BI 111 Bio Principles - Ecology
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 4 Study Guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Ecology
study relationship btwn organisms and environ (abiotic + biotic)
Biological Organization Hierarchy
Individual
Population
Community
Landscapes
Ecosystem
Biosphere
Community
dif pops that interact
Landscape
multiple communities
Ecosystem
abiotic and biotic that interact
Biosphere
all landscapes
Demography
study of processes that influ birth, death and pop growth rates
Population size estimated from? (2)
density and spatial area
pop density
number indiv per unit of area
geographic range
total spatial area where species can be found
BD Model purpose
pop change over time
per capita model purposes
standardizes pop change
per capita birth rate
number of offspring avg indiv produces
per capita death rate
avg indiv chance of dying
per capita growth rate
avg indiv contribution to total pop growth rate
per capita conditions (3)
if b>d, r>o, pop grows
if b<d, r<o, pop shrinks
if b=d, r=o, pop stays
Multiplicative growth (+ ex)
exponential growth
ex = humans
additive growth
constant number added each time
what is density dependent
per capita growth rate
density dependent
any factor that varies with density
carrying capacity
max pop or density that particular envirn can support
Life history
sequence/duration of stages passed through life
7 things to know from life history
REGSFPP
avg lifetime reproductive success
life expectancy
generation time
survivorship
fecundity
per capita growth rate
projected pop growth
survivorship
proportion of indiv that survive from birth to certain stage
fecundity
avg # daughters each surviving female produces during particular life stage
life expectancy
avg age at death
generation time
avg age mother has daughters
avg lifetime reproductive success
avg number of offspring of indiv
principle of allocation
resources cannot be used for two functions
resources up = 2 things up
fecundity and survivorship
life history tradeoffs
negative relationships among growth, reprod, survival
3 life history tradeoffs
early growth vs longevity
early reprod vs size
parental care vs # of offspring
what max fitness
allocation patterns
fitness
ability to survive and reproduce
intraspecific
w/in species
interspecific
btwn species
Mutualism
+/+
Consumption (ex)
+/-
ex: parasitism
Commensalism
+/0
Amensalism
-/0
Competition
-/-
competitive exclusion
species competing cannot coexist
ecological niche
abiotic and biotic (envir) and species role w/in community
fundamental niche
entire range of envir conditions/resources species could occupy (no limiting factors)
realized niche
actual range (w/ limiting factors)
3 things about complex interaction
more than 2 species
indirect or direct
change through time
Trophic
feeding inerations
food web
diagram of consumption
Trophic cascades
change one species, effect multiple trophic levels
Invasive species
inc, spreads, negative effect
Evolutionary theory
genetic change in pop over time casues
Darwins postulates (3)
species are not immutable (they change)
descent w/ modification (divergent evolution)
natural selection (inc survival/ reprod based on traits)
evolution
change in genetic composition in POP over time
natural selction
dif contribution of offspring to next gen by various genetic type (indiv level)
conditions required for natural selection (3)
variation
heredity
fitness
variation
dif phenotype bs dif genotype
heredity
traits have genetic basis
adaptation
favored trait that spreads through pop via nat select
natural vs artificial selection
both do?
traits that help survival/reprod
or traits preferred by humans
both inc frequency of favored trait from one gen to next
Mechanisms of evolution
NNMGG
natural selection
nonrandom mating
mutation
genetic drift
gene flow
mutation purpose
generate variation that nat select acts on
allele
dif forms of gene
locus
where gene on chromosome
gene pool
all alleles in pop
Genetic drift
random change in allele frequency from one gen to nxt (greatest effect in small pop)
lead to genetic drift (2)
population bottleneck
founder’s effect
population bottleneck
only few indiv survive
founders effect
pop estb by very small pop
gene flow
migration of indiv from one pop to another (changes allele frequencies)
nonrandom mating (3 types)
self fertilization
assortive mating
sexual selection
assortive mating
pos- mate w/ similar traits
neg - mate with dif traits
sexual selection
traits favored reprod potential (even if reduces survival)
stabilizing selection
intermediates favored
directional selection
one extreme favored
disruptive selection
both extremes favored
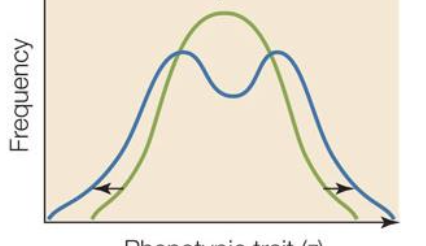
disruptive
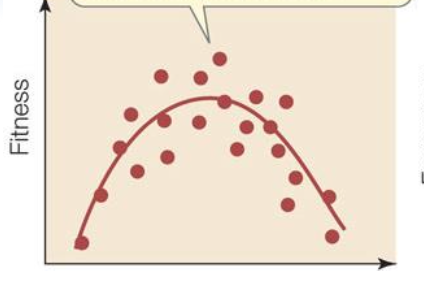
stabilizing
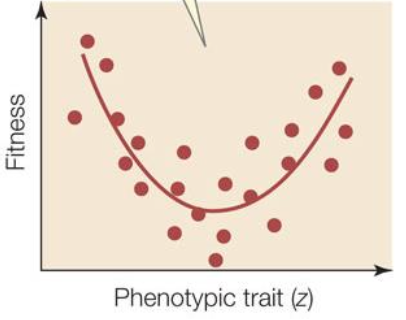
disruptive
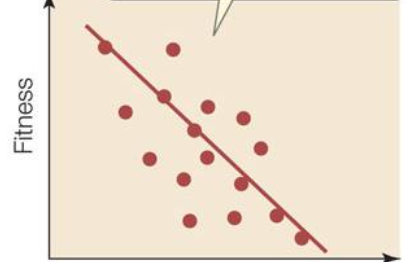
directional
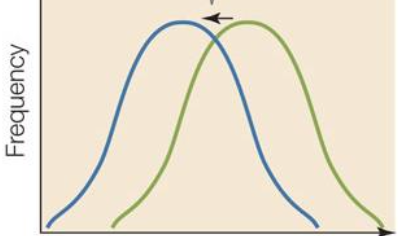
directional
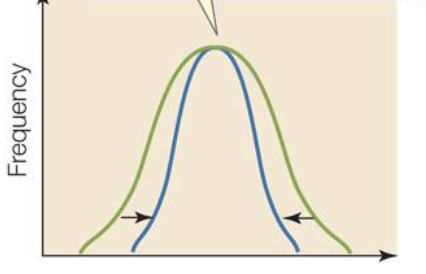
stabilizing
lineage
descended from single ancestor
phylogeny
evol history of particular group and their genes
node =
speciation event
Taxon
named group
clade
ancestor and all decedents
sister clade/taxon
closest relatives
homologous
similarity features bc inheritance
synamorphy
derived from ancestors and present in all descendents
ancestral trait
present in ancestor
derived trait
evolved from ancestral form
homoplasties
similar traits not inherited
convergent evolution
indep changes to same trait
evolutionary reversal
reappearance of ancestral trait
phylogenic tree assumptions (2)
no reversals, no convergence
ingroup
primary interest group
outgroup
closely related, for comparison
parsimony analysis
simplest explanation (fewest evolutionary changes)
phylogeny dats sources
morphology
developmental
paleontology
behavior (based in genetics)
molecular
5 phylogenetic usages
zoonotic disease tracking
forensics
evolution of traits
revealing convergent evolution
dating past events