HTN - Pathophys
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Define HTN
Persistently elevated arterial BP
(usually asymptomatic)
How is HTN diagnosed?
An elevated value from the average of 2 or more measurements, present during 2 or more clinical encounters
What is the most significant risk factor for CVD?
HTN
Prevalence of HTN in Canada
1 in 4 Canadians aged 18 or older
Does HTN typically occur earlier in life in men or women?
Men (but overall incidence is similar)
What is “essential” HTN? (AKA primary HTN)
When we do not know the cause of the HTN (this type cann only be controlled, not cured)
Which type of HTN can potentially be “cured”?
Secondary HTN
What genetic defects can contribute to HTN?
Defects related to:
sodium imbalance
nitric oxide release
aldosterone excretion
angiotensin physiology
(+ others)
Since we can’t identify the genetic defect to guide our therapy, what can be used to guide our choice of therapy?
Population studies
(e.g., stroke is the most important complication among black patients; CHD is more prevalent among Europeans and Americans)
Why are ACEi not recommended as first line therapy for black patients (according to Canadian guidelines)?
Renin is thought to be less active in black patients, so ACEi are believed to be less effective (although mixed results in systematic review)
What % of HTN cases are considered to be 2° HTN?
~10% (either disease or drug or combination cause elevation in BP)
What common OTC medication can lead to secondary HTN?
NSAIDs (always need to ask about their use)
Drugs/substances that can lead to 2° HTN
NSAIDs
OCPs
Corticosteroids
licorice root
SSRIs and SNRIs
cocaine (and other stimulants)
alcohol
sodium
St. John’s wart
(and others)
Withdrawal from which drugs can lead to 2° HTN?
beta blockers
centrally acting alpha agonists (clonidine, methyldopa)
cocaine
nicotine
What is systolic BP?
Pressure when the heart is contracting
What is diastolic BP?
Pressure when the heart is relaxed
How is MAP calculated?
MAP = (1/3 SBP) + (2/3 DBP)
(since heart spends only 1/3 of the time in systole)
When is MAP used clinically?
During hypertensive emergency
What is pulse pressure?
Difference between SBP and DBP (measure of arterial wall TENSION)
When is pulse pressure used clinically?
For isolated HTN (when only systolic is elevated)
How is BP calculated?
BP = CO x TPR
__ is mainly determined by cardiac output
Systolic BP
__ is mainly determined by total peripheral resistance (TPR)
Diastolic BP
What is cardiac output a function of?
Stroke volume
HR
What is stroke volume?
Amount of blood that is pushed out after systole
What is TPR determined by?
functional vascular constriction
structural vascular hypertrophy
What can lead to increased cardiac output?
increased fluid volume (excess sodium intake or reabsorption by kidneys)
venous constriction due to excess RAAS or SNS activity (means more coming back to the heart)
How does BP change with circadian rhythm?
lowest while sleeping
rises sharply a few hours before waking
highest in midmorning
How is BP classified?
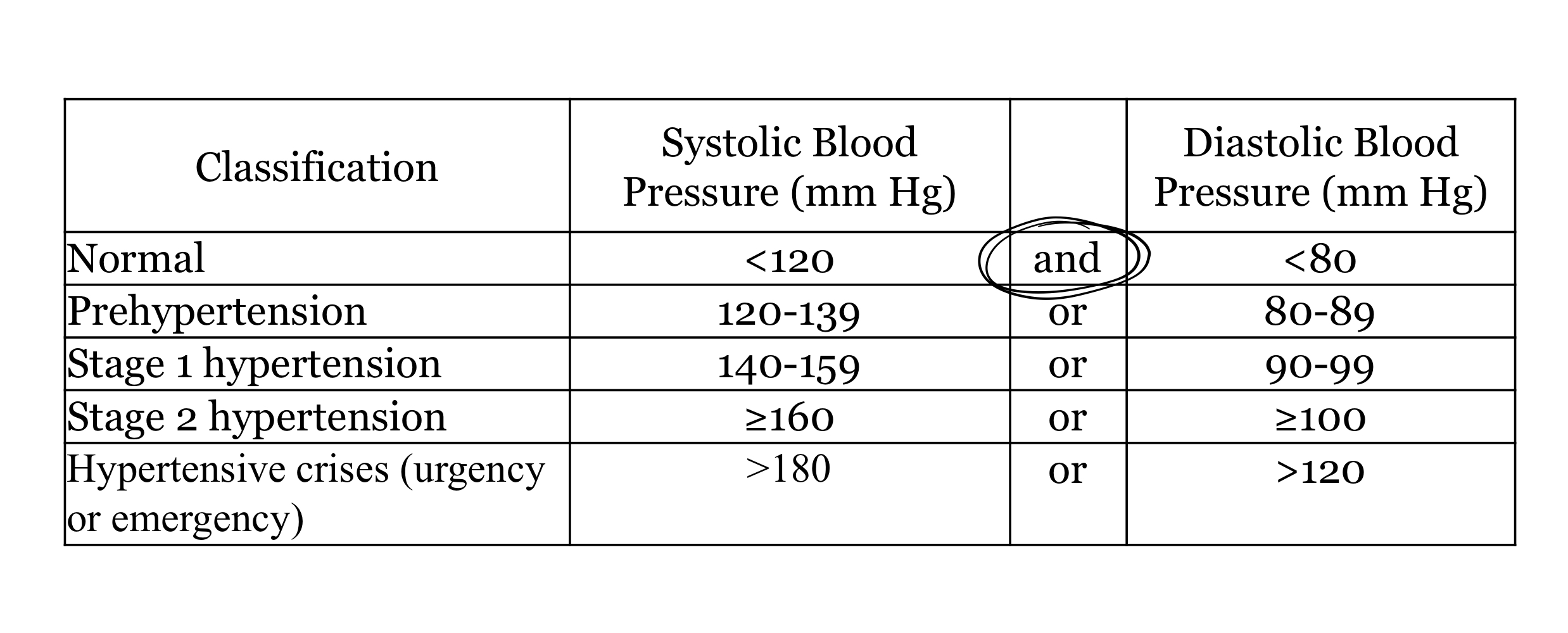
What is believed to be the cause of isolated systolic HTN?
Changes in the arterial vasculature consistent with aging
Why does isolated systolic HTN indicate increased risk of CV morbidity and mortality?
higher pulse pressure = increased arterial stiffness
higher pulse pressure directly correlated with risk of CV mortality in those with isolated systolic HTN
Malfunctions in which mechanisms can lead to essential HTN?
humoral mechanism
RAAS
Natriuretic hormone
Insulin resistance
neuronal mechanisms
peripheral autoregulation
vascular endothelial mechanisms
disturbances in electrolytes (Na, Ca, K)
What is the most important regulator of BP?
RAAS
Where is renin stored?
In juxtaglomerular cells in afferent arterioles of the kidney
What do juxtaglomerular cells do?
They are baroreceptors
How is renin release regulated?
Intra-renal factors:
renal perfusion pressure
level of catecholamines
angiotensin II levels
Extra-renal factors:
levels of Na, Cl, and K (affect macula densa)
What are the different angiotensin II receptors?
AT-1 (brain, kidney, myocardium, peripheral vasculature, adrenal glands)
AT-2 (adrenal medullary tissue, uterus, brain)
What is the target of natriuretic hormone?
Na/K-ATPase
Effects of natriuretic hormone
reduce Na and water in the system (decreases BP)
but also interfere with sodium transport out of arteriolar smooth muscle cells, which leads to increased intracellular sodium and calcium which increases vascular tone (increases BP)
How does insulin resistance lead to HTN?
increased insulin = increased renal sodium retention and sympathomimetic effects
has growth-hormone effects = hypertrophy of vascular walls = increased TPR
How does the baroreceptor reflex work?
baroreceptors are nerve endings in the walls of large arteries (like carotids and aortic arch)
stimulated by changes in BP and send signals to brain stem to maintain homeostasis
What effect does decreased BP have on the baroreceptor reflex?
Causes reflex vasoconstriction and increased HR
What effect does increased BP have on the baroreceptor reflex?
Causes reflex vasodilation and decreased HR
In what age group is the baroreceptor reflex less effective?
Elderly
What is caused by a defect in any part of the baroreceptor reflex?
HTN
How do the kidneys sense changes in BP?
Sense oxygen level in local arterial bed
(low oxygen = low BP)
What is secreted in vasculature to cause vasodilation?
NO
Prostacyclin
Bradykinin
What is secreted in vasculature to cause vasoconstriction?
Angiotensin II
Endothelin I
Why could calcium supplementation theoretically decrease BP?
When dietary Ca is decreased, intracellular Ca increases (cells try to hold on to Ca)
This increases BP by increasing peripheral vascular resistance
Increasing potassium intake ___ sodium levels
Decreases (increases the excretion of sodium)
Starting at 115/75, risk of CVD increases with every ____ mmHg increase
20/10
What are the major predictors of CHD in patients 60+?
SBP and pulse pressure
What is the major predictor of CHD in patients <50 yrs?
Diastolic blood pressure
What seems to be the most important clinical BP parameter for most patients?
Systolic BP
CV risk factors
age
55 or older for men
65 or older for women
DM
Dyslipidemia
Albuminuria
Family hx of premature CV
<55 yrs in dad
<65 yrs in mom
Obesity (BMI 30 or higher)
Physical inactivity
Tobacco use
Patient preparation before taking a BP reading
avoid nicotine, caffeine, food, and extraneous effort for at least 30 min before (Wasem said 60 min in class)
remove all clothing that covers cuff placement
sitting comfortably with legs uncrossed, back and arm supported
middle of cuff on upper arm at level of right atrium (mid-point of sternum)
lower part of cuff 3 cm above the elbow
patient should not be talking
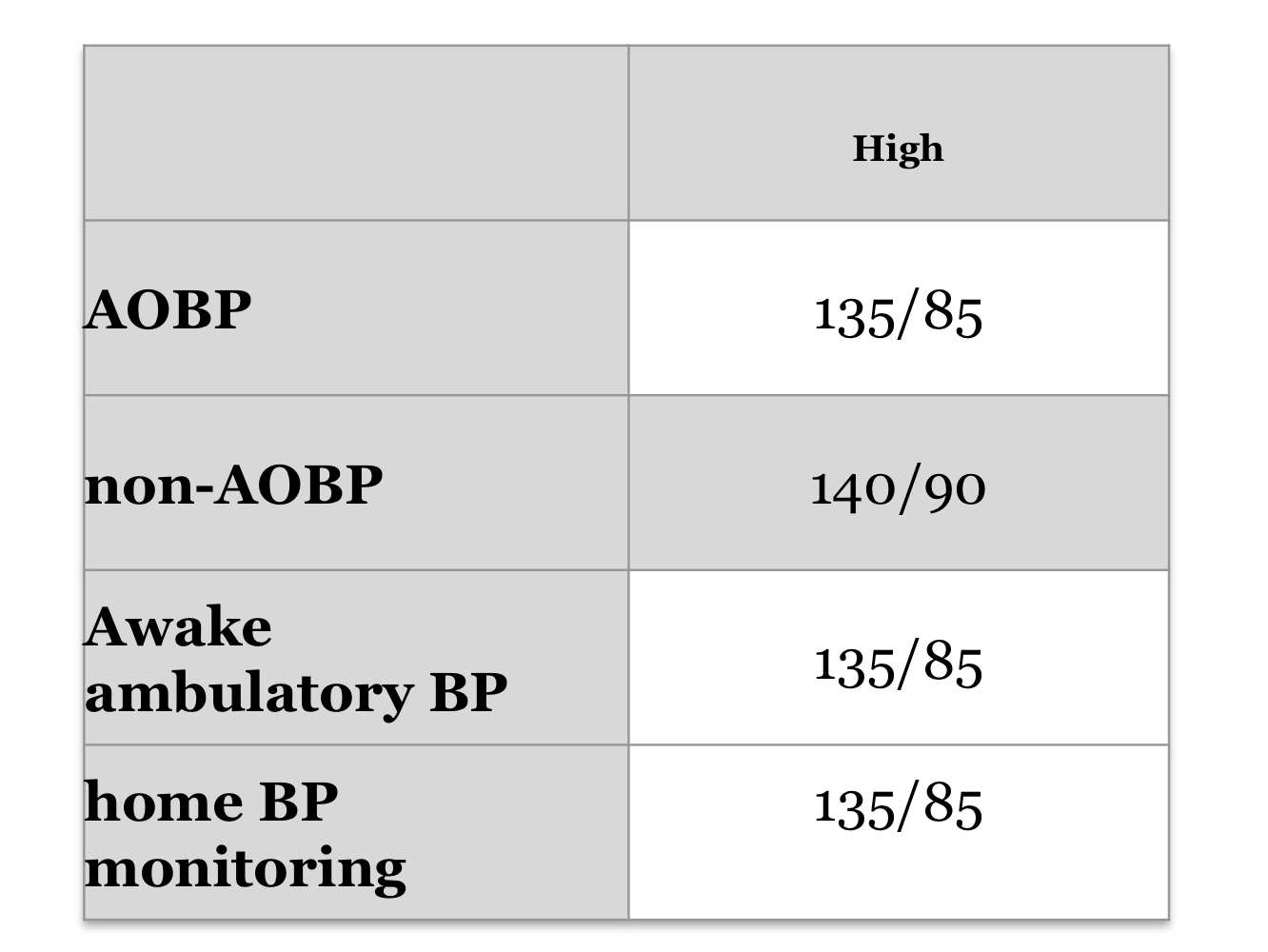
What is AOBP?
Automated office blood pressure
What time intervals does AOBP measure BP?
1 or 2 minute intervals
How should a blood pressure cuff fit if measuring by auscultation (non-AOBP)?
bladder width ~40% of arm circumference
bladder length should cover 80-100% of arm circumference
How is non-AOBP performed?
increase pressure rapidly to 30 mmHg above the level at which the radial pulse is extinguished
open control valve with rate of deflation of 2 mmgHg per heart beat
read systolic (first appearance of clear tapping sound)
read diastolic (point at which sounds disappear
perform 3 tests on same arm at least 2 minutes apart (discard first reading and average the rest)
repeat on other arm and use the higher reading arm for later visits
What is ABPM?
Ambulatory BP monitoring
How does ABPM work?
at least 24 hrs with a frequency of one measurement q 20-30 min during the day and q 30-60 min at night
Note: threshold for 24-hr mean is lower than for other tests
What technique can be used to measure BP in patients with office-induced increased BP
ABPM
How do all BP-measuring techniques compare?
Non-AOBP is slightly higher, all others are similar
What is considered a hypertensive crisis?
180/120 or higher
Differentiate between hypertensive urgency and hypertensive emergency
Urgency = no target organ damage
Emergency = evidence of acute or progressive end organ damage (CNS, eyes, heart, kidneys)
Examples of end organ damage that would indicate hypertensive emergency if BP 180/120 or higher
hypertensive encephalopathy
acute aortic dissection
acute left ventricular failure
acute myocardial ischemia
What matters more than BP values in hypertensive crises?
The rate of BP increase
How does treatment strategy change between hypertensive urgency and emergency?
Urgency: reduce BP over several hours to days and give oral therapy
Emergency: immediate reduction of BP within hours and give parenteral therapy
Risk factors for hypertensive crises
medication non-adherence
cocaine use
drug interactionsø
Options for IV meds in hypertensive emergency
labetalol
nitroglycerin
nitroprusside
Options for PO meds for hypertensive urgency
clonidine
labetalol
captopril
Goal BP reductions for hypertensive emergencies
initially reduced by 25%
then to target of 160/100 within next 2 hrs
gradually reduce to normal BP within next 24 hrs
Goal BP reductions for hypertensive urgency
Gradual reduction to normal BP within 24-48 hrs
What routine tests should be done for investigation of all patients with HTN ?
urinalysis (look for albuminuria)
blood chemistry (K, Na, Cr)
FPG and/or A1c
Lipid panel
standard 12-lead ECG
True or false. All treated hypertensive pts should be monitored according to the current Diabetes Canada guidelines for the new appearance of diabetes.
True (grade B recommendation)