Beer Fermentations
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Largest beer production by…
China
Which country drinks the most beer?
Czech Republic
History of Beer
Safer than water
Beer jar contained pale yellow residue - oxalate ion
Ales
Top-fermenting yeasts
Warm temp (faster ferm)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Lagers
Bottom-fermenting yeasts
Fermented cold (slow fermentation)
Saccharomyces pastorianus
Wild Brewing (Lambic styles)
Open top fermentations, spontaneous
Use wild yeasts
High (uncontrolled) alcohol
Sweet/fruity
Seasonal fruits/herbs
Ingredients Needed
Water
Grains
Hops
Yeast
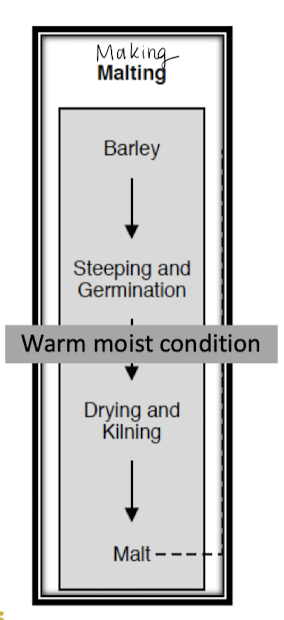
Beer Process: Malting
Put barley in water, then remove.
incubate cold and humid
germinate - generates rootless
induces various hydrolases
Dry germinated barley to preserve it… w/o losing enzymatic activity
Decreased moisture consumption
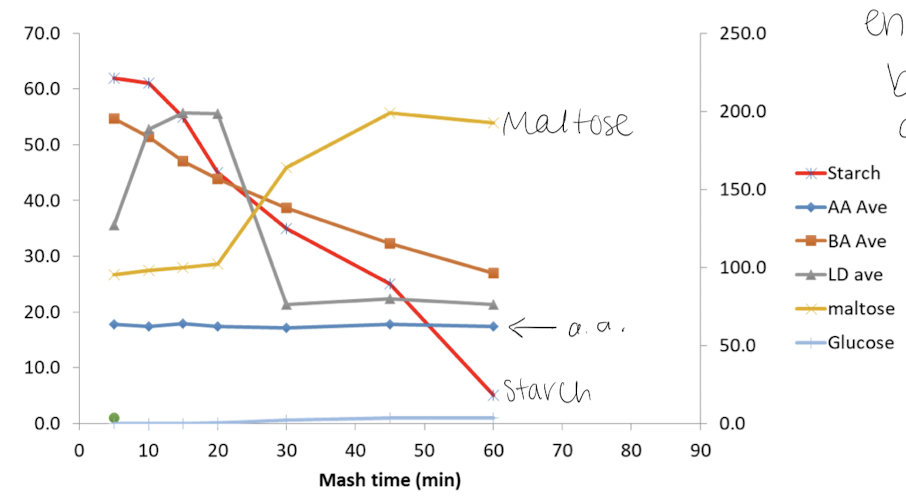
Beer process: Mashing
Milling dried barley
Goal: to release the fermentable sugars into a liquid
Need enzymes to work on locked up substrates to release monomers (or dimer) and a.a. into liquid
Heating
Heating malt/water mix slowly in stages
From lower to higher temps
Assortment of enzymes have an assortment of temp. optima
Mian starch degrading enzymes: alpha-amylases and beta-amylases
Pigments/flavors etc. are also extracted
Kettle Boil - raise temp to 75 ℃, inactivating enzymes, denatures (some) proteins
Stuff precipitates, soluble fraction has fermentable in it, filter away precipitates
Wort: 75% small fermentable sugars (glc, fru, mal, suc, etc.), 25% larger non-fermentable oligosaccharides (DP 4 and larger) —> prebiotics for humans. nitrgoen: 3-6% proteins/peptides/amino acids
Reduce large substrates (starch and protein base units), making food for yeast
Adding Hops (Homolus lupulus)
Add flavor and aroma
Flavor —> bitter due to hop alpha-acids
Aroma —> hop oils (terpenoids, esters ketones)
Add hops to kettle boil
Fermentation by Saccharomyces
Ale
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Lager
Saccharomyces pastorianus
Fernentation occurs by Crabtree effect (lots of O2 around but still ferments
Glucose consumed first, catabolite repression blocks others from being consumed
Vegemite/Marmite
Made from yeast waste
Flocculation by Saccharomyces
Yeasts clump together and settle
Clarifies the beer
Allows for easier filtration

Wild Yeasts
Brettanomyces is a non-spore forming genus of yeast (family Saccharomycetaceae). The genus name Dekkera.
Used for long-term fermentations (months/years) after initial fermentation by Saccharomyces
Funky flavors and aromas (barnyard and horse-blanket)
Only used in brewers making specific ‘Brett’ beers
If not wanting Brett, then major infection - “Burn it down”
Beer Spoilage
LAB
Acidification, exopolysaccharide, diacetyl
AAB
HOP resistance in LAB
HOPs are antimicrobial
Most common LAB resistant:
Pediococcus damnosus
Lactobacillus brevis
Transport hops out to keep themselves alive
Hop-sensitive LAB
Hop-resistance LAB