Pathology of the bronchi and bronchioles
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
true
true/false: acute injury and repair in the bronchi and bronchioles are very similar to the responses in the upper airways
necrosis, exfoliation, bronchoconstriction
Damage to ciliated epithelium leads to __________ and ________.
Inflammatory mediators and neural reflexes to irritation often cause _________________________
cough, dyspnea, may expel exudates
What are some clinical signs or acute injury or inflammation in bronchi?
club cells, CC10, phospholipase A2
As long as the basement membrane is intact, re-epithelization by proliferation of __________ leads to complete repair.
These cells produce _________which inhibits _________________. (major mediator for arachiodontic acid cascade)
fibrosis
If the basement membrane is extremely damaged and repair is not possible, ______ can occur.
exudate, abscesses
purulent, bronchial wall
Lesions associated with acute bronchitis often include bronchi that are filled with _______ and look like _________.
___________ material is surrounded by remnants of ____________________
Goblet cell hyperplasia
__________________: Increased mucus fills the airways and accumulation leads to chronic obstructive bronchitis
thick mucus reduces its function
Why doesn't the mucociliary escalator take care of the mucus in goblet cell hyperplasia?
Bronchiectasis
_______________________: Chronic release of inflammatory mediators damages the wall of the bronchus, leading to permanent dilation.
squamous metaplasia
ciliated epithelial
squamous epithelium
other infections
In chronic bronchitis, the basement membrane is often damaged, and re-epithelization leads to ______________________.
In other words, __________ cells are replaced with _____________. This reduces the mucociliary escalator function and causes increased risk of ___________>
bronchiectasis
bacteria can travel deeper into the lungs easier
pneumonia
What is this?
What does it allow for?
Which predisposes the animal to what?
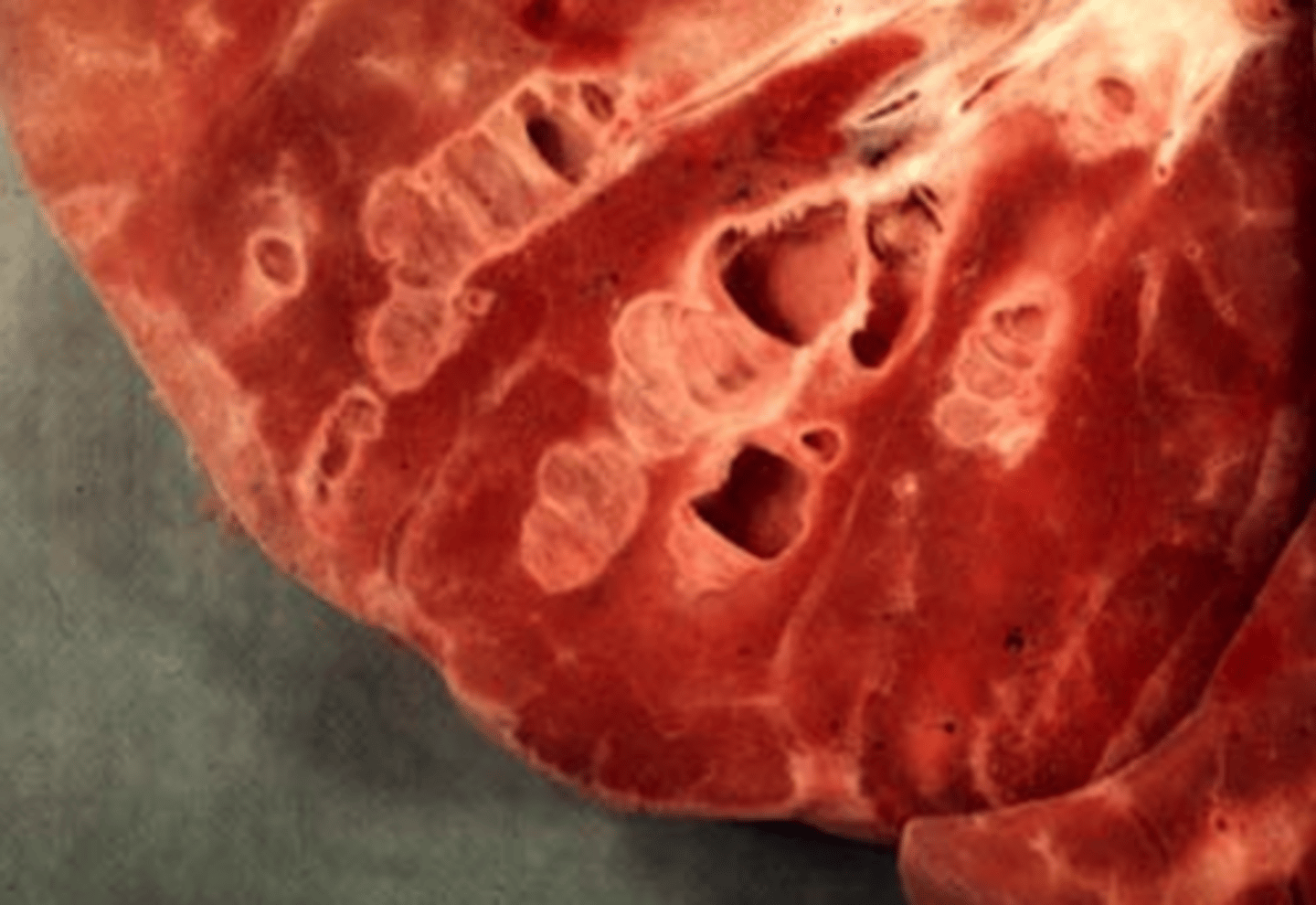
exudate
proteolytic enzymes
bronchial smooth muscle & cartilage
In bronchiectasis, _______ accumulates in bronchi, and ___________________ released from phagocytes weaken _____________ and ______________ leading to permanent dilation.
cool
All that before was about BRONCHI, now we're talking about BRONCHIOLES.
Cool?
more, impact site for inhaled agents (increased exposure), metabolic activity from club cells, PAMs and Leukocytes accumulate here
Is the Bronchiolar epithelium more or less sensitive to injury by viruses, bacteria, toxins and oxidant gases?
Why?
bronchiolitis obliterans
___________________: a fibrotic process that occludes airways and causes permanent scarring of the lungs, specifically from severe injury to the bronchioles
trick question, they are not normally present in bronchioles
Are the goblet cells within the bronchioles more or less susceptible to goblet cell hyperplasia?
yeahhh, the increased mucus can still lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema and atelectasis.
So... if there aren't goblet cells in the bronchioles... are the bronchioles still affected by goblet cell hyperplasia?
exudate & fibrin
bronchiolar wall
mucus
In the bronchioles during bronchiolitis obliterans, accumulations of _______ and _________in the bronchiole cause excessive damage of the ___________ and Goblet cell hyperplasia produces excess __________.
collapses
fibroblasts
granulation tissue
In bronchiolitis obliterans, as the exudate increases in the bronchioles, the affected bronchiole _________ resulting in complete obstruction.
Eventually, the obstructed bronchiole is infiltrated by __________ that progresses to form ________________.
Recurrent airway obstruction, heaves, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
What is the classic example of bronchi and bronchiolar disease in horses?
Also referred to as ________ or _____________________.
small airways are hyper-responsive to allergens
In heaves, whats... happening?
Chronic cough, poor performance, respiratory distress
What are the clinical signs of recurrent airway obstruction
alveolar emphysema, metaplasia, hyperplasia, mucus, eosinophils
Lesions surrounding recurrent airway obstruction:
Chronic bronchiolitis with _________________.
Goblet cell _________, smooth muscle ___________ and _________ plugging of bronchioles.
___________ may be present due to preposed allergic etiology.