AP Gov Unit 3 - The Legislature
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Article I
The Legislature Article; First and Longest Article
Hopkinton’s Representatives
Edward Markey and Elizabeth Warren (Senators), James McGovern (4th District MA HOR)
3 Primary Functions of Congress
Representative, Legislature, Oversight
2 Important Political Truths about Congress
Partisanship: #1 indicator of how members of Congress vote
Incumbency: #1 factor in the outcome of Congressional Elections
Achieving Incumbency and Electoral Mastery (4)
Name Recognition
Partisan Constituency (Democrats win in MA)
Service Strategy/Casework/Constituent Service (franking, emails, grad speeches)
Pork Barreling (bringing home funds, grants) (The Big Dig)
Senate Terms of Office
Elected to 6 year terms (1/3 of the body up for election every 2 years)
House Terms of Office
Elected for 2 year terms (every member up for reelection every 2 years)
Term Limits (Pros vs Cons)
Pros: Fresh ideas, Younger blood, Less concern with Campaigning
Cons: More experience, More democratic
Article 1 Section 2 Clause 3
The Number of Representatives shall not exceed one for every thirty Thousand, but each State shall have at Least one Representative
Every 10 Years
Census
Reapportionment
Redistricting
Baker v Carr (1962)
allowed that redistricting issues could be resolved in the courts as racial discrimination and voting power inequality are illegal
Reynolds v Sims (1964)
“1 person-1 vote” principle reinforced by requiring all congressional districts to be relatively the same size
Shaw v Reno (1993)
ruled that there must be a “compelling government interest” to use race as a factor when redistricting
How many committees are House and Senate members on?
House members are on 2 committees each, while Senators serve on 3-4 each
Who controls committees?
Committees are controlled by the majority party, with the ratio of members reflecting the same ratio as the entire House or Senate
How is leadership determined on committees?
Leadership on Committees is usually based on seniority, which is based on most years served on a particular committee
Speaker of the House
The overall leader and presiding officer of the entire House
How are chairpersons chosen for committees?
Most senior member of the majority party in a committee
Ranking Member
the most senior minority party member of a committee
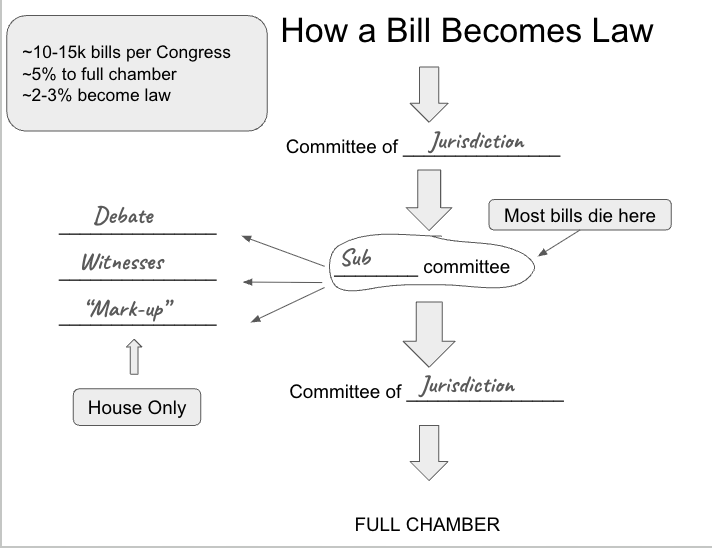
How a Bill Becomes a Law (Introduction to Full Chamber)
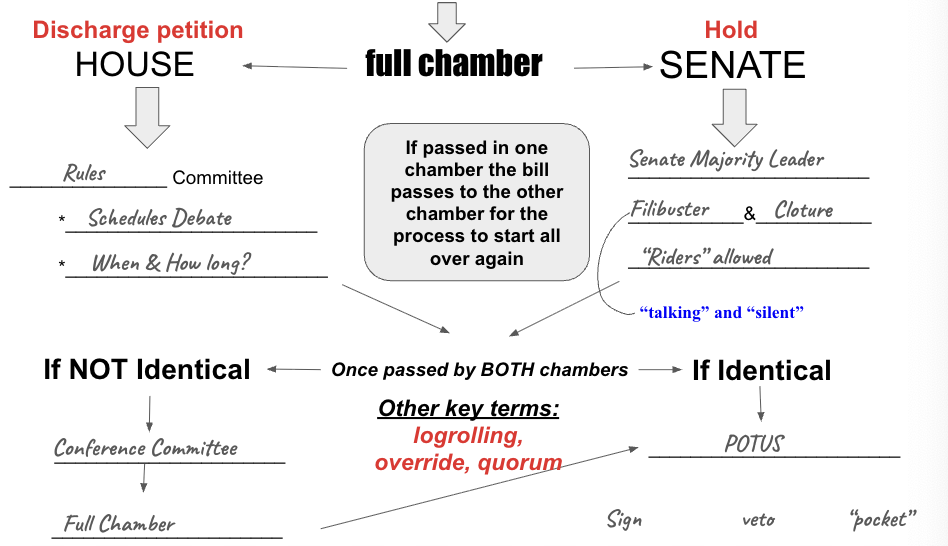
How a Bill Becomes a Law (Full Chamber to Passing)
Where do bills start?
Bills can start in either the House or the Senate except for revenue bills, which start in the House
“Mark-up”
members formally debate, propose amendments, and vote on changes to a bill before it goes to the full House floor
“Riders”
amendments or policy provisions attached to must-pass bills (like spending bills) to sneak controversial changes into law in the Senate
HOUSE WAYS & MEANS COMMITTEE
legislation for raising revenue, including income, payroll, and excise taxes, plus tariffs
HOUSE APPROPRIATIONS COMMITTEE
funding the federal government’s vital activities; allocating budget
SENATE JUDICIARY
Drafts and reviews bills related to federal law; handles legislation and oversight for the justice system
SENATE FOREIGN RELATIONS
oversees and shapes American foreign policy, handling treaties, presidential nominations for foreign posts, and providing oversight for the State Department and foreign aid
Standing Committee
The permanent committees of Congress that focus on fairly narrow area of expertise (known as committees of jurisdiction for their responsibility in handling distinct areas of policy)
Sub-Committees
smaller groups within Standing Committees that are ”expert” on even more specific policy
Joint Committee
any committee with members from both the House and Senate
Conference Committee
Committee put together to iron out out the specifics of a bill passed in slightly different versions by House and Senate. Made up of Standing Committee members from each chamber
Select (special) Committee
committee put together for a specific, temporary purpose
Nuclear Option
Changing Senate Rules to lower the requirement for cloture from 60 to 51; lower and supreme court justices (2013, 2017), only legislation left
3 Key Periods of Growth of the Federal Government
New Deal
Great Society
World War II
All made the executive MUCH bigger with new committees, etc.
Congressional Budget Act (1974)
Created the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) to watch over the Executive Budget
Created the Senate & House standing budget committees
War Powers Act (1973)
President must inform Congress of troop movement within 48 hours
Troops can be deployed for 60 days max without Congressional extension
“Whenever possible”, Congress must be consulted before troops are dispatched into hostile situations
General Accounting Office (GAO)
monitors spending of appropriated $
Congressional Research Service (CRS)
“errand boy” of Congress doing research and providing legislative summaries
Cup & Saucer Analogy
Cup = The House
Saucer = The Senate
The Senate “cools” the House legislation down
Conference Committee
a temporary, joint legislative body formed by members from both the House and Senate to resolve disagreements and reconcile different versions of a bill, creating a single, identical text for both chambers to pass and send to the President for enactment
Mandatory Spending and Earmarks
Mandatory = must pay (ss, medicare, medicaid, interest on debt)
Earmarks = pork barreling, $ for projects set aside by Congress
Whip
Ensures party discipline, communication across chambers, and coordinated voting
Advice and Consent Clause
Article II Section II, Powers of Congress (ratify treaties, approve nominees, etc.)
Hopper
basket next to the clerk's desk in the House Chamber where bills are placed to await their first reading