Fin453 Lecture 6
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary terms and definitions related to the concept of infrastructure as outlined in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Infrastructure Equity
A sub-asset class of Alternative Investments positioned between Private Equity and Real Estate.
AuM
Assets under Management, indicating the total market value of investments that an asset manager or financial institution manages on behalf of investors.
Greenfield Assets
Assets that do not exist yet and do not generate revenue until they are operational; associated with higher risks including construction delays.

Brownfield Assets
Existing assets that are (partially) operational and already generate income, posing no construction risks.

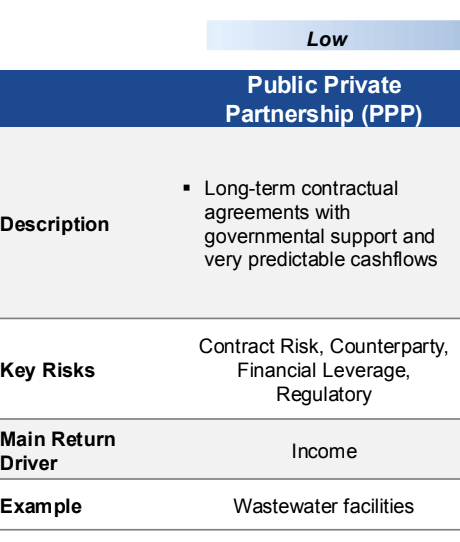
Public Private Partnership (PPP)
Long-term contractual agreements between a public agency and private sector entity, aimed at delivering public services or facilities.
Valuation
The analytical process of determining the current (or projected) worth of an asset or a company.
Demand Elasticity
A measure of how much the demand for a good or service changes in response to a change in price.
ESG
Environmental, Social, and Governance, a set of criteria used to evaluate the ethical impact and sustainability of an investment.
J-Curve
The pattern of returns experienced by private equity investments, notably negative cash flows during early stages followed by positive cash flows over time.
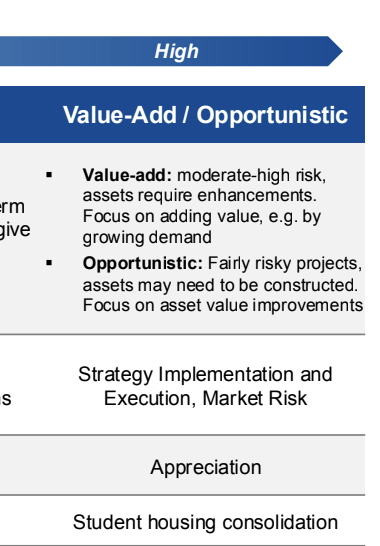
Value-Add Strategy
An investment strategy that seeks to enhance the value of an asset through various improvements or enhancements.
Dry Powder
Capital available for investment that has not yet been deployed.
Regulatory Risk
The risk that changes in laws or regulations will materially impact an investment.
Leverage
The use of borrowed capital in order to increase the potential return of an investment.
Income & Appreciation
The dual focus of investments generating income through cash flow and increasing in value over time.
Counterparty Risk
The risk that the other party in a financial transaction may not fulfill their part of the deal.
Operational Risk
The risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, or systems.
Types
Economic (energy, utilities, waste management..) and social (education, healthcare, government buildings)