circulatory system
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms

B
white blood cells (leukocytes)
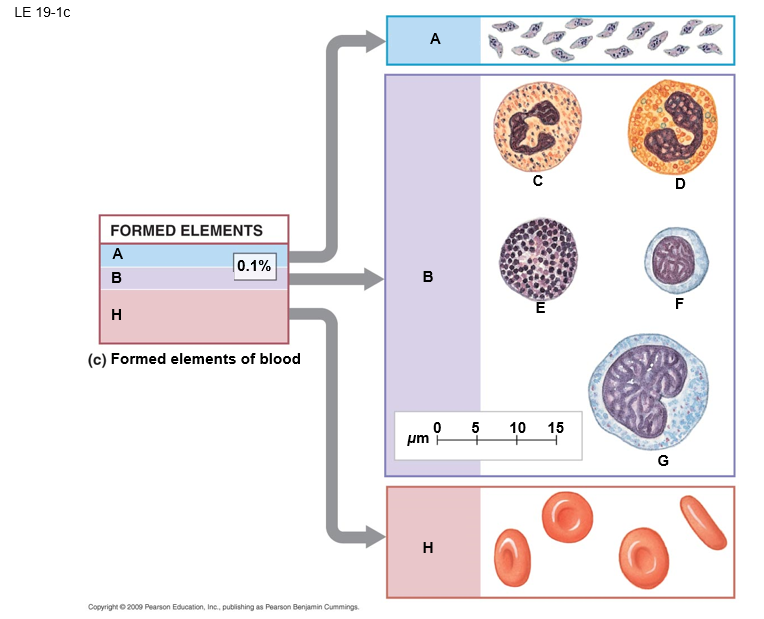
E
basophil
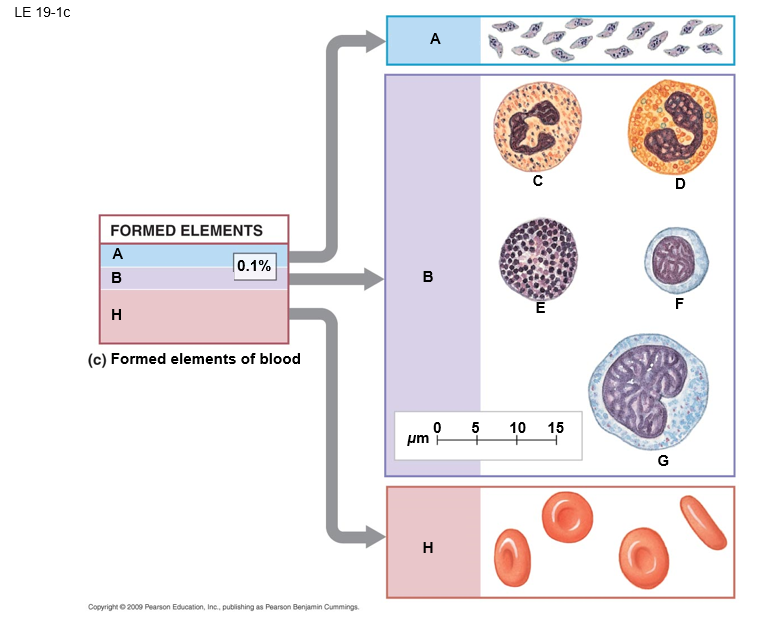
F
lymphocyte
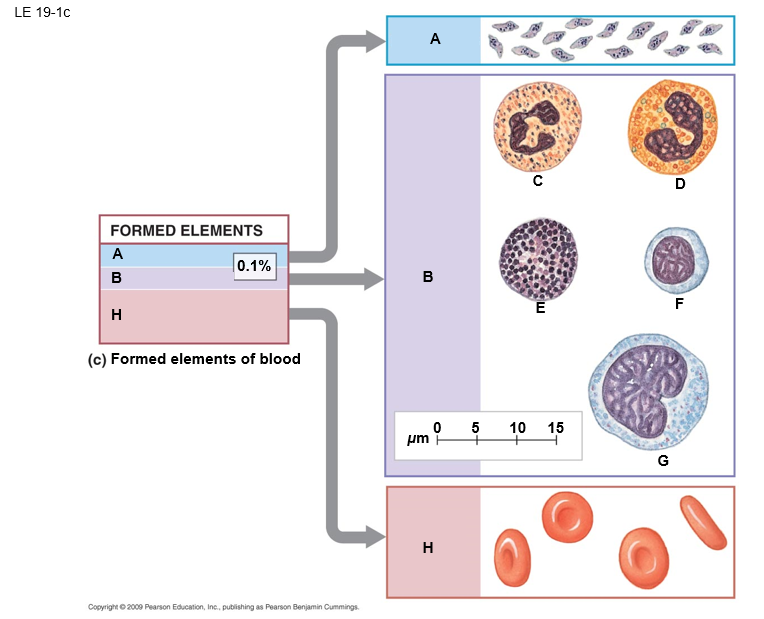
D
eosinphil
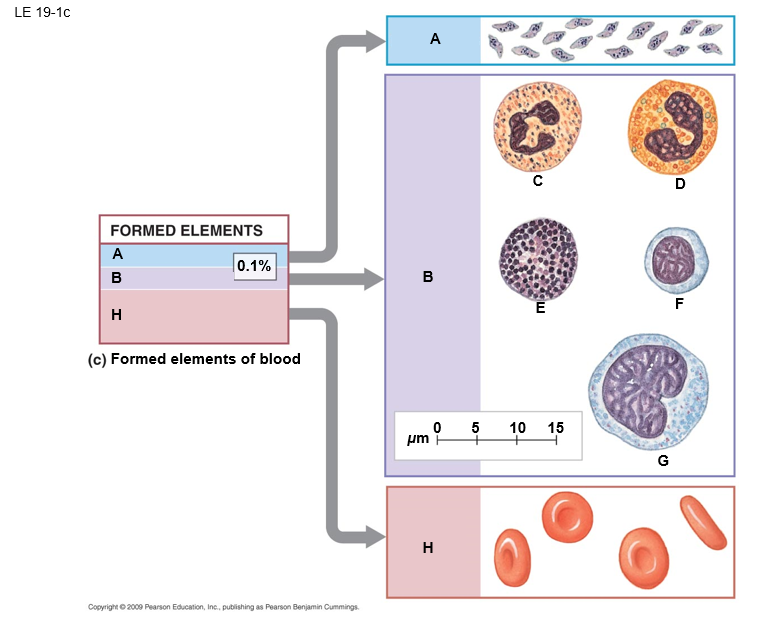
C
neutrophil
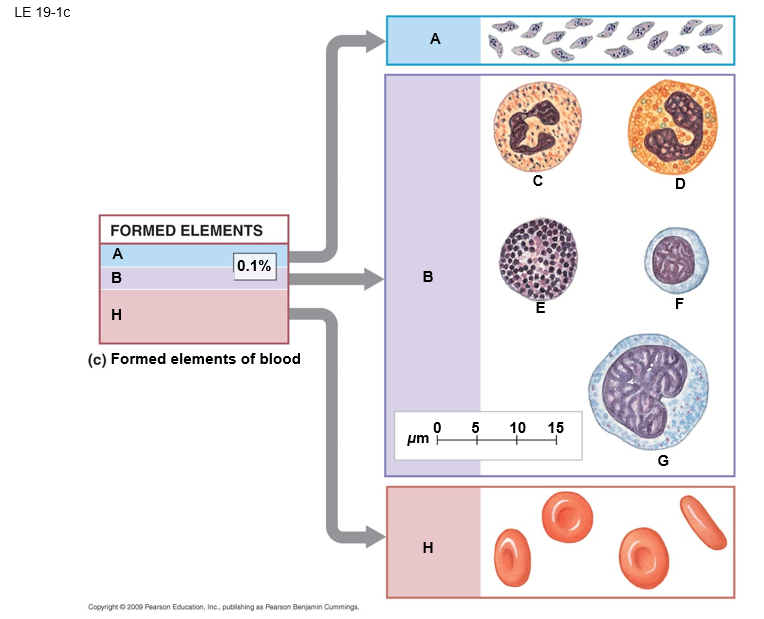
A
platelets
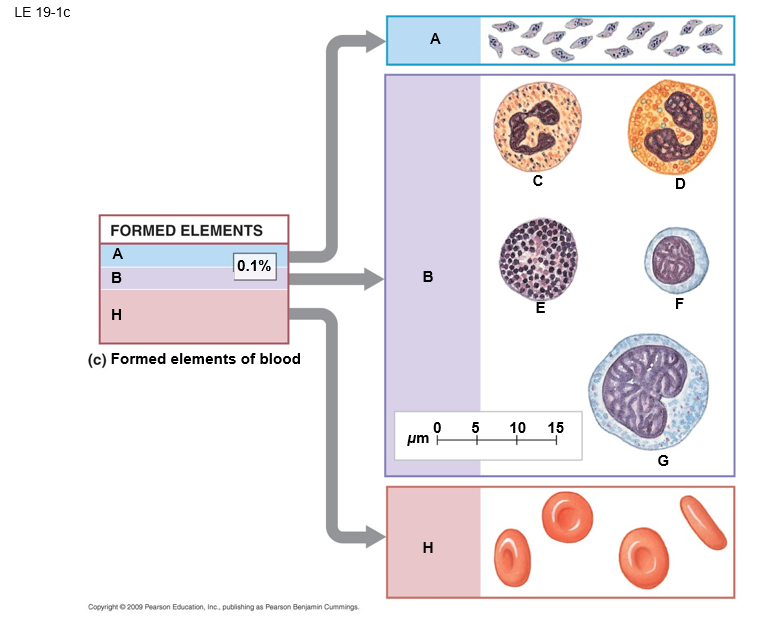
G
monocyte
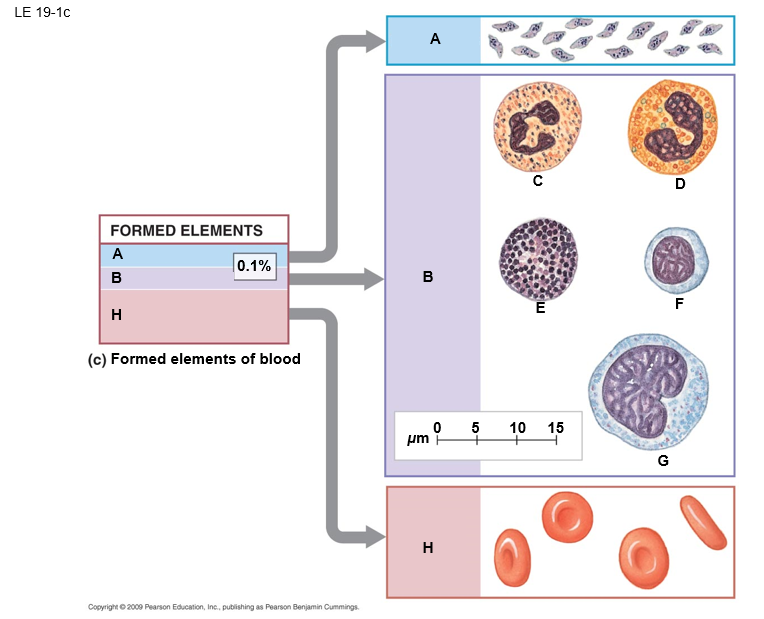
H
red blood cells (erthrocytes)
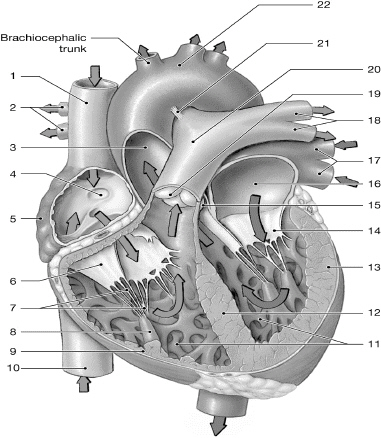
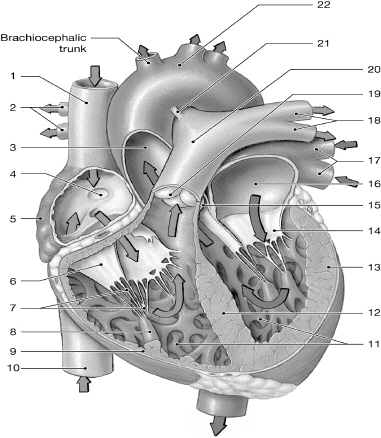
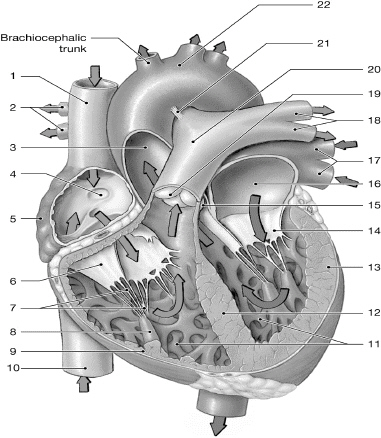
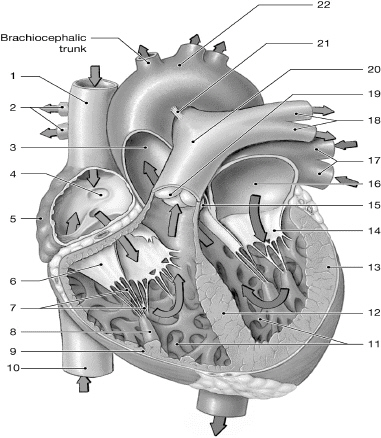
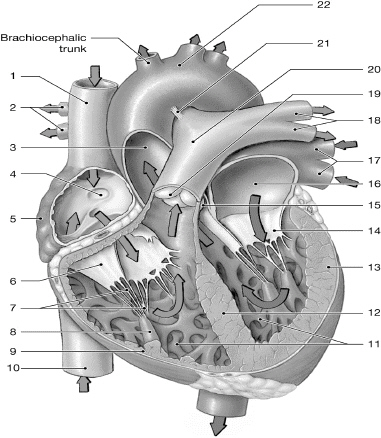
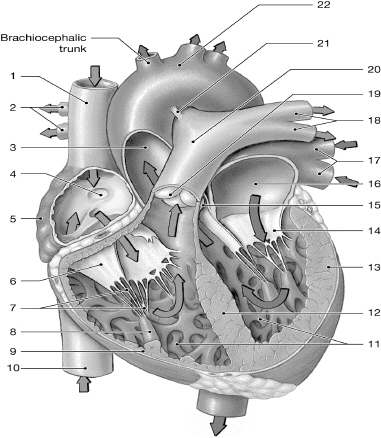
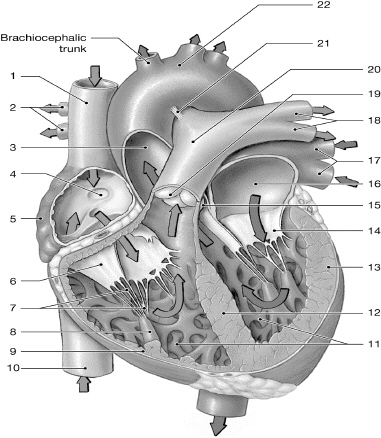
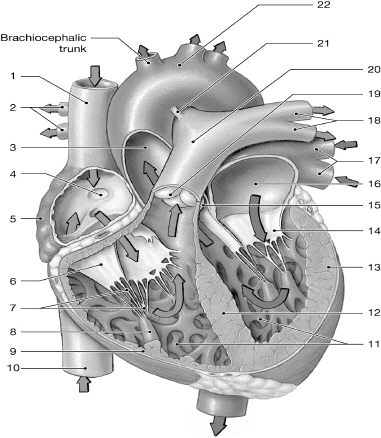
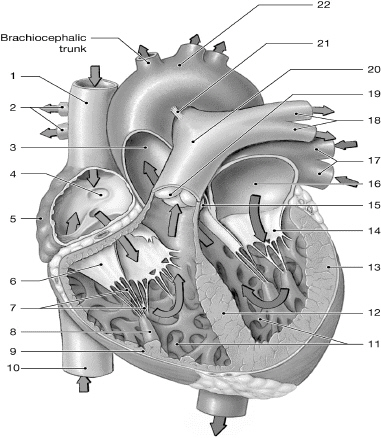
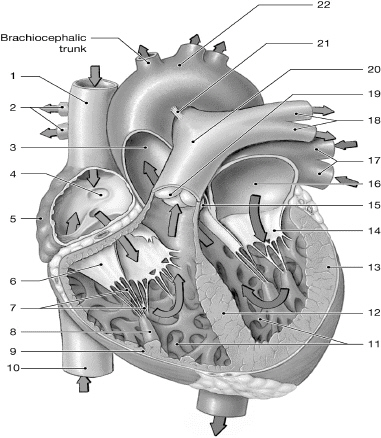
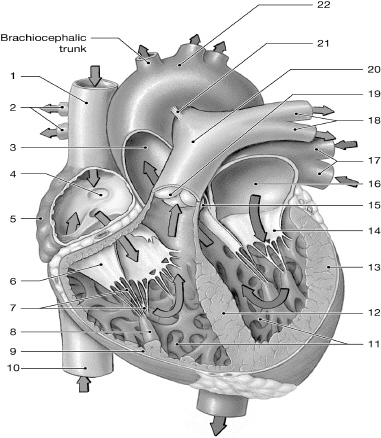
14
left AV (bicuspid/mitral) valve
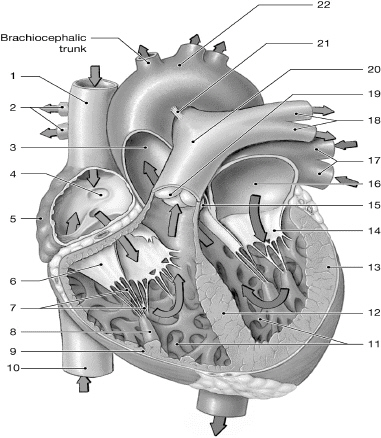
16
left atrium
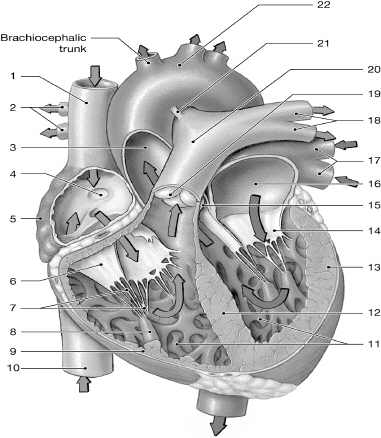
10
inferior vena cava
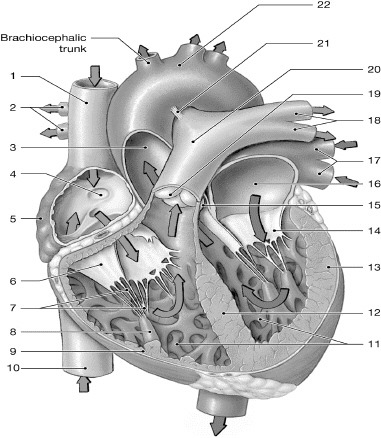
1
superior vena cava
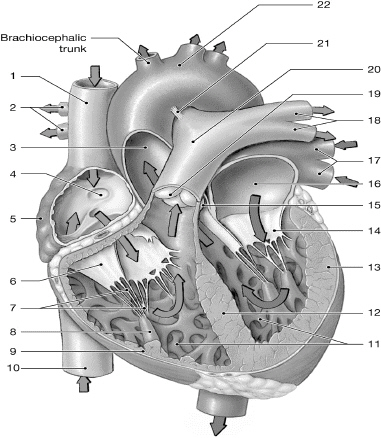
17
left pulmonary veins
7
chordate tendinae
5
right atrium
13
left ventricle
6
right AV (tricuspid) valve
12
interventricular septum
2
right pulmonary arteries
18
left pulmonary arteries
3
aorta
19
pulmonary valve
9
right ventricle
7
aortic
8
deoxygenated blood
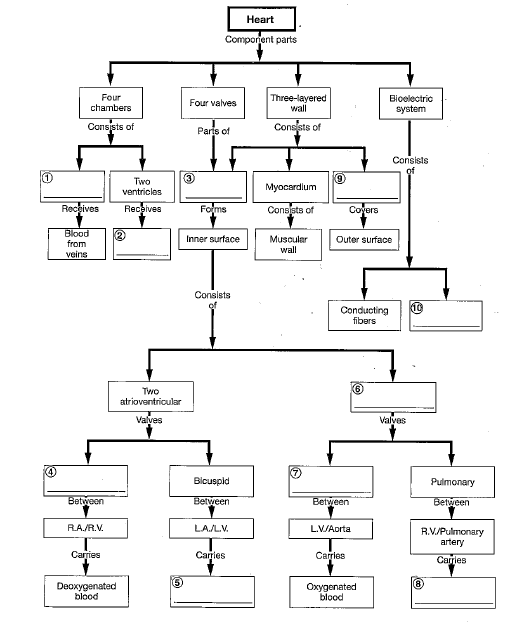
10
pacemaker cells
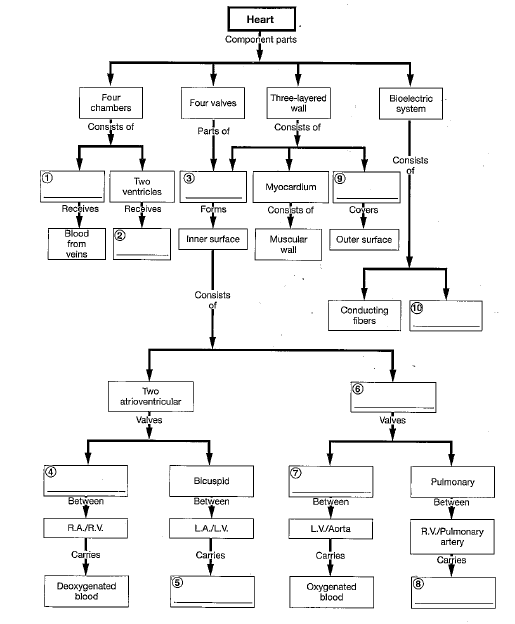
4
tricuspid
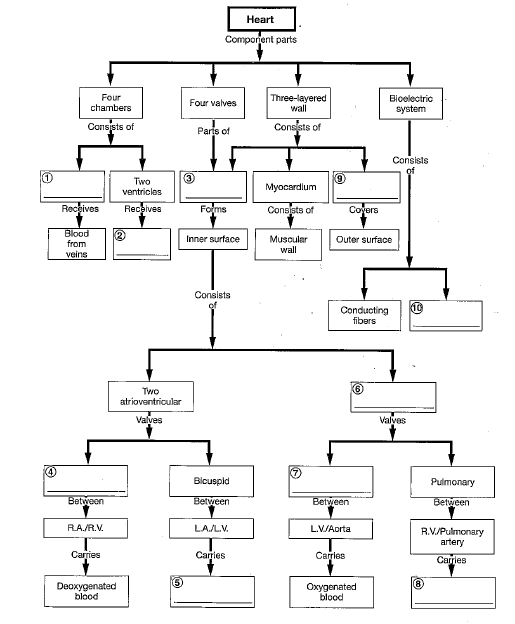
2
blood from atria
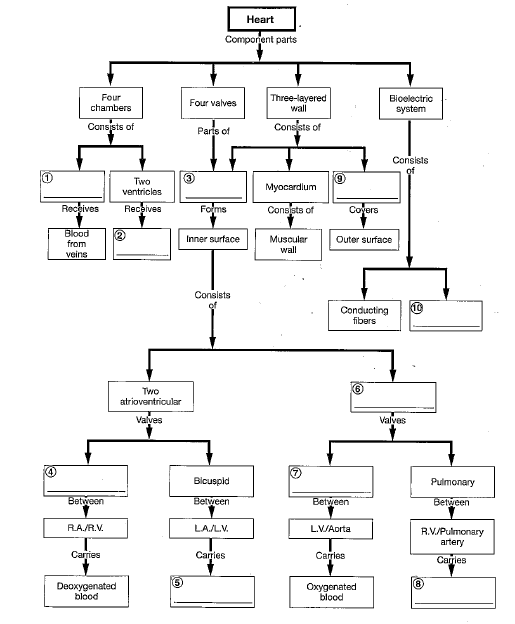
9
epicardium
5
oxygenated blood
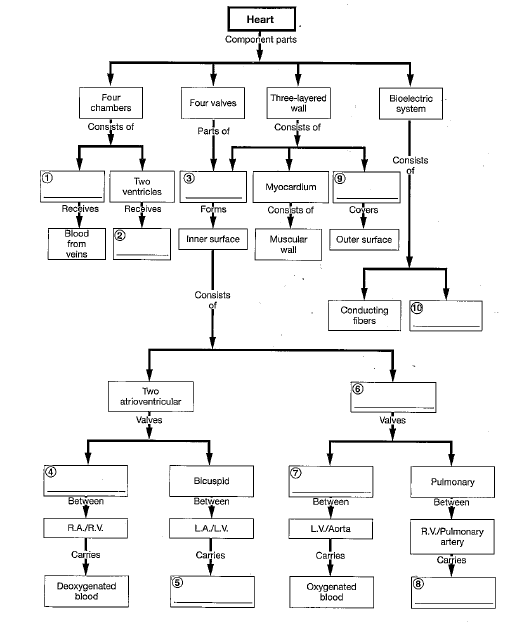
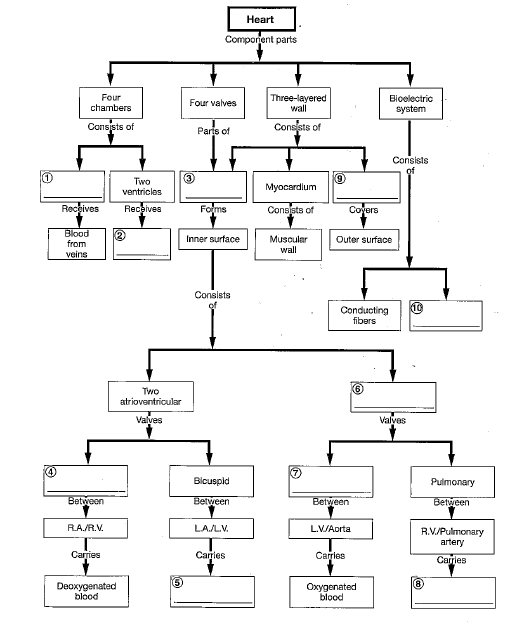
1
two atria
1
pulmonary veins
2
arteries and arterioles
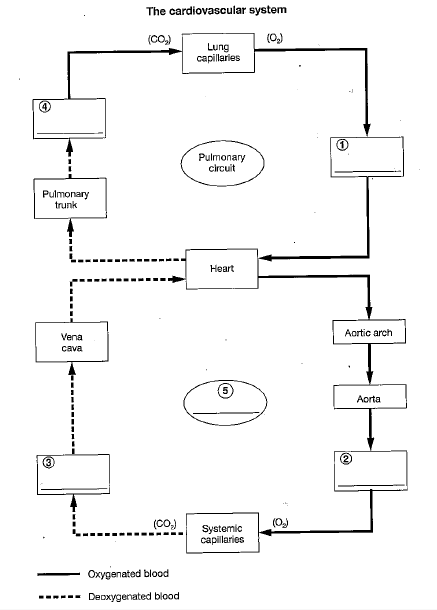
4
pulmonary arteries
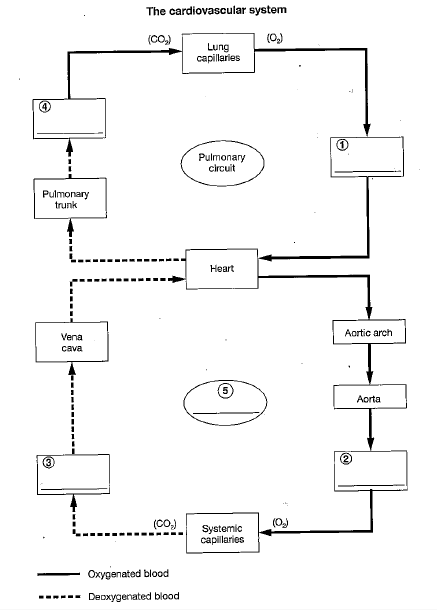
5
systemic circuit
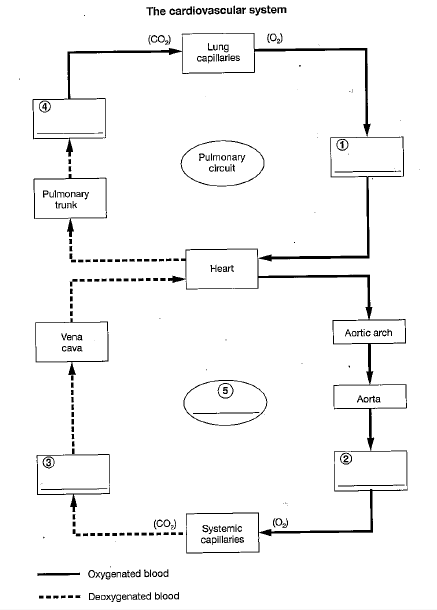
3
veins and venues
The insoluble fibers that provide the basic framework for a blood clot are called _____.
fibrin
After a clot has formed, the clot shrinks due tot the action of actin and myosin filaments contained in _____.
platelets
A low number of white blood cells is called _____.
leukopenia
The part of the RBC responsible for the cell’s ability to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide is _____.
hemoglobin
A low platelet count refers to a condition called _____.
thrombocytopenia
T cells and B cells are representative cell populations of WBCs identified as _____.
leukocytes
The afferent vessels that return blood to the heart are _____.
veins
Oxygenated blood is returned to the left atrium via the _____.
pulmonary veins
The chambers of in the heart with thin walls that receive blood from the vessels are the _____.
atria
The action of cardiac muscle tissue contracting on its own in the absence of neural stimulation is called ____
authorhymitcity
The ____ is the primary source of the impulses that establish the heart rate.
SA node
The right side of the heart contains blood which is _____.
deoxygenated
The serous membrane lining the pericardial cavity is called the _____.
pericardium
The right atrium receives blood from the systemic circuit and passes it to the _____.
right vebtricle
When blood leaves the left atrium, it is forced through an atrioventricular valve into the _____.
left ventricle
The only arteries in the body that carry deoxygenated blood are the _____ arteries.
pulmonary
The part of the hemoglobin molecule that directly interacts with oxygen is:
the iron ion
Antigens (agglutinogens) are contained (on, in) the _____, while the antibodies (agglutinins) are found (on, in) the _____.
cell membrane of RBC; plasma
If you have type A blood, your plasma holds circulating _____ that will attack _____ erythrocytes.
anti–B antibodies; Type B
Megakaryocytes are specialized cells of the bone marrow responsible for:
formation of platelets.
Basophils are specialized in that they:
contain histamine that exaggerates the inflammation response at the injury site.
If antigen “B” meets with antibody “anti-A”, the result would be:
clotting or agglutination would not occur.
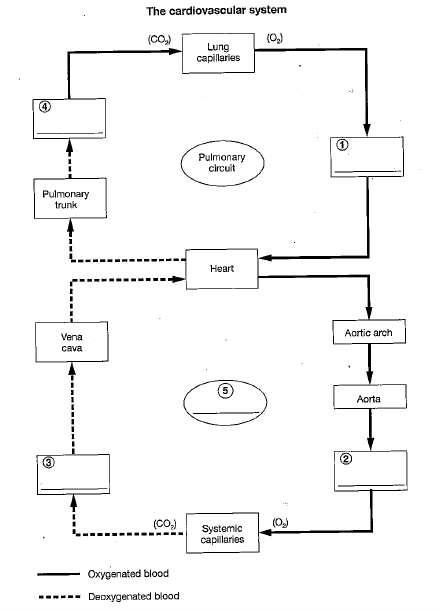
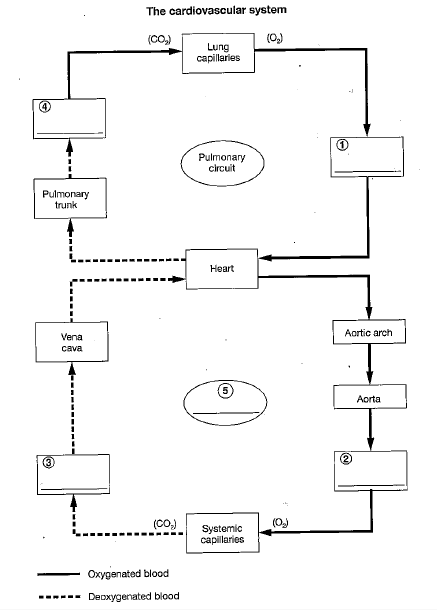
The blood vessels in the cardiovascular system are subdivided into the:
pulmonary and systemic circuits.
Blood is carried away from the heart by
arteries.
The left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circuit and empties into the:
left ventricle.
The major difference between the left and right ventricles relative to their role in heart function is:
the L.V. pumps blood through the high-resistance systemic circulation.
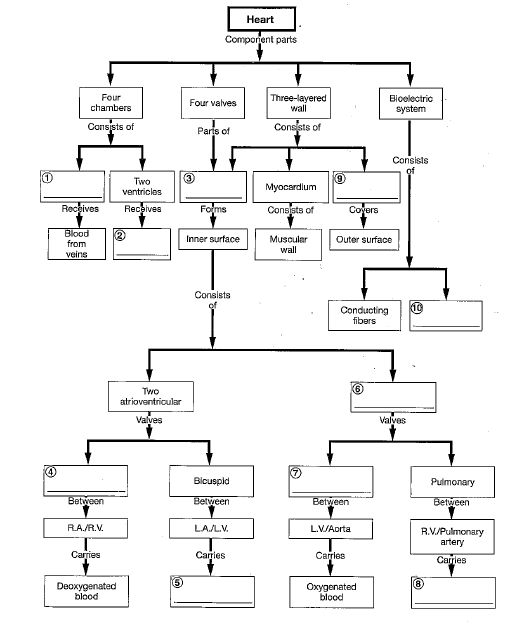
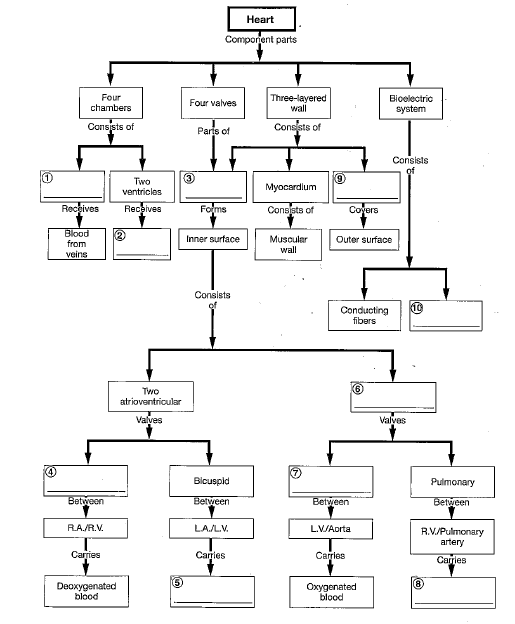
The three distinct layers of the heart wall include the:
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium.
Atrioventricular valves prevent backflow into the _____; semilunar valves prevent backflow into the _____.
atria; ventricles
When deoxygenated blood leaves the right ventricle through a semilunar valve, it is forced into the:
pulmonary arteries.
Blood from the systemic circulation is returned to the right atrium by the:
superior and inferior vena cava.
The correct sequence of a normal action potential is
SA node → AV node → bundle branches → Purkinje fibers.
The sinoatrial node acts as the pacemaker of the heart because these cells are:
the ones that depolarize and reach threshold first.
ECG’s are useful in detecting and diagnosing abnormal patters of cardiac activity called:
cardiac arrhythmias.
When a chamber of the heart fills with blood and prepares for the start of the next beat the chamber is in:
diastole
The only blood vessels whose walls permit exchange between the blood and the surrounding interstitial fluids are:
capillaries
Circulating RBC’s lack:
ribosomes, mitochondria. nuclei
The primary function of a mature red blood cell is:
transport respiratory gases.
The left ventricle is thicker than the right ventricle because.
it requires more pressure to pump to the systemic circuit.
Which is not a difference between arteries and veins?
arteries always carry oxygenated blood while veins always carry deoxygenated blood.