Week 8 - Self study - Structure and Function of Blood Vessels
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts about the structure and function of blood vessels.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the three tunics of blood vessels?
Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa.
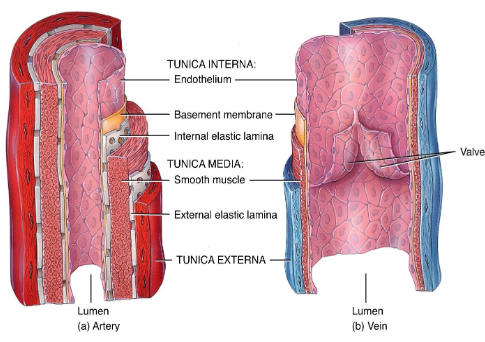
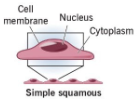
What type of epithelium lines the tunica intima?
Simple squamous epithelium (endothelium).
What is the function of the basement membrane in blood vessels?
Anchors the endothelium to connective tissue.
Which tunic regulates blood pressure?
Tunica media, through vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
What tissue type makes up the tunica externa?
Collagen and elastic fibers.
What are the two main types of arteries?
Elastic (conducting) and muscular (distributing) arteries.
What is the function of elastic arteries?
To accommodate high-pressure blood flow from the heart.
Give an example of an elastic artery.
Aorta or pulmonary trunk.
Why can elastic arteries stretch and recoil?
Because they have elastic fibers in all three tunics.
What is the main role of muscular arteries?
To distribute blood to organs and regulate blood pressure.
What layer is thicker in muscular arteries compared to elastic arteries?
Tunica media.
What are arterioles?
Small branches of arteries controlling flow into capillaries.
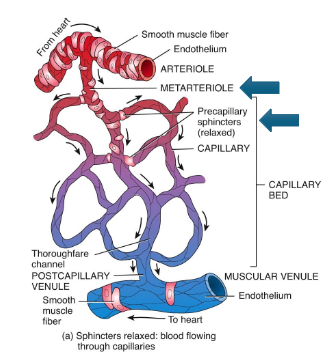
How do arterioles regulate blood pressure?
By constricting or dilating via smooth muscle action.
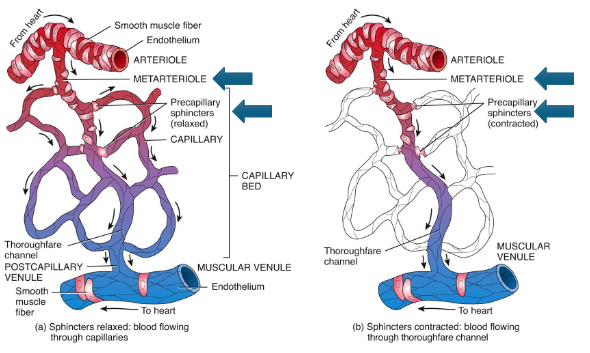
What controls arteriole diameter?
Autonomic (especially sympathetic) innervation.
What is a metarteriole?
A vessel connecting an arteriole to a capillary bed.
What are precapillary sphincters?
Rings of smooth muscle regulating capillary blood flow.
What happens if all sphincters close?
Blood bypasses capillaries via the metarteriole → thoroughfare channel.
Which vessels have only a tunica intima?
Capillaries.
What is the main function of capillaries?
Exchange of gases, nutrients, and hormones.
Why is capillary blood flow slow?
To allow maximum time for exchange.
What connects arterioles and venules?
Capillary beds.
What is the function of venules?
Drain deoxygenated blood from capillaries.
What structural feature distinguishes veins from arteries?
Veins have thinner walls and larger lumens.
Why do veins have valves?
To prevent backflow and assist blood return to the heart.
What assists venous return besides valves?
Skeletal muscle contractions.
What happens during skeletal muscle contraction?
Veins are compressed, pushing blood toward the heart.
What causes varicose veins?
Leaky valves leading to blood pooling and vein stretching.
What is a blood reservoir?
The venous system holding most of the body’s blood.
How does the body redirect blood during activity?
Via sympathetic vasoconstriction.
Which vessel has the thickest tunica media?
Muscular arteries.
Which vessels have the thinnest walls overall?
Capillaries.
Which vessels carry blood away from the heart?
Arteries and arterioles.
Which vessels carry blood toward the heart?
Veins and venules.
Which vessels control resistance and blood pressure the most?
Arterioles.
What vessel type acts as a transition between arteries and capillaries?
Arterioles (via metarterioles).
Which layer is absent in capillaries?
Tunica media and externa.
What ensures veins don’t collapse under pressure?
Collagen fibers in the tunica externa.
What part of the vessel wall allows elasticity?
Elastic fibers, especially in elastic arteries.
Why is venous blood flow slower than arterial?
Lower pressure and reliance on muscle contraction and valves.