Dispatch Navigation
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms

What does this symbol mean?
VOR

What does this symbol mean?
DME

What does this symbol mean?
VOR/DME

What does this symbol mean?
TACAN

What does this symbol mean?
VORTAC

What does this symbol mean?
NDB

What does this symbol mean?
RNAV

What does this symbol mean?
Fix
What does VOR stand for?
Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range
What does DME stand for?
Distance Measuring Equipment
What does TACAN stand for?
Tactical Air Navigation
What does NBD stand for?
Non-directional beacon
What does RNAV stand for?
Area Navigation

What does this symbol mean?
Civil use

What does this symbol mean?
Civil and Military use

What does this symbol mean?
Military use

What does this symbol mean?
Jet route

What does this symbol mean?
Q Route
What does this symbol mean?
Denotes a DME fix

What does this symbol mean?
Miles between fixes and/or NAVAIDS
What does this symbol mean?
Mileage between other fixes, NAVAIDS, and/ or mileage breakdown

What does this symbol mean?
Unusable route

What does this symbol mean?
Holding pattern
What is a VOR?
a ground-based radio navigation system that represents 360 degrees of a compass and tells aircraft what radial they are on
If you are on the 180 radial from a VOR, what does that mean?
You are directly south of it
What is the VOR/DME/TACAN terminal service volume?
1,000 ft up to and including 12,000 ft and out to 25 NM
What is the VOR/DME/TACAN low altitude service volume?
1,000 ft up to and including 18,000 ft and out to 40 NM
What is the VOR/DME/TACAN high altitude service volume?
1,000 feet up to and including 14,500 feet and out to 40 NM
From 14,500 ft up to and including 60,000 ft and out to 100 NM
From 18,000 ft up to and including 45,000 ft and out to 130 NM
How does DME work?
plane and ground station send pings to each other to measure the distance from one another. tells you how far you are in NM
What is a TACAN?
developed by the military because VOR/DME was not suitable for their use, but produces the same result
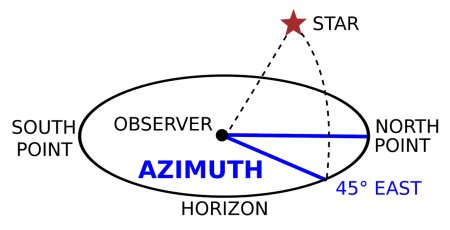
What is azimuth?
horizontal angle formed between a referenced direction (North or South)
What is an example of Azimuth?
45° from the north
What is VORTAC?
VOR and TACAN combined which produces azimuth and distance, considered to be a unified nav aid
What is RNAV?
any flight path, fly directly between waypoints instead of navaid to navaid
When is RNAV used?
During DPs and STARs
What is a NDB?
Transmits signals in all directions to the aircraft and gives a reference point or beacon, which can determine relative position
What does ILS stand for?
Instrument landing system
What is an ILS?
Designed to provide an approach path for exact alignment and descent of an aircraft on final approach to a runway
What are the components of an ILS?
Localizer, glide slope, Outer Marker (OM), and Inner Marker (IM)
On an ILS, what gives guidance information?
Localizer and glide slope
On an ILS, what gives range information?
Marker beacon and DME
On an ILS, what gives visual information?
Approach lights, touchdown and centerline lights, and runway lights
What is a Localizer?
A signal that provides the pilot with course guidance to the runway’s centerline, keeps you aligned left/ right with the runway
How does a Localizer work?
Antenna located at the far end of a runway that transmits two signals, left and right
When using a localizer your receiver has more left signal what does this indicate?
Right of the centerline
When using a localizer your receiver has more right signal what does this indicate?
Left of the centerline
What is Glideslope?
Keeps you on the correct descent
How does Glideslope work?
An antenna located beside the runway near the touchdown zone that transmits two vertical signals, above and below glidepath
When using the glideslope, your receiver has more above signal. What does this indicate?
Too low
When using the glideslope, your receiver has more below signal. What does this indicate?
Too high
On an ILS, what is the Outer Marker (OM)?
Identifies the final approach fix
On an ILS, what is the Middle Marker (MM)?
Indicates a position approximately 3,500 feet from the landing threshold
On an ILS, what is the Inner Marker (IM)?
Indicates the point that an aircraft is at decision height (CAT II only)
What is decision height (DH)?
Height above the runway (TDZ) where a pilot must decide to either continue the landing or execute a missed approach
What is decision altitude (DA)?
Height in MSL where a pilot must decide to either continue the landing or execute a missed approach
What is the difference between DA and DH?
ILS uses DH and RNAV uses DA
What makes a non-precision approach different from a precision approach?
Horizontal guidance only, no vertical guidance because it doesn’t have a glidepath
What is the Minimum Descent Altitude (MDA)?
Lowest altitude allowed to descend to a non-precision instrument approach
What is the Final Approach Fix (FAF)?
Final point on an instrument approach where you’re transitioning from the approach to the start of descent
What is the compass locator?
A type of NDB that identifies position and is used as an aid to an ILS approach when other equipment fails
What is a transponder?
Device installed in aircraft that shows ATC squawk code and location of plane by sending signals back and forth from ground-based radar systems
If you’re heading East, what flight levels should you be using?
Odd altitudes
If you’re heading West, what flight levels should you be using?
Even altitudes
What does MOCA stand for?
Minimum Obstruction Clearance Altitude
What does Minimum Obstruction Clearance Altitude (MOCA) mean?
Lowest altitude on an airway or route that guarantees you will clear obstacles
If an aircraft is using a VOR what is the distance that the MOCA will be reliable?
22 nm from the VOR
At or above the MOCA, what is your assured obstacle clearance?
At least 1,000 ft
What symbolizes the MOCA on an IFR high chart?
Asterisk symbol (*) before the altitude
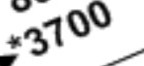
What does the star symbol indicate before the altitude?
Indicates the Minimum Obstruction Clearance Altitude (MOCA)
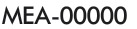
What does this symbol mean?
Minimum Enroute Altitude

What does this symbol mean?
Maximum Authorized Altitude

What is the minimum enroute altitude for J30?
20,000 ft

During what times is J30 available to use?
1100-0300z

What is the maximum authorized altitude for J96?
35,000 ft
What is a Q route?
High altitude RNAV (GPS) routes that aren’t dependent on VORs
What is a J-route (Jet route)?
High altitude IFR airways that use NAVAIDs (mostly VORs)
What altitudes can Jet routes range from?
FL180 to 450
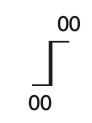
What is this symbol?
Changeover point from NAVAIDs
What is Runway Visual Range (RVR)?
Value representing horizontal distance that can be seen down a runway
What are the three RVR sensors?
Touchdown, midpoint, and roll out
Which RVR is controlling for takeoff minimums?
Touchdown zone