CMP and LFTs
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Liver
- largest organ of the body
- receives dual blood supply (20% from hepatic artery, 80% from portal vein)
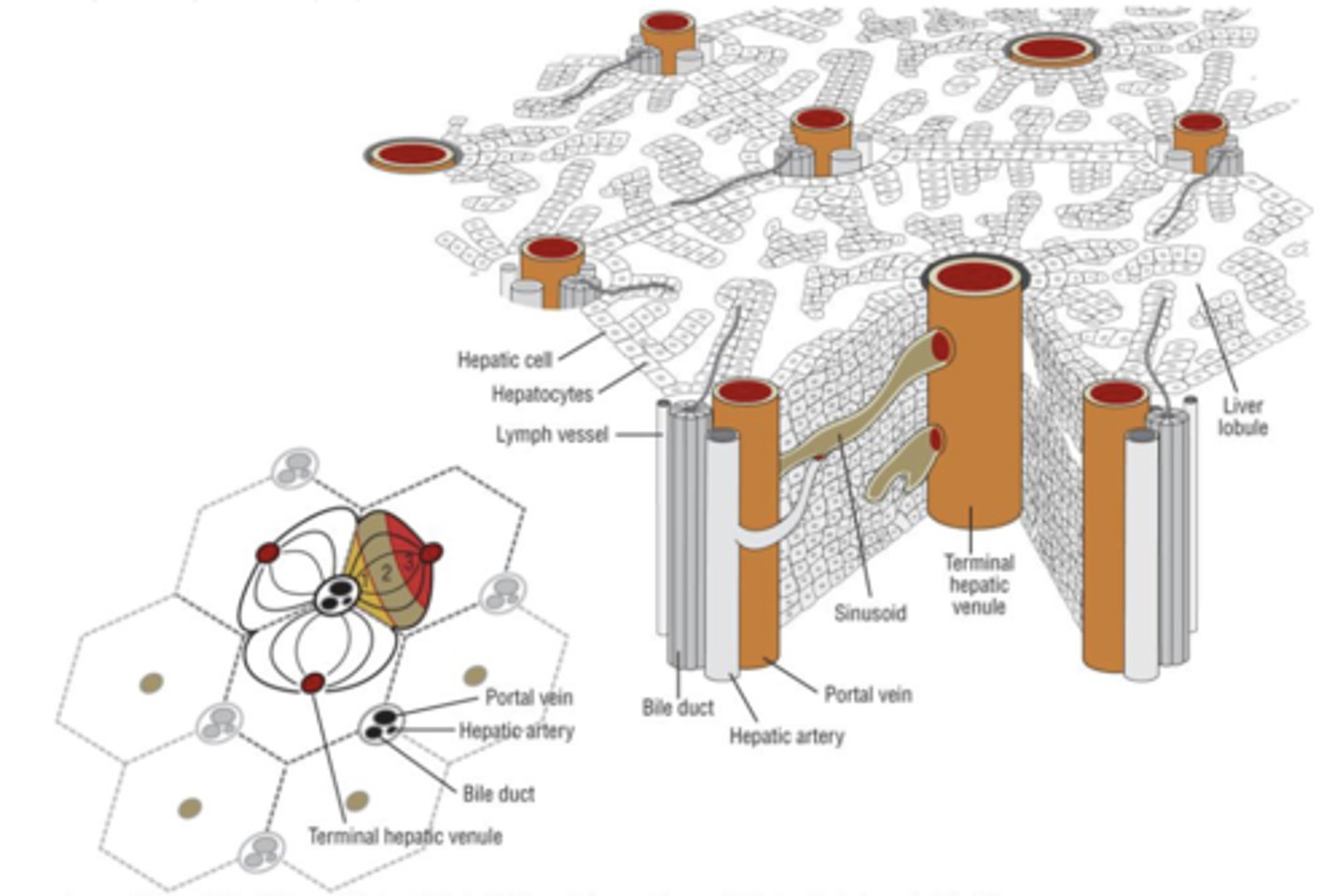
_______________ are the primary cells of the liver
hepatocytes (2/3 liver mass)
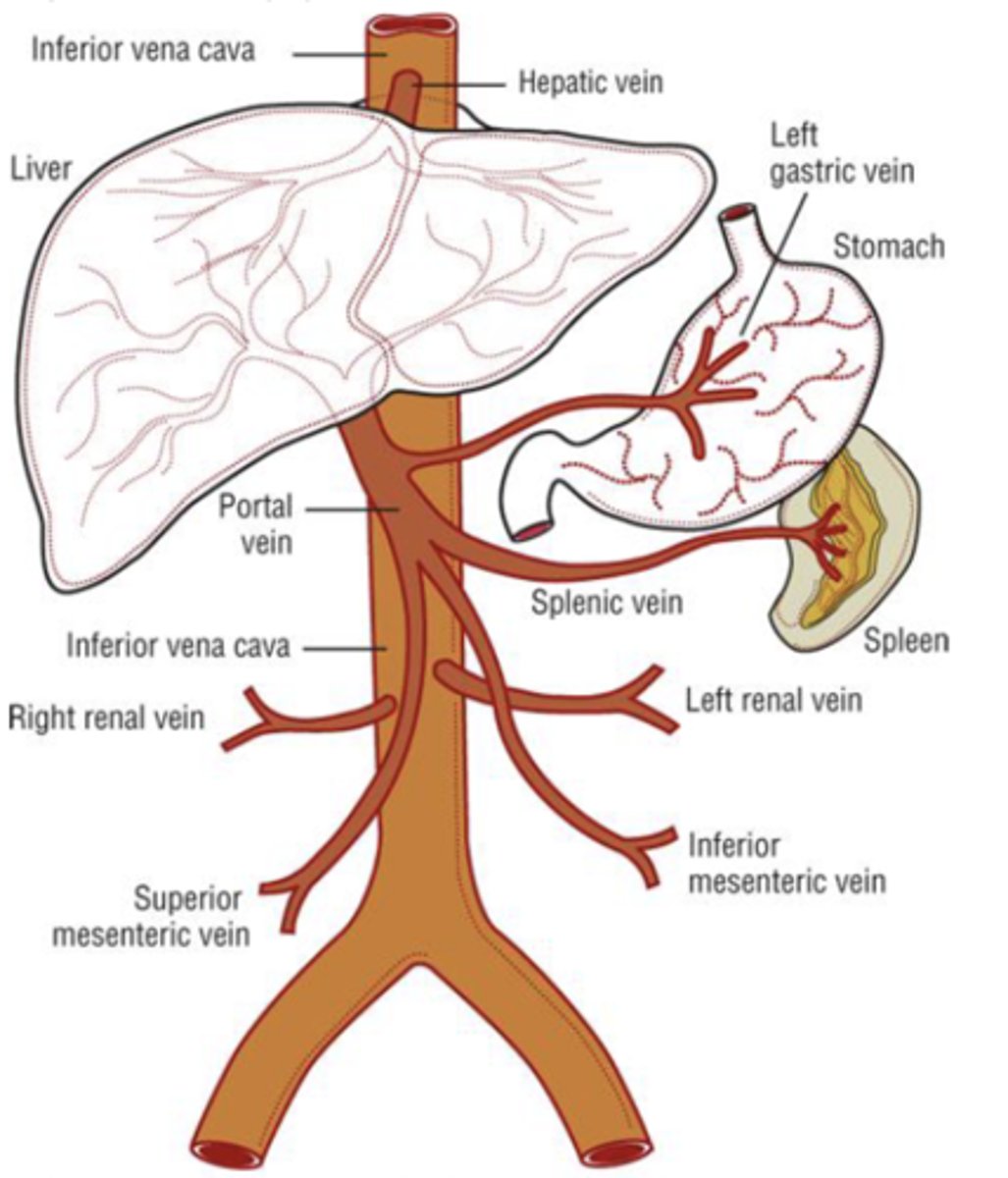
- Blood enters liver via the ______________ and drains through the _______________ of the hepatic ____________.
- Bile flows in the _______________ direction
- enters via the portal triad
- drains through the sinusoidal space
- hepatic lobule
- opposite direction
Function of hepatocytes
- synthesis of serum proteins
- production of bile
- regulation of nutrients
- metabolism & conjugation of lipophilic compounds for excretion in bile or urine
What serum proteins do hepatocytes synthesize? (3)
- albumin
- coagulation factors (Protein C and S)
- growth factors
What do hepatocytes produce? (3)
- bile acids
- cholesterol
- phospholipids
What processes do hepatocytes do to regulate nutrients?
- gluconeogenesis
- glycolysis
- lipogenesis
What kind of compounds undergo metabolism and conjugating for excretion in bile or urine
- bilirubin
- urea
What are markers of hepatocellular function?
- serum bilirubin
- serum albumin
- coagulation factors-prothrombin time (INR)
Normal serum values of total bilirubin
0.3-1 mg/dL- comprised of direct and indirect bilirubin
Unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin
- insoluble in water, bound to albumin
- byproduct of heme degradation
What is elevation in indirect bilirubin typically due to?
other causes, such as hemolysis
Conjugated (direct) bilirubin
- water-soluble, excreted by kidney
- ULN= 0.3 mg/dL
The liver is responsible for the metabolism (conjugation) of bilirubin to a...
water-soluble form that can be eliminated from body
What can an elevation in direct bilirubin indicate?
an obstruction or liver injury
Normal serum albumin value
3.5-5 g/dL
Serum albumin is exclusively synthesized by....
hepatocytes
What is the half-life (t1/2) of serum albumin?
18-20 days
Serum albumin < _______ g/dL is indicative of chronic liver disease
<3 g/dL
T/F: Hypoalbuminemia is often seen in acute liver condition (viral hepatitis drug-related hepatotoxicity)
FALSE
not often seen
T/F: Hypoalbuminemia is not specific for liver disease
TRUE
- can also see hypoalbuminemia in malnutrition, nephrotic syndrome, chronic infections
With the exception of ________, clotting factors are synthesized exclusively by hepatocytes
factor VIII
What is the t1/2 of factor VII?
6 hrs
What is the t1/2 of fibrinogen?
5 days
Prothrombin time (INR) normal value
0.8-1.2
Prothrombin time is measured in _______________ and reported as a ratio compared to an __________________________
- seconds
- average reference group
Can see an increase in clotting time with.......
acute injury and chronic liver disease
Markers of liver injury
- aminotransferases- AST, ALT
- alkaline phosphatase ALP
- GGT
Normal ranges for AST and ALT are typically between...
10-40 units/L
Normal levels of AST and ALT should be...
low
AST and ALT are released into the blood in response to....
hepatocyte injury and death
Where is AST found? (5)
- liver
- cardiac tissue
- skeletal muscle
- kidney
- brain
AST:ALT ratio > ______ is indicative of alcoholic liver disease etiology
>2:1
Where is ALT found?
primarily in liver
Typically ______ is higher than or equal to _______ in most hepatocellular disorders
- ALT
- AST
Acute or chronic liver injury will cause ____________ in serum concentrations of AST and ALT
increases
Elevations of AST and ALT are associated with hepatocellular injury such as:
- viral hepatitis
- ischemic liver injury
- toxin- or drug-induced liver injury
Normal serum value for alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
30-120 units/L
Where is alkaline phosphatase (ALP) found?
- liver
- bone
- placenta
- small intestine
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) can be elevated due to.....
- cholestatic liver disease
- increased amount of bone turnover
Normal serum value of GGT
8-61 units/L
GGT is specific for...
liver
GGT is often tested if ____ is elevated to rule in or out liver disease
ALP
Is GGT increased or decreased in the setting of liver disease?
increased in liver disease
Liver is responsible for converting ammonia into....
urea for excretion by the kidneys
Normal serum value of ammonia
11-35 micromoles/L
Ammonia may be ____________ in the setting of chronic liver disease & hepatic encephalopathy
elevated
T/F: There is a clinical correlation between the degree of elevation of blood ammonia and severity of acute encephalopathy
FALSE
there is NO correlation
What is the gold standard for determining the presence of cirrhosis (fibrotic liver tissue)?
Liver biopsy
In practice, ____________ is often used, which can detect the presence of fibrosis
- ultrasound
- used in combination with clinical picture (presence of portal hypertension, ascites)
The 14 different tests contained in a metabolic panel
- glucose
- calcium
- sodium, potassium, carbon dioxide, and chloride
- albumin
- total protein
- ALP, AST, and ALT
- total bilirubin
- BUN and creatinine
Fishbone diagram for CMP
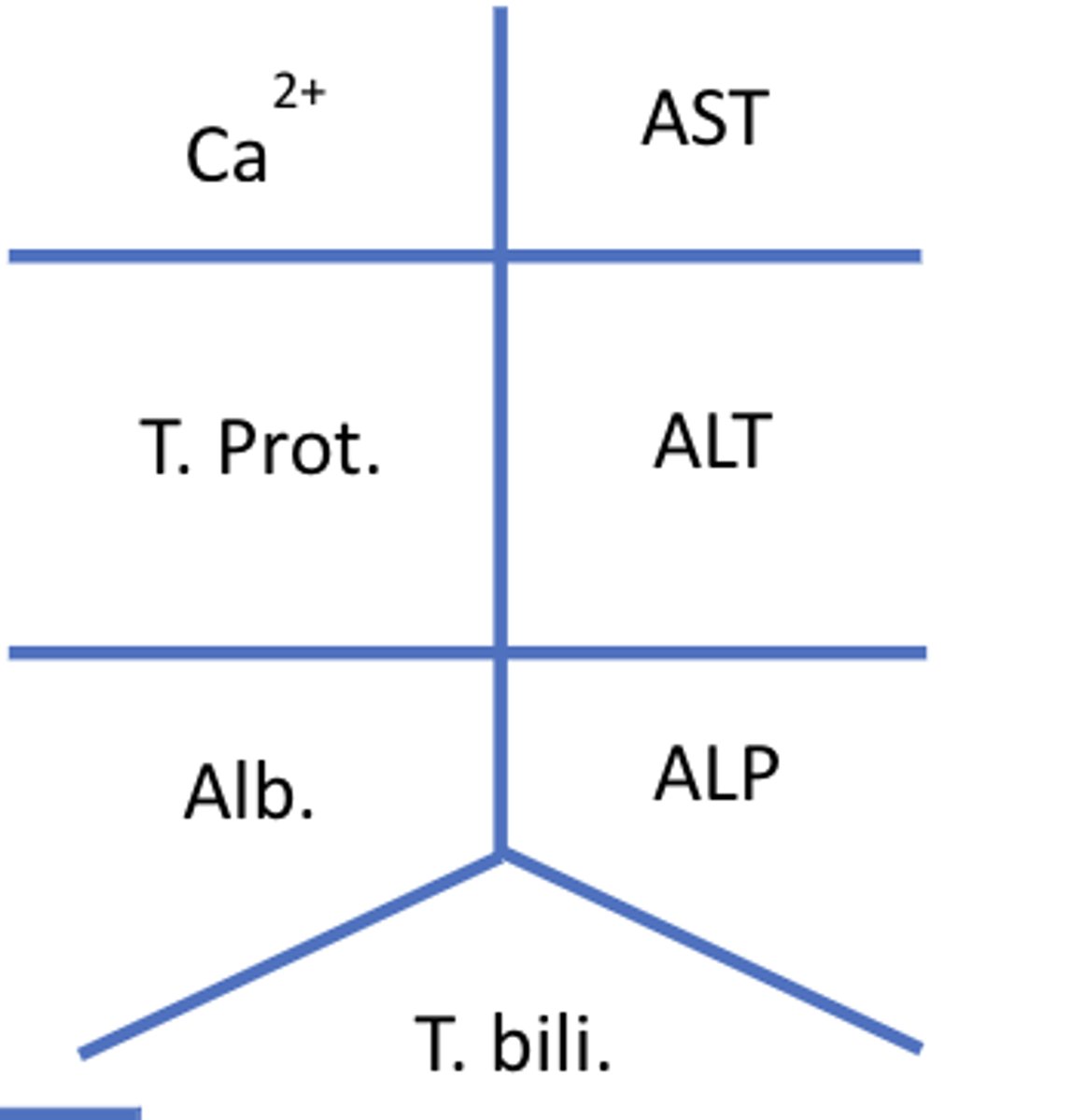
Normal range for ALT
<35 units/L
Normal range for AST
<35 units/L
Normal range for ALP
30-120 units/L
Normal range for albumin
3.5 - 5 g/dL
Normal range for total protein
6.3 - 7.9 g/dL
Normal range for total bilirubin T. bili
0.3 - 1.0 mg/dL
Normal range for direct (conjugated/water soluble) bilirubin
0.1 - 0.3 mg/dL
Normal range for indirect (unconjugated/insoluble) bilirubin
0.2 - 0.7 mg/dL
Normal range for GGT (Gamma-glutamyl transferase)
8 - 61 units/L
Normal range for INR
0.8 - 1.2
Normal range for ammonia
11-35 mcmol/L
Which of the following would be considered markers of liver injury?
a. Serum albumin
b. Serum bilirubin
c. ALT
d. Prothrombin time
c. ALT
Which of the following lab values would you expect to be DECREASED in the setting of chronic liver disease?
a. Albumin
b. Total bilirubin
c. GGT
d. INR
a. Albumin
Child-Pugh - staging/severity classification system
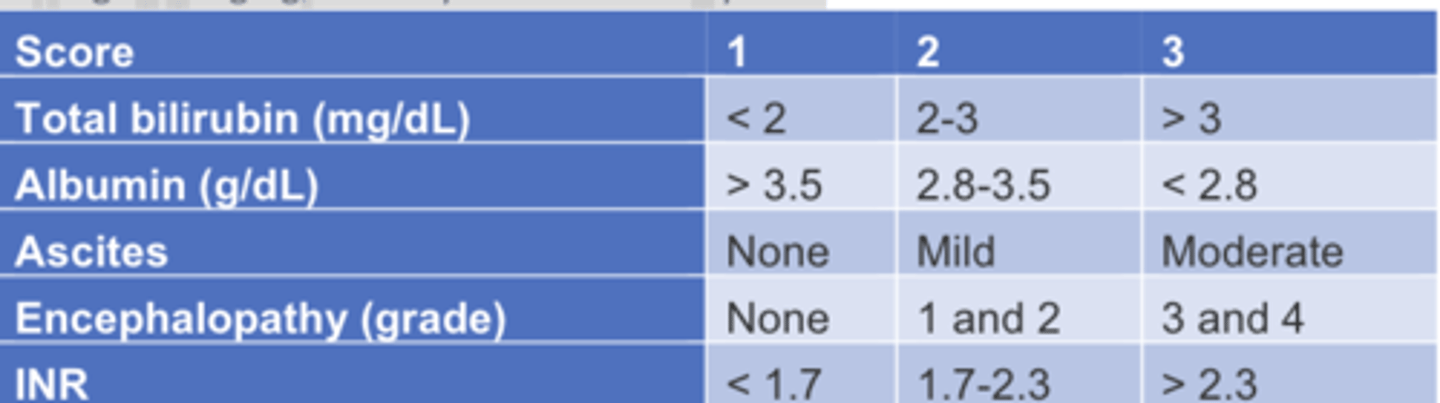
Child-Pugh - staging/severity classification system
Grade A < ____________, considered mild
Grade B = ___________
Grade C = ___________, considered severe
Grade A < 7 points
Grade B = 7-9 points
Grade C = 10-15 points
Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)
prognostic indicator, used for staging of liver transplantation patients
4 variables in the MELD
1. INR
2. Serum bilirubin
3. Serum creatinine
4. Serum sodium
- MELD score ranges from ____ to ____
- What are higher scores correlated with?
- 6 to 40
- with increased severity and higher 3-month mortality
MELD score of 30-39 associated with a....
3-month mortality rate of 52.6%