AP LANG
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Simple Sentence
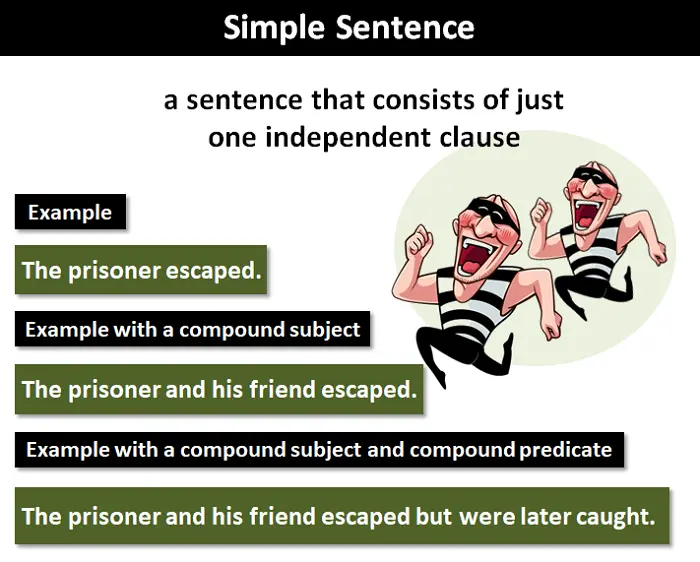
a sentence consisting of only one clause, with a single subject and predicate.
Complex Sentence
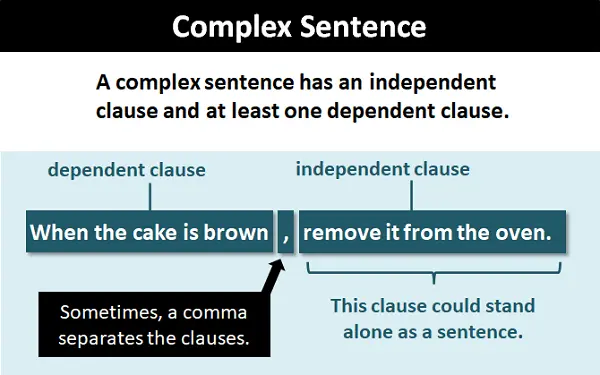
combines an independent clause (a complete thought) with one or more dependent clauses (incomplete thoughts)
Compound, Complex

a sentence containing one or more dependent clauses and two or more independent clauses joined by a conjunction or semicolon
Run On Sentences

occurs when two or more independent clauses are improperly joined, often without proper punctuation or a coordinating conjunction. It's essentially a "sentence" that's actually two or more sentences mashed together.
Comma Splice

occurs when two independent clauses are connected with only a comma, instead of being joined with a period, semicolon, colon, or a coordinating conjunction
Semicolon

a punctuation mark (;) indicating a pause, typically between two main clauses, that is more pronounced than that indicated by a comma.
Colon

used to signal that what follows is directly related to the preceding sentence, often to introduce a list, explanation, or quotation. They are placed after complete sentences, not fragments, and are used to clarify or emphasize information.
Restrictive Clause
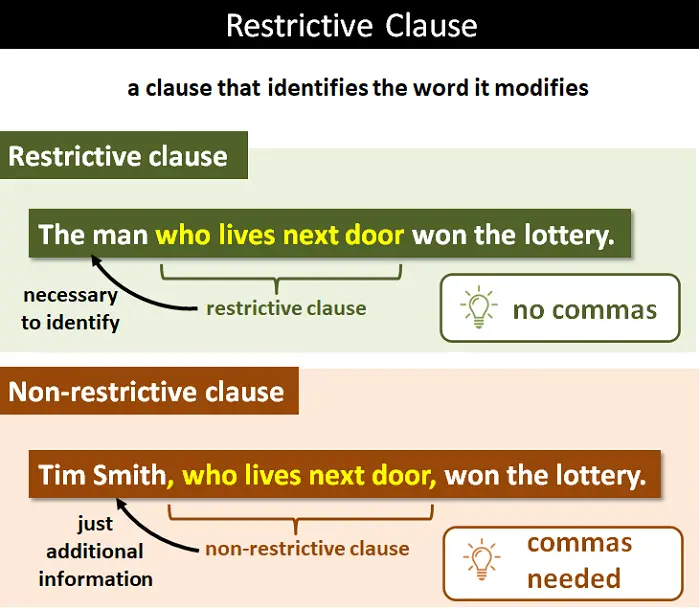
provides essential information that's necessary for understanding the sentence's meaning.
Non Restrictive Clause
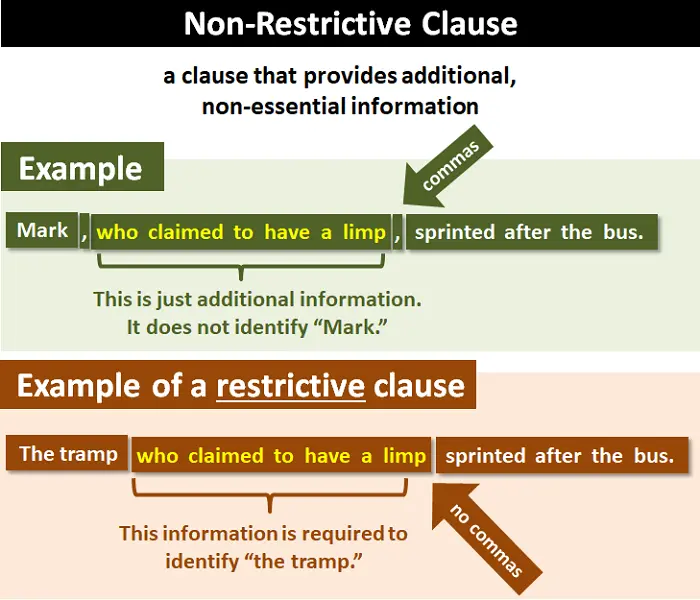
adds extra information to a sentence that isn't crucial to its meaning. This clause is usually set off by commas, as removing it wouldn't alter the fundamental meaning of the sentence.
Dash
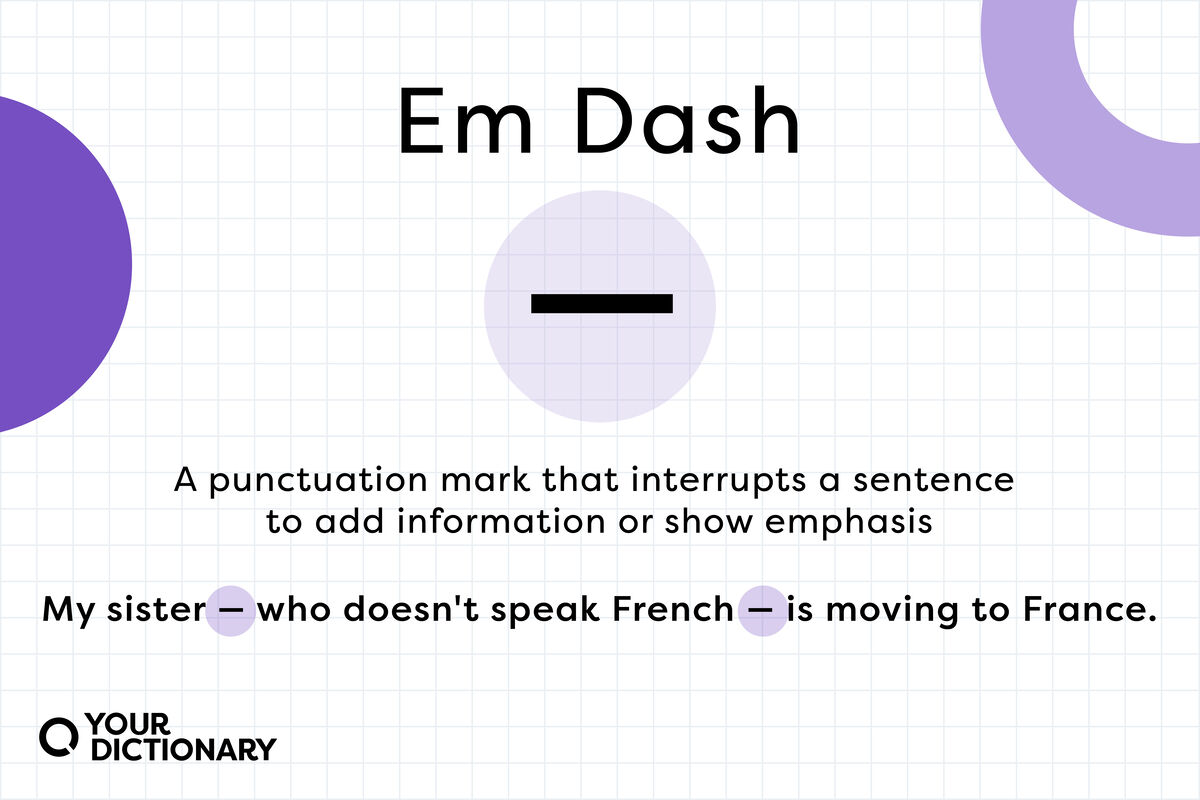
(—) is a punctuation mark used to separate parts of a sentence, similar to a comma or parenthesis, but indicating a stronger break or pause.
Split Infinitive

a construction consisting of an infinitive with an adverb or other word inserted between to and the verb, e.g. she seems to really like it.
MLA Citations
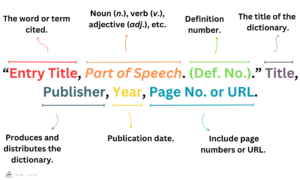
standardized format for citing sources in academic writing, especially within the humanities, and are used in papers, essays, and other research works
MLA Format
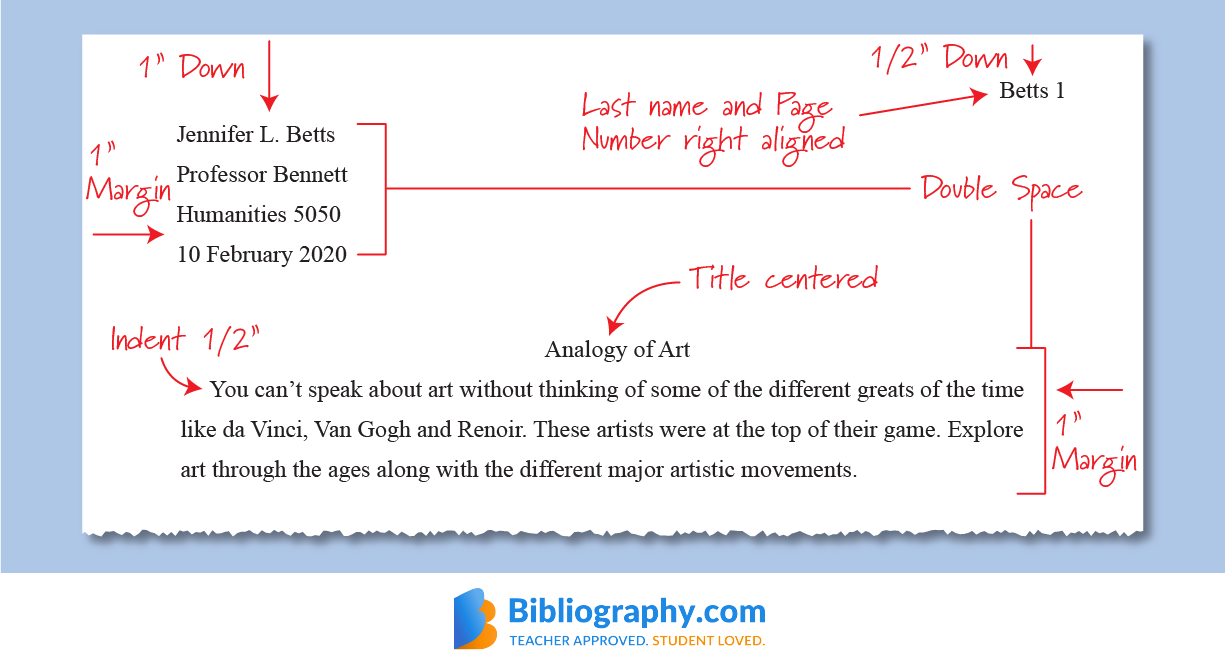
widely used formatting and citation style, primarily employed in the humanities, especially in fields like language, literature, and philosophy
Synthesis

the act of combining information from multiple sources to form a coherent argument or position on a topic. A synthesis essay requires students to identify, evaluate, and incorporate evidence from various sources to support their claims
Argumentative

piece of writing that aims to persuade an audience to accept a particular point of view or claim by presenting logical evidence and reasoned arguments
Rhetorical Analysis

form of close reading that examines how a text, or rhetorical situation, achieves its communicative purpose by analyzing the interactions between the author, the message, and the audience.
Rhetorical Strategies
specific devices or techniques authors use to persuade, inform, or entertain their audience