4.1- (N/A) Economics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
International Trade
Exchange of goods and services between countries
Benefits of trade
Greater choice of goods and service that improves living quality
Lower prices from international competition that allow household to choose goods that are cheaper
Allows countries to cooperate with eachother which enhances relationship between countries and reduce hostilities
Exchange of new ideas or technologies between countries
Benefit of free trade when world price is above domestic price
When world price is above domestic price, it allows domestic producers to export excess supply
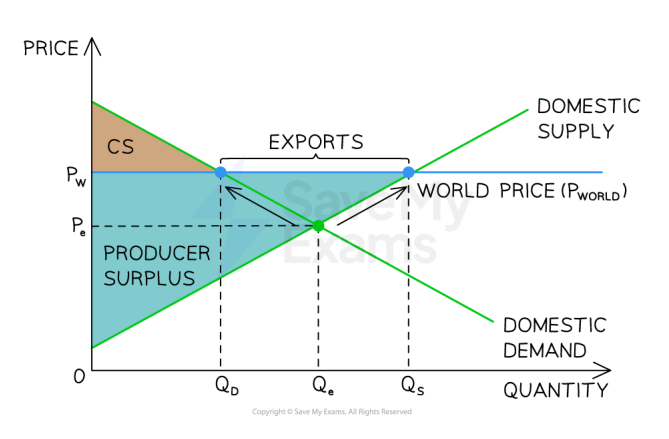
Export revenue
Amount exported x World price
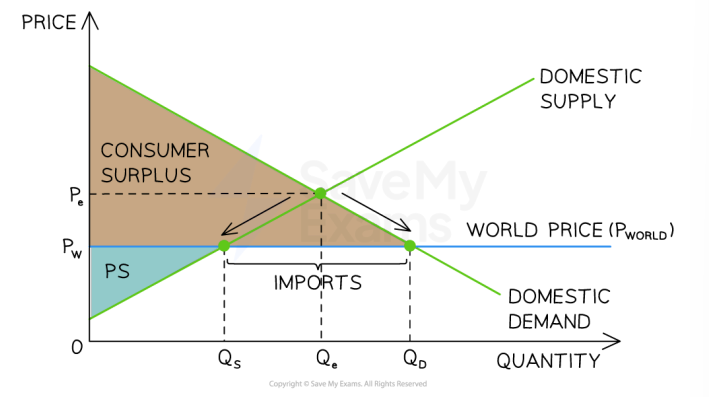
Benefits of free trade when price is below domestic price
Households and firms are incentivised to increase their imports. This is because they cannot compete with the lower prices and domestic supply contracts from Qe to Qs. Excess domestic demand (Qd-Qe) is met thru imports.
Comparitive Advantage
A country should specialize in a good/ service that can produce at the lowest opportunity cost. This causes volume of production to increase as well.
Absolute Advantage
Country is able to produce a good with lower fop than another country.
Sources of comparitive advantage
Natural resoirces
Labour forces
Tech
Capital & Infrastructure
Government support
Economies of scale
Function of Production possibility frontier (PPC)
illustrate gains from trade
Limitations of theory of comparitive advantage
Over-dependence: Specialisation creates dependence on other countries which creates vulnerability.
Environmental damage: Negative externalities arent taken into account by these theories which may harm the quality of life of local areas
Distribution of income: GDP/ capital is likely to increase but the dist of the extra income is likely to be uneven with those more wealthy gaining more
Structural Unemployment: Specialisation cause some industries to shut-down which results in unemployment (long-term unemloyed will rise).
Flawed assumptions
Flawed Assumptions in theory of comparitive advantage
No transportation cost: in reality it costs something to move goods/ services from one location to another
There is perfect knowledge: Countries always know what industry they have comparitive advantage in, and also about other countries-often unture.
Factor substitution is easily achieved
Constant COP: theory doesnt take into acc economies of scale that can be achieved by an inc in output.
Protectionism
Limiting free trade to protect its country through implementing import tariffs, export subsidies, quotas and embargoes.
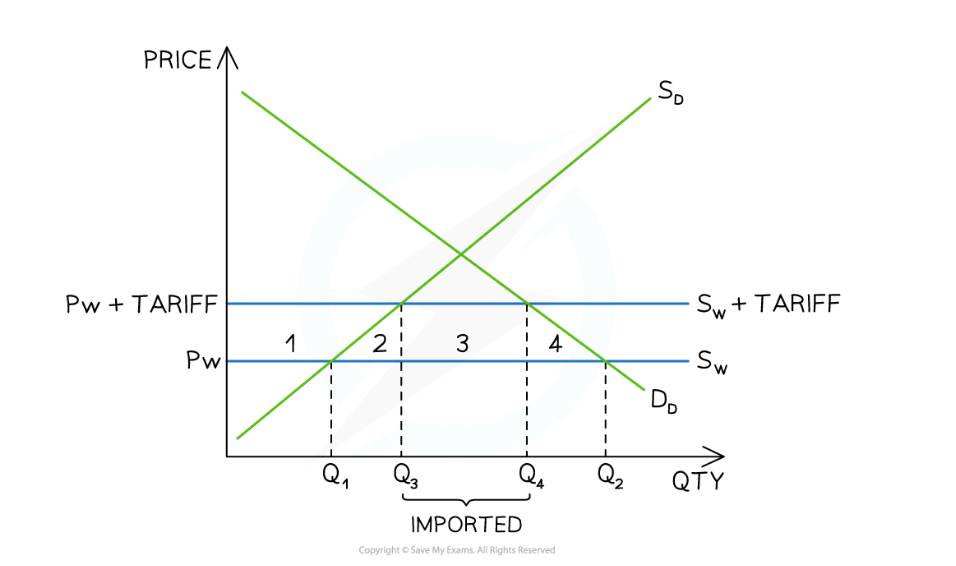
Tariff
Tax imposed on imported goods/ services
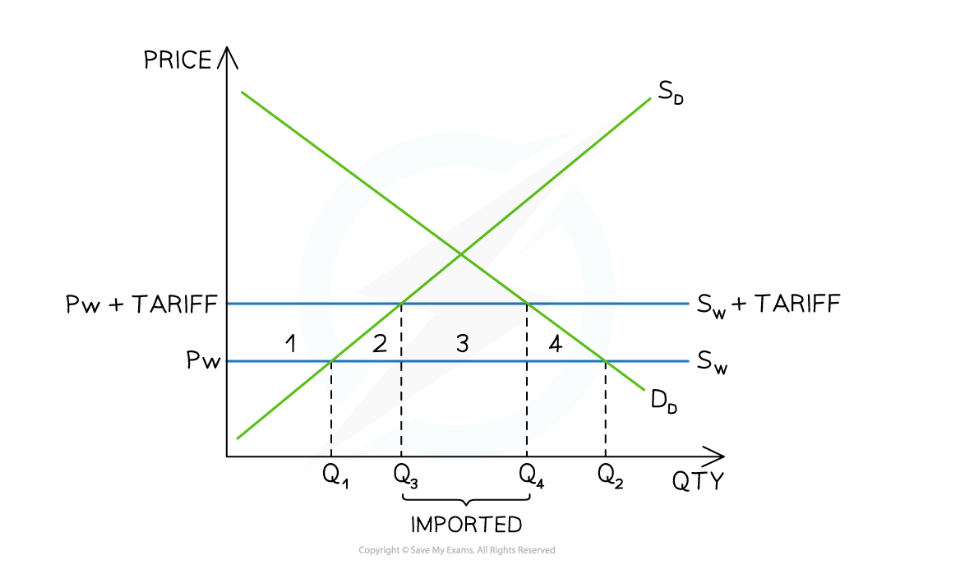
Effect of tariff
It encourages inefficient domestic producers to increase output and market share. This is because foreign producers reduce their output due to tariff. And thru increasing domestic output, employment may increase as well.
Tariff impact on domestic producer
It encourages them to increase in output making them more efficient. This increase in output may also increase employment.
After the tariff was imposed domestic producers produced 0Q3 and their revenue was equal to Pw+tariff x Q3
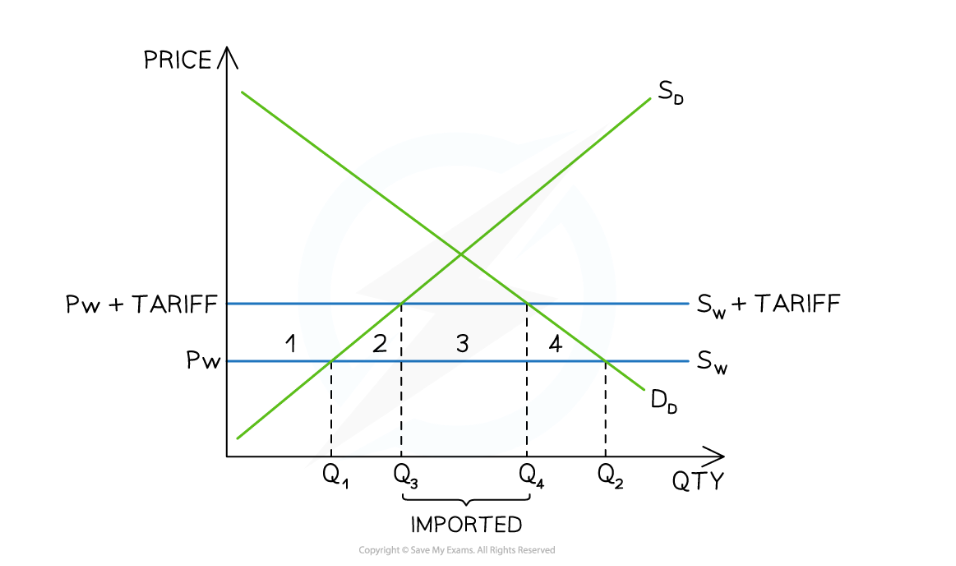
Impact of tariff on foreign producers
Increase in price cause decline in output (Q3Q4) and thus decreasing their revenue too (Q4-Q3). This causs foreign producer surplus.
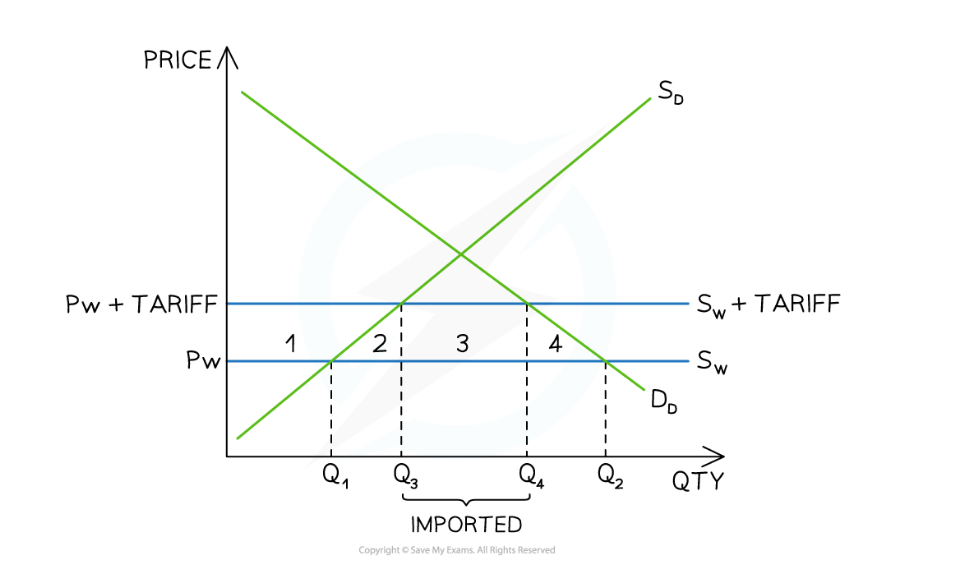
Impact of tariff on Domestic consumers
Domestic consumer purchase less products (Q4) due to increase in price (Pw + tariff). This causes domestic consumer surplus to decrease (area 1,2,3, & 4).
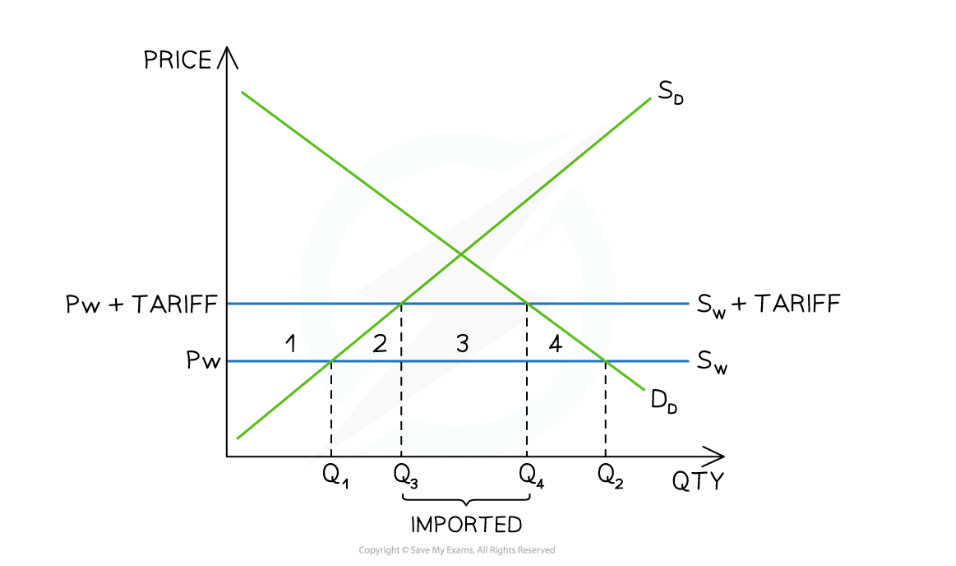
Impact of tariff at government
Receive tax revenue ((Pw+tariff)-Pw) x (Q4-Q3)
Impact of tariff on downstream producers
Since they rely on imported goods for the resource their COP will increase causing an increase in price of their goods/ services. This results in reduction of output and inc in unemployment levels.
Impact of tariff on society
Less efficient domestic firms are now producing at the expense of more efficient foreign producers - there is a welfare loss equal to area 2
Consumers are frustrated with the higher prices and there is no longer allocative efficiency - there is a welfare loss equal to area 4
The net welfare loss is equal to areas 2 and 4