Cross Sectional Anatomy - cranium & facial bones
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
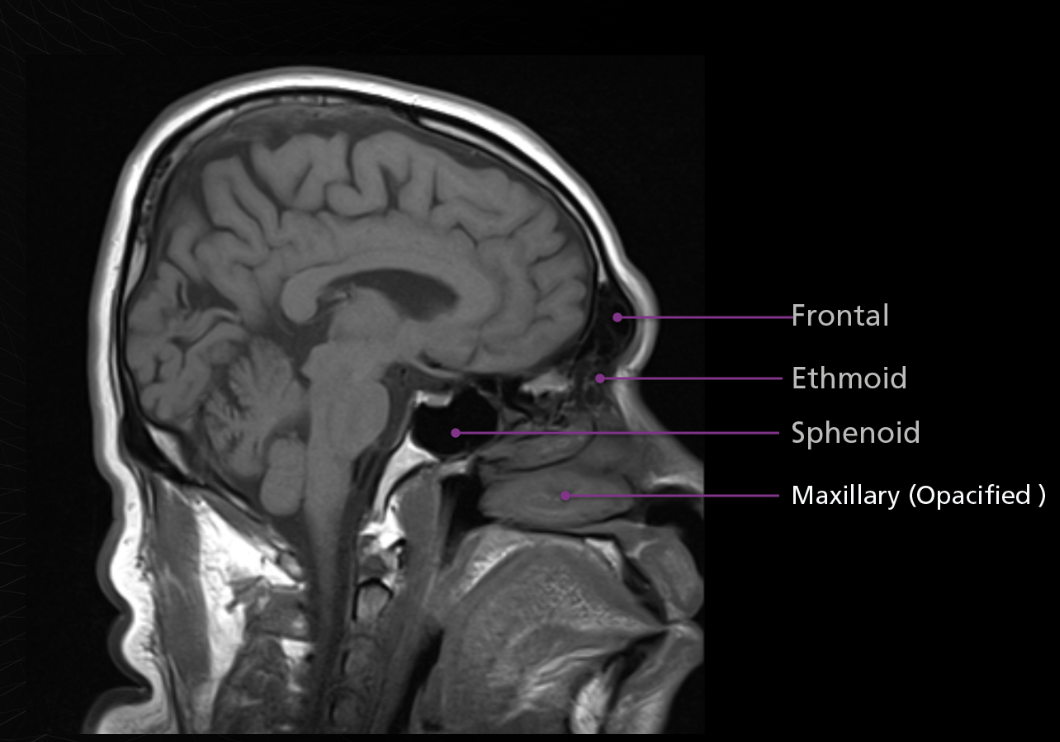
4 sinus names
Ostia
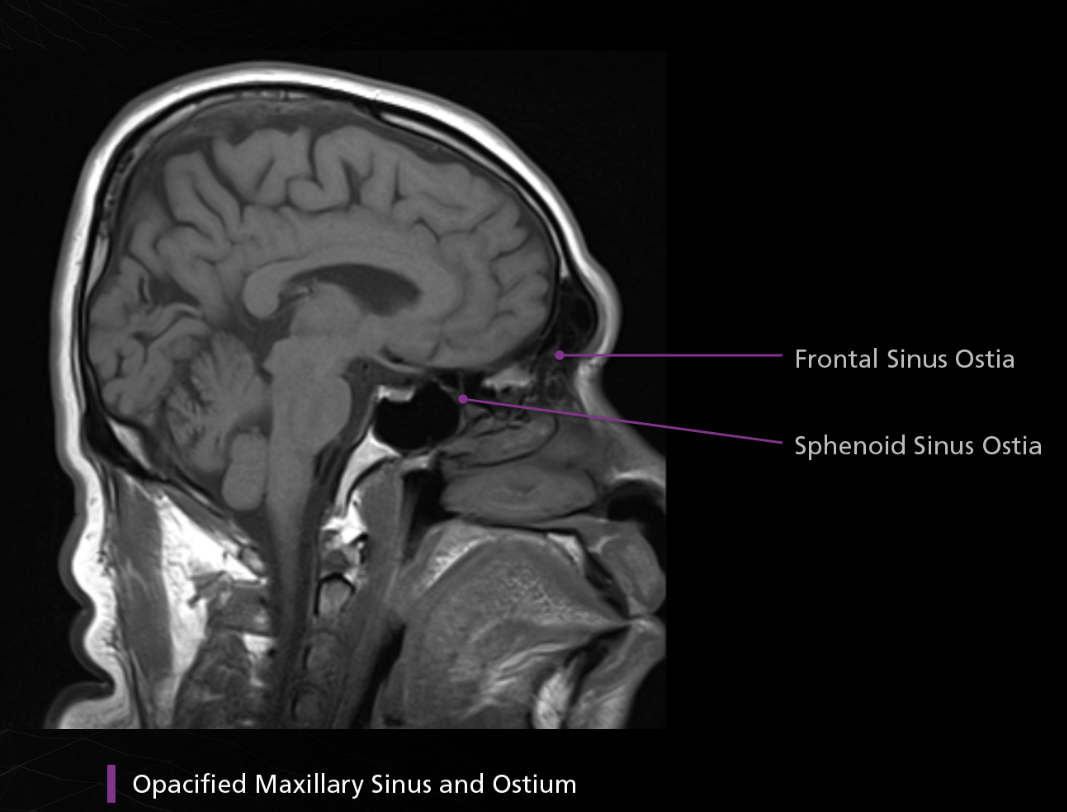
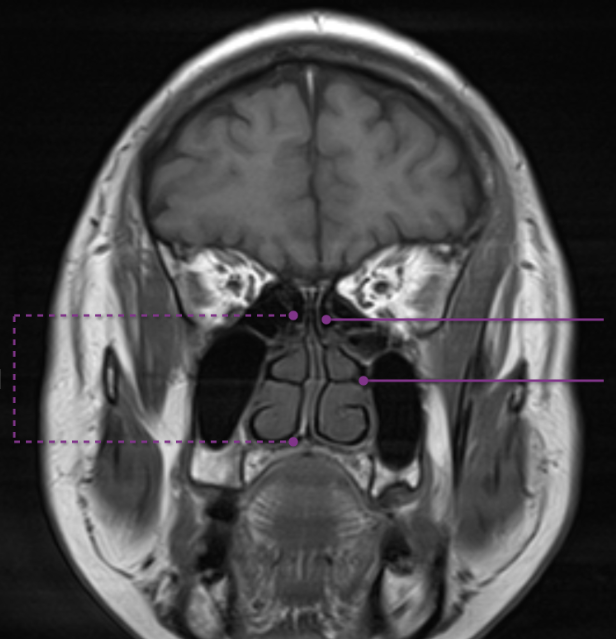
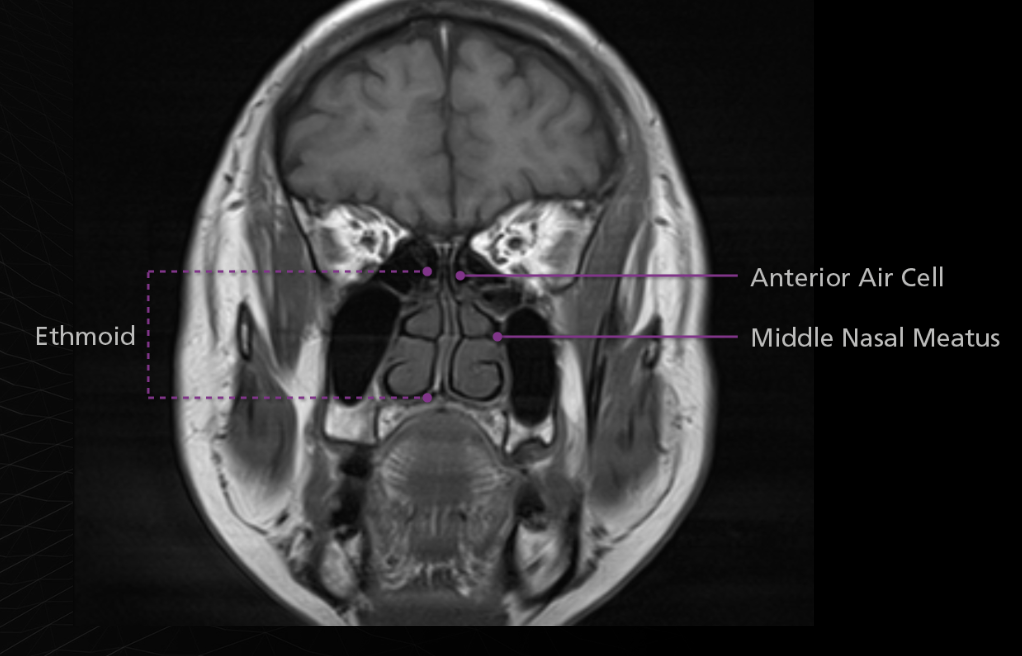
ethmoid sinuses
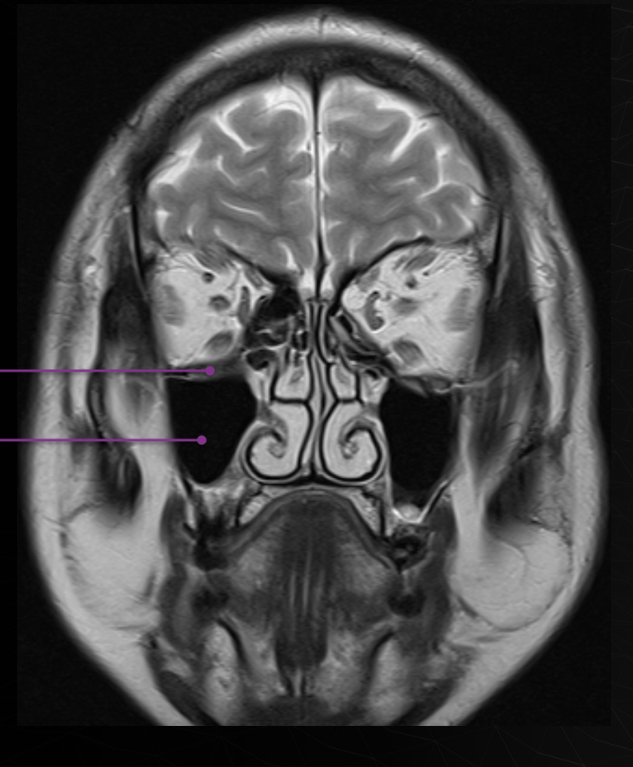
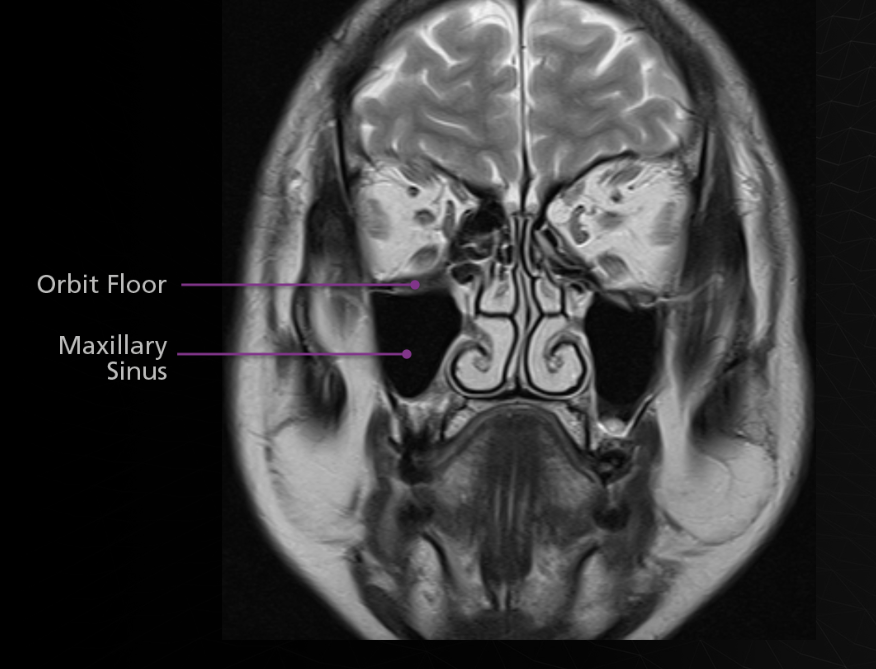
Maxillary
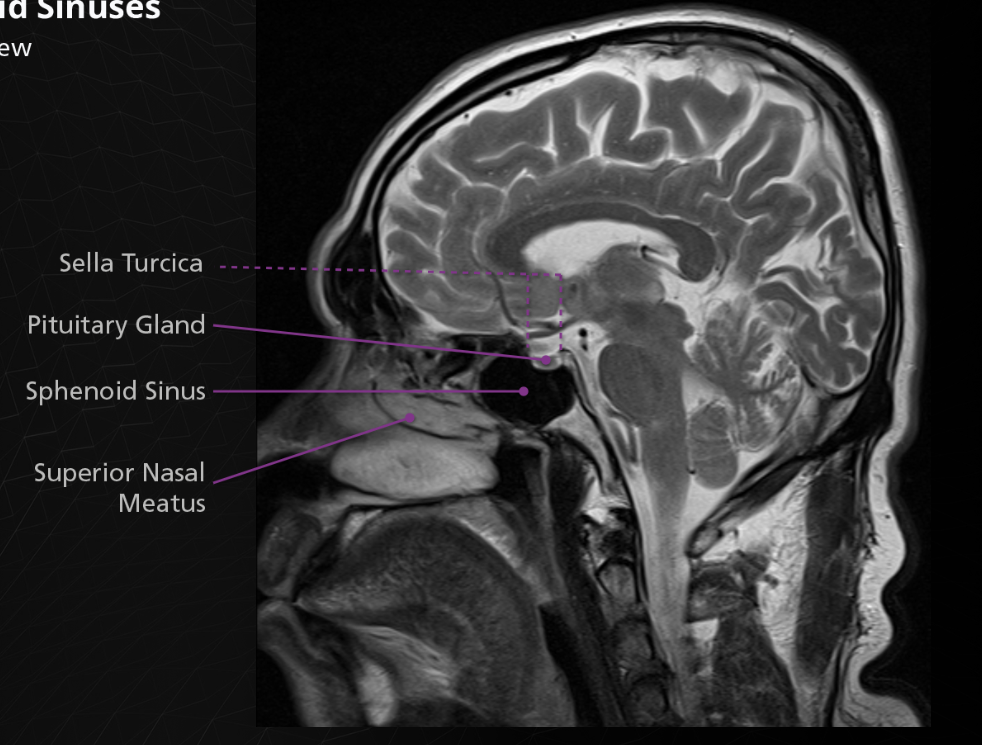
Sphenoid
Aplastic Sinus
missing sinus
Hypoplastic Sinus
smaller than normal sinus
hyperplastic sinus
Larger than normal or pneumatized sinus
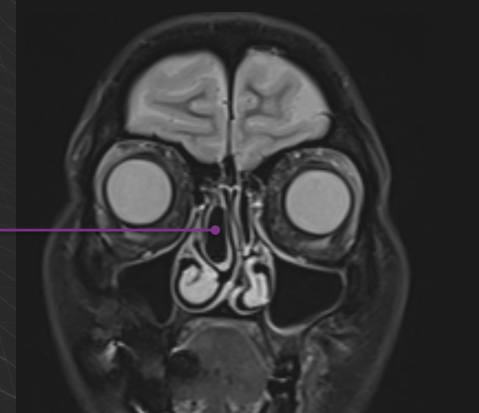
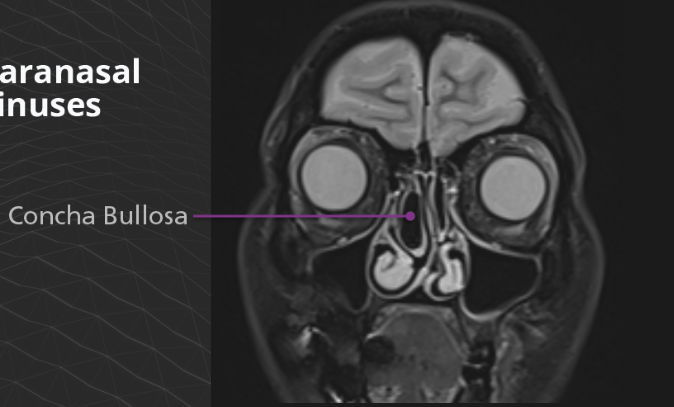
Concha bullosa is an air cell within the middle turbinate and is often associated with chronic sinusitis or nasal obstruction.
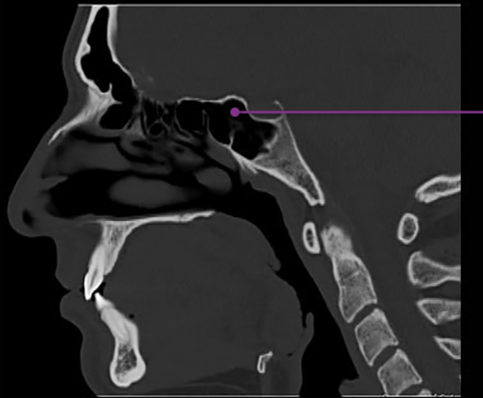
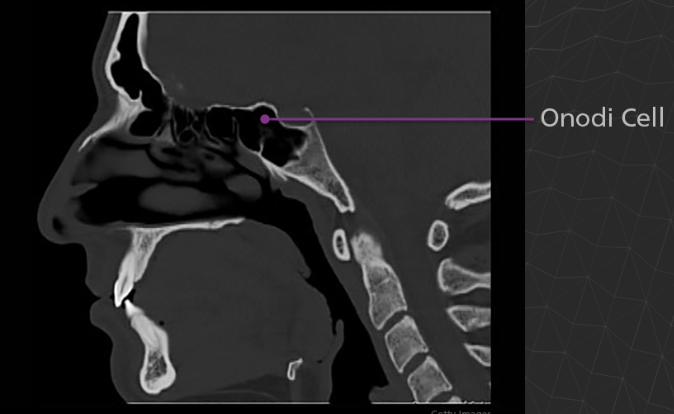
An Onodi cell is a posteriorly location ethmoid air cell, occurring extremely close to the optic nerve and sometimes the internal carotid artery. It is clinically significant due to its proximity to vital structures and potential complications during sinus surgery. If a surgeon goes through an Onodi cell rather than the posterior ethmoid cell, the optic nerve may be damaged.
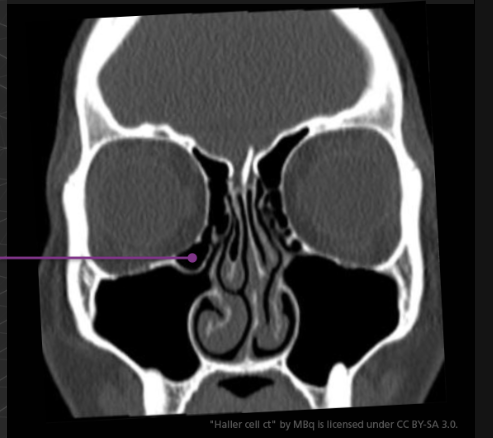
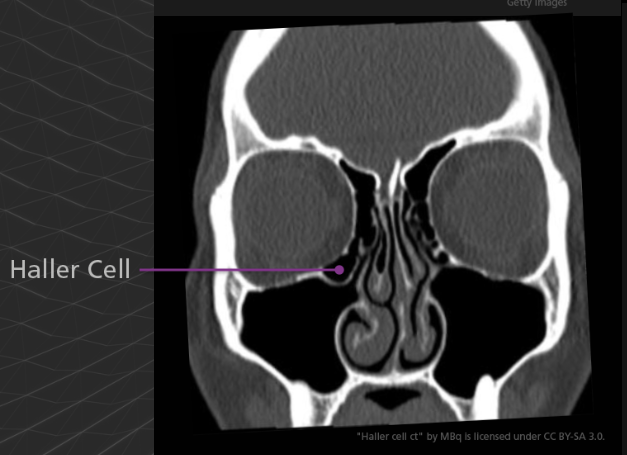
A Haller cell is an extension of an ethmoid air cell into the inferomedial orbital floor. Although usually asymptomatic, is can become significant the same way as an Onodi cell. For example, an endoscopic surgeon who is unaware of a Haller cell may accidentally penetrate the orbit.
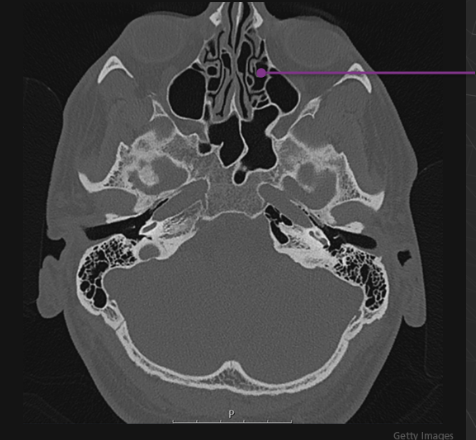
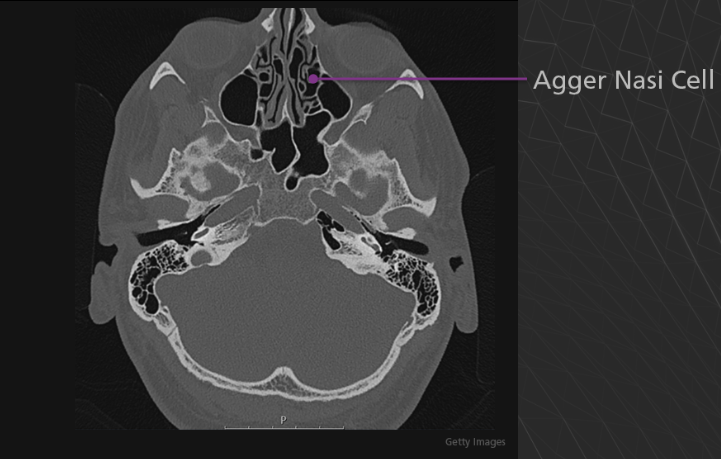
Agger Nasi cell - Agger means “mound” or “heap” in Latin. This structure is the anterior-most ethmoid air cell. It is located inferolateral to the frontal recess, the channel which communicates between the anterior ethmoid and frontal sinuses. The agger nasi cell is an important landmark for front sinus surgery because the roof of the cell is the floor of the frontal sinus.
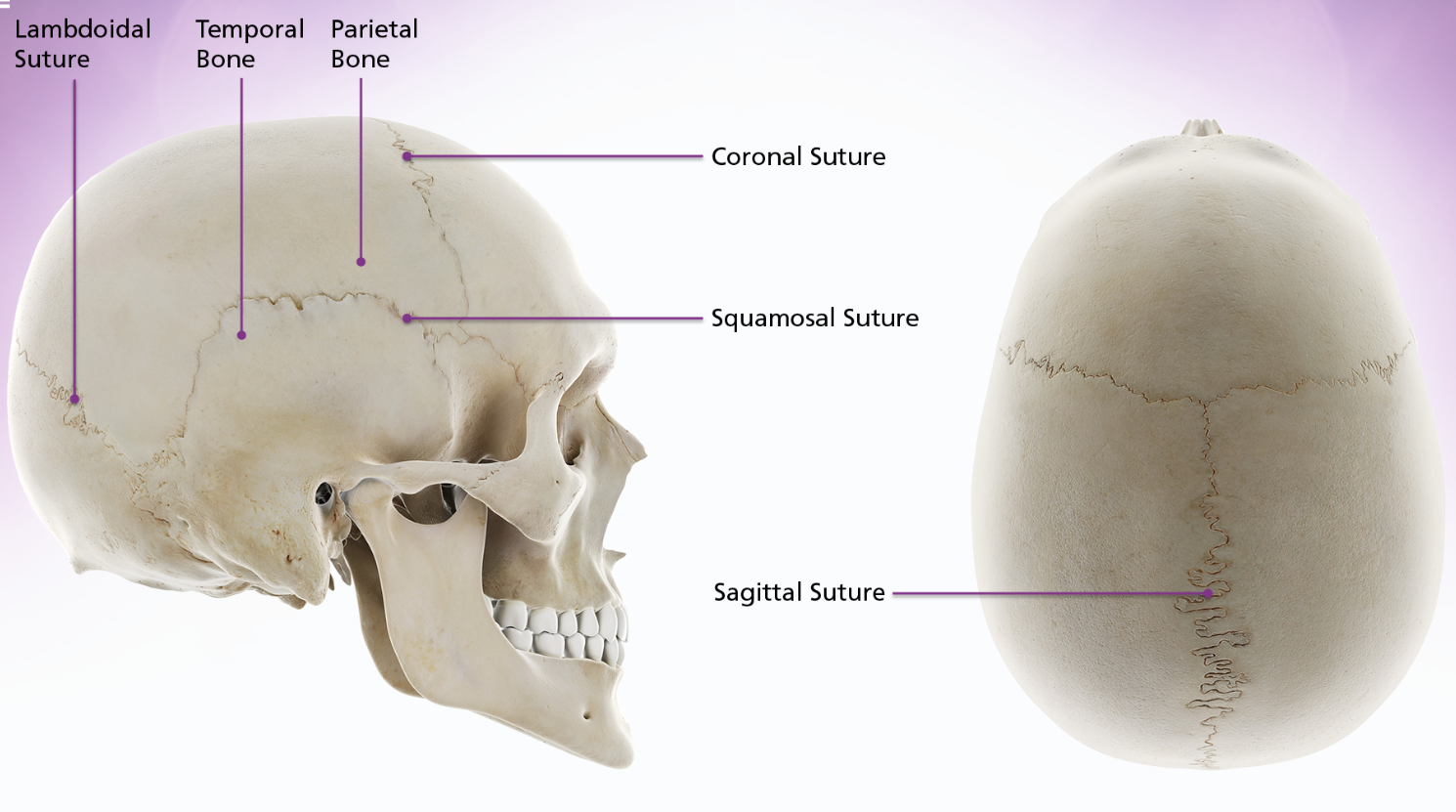
sutures
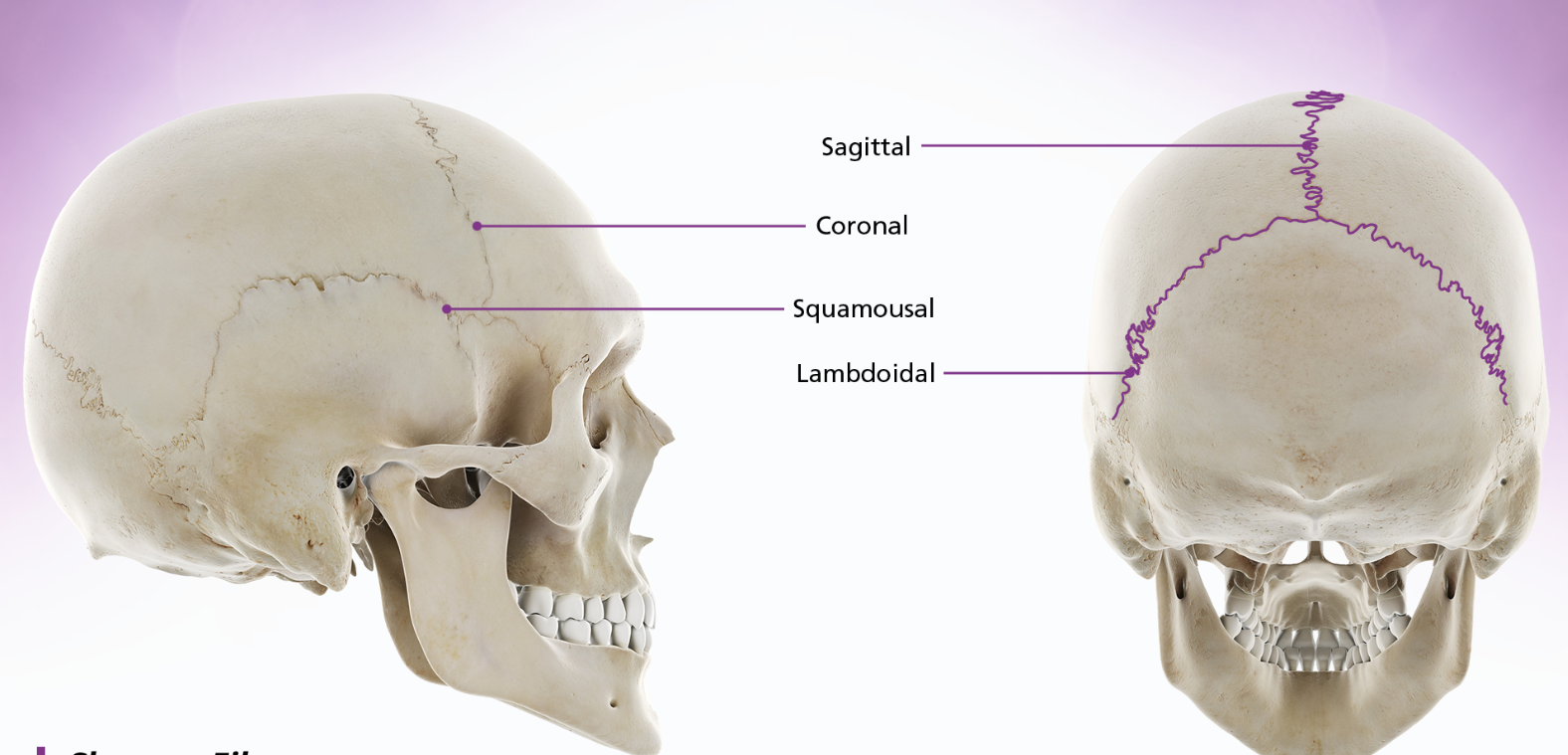
sutures and bone
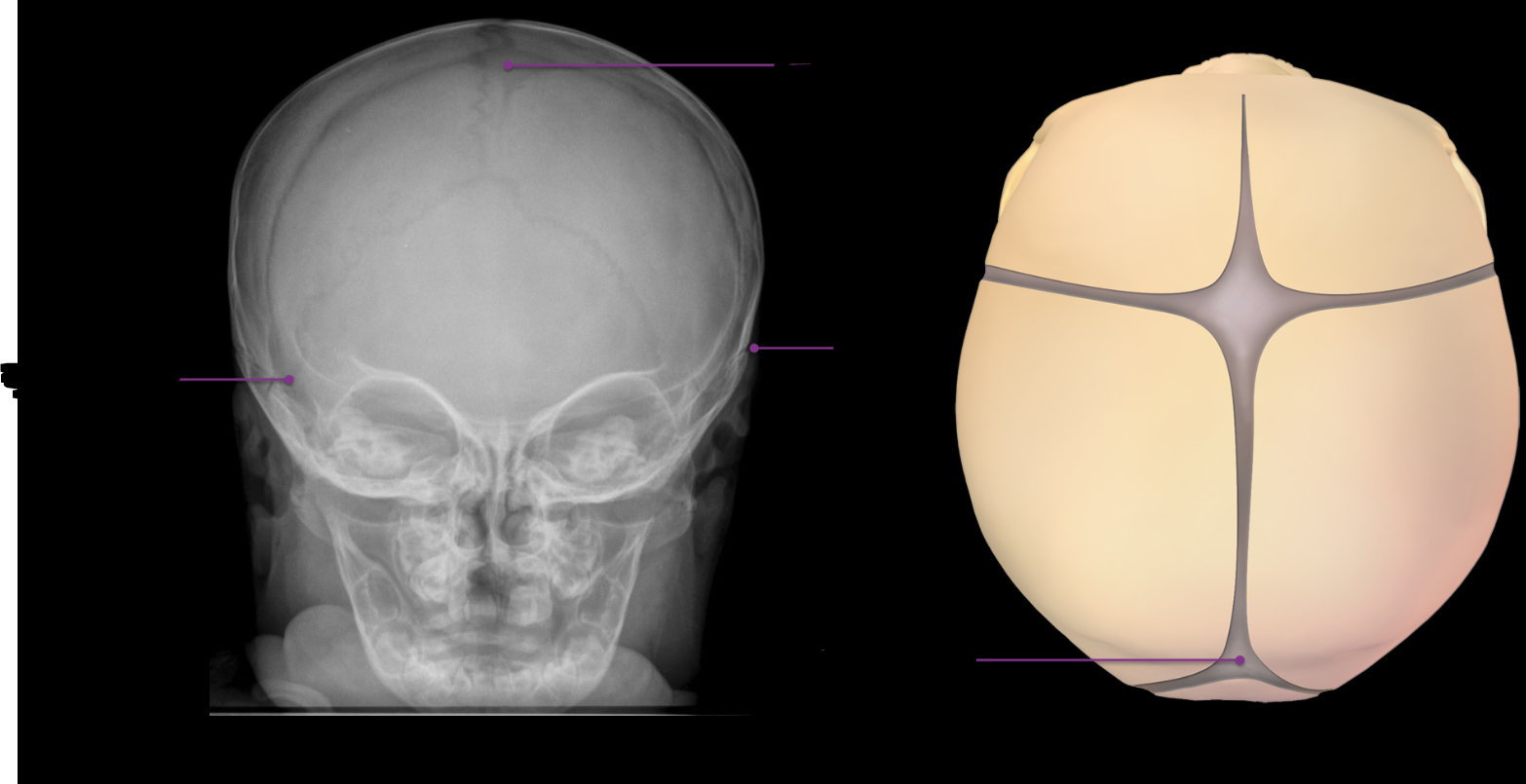
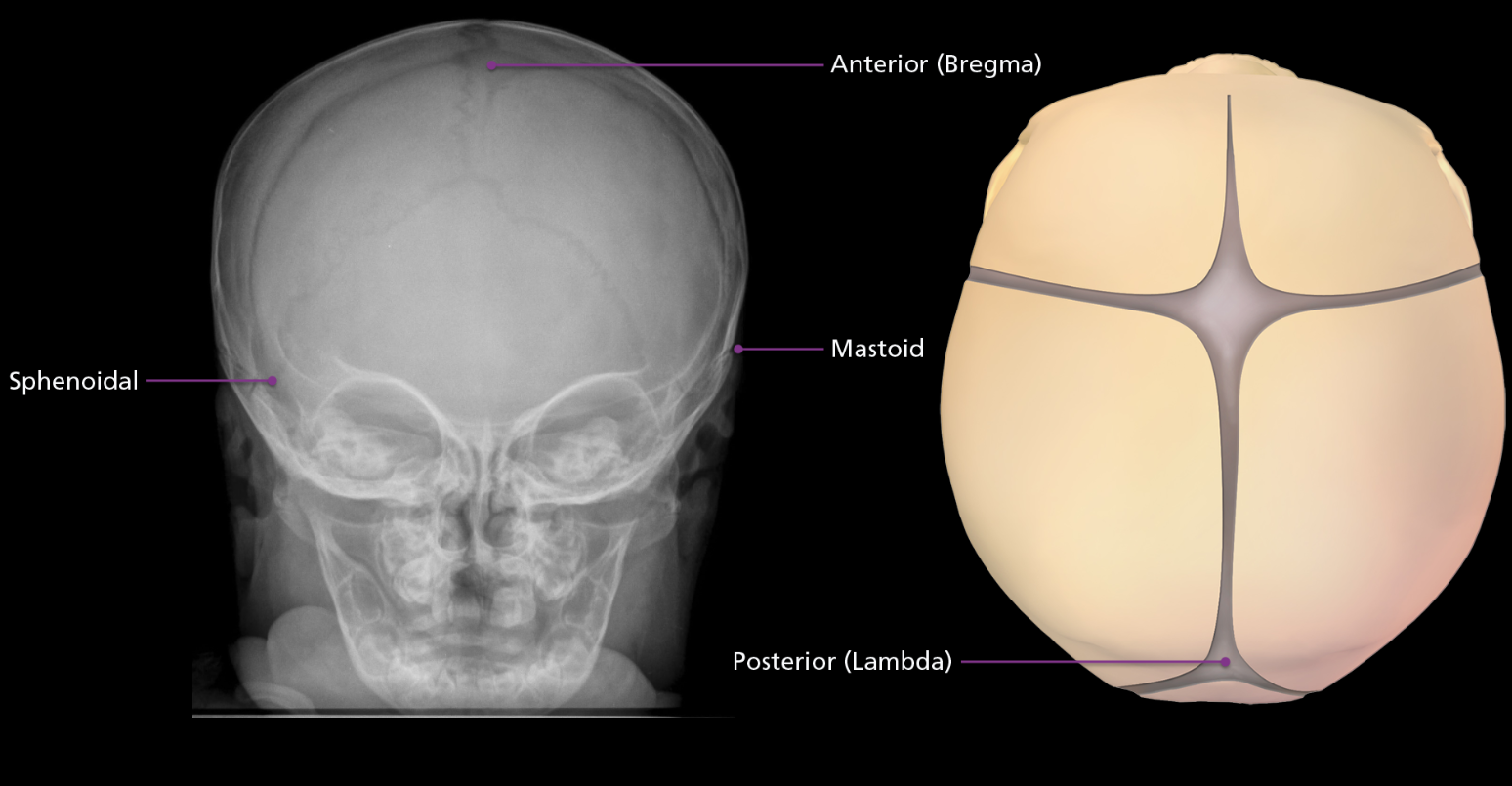
Fontanelles
A total of 6 “soft spots” that allow the cranium to flex and mold during birth and accommodate brain growth. The two largest are the anterior fontanelle called the bregma, located at the junction of the patal and frontal bones. The posterior fontanelle is known as the lambda, located at the junction of the parietal and occipital bones. Anterior fontanelle closes around 2 years old, posterior within first few years of life. On the side of the skull are 2 sphenoidal fontanelles found at the junction of the frontal, sphenoid, parietal, and temporal bones. The mastoid fontanelles are location at the intersection of the occipital, parietal, and temporal bones.
Cephalic Index
(Width of cranium x 100) / Length of cranium = index. If less than 75 in women or 75.9 in men, the individual is said to be “long headed” or dolichocephalic, which occurs when the sagittal suture closes too soon. If the index is greater than 83 in women or 81.1 in men, the individual is “short headed” or brachycephalic, which is when the coronal suture fuses too soon
How do you differentiate between and sture and a fracture?
Suture lines have a symmetric, well-corticated borders (smooth outer layer). A fracture does not, with the exception of a diastatic fracture that follows the suture line in newborns. In this case though, the suture is abnormally widened.
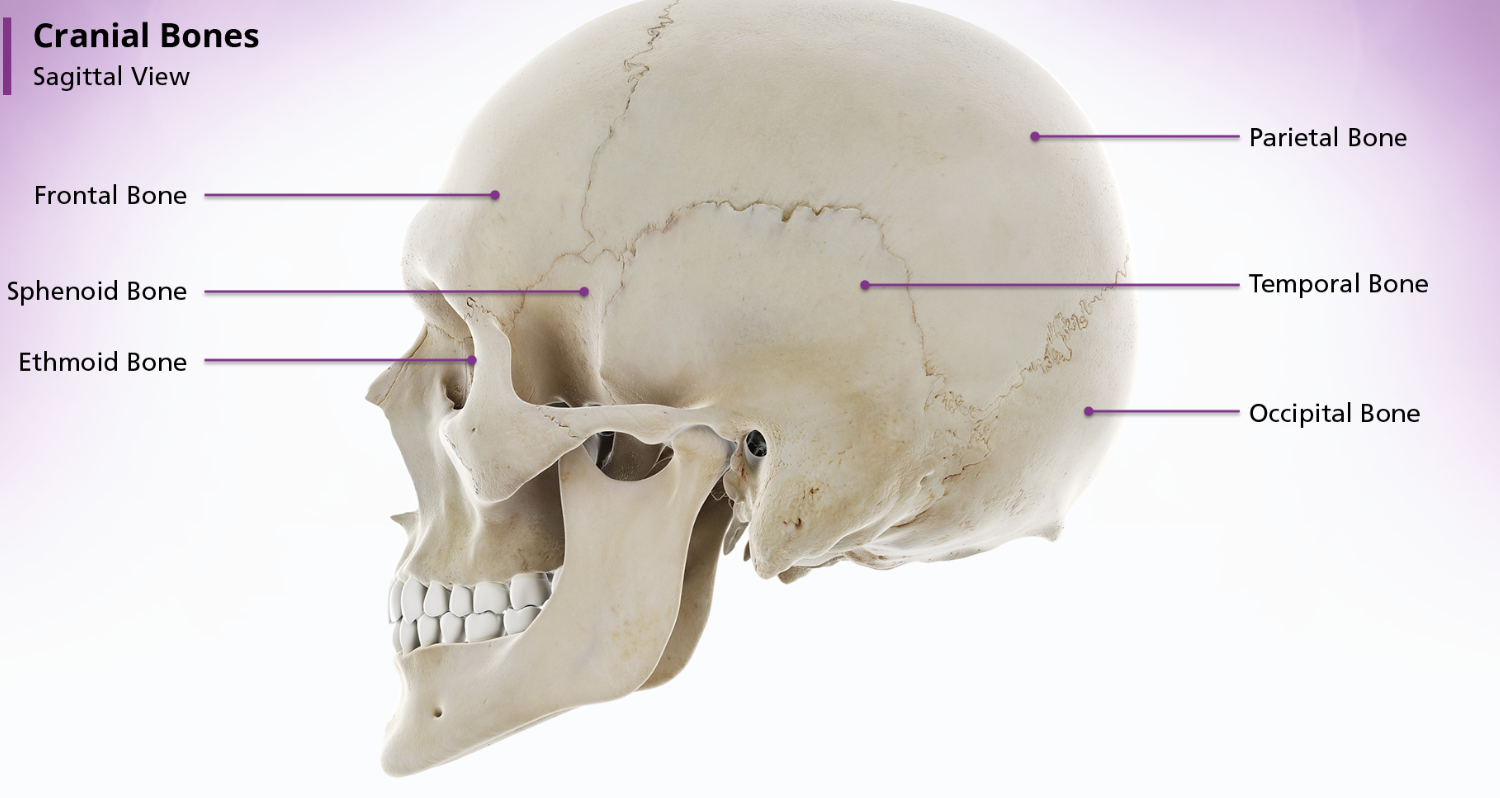
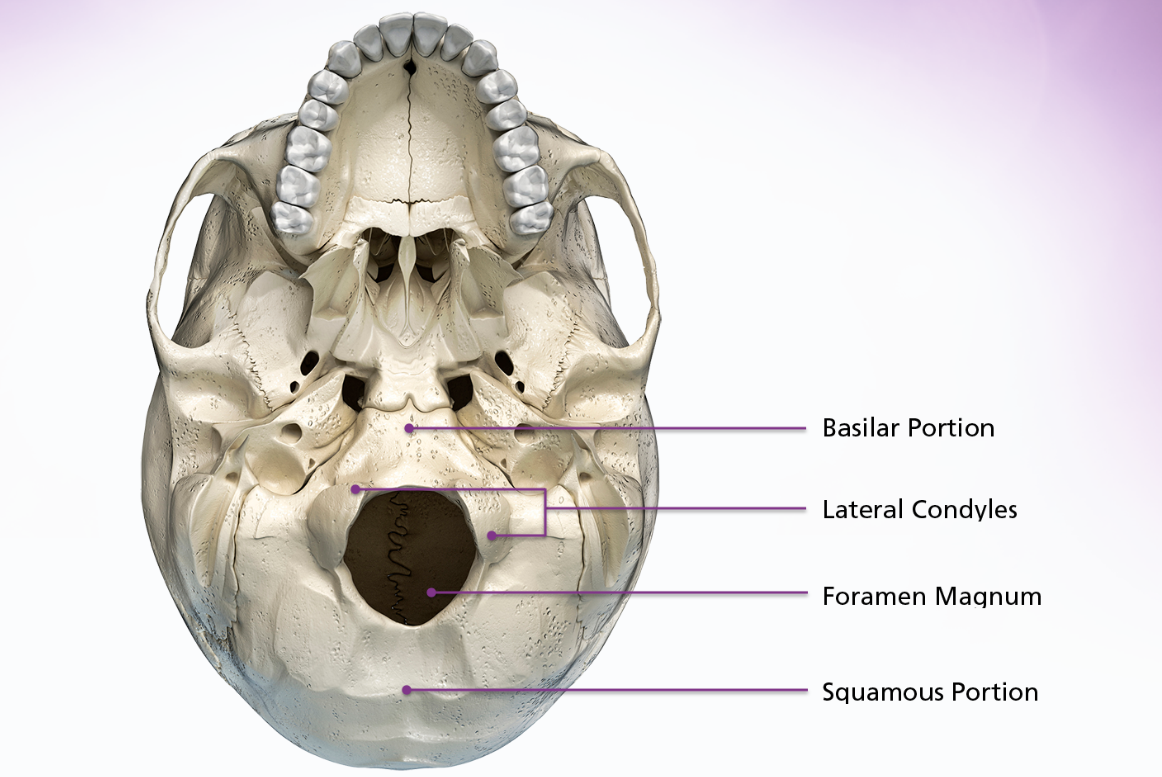
occipital
The occipital bone is located inferoposteriorly and makes up the posterior cranial fossa. It is generally divided into 4 parts the 2 lateral condyles, the basilar portion and the squamous portion. The 4 parts are divided by the foramen magnum, which is the massage for the medulla oblongata and spinal cord.
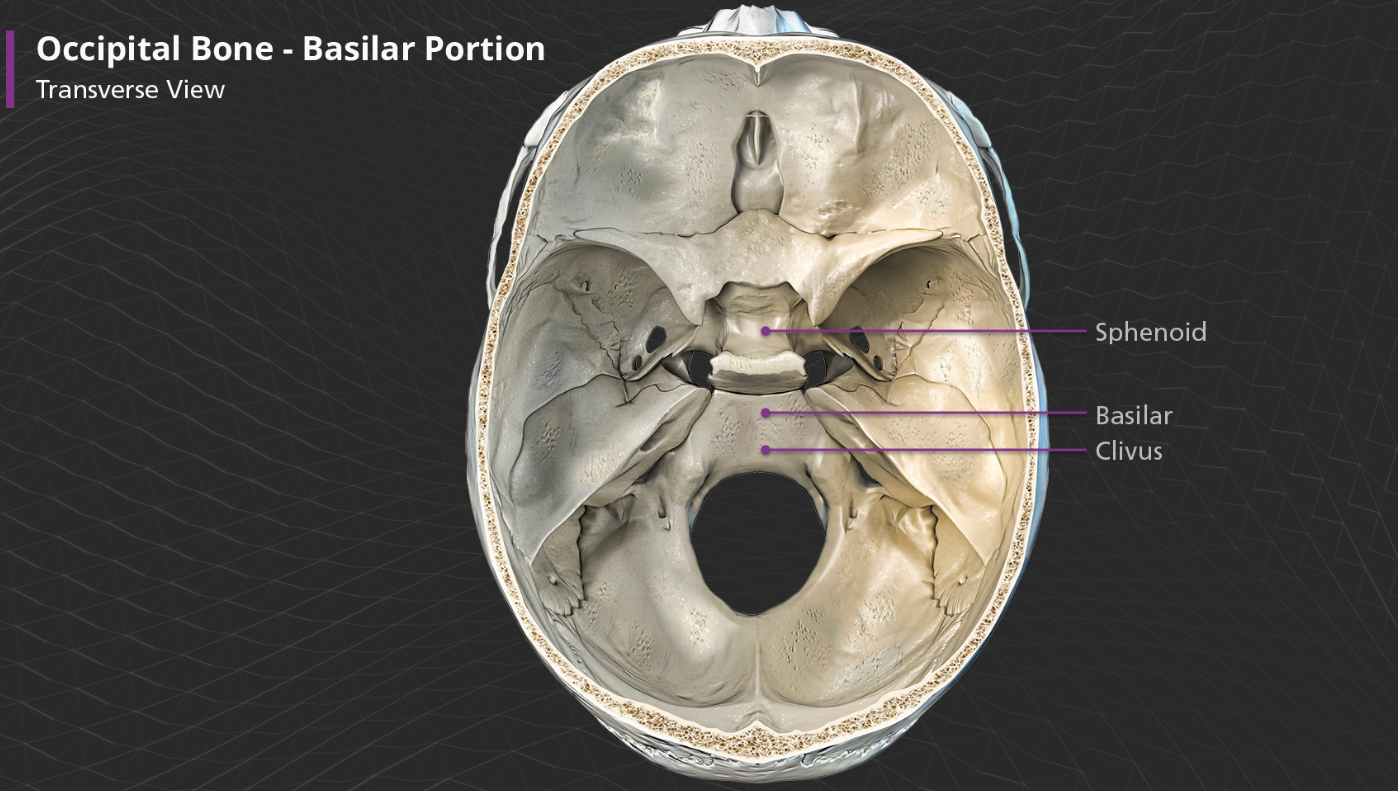
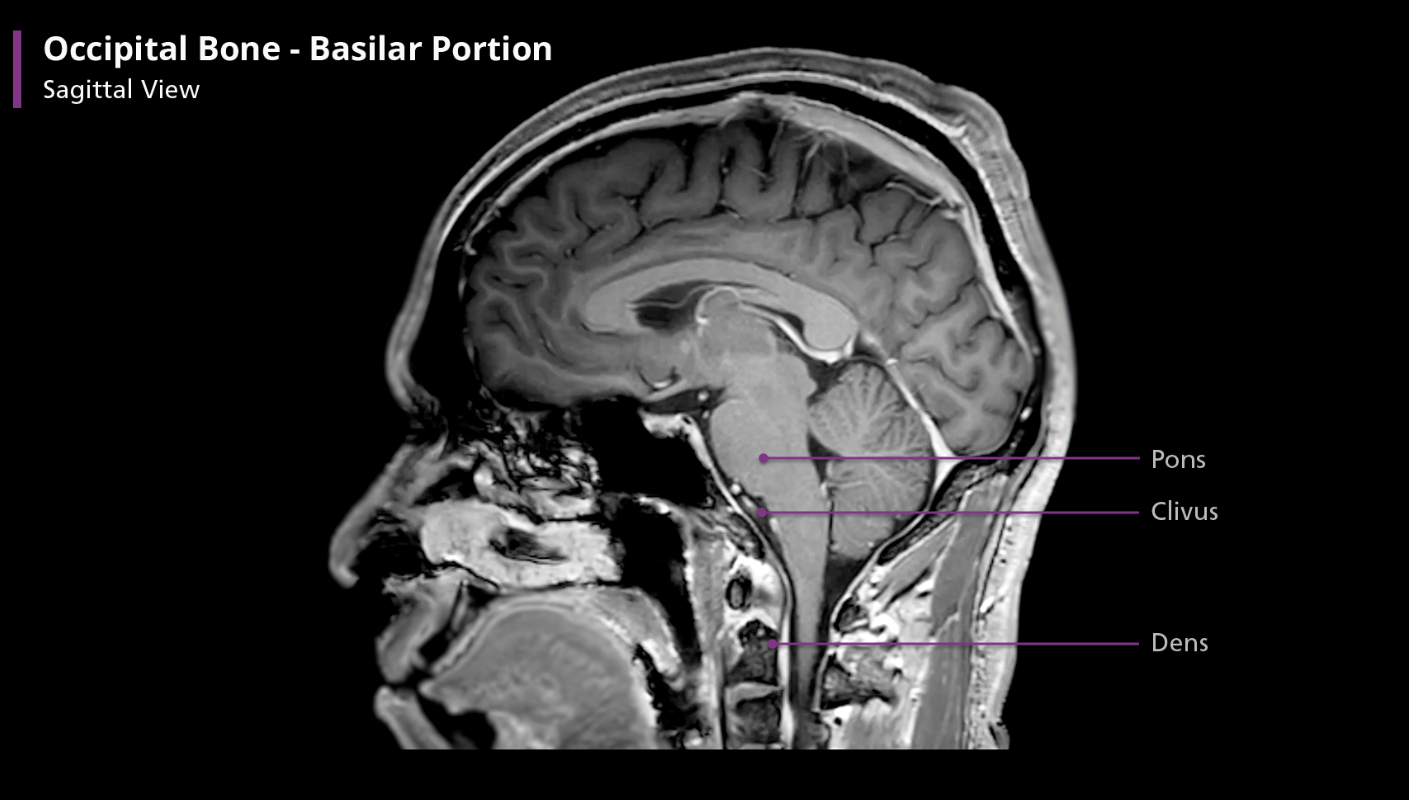
Occipital bone - basilar portion
Anterior to the foramen magnum, the basilar portion articulates with the sphenoid bone by means of a thin plate of cartilage, which becomes ossified by approx. age 25. The very most anterior part of the basilar portion contains a shallow depression and slopes anterosuperiorly before connecting to the sphenoid bone. This part f the bone is called the clivus, which is latin for “slope”
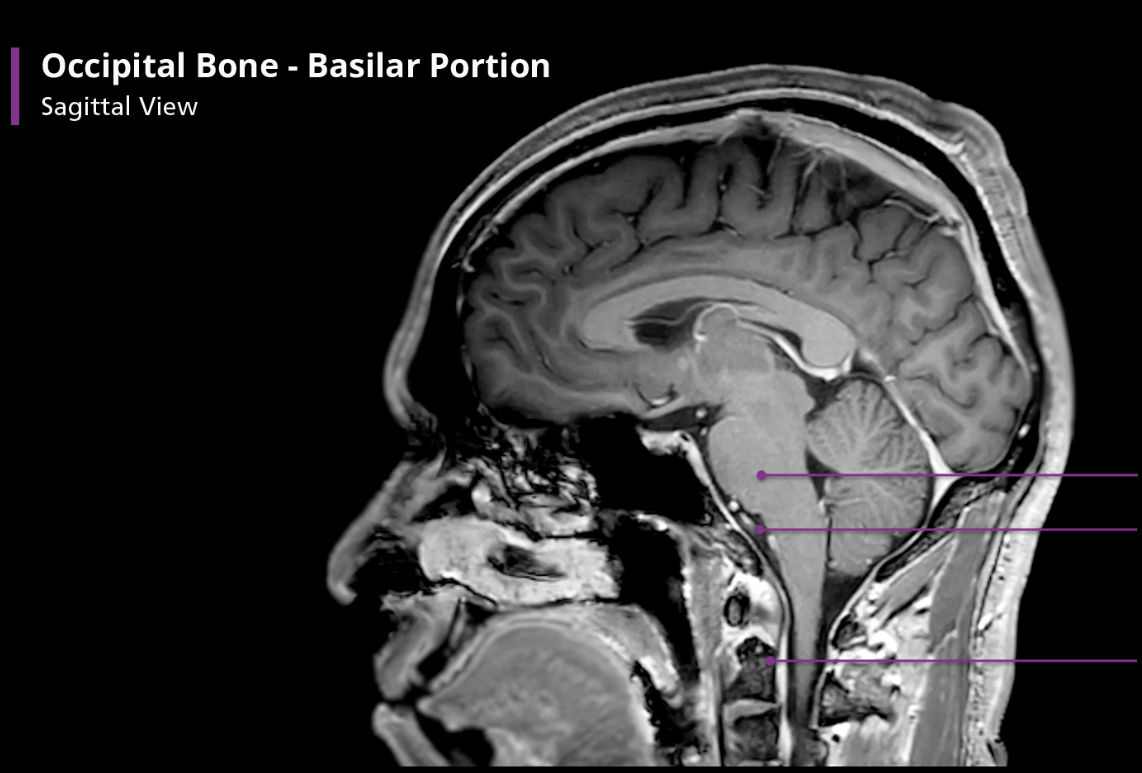
Occipital Bone - Basilar portion
The clivus is important because it supports the pons. If you draw a line from the clivus posteriorly on a sagittal view, it should transect, or at least be tangential to, the dens. If not, there is an atlanto-occipital dislocation, which is often a fatal injury. Incidentally, the clivus contains more fat than other bones, giving it a unique appearance on T1-weighted MR imaging.
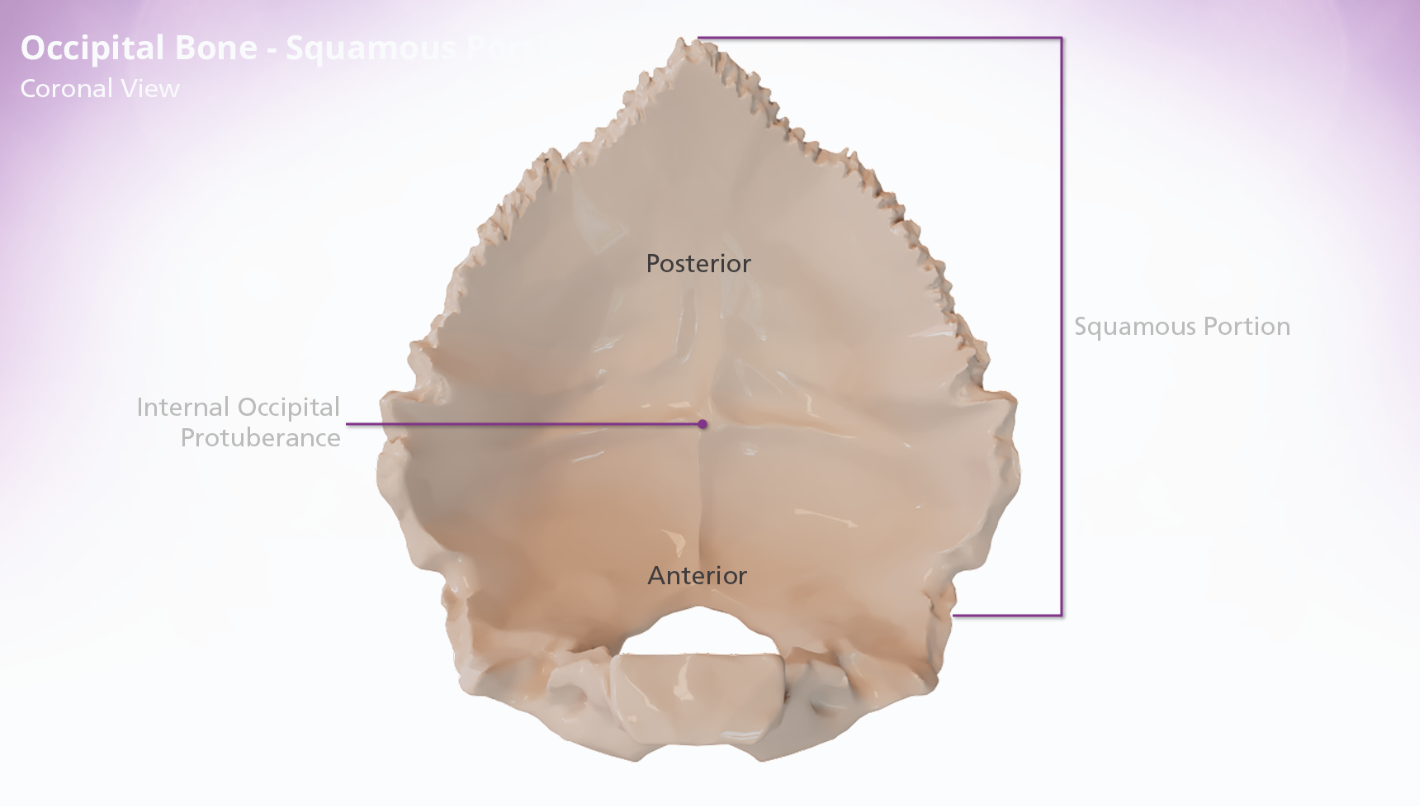
occipital bone - squamous portion
The squamous portion of the occipital bone is located posterior to the foramen magnum. The internal surface of the squamous portion of the occipital bone is concave and divided into 4 fossae. The posterior 2 fossae accommodate the cerebrum and the anterior hold the cerebellum. The fossae are divided by the cruciform eminence, which forms a cross. The junction of the 4 arms of the cruciform eminence form the internal occipital protuberance.
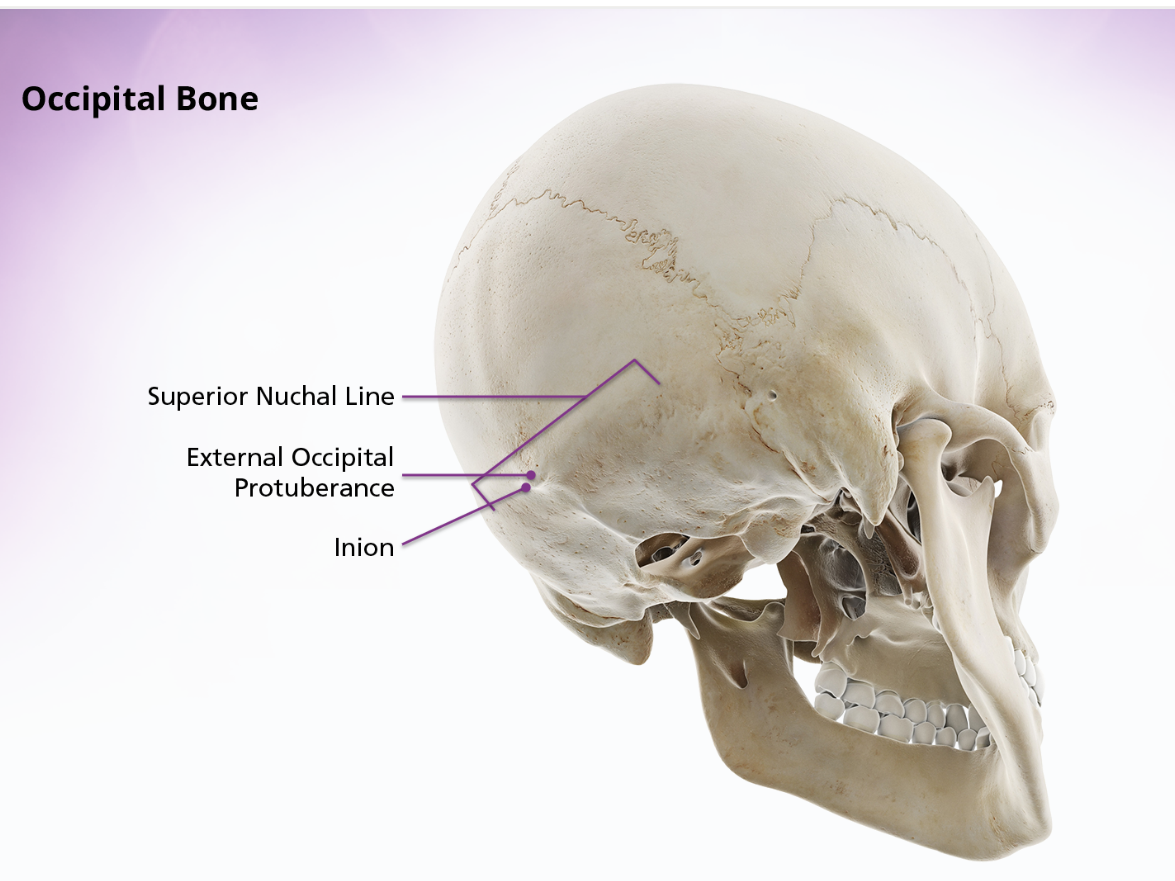
Occipital Bone
The external surface of the squamous portion of the occipital bone is convex. If you palpate the upper posterior portion of your neck and move you fingers upwards, you can feel a ridge of bone running transversely across the base of the skull. This ridge is the superior nuchal line. The external occipital protuberance is location in the middle of this ridge, at approx the center of the external surface of the occipital bone. The peak of the external occipital protuberance is called the inion.
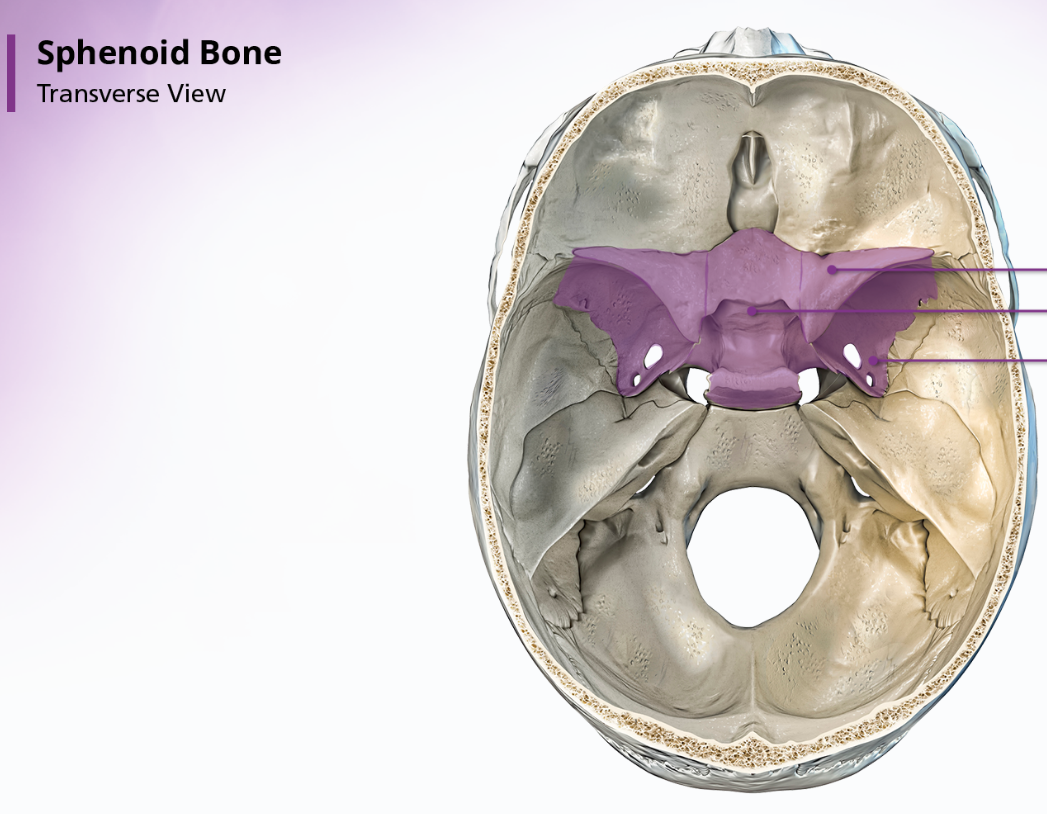
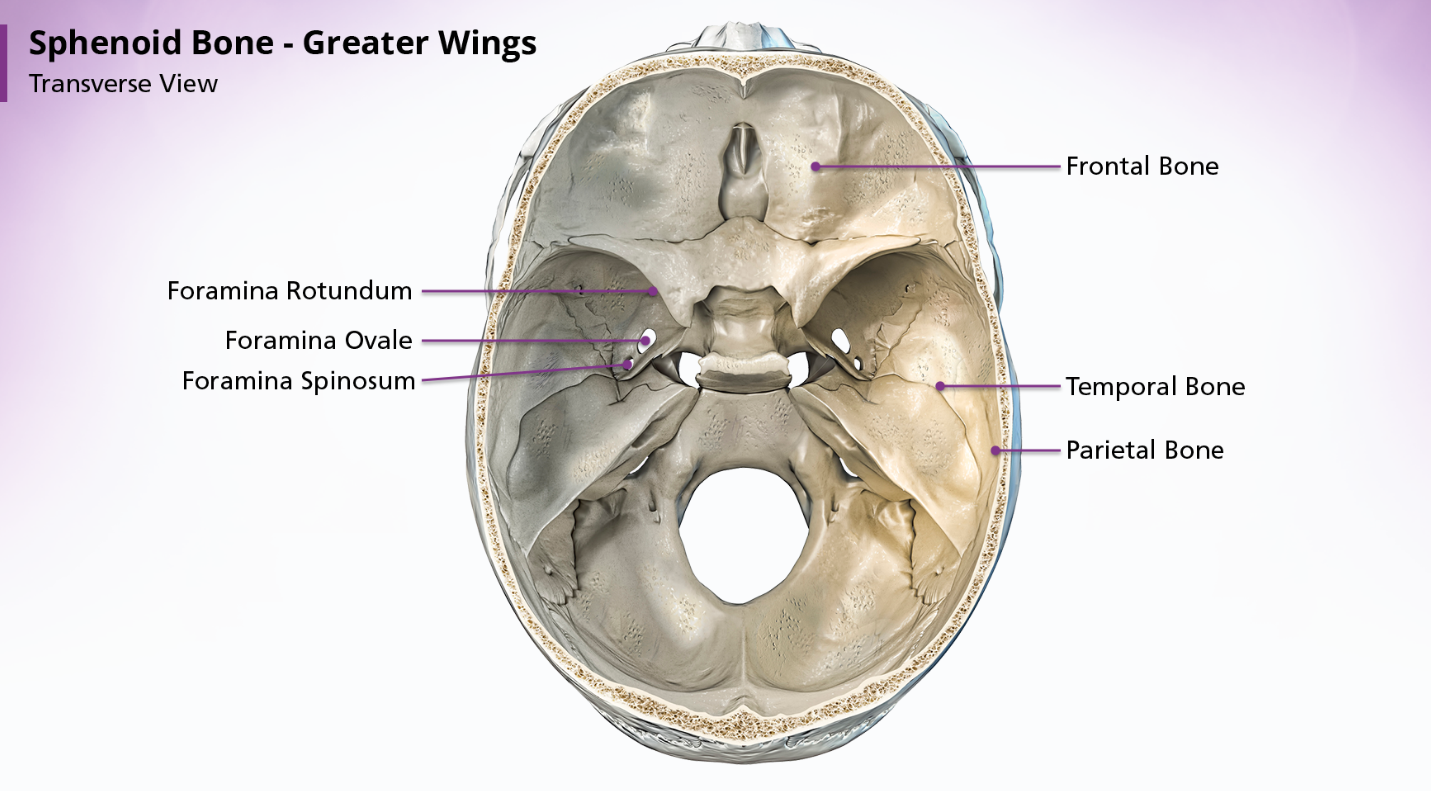
Sphenoid Bone
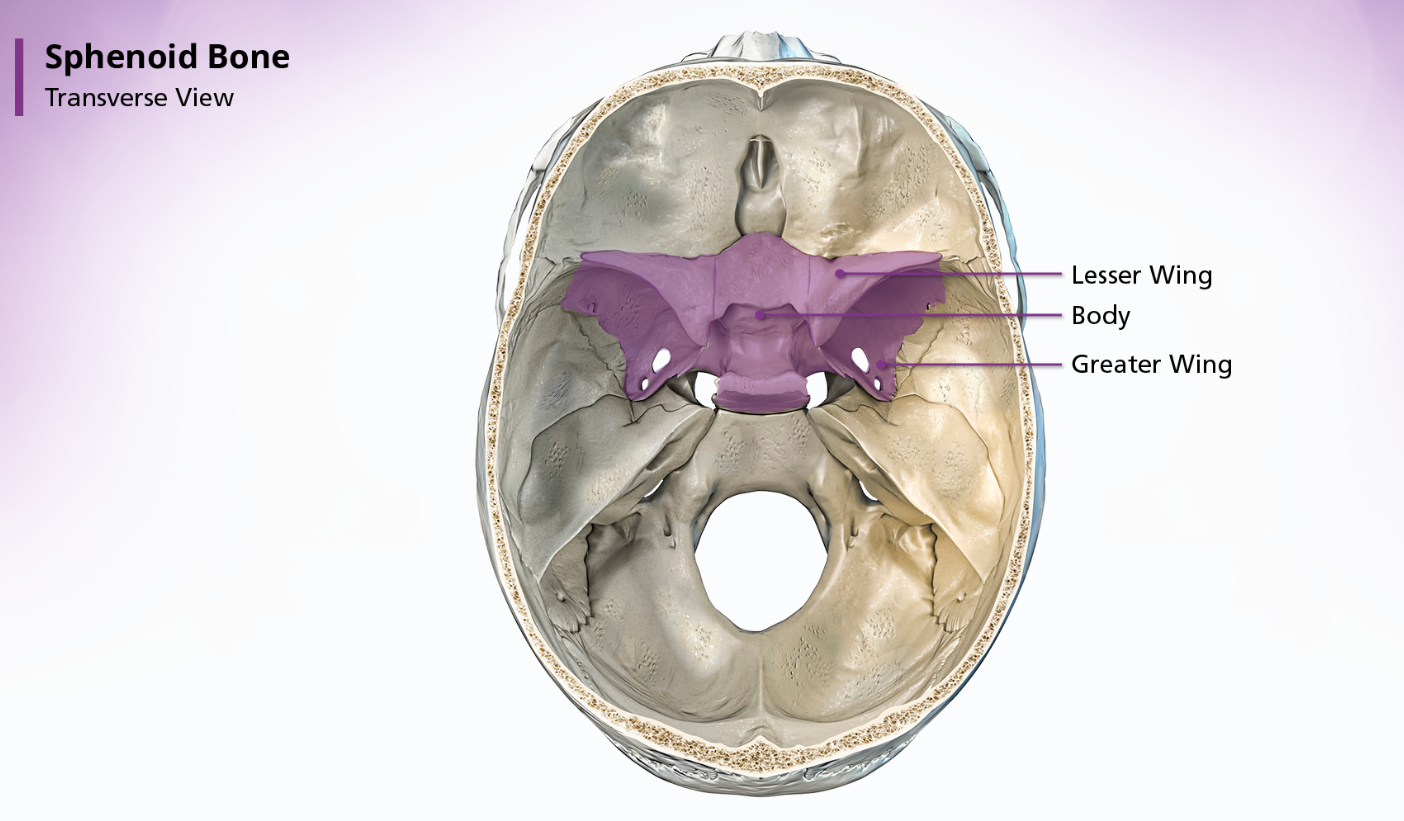
The sphenoid bone is located anterior to the basilar portion of the occipital bone. When looking at the shape of the sphenoid bone, many people think it resembled a bat or a butterfly. The sphenoid bone is divided into 3 parts: the body, the greater wings, and the lesser wings.
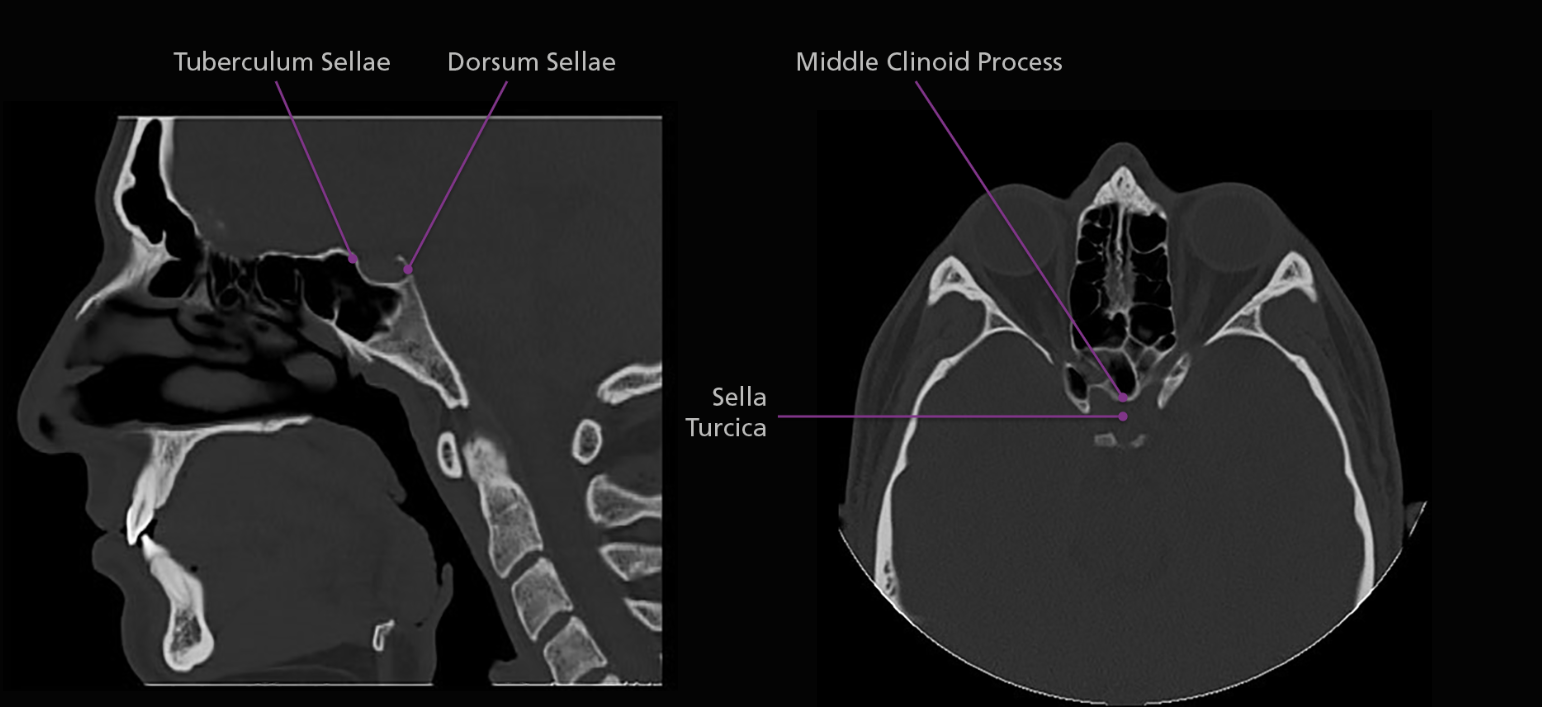
The body of the sphenoid bone is cube-shaped and articulates posteriorly with the basilar portion of the occipital bone. The sphenoid sinuses are located within the body of the sphenoid bone, as is the sella turcica. The sella turcica, or “turkish saddle”, is a deep indentation in the superior surface of the posterior position of the body; it houses and protects the pituitary gland.
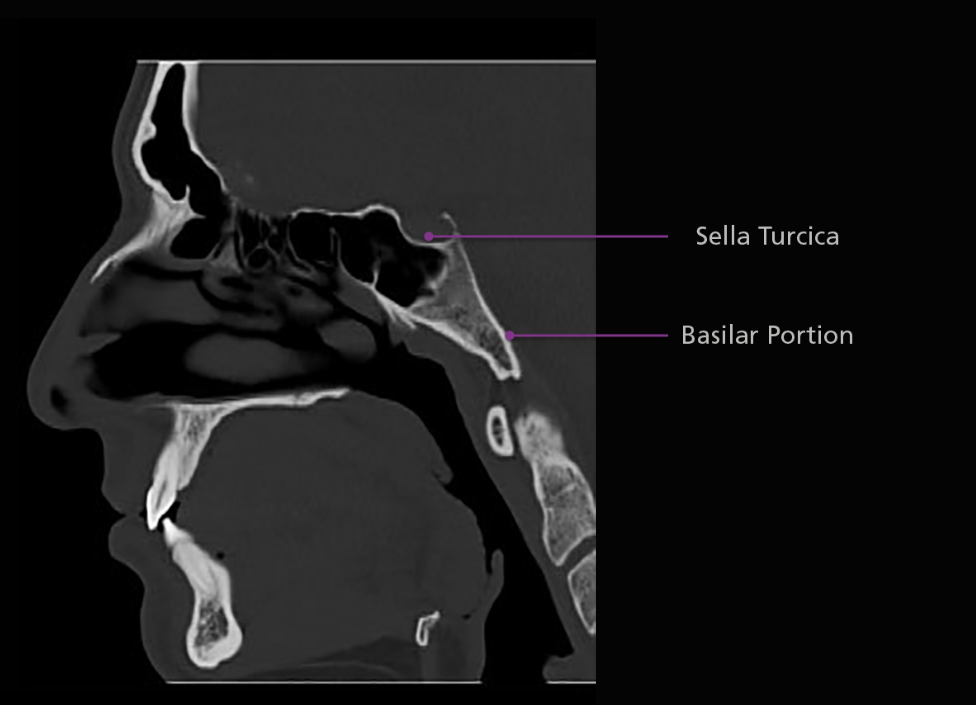

The sella turcica is surrounded by 4 elevations: the tuberculum sellae anteriorly, the middle clinoid processes laterally and the dorsum sellae posteriorly. Arising from the superior border of the dorsum sellae are the posterior clinoid processes. The body of the sphenoid articulates anteriorly with the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone via a midline crest called the sphenoidal crest.
sphenoid bone - greater wings
The paired greater wings of the sphenoid bone arise posteriorly from the lateral borders of the body. They extend upwards, laterally and backward. Within the greater wings are the foramina rotundum, foramina ovale, and foramina