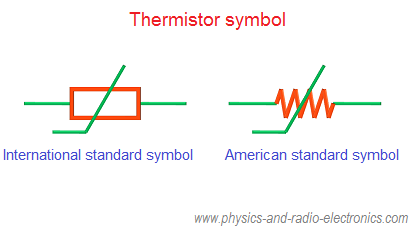
What is a thermistor?
A temperature-dependent resistor.
Thermistor
Component whose resistance decreases as temperature increases.
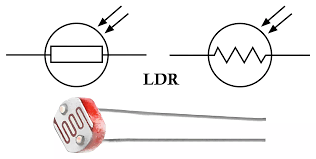
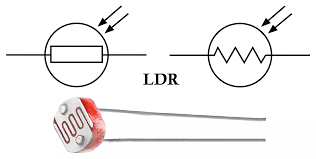
What is an LDR?
A light-dependent resistor whose resistance decreases with light.
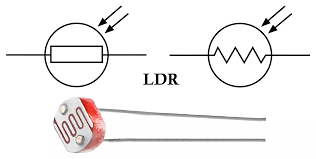
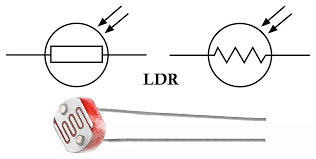
Light-Dependent Resistor (LDR)
A resistor whose resistance decreases as light intensity increases.

What is a diode?
A component that allows current in only one direction.

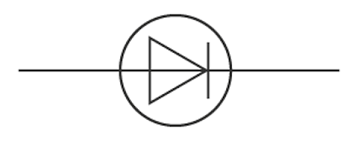
Diode
Component that conducts current in one direction only.

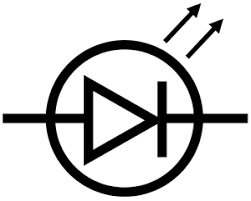
LED
(Light emitting diode) A diode that emits light when current flows.

What is a series circuit?
A circuit with a single complete loop.
Series Circuit
One loop where current is the same at all points.
What is true about current in a series circuit?
It is the same everywhere in the loop.
Current in Series Circuit
Same current flows through all components.
What affects current in a series circuit?
Voltage of the source and total resistance.
Effect of Resistance in Series
More resistance = less current.
Effect of Voltage on Current
Higher voltage = higher current.
What is a parallel circuit?
A circuit with multiple loops or branches.
Parallel Circuit
Multiple loops where current splits at junctions.
What happens to current at a junction?
It splits into branches but total entering = total leaving.
Current at Junction
Incoming current equals outgoing current (conservation of charge).
Lighting Circuits
Parallel circuits used so bulbs have same brightness and work independently.
What is EMF?
The total energy supplied per coulomb of charge by a power source.
EMF in Series
Total EMF is the sum of individual cell EMFs.
Rule for potential difference in series
Sum of PDs across components = total EMF.
Rule for potential difference in parallel
PD across each branch equals the EMF of the power source.
What is the combined resistance in series?
Sum of all individual resistances.
What is the combined resistance in parallel?
Less than the smallest individual resistance.
Resistors in Parallel
Combined resistance drops as more parallel resistors are added.
What is a potential divider?
A circuit that splits voltage between two resistors.
Potential Divider
A pair of series resistors that share the supply voltage.
What does increasing one resistor in a potential divider do?
It increases its share of the PD.
What are common electrical hazards?
Damaged insulation
Electrical Hazard
Any condition increasing the risk of electrocution or fire.
Why is damaged insulation dangerous?
It exposes wires and can cause electric shock.
Why is overheating dangerous?
It may melt insulation or start a fire.
Why are damp conditions dangerous?
Water conducts electricity leading to risk of shock or short circuit.
What are the three wires in mains electricity?
Live, neutral, earth.
Live Wire
Carries alternating current from mains and is the most dangerous wire.
Neutral Wire
Completes the circuit and carries current away at low voltage.
Earth Wire
Safety wire preventing appliance casings from becoming live.
Why is the live wire dangerous?
It carries high alternating voltage.
Why is the earth wire important?
Provides safe path for fault current to prevent electric shock.
What is double insulation?
Two layers of insulation removing need for an earth wire.
Double Insulation
Insulated wires/insulating (non-metallic) case.
Why don’t double-insulated appliances need an earth wire?
Their casing cannot become live.
What is earthing?
Connecting appliance casing to the earth via low-resistance wire.
Purpose of Earthing
Provides a safe path so fault current melts the fuse.
What happens if the live wire touches the metal case?
Earth wire carries current, fuse blows, circuit breaks.
What is a fuse?
A safety device that melts when current is too high.
Fuse Ratings
3 A
How do you choose a fuse?
Select the value just above the appliance’s operating current.
Why does a fuse melt?
Excess current heats the wire until it breaks.
What is a trip switch?
A circuit breaker that turns off automatically when current is too high.
Circuit Breaker
Resettable device that protects circuits from surges.
Consumer Unit
Panel containing trip switches controlling household circuits.
Why are trip switches better than fuses?
They can be reset and respond quickly to surges.