AP Biology final exam
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
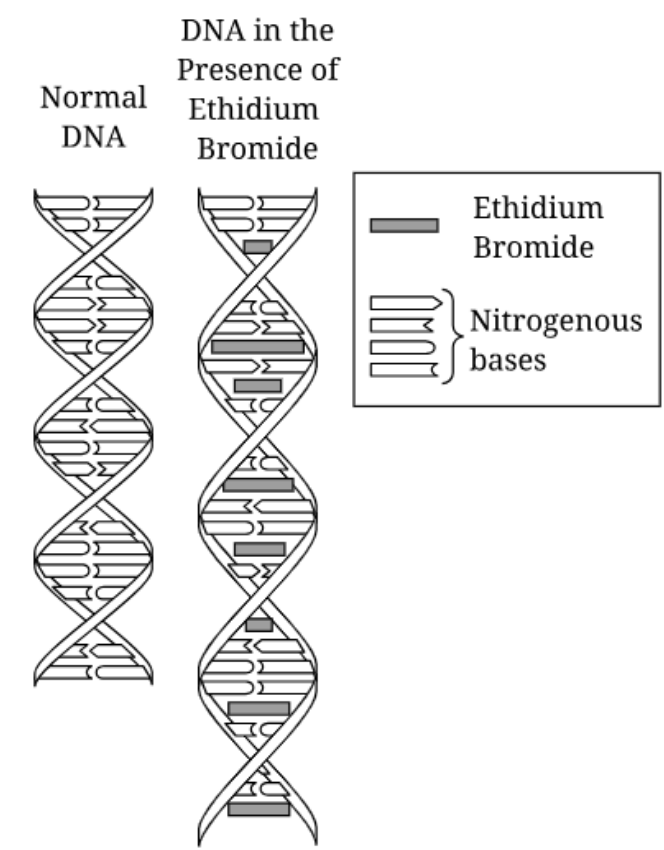
How does Ethidium Bromide effect the normal DNA structure?
It is inserted between sequential nitrogenous base pairs, increasing the length of the DNA molecule
Which two cellular organelles in eukaryotes have both electron transport systems and chemiosmotic mechanisms
Chloroplasts and Mitochondria
What is the response of lysosomes to a signal to start apoptosis?
Release digestive enzymes into the cytosol
List the components that are not found in prokaryotic cells.
nuclear envelope
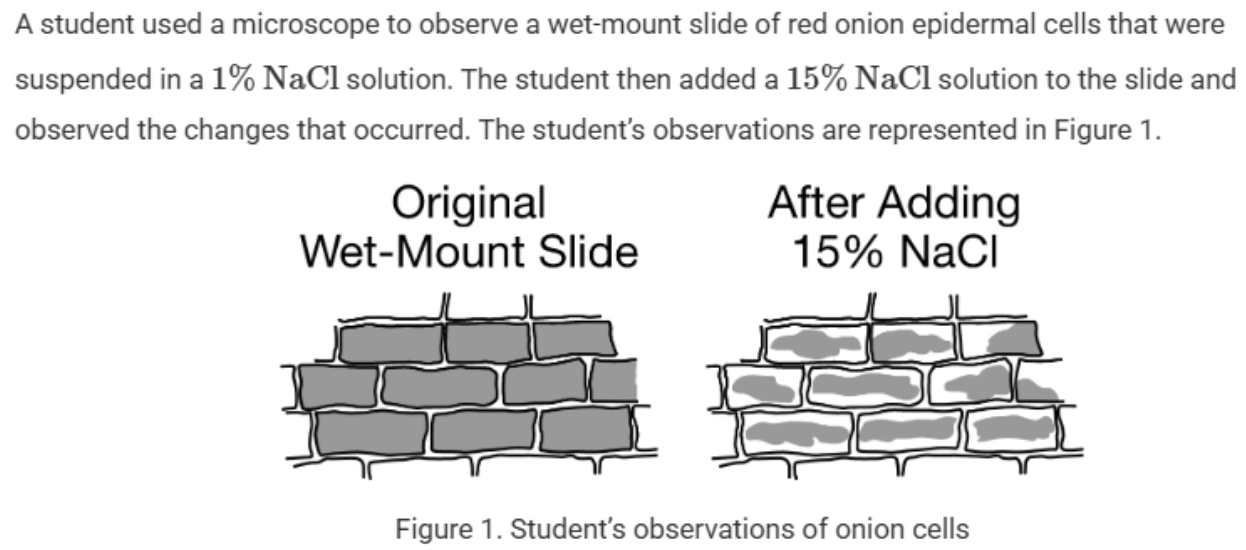
Know the response of water within cells in hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic solutions.
The movement of water from the central vacuoles of the cells into the solution
What is the process in which O2 is released as a by-product of oxidation-reduction reactions?
Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
What is the process in which CO2, is released as a by-product of oxidation-reduction reactions?
Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)
What is the process in which carbon from CO2 is incorporated into organic molecules?
Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions of photosynthesis)
What is the process found in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Chemiosmosis
What is the process in which sugar is oxidized to pyruvic acid?
Glycolysis
Explain how small molecules move between adjacent cells in a plant shoot.
The molecules pass freely through plasmodesmata, which are cytoplasmic strands connecting two cells.
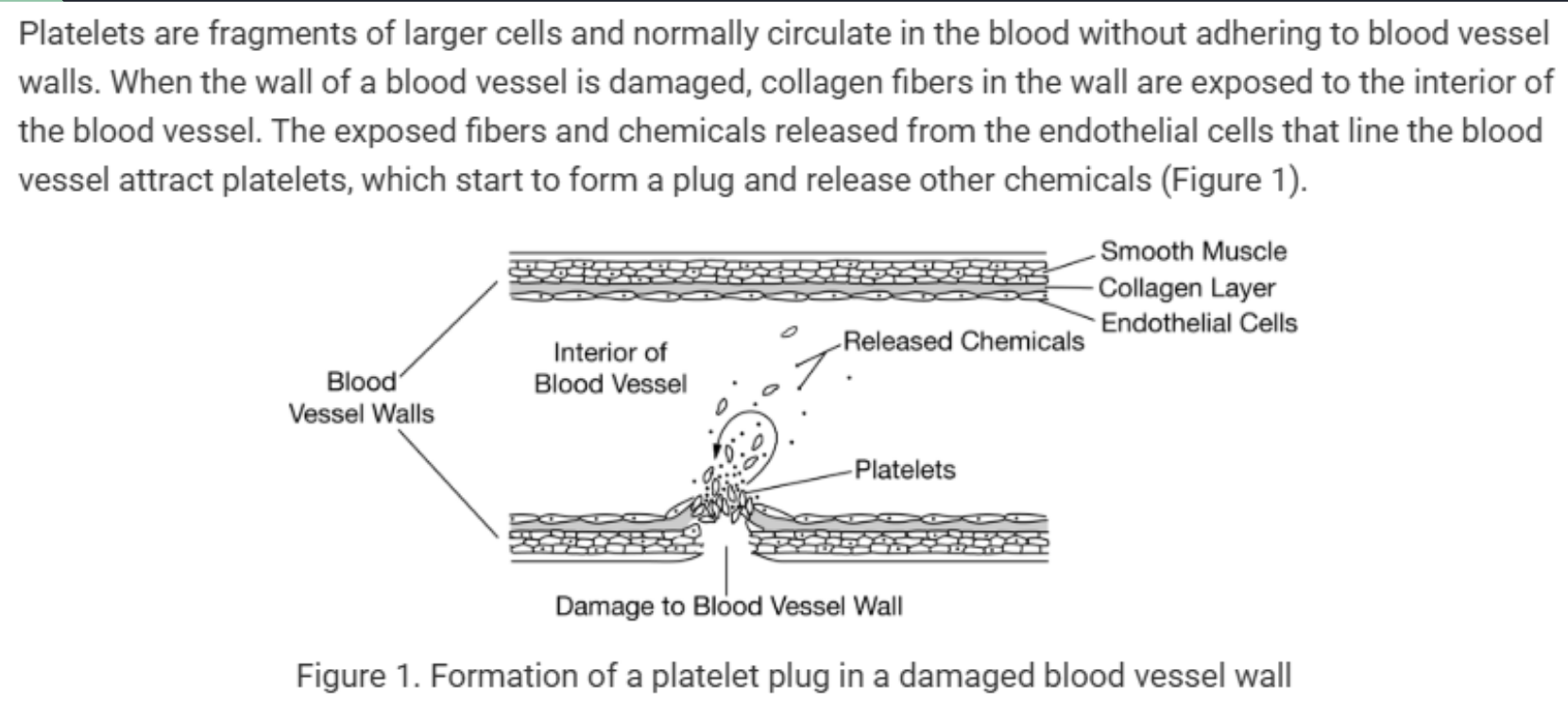
What type of feedback mechanism is occurring in the figure?
This is an example of positive feedback, because the few platelets that initially bind attract more platelets to the damaged area.
Explain the structure and function of the macromolecules found in plasma membranes of eukaryotic cells.
Phopholipids are made up of glycerol, 2 fatty acids, a polar head group with phosphate, and hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail. Its function is maintaining fluidity, to be selectively permeable, compartmenilzation, and to signal.
Cholesterol is a steroid with a ring structure embedded in bilayer, it moderates fluidity and stabilizes membrane.
glycolipid/glycoprotein is a carbohydrate linked to a lipid/protein, its function is cell recognition, attaching to external molecule/other cell
Explain how membranes participate in muscle contraction
Motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), which binds to receptors on the muscle cell and causes depolarization as sodium enters. This depolarization creates an action potential that travels along the sarcolemma and T-tubules. The signal makes the sarcoplasmic reticulum release calcium, which causes muscle contraction, and calcium is later pumped back in to relax the muscle.The Na⁺/K⁺ pump restores the membrane potential, and in smooth and cardiac muscle, gap junctions spread the signal between cells.
Explain how membranes participate in chemiosmotic production in atp
The electron transport chain pumps hydrogen ions (H⁺) across a membrane, creating a concentration gradient.Hydrogen ions then flow back through ATP synthase, which uses this energy to make ATP. Membrane infolding increases surface area, allowing more ATP to be produced.
Explain how membranes participate in intracellular signaling
Cells communicate by releasing chemical signals through exocytosis.
These signals bind to receptors on the cell membrane or pass through it, opening or closing ligand-gated ion channels.
Signal binding triggers a cascade of events inside the cell using second messengers like G-proteins, cAMP, or IP₃.
Cells can also communicate directly through gap junctions (animals) or plasmodesmata (plants), and antibodies help activate immune responses.
role of mitosis in the cell cycle
Mitosis is the stage of the cell cycle where the nucleus divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells, allowing for growth, repair, and maintenance of genetic stability.
basic knowledge of aquaporins
Aquaporins are membrane channel proteins that allow water to move quickly and selectively across the cell membrane by facilitated diffusion.
unique properties of water
Water’s polarity and hydrogen bonding give it cohesion, adhesion, high specific heat and heat of vaporization, lower density as a solid, and the ability to act as an excellent solvent for polar and ionic substances.