ectoparasiticides
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
chemical control and applications
act systemically or via skin contact - parenterally, orally or topically
dogs and cats = spot-ons, chewable tablets, collars, environment, injectable
livestock = ear tags(cattle), pour-ons, spot-ons, injectable, dip, oral e.g drinking water(poultry)
equine = sprays, pour-ons, oral
ectoparasticide R&D and regulation
different regulatory requirements worldwide
discovery, research and development is lengthy and expensive process
R&D to demonstrate efficacy, develop formulation, dosage
demonstrate safety, quality and efficacy to obtain market authorisation
implications for veterinarians - prescribing under cascade
products not classed as veterinary medicinal products have not undergone same level of testing
veterinary medicines vs biocides - different testing requirements
market authorisation may be withdrawn
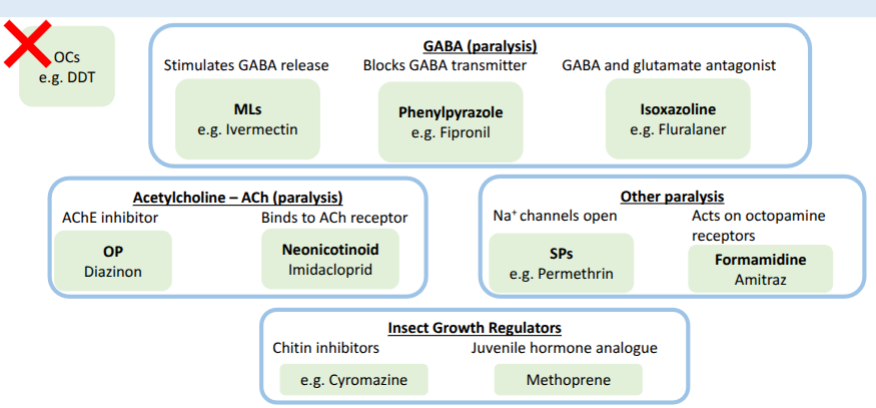
major classes of ectoparasticides
organochlorines
organophosphates
synthetic pyrethroids
macrocyclic lactones
neonicotinoid
phenylpyrazole
isoxazolines
formamidine
insect growth regulators
organochlorines(OCs)
e.g DDT
global malaria eradication programme but resistance
highly toxic - bioaccumulation, food chain, immune impairement and others
banned in many countries - UK - 1984, USA - 1972
organophosphates(OPs)
e.g diazinon
delivery = plunge dip - sheep only
targets - blowfly, lice, mites, ticks, keds
mode of action - acetylcholine released from insect nerve ending, normally inactivated by acetylcholinesterase. OPs bind to AChE, acetyl choline builds up = paralysis
safety = lipid soluble, high toxicity to humans
synthetic pyrethroids(SPs)
e.g permethrin, cypermethrin, deltamethrin
delivery = ear tags, pour-on, spray-on, collars
targets = flies, lice, ticks
mode of action = excites cell membranes by maintaining depolarisation, Na+ channels stay open = paralysis
safety = repellency and rapid kill, not residual, low mammalian toxicity
contraindications = permethrin toxicity in cats
macrocyclic lactones(MLs) - endectocides
e.g ivermectin, doramectin, moxidectin, selamectin
delivery = IM or SC injection, spot-on, pour-on
targets = broad spectrum - mites, lice,bots, warbles, fleas
endectocidal class of drugs
mode of action = stimulate GABA(inhibitory neurotransmitter) release from nerve endings, enhancing binding to its receptors in post- synaptic motor neurone membrane, increasing flow Cl- = paralysis
safety = safe, GABA neurotransmission confined to CNS in mammals, large molecules don’t readily cross blood-brain barrier
lipophillic = systemic slow release, persistent, extended protection(some products)
contraindication = collies(and other breeds) sensitive to ivermectin(mdr1 gene). long meat and milk withdrawl
neonicotinoid
imidacloprid
delivery = spot-on
targets = fleas, T.canis
mode of action = binds to nicotinic ACh receptors in insect nervous system = paralysis
safety = toxic to aquatic invertebrates, toxic to bees, agriculture use restricted across the EU
phenylpyrazole
fipronil
delivery = spot-on, spray
targets = fleas, ticks
mode of action = blocks GABA transmitter = paralysis
safety = toxic to fish and bees
lipophillic, diffuses into sebaceous glands of hair follicules which act as resevoir = long residual activity
formamidine
amitraz -generally now unavailable
delivery = wash, impregnated strips
targets = demodectic mange in dogs
mode of action = interacts with octopamine receptors, hyperexcitation = paralysis
safety = some dogs are sensitive
contraindications = toxic to horses and cats
superseded by other products licensed for this parasite
also available for varroa mite treatment in honey bees
isoxazolines
fluralaner, afoxolaner, lotilaner
delivery = chewable tablets and spot-ons, now injectable
targets = fleas, ticks, mites
mode of action = GABA and glutamate recpetor antagonist = paralysis
safety = safe, although enviromental/invertebrae toxicity not fully established
novelty = fluralaner and afoxolaner kills fleas within 8 hrs and ticks within 48hrs. active for 3 months. lotilaner kills fleas within 2hrs and ticks within 12 hrs = can prevent borrelia and babesia transmission
bispyrazoles
tigolaner
newer drug, licensed in cats
delivery = spot on
targets = fleas, ticks, mites
mode of action - GABA and glutamate
insect growth regulators(IGRs)
chitin inhibitors
cyromazine, dicyclanil, diflubenzuron, lufenuron
delivery = spot-on, injection, pour-on
targets = blowflies, fleas
mode of action = chitin inhibitor, prevent egg hatch and moulting. cyromazine protects against blowflies for ~14w
juvenile hormone analogues
methoprene
delivery = spot-on
targets = fleas
mode of action = mimics the prohormone ecdysone which keeps fleas young
classes by modes of action