C2.1 Seperating Mixture OCR A GCSE Chemistry
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quizlet Official Flashcards.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
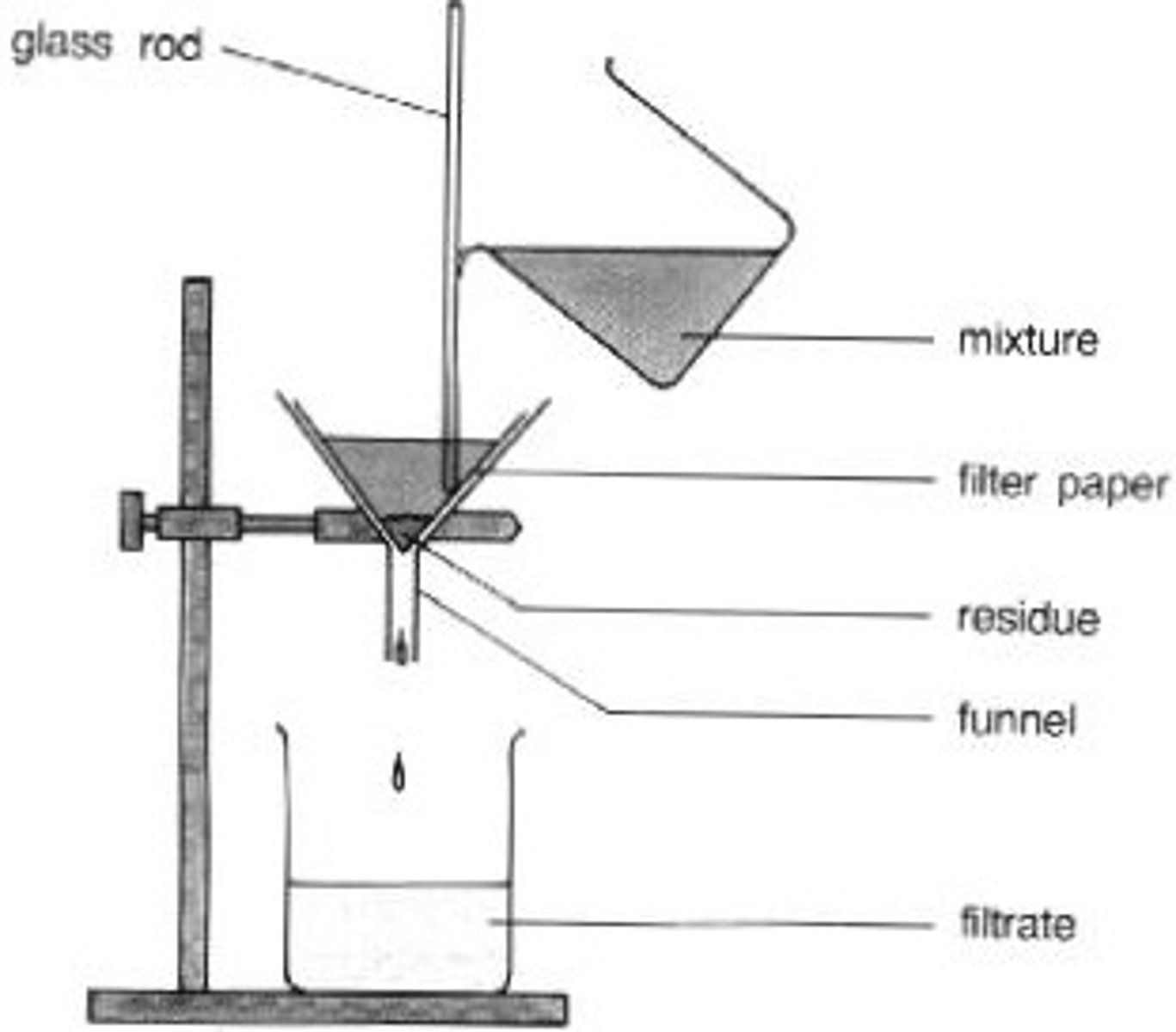
Filtration
Separates insoluble solids from liquids.
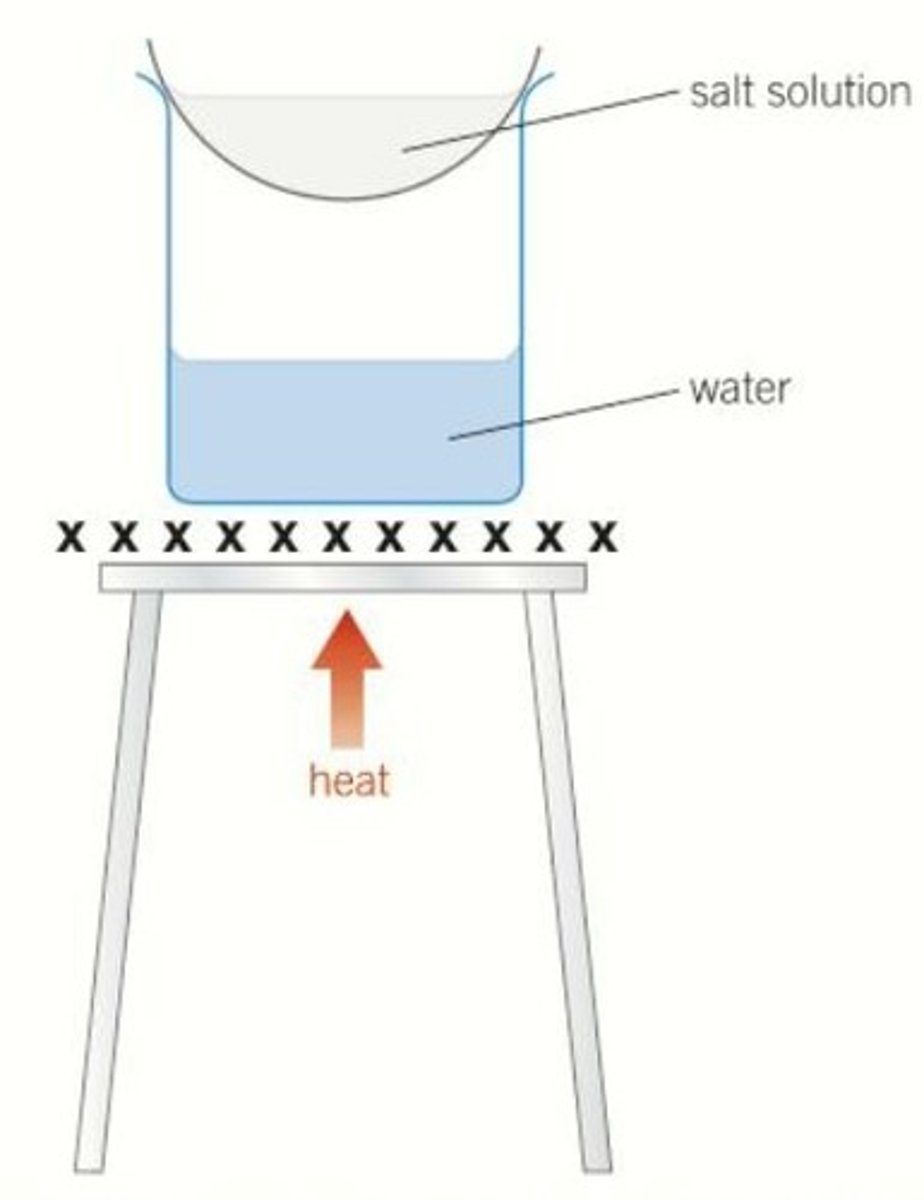
Crystallisation
The formation of crystals by cooling a saturated solution
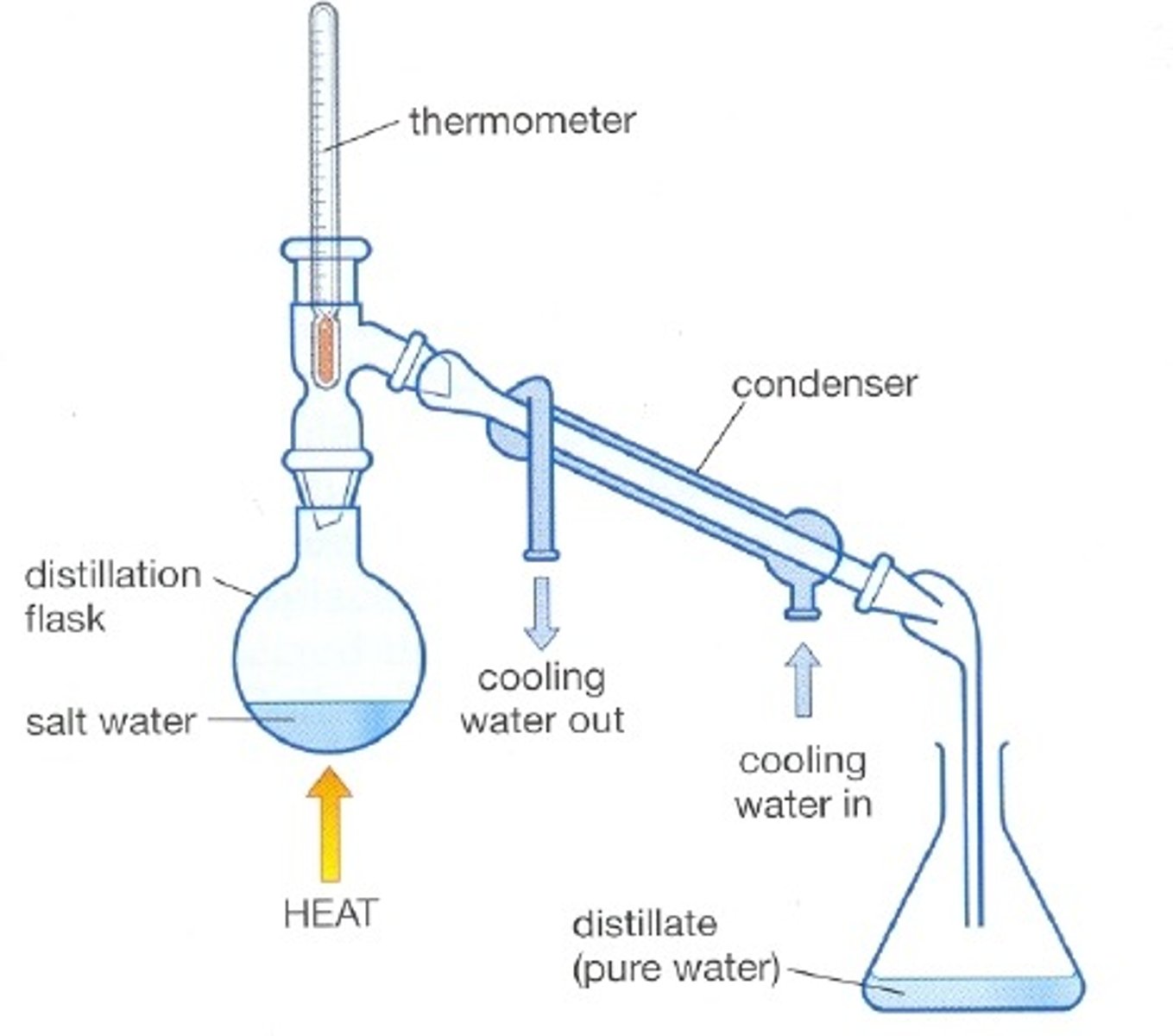
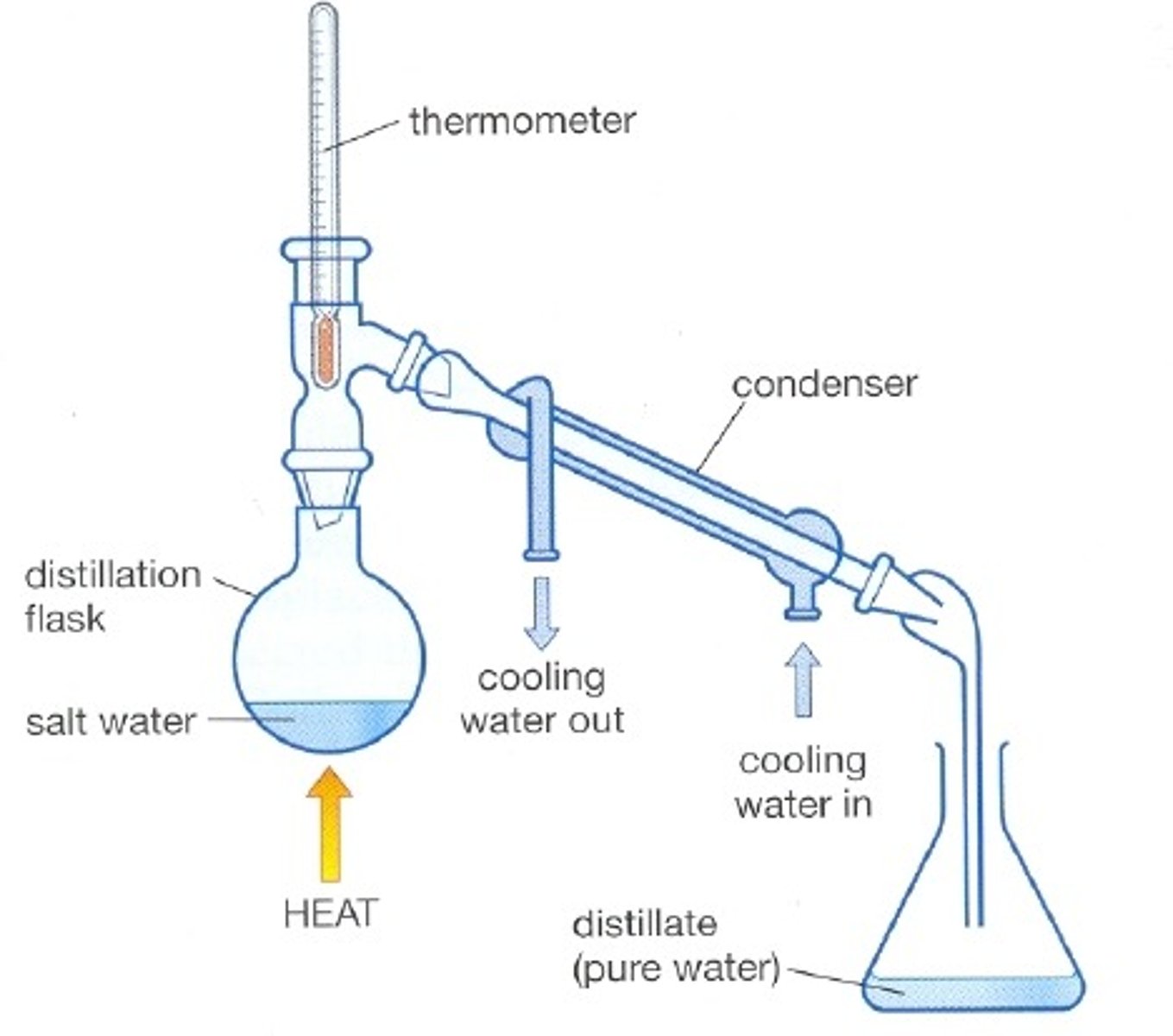
Simple distillation (uses)
Used to separate a liquid from a solution
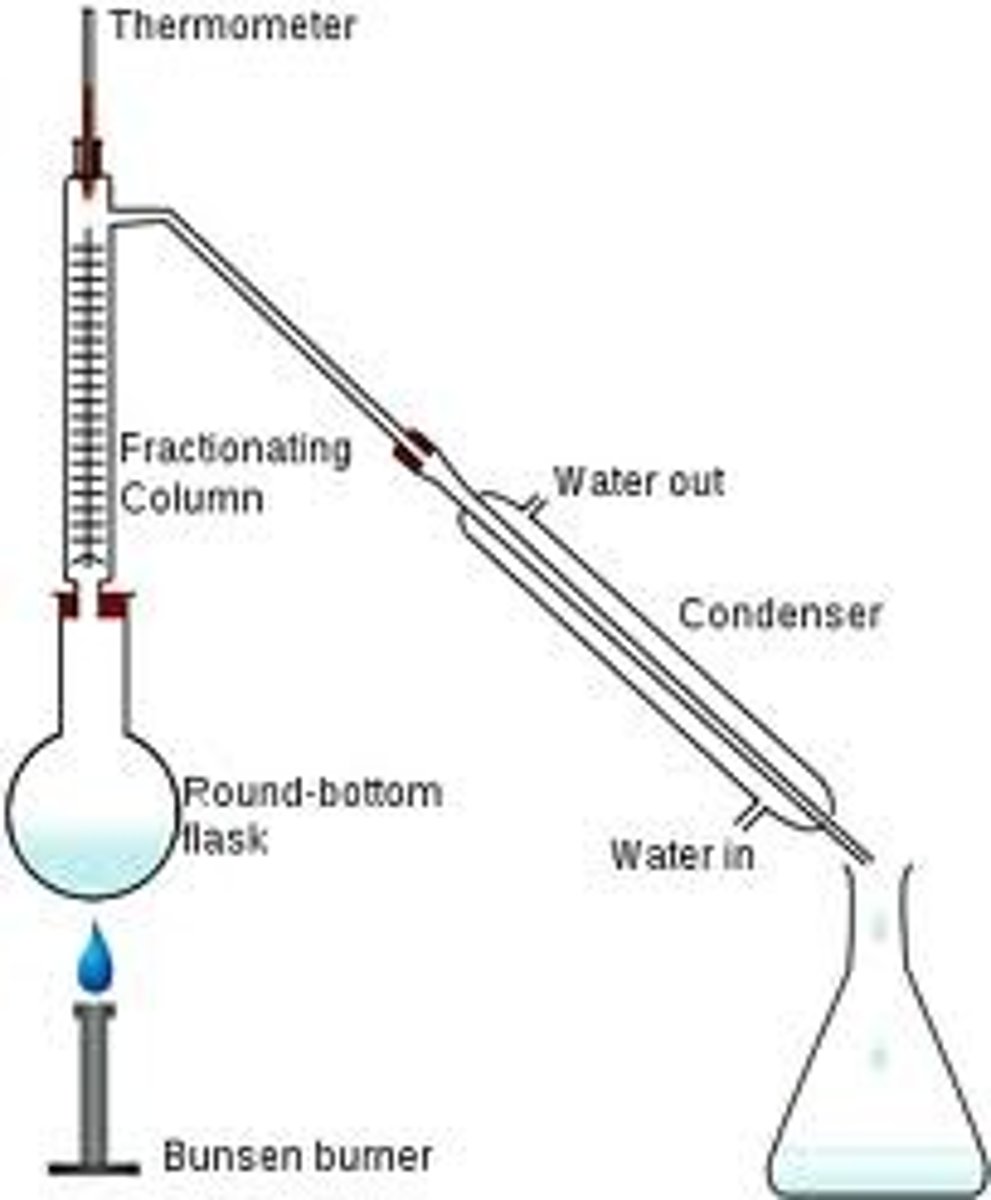
Fractional distillation
separation of a liquid mixture into fractions with different boiling points using a fractionating column.
Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another.
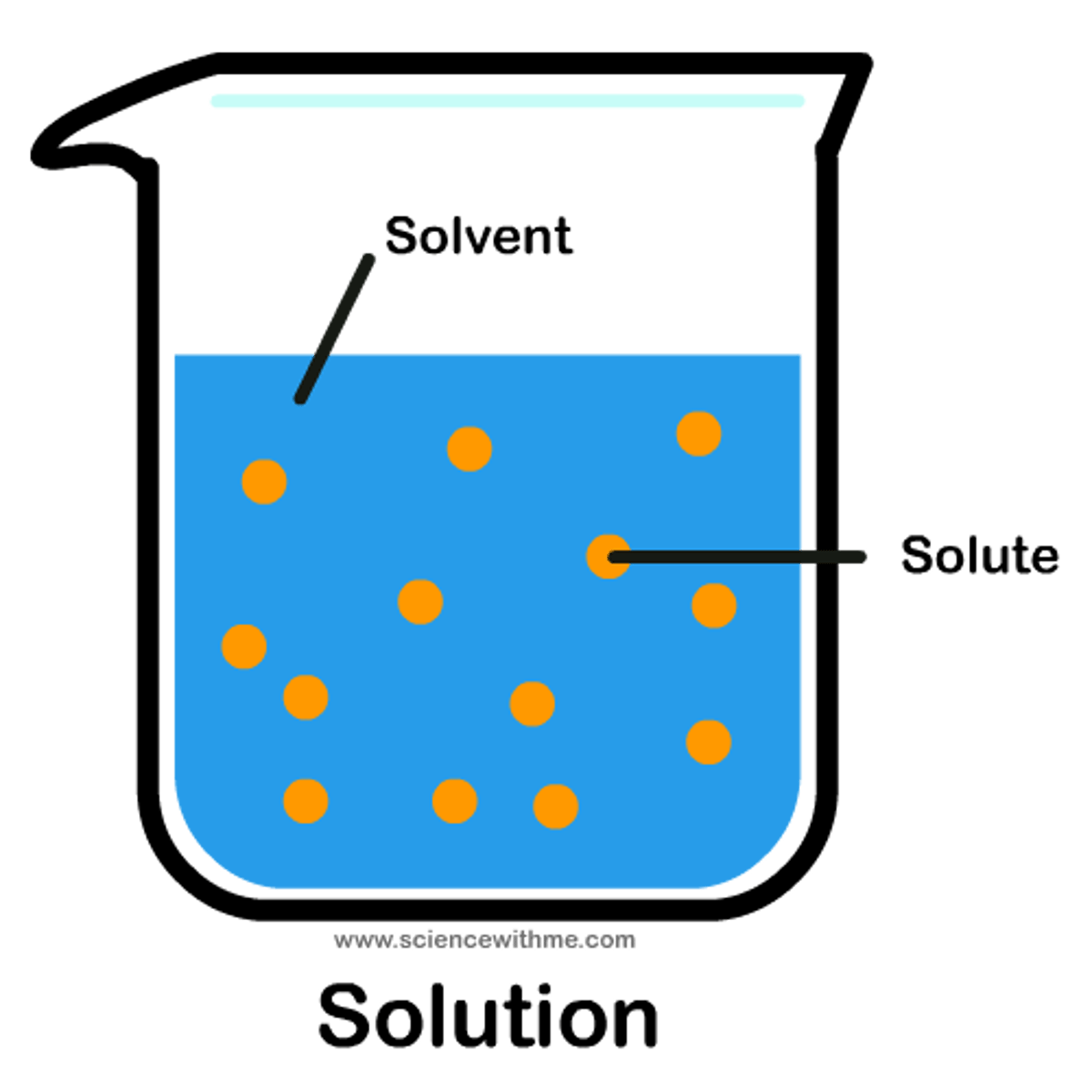
Solvent
A substance which is capable of dissolving other substances
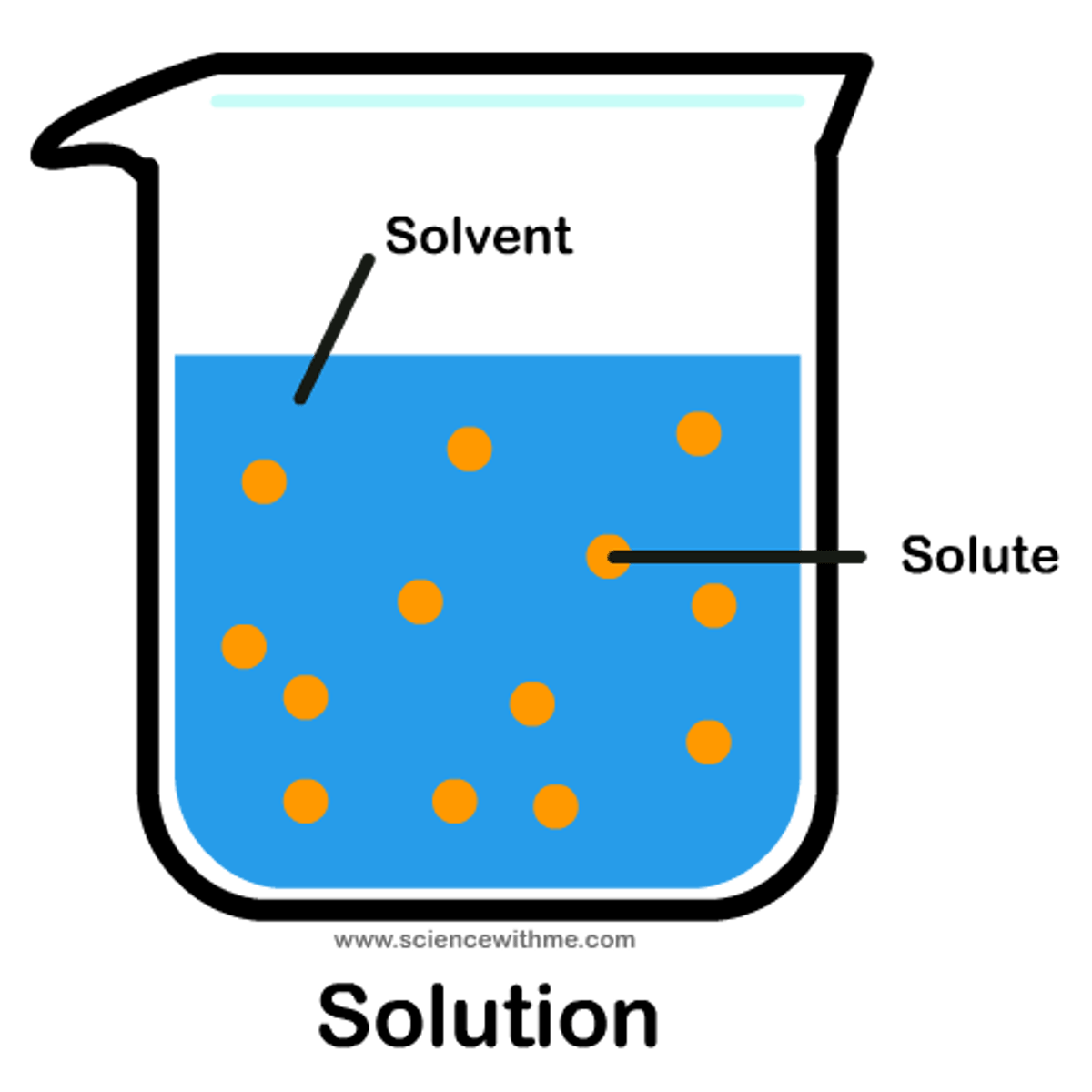
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
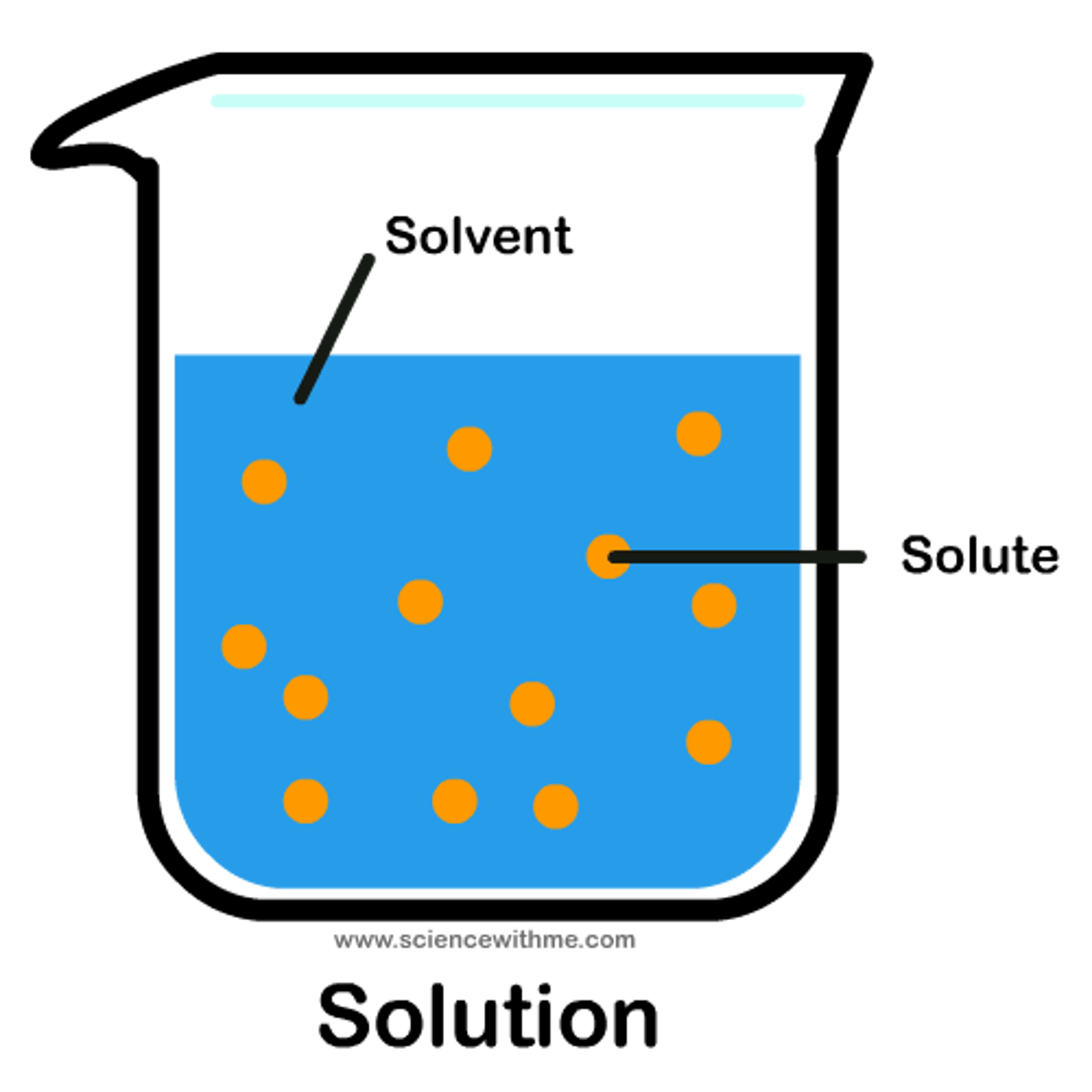
Insoluble
incapable of being dissolved in a given solvent

Soluble
capable of being dissolved in a given solvent

Saturated
A solution that cannot dissolve any more solute at a given temperature

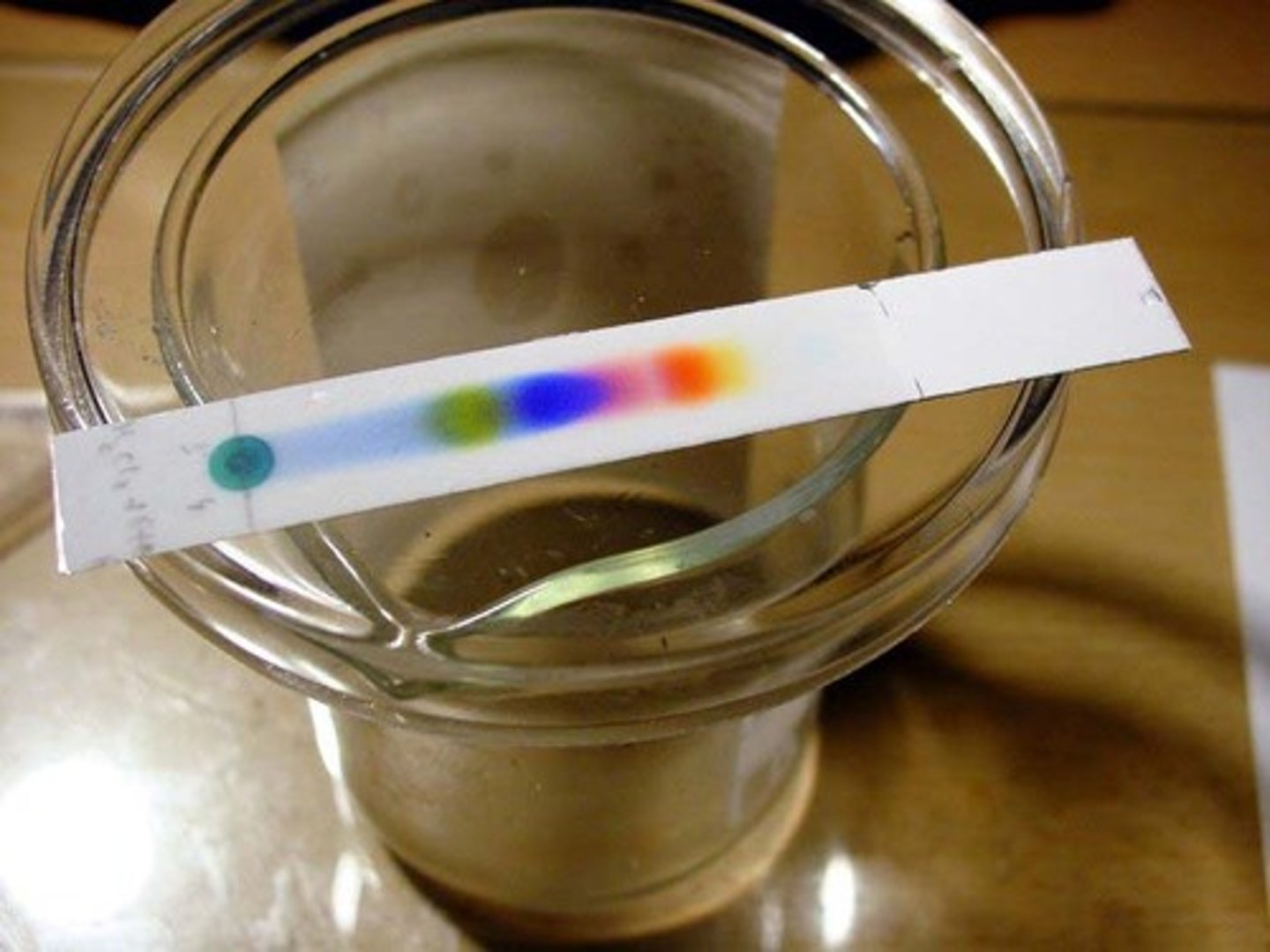
Chromatography
Separates the components of a mixture based on their solubility.
Filtrate
Liquid that has passed through a filter
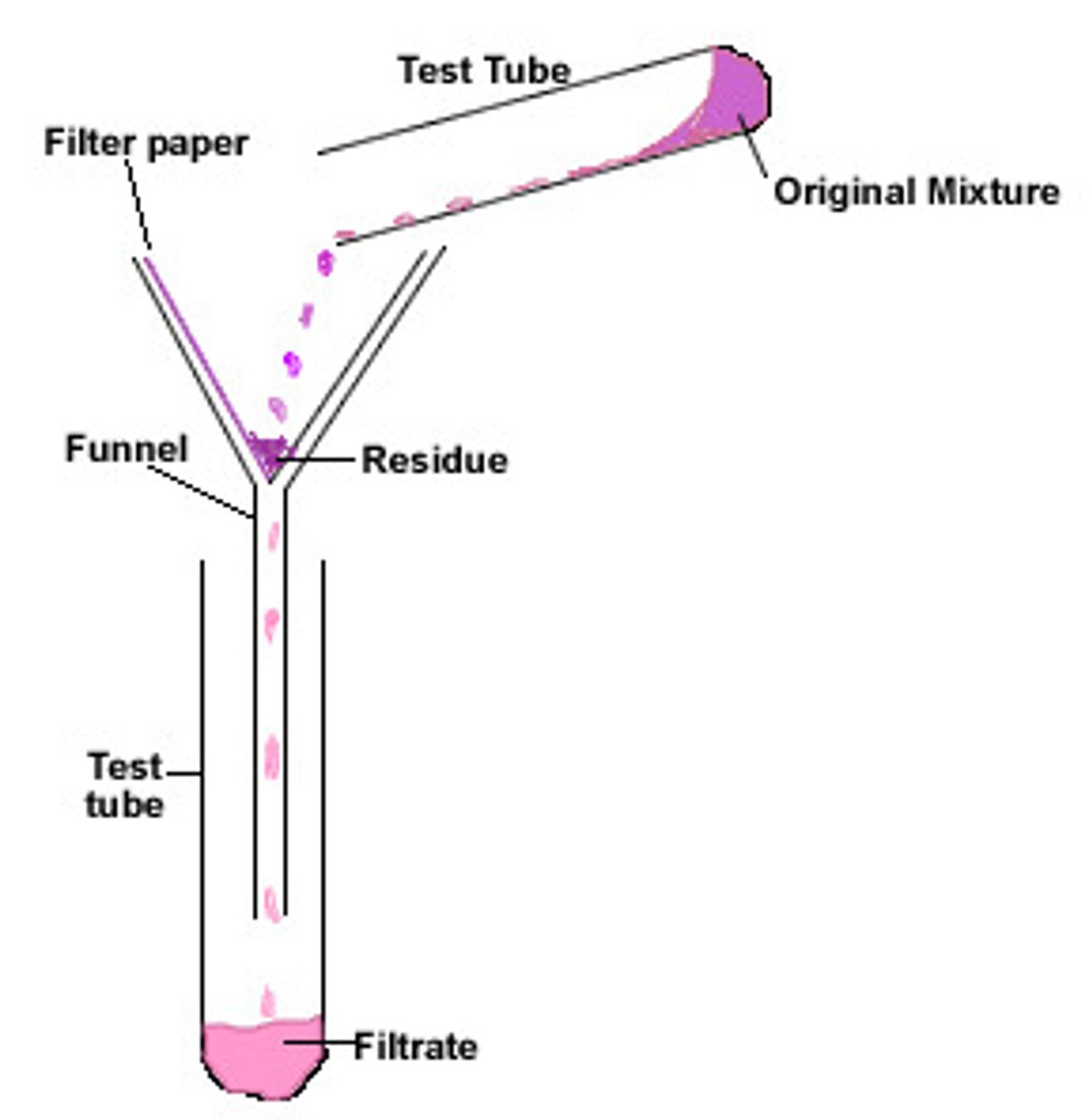
Residue
Insoluble solid which remains in the filter paper
Reason simple distillation works
Separates substances with different boiling points
Condenser
Gases pass through the tube, are cooled by the cold water and condense

First step of simple distillation
Heat the mixture so the solvent evaporates
Pure substance
Either a single element or a single compound
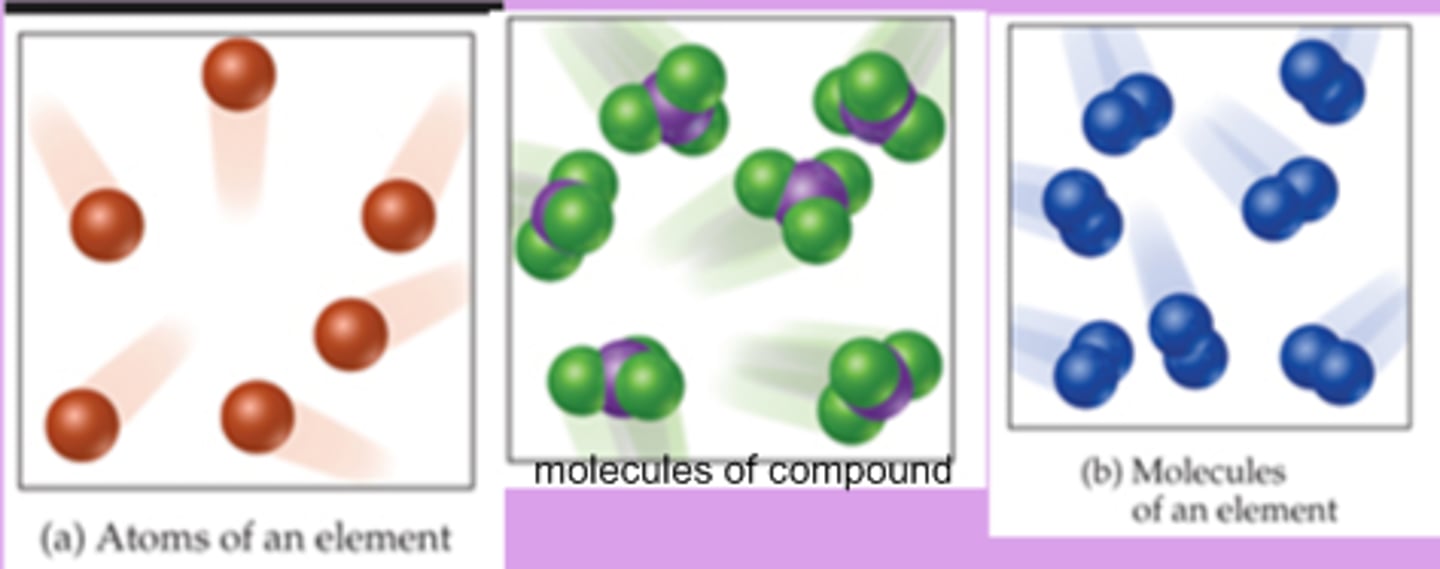
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined
Formulation
A mixture that has been designed for a specific purpose

Melting/boiling point of pure substances
A single defined temperature
Melting/boiling points of mixtures
A range of temperatures
Melting point of pure water
0 °C

Boiling point of pure water
100 °C

Examples of formulations
Paint, processed food, fuels, cleaning products, cosmetics

Test for purity
Test melting/boiling point
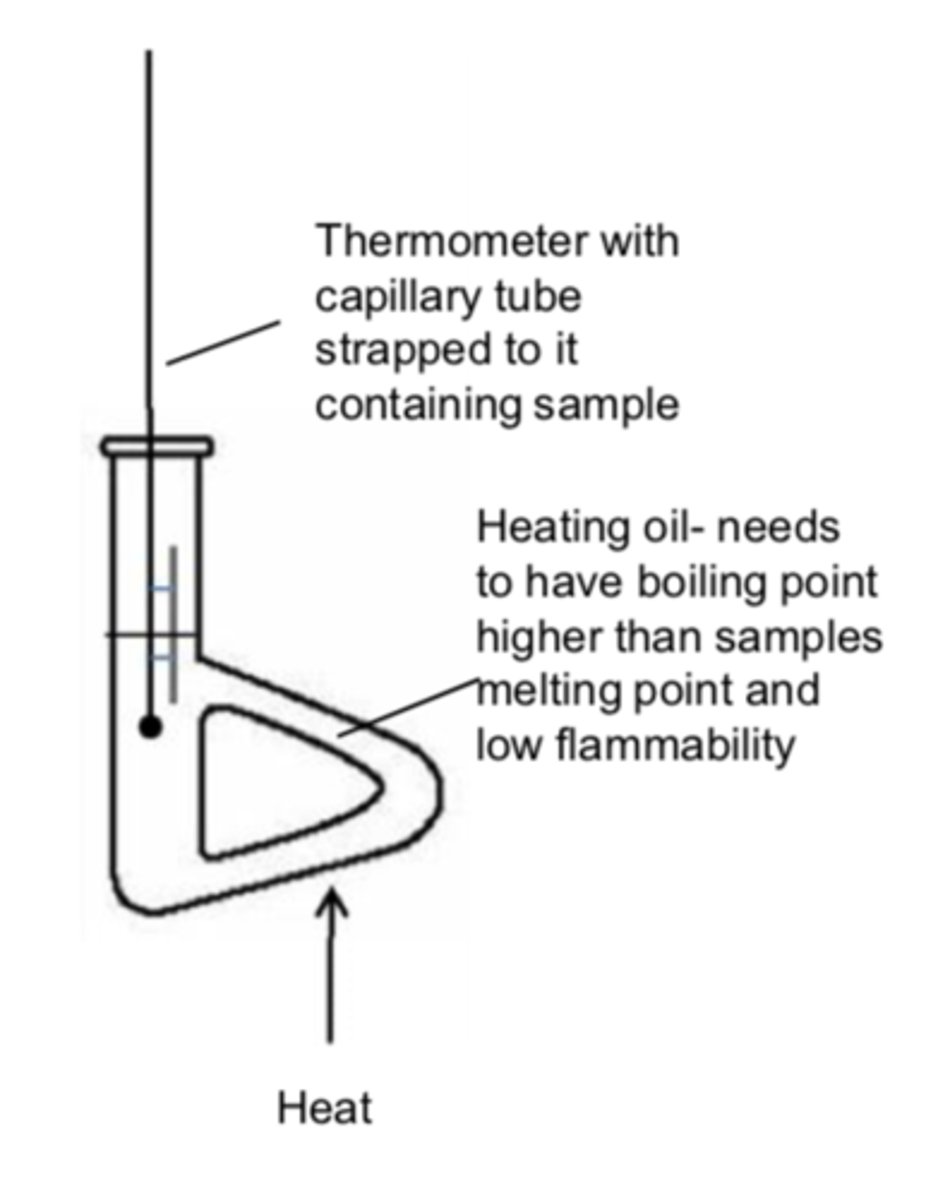
Test if water is pure
Test if boiling point is exactly 100 °C
Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another
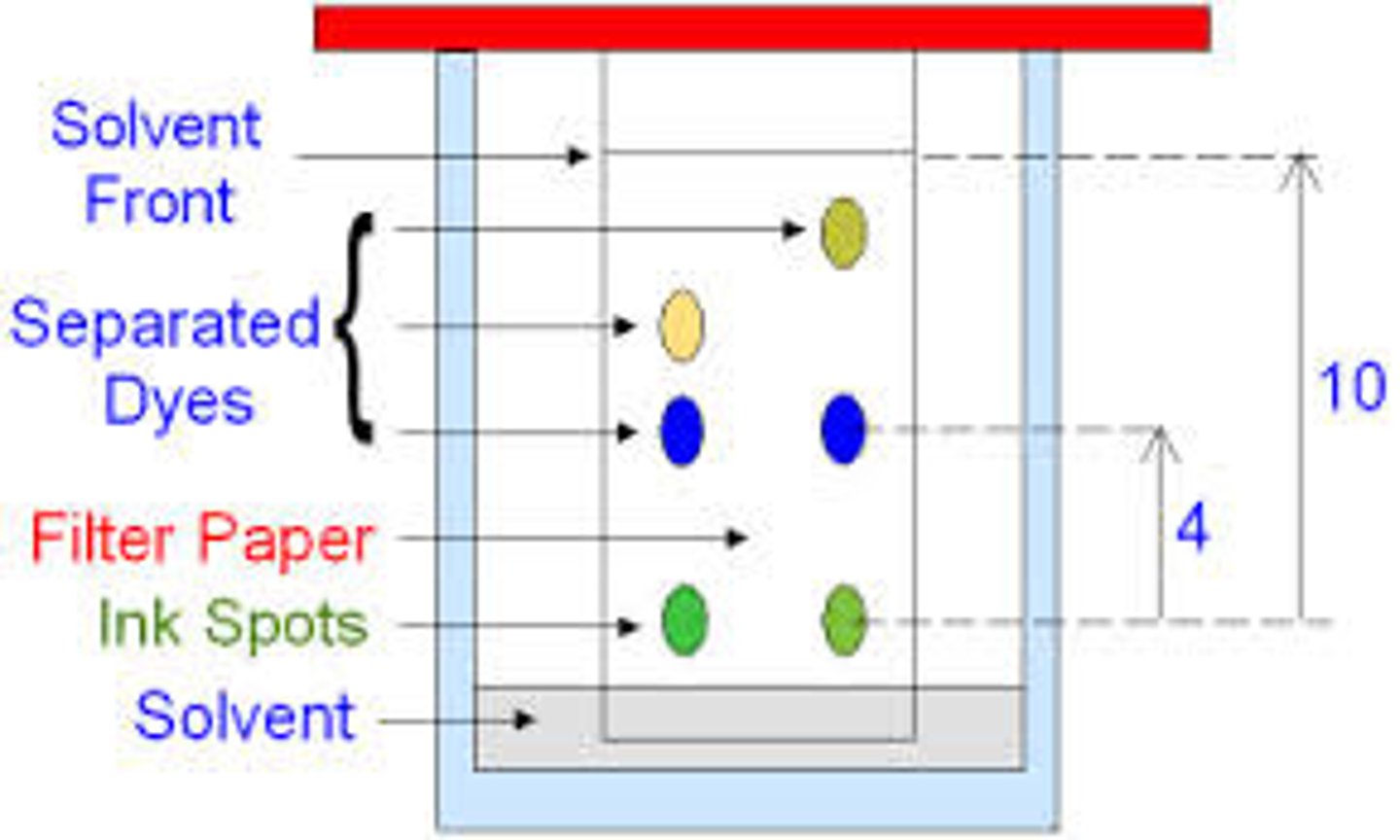
Chromatography
Separates the components of a mixture based on their solubility
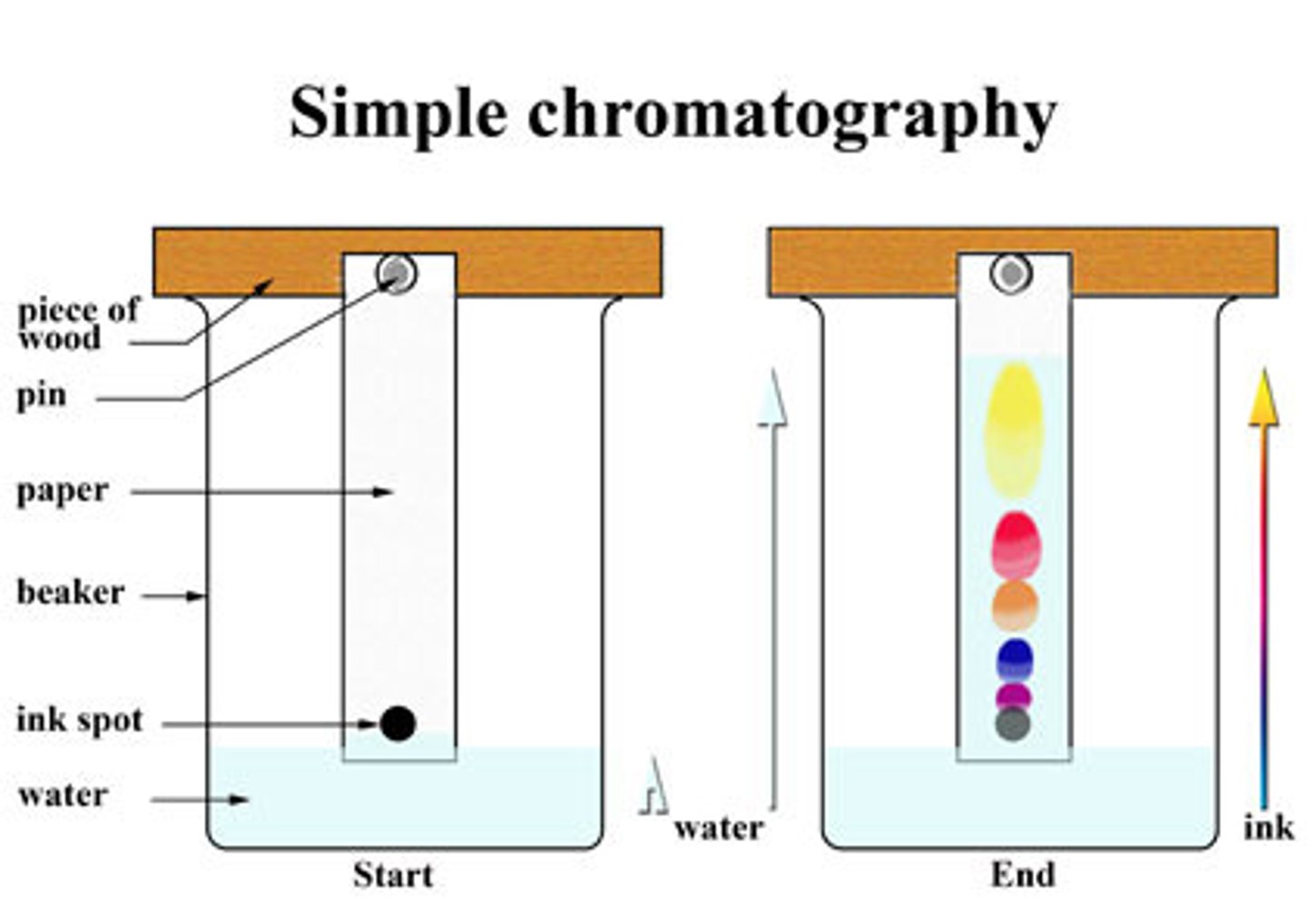
Mobile phase of chromatography
Solvent, which moves up the stationary phase
Stationary phase of chromatography
The substances the mobile phase moves through, usually paper
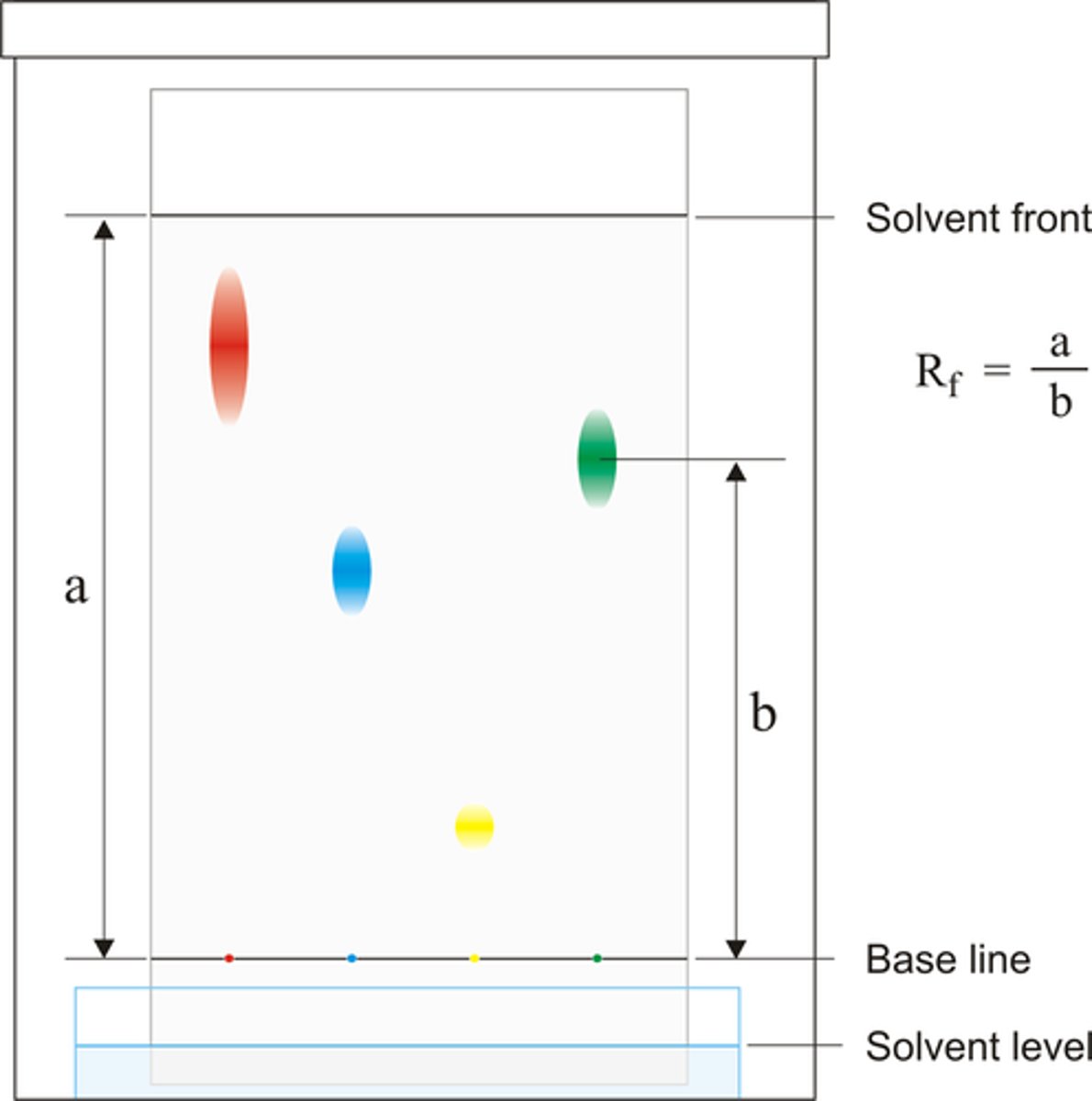
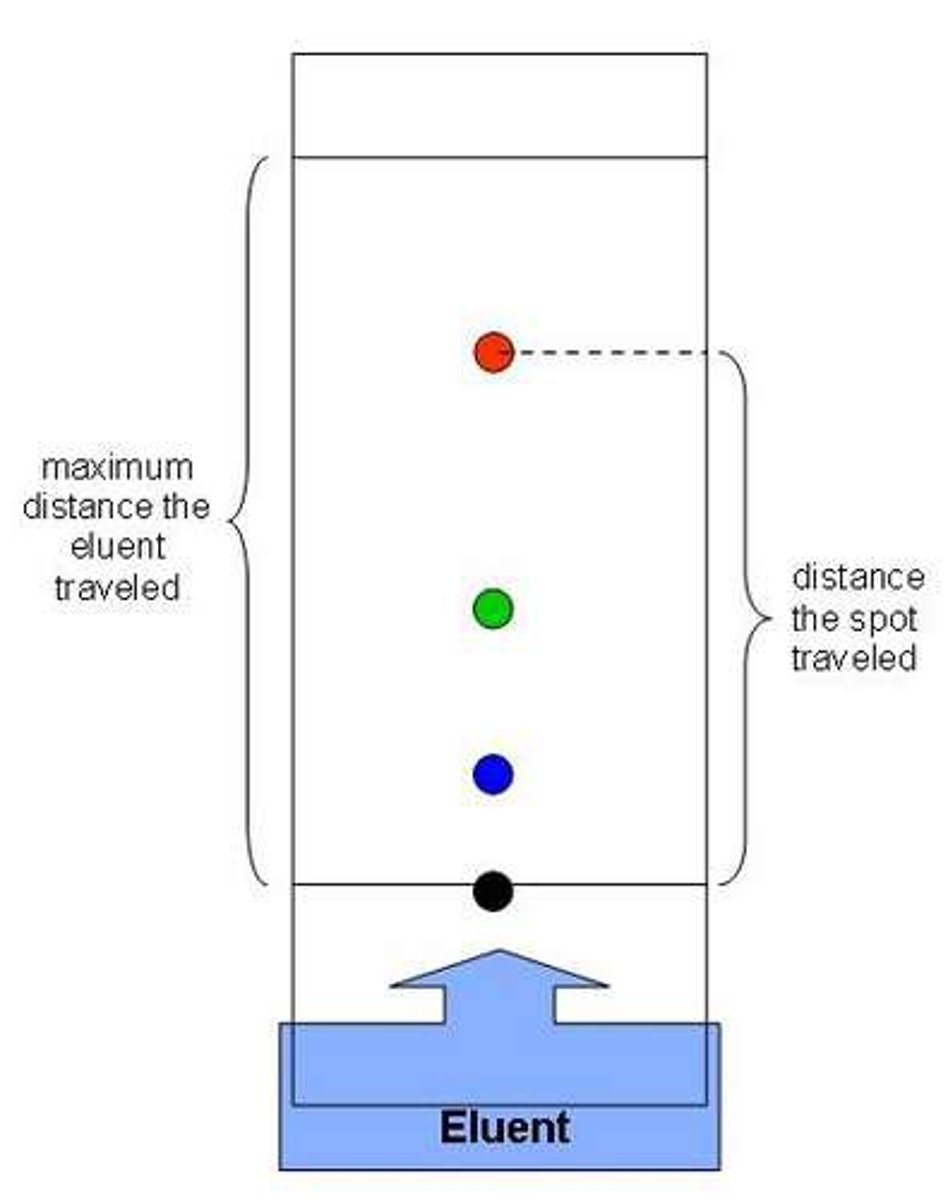
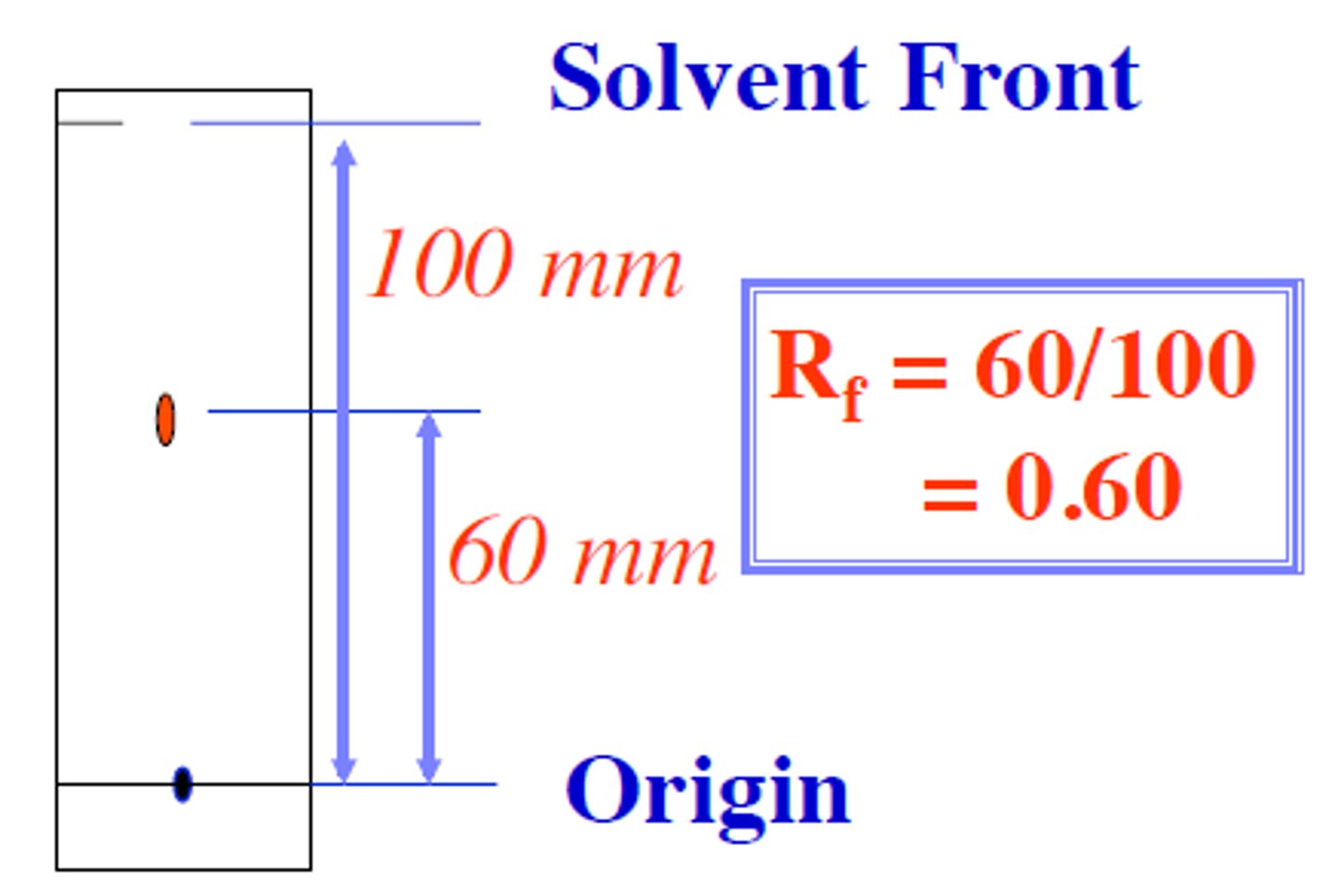
Rf factor
A measurement of how far components of a mixture moves up a chromatogram
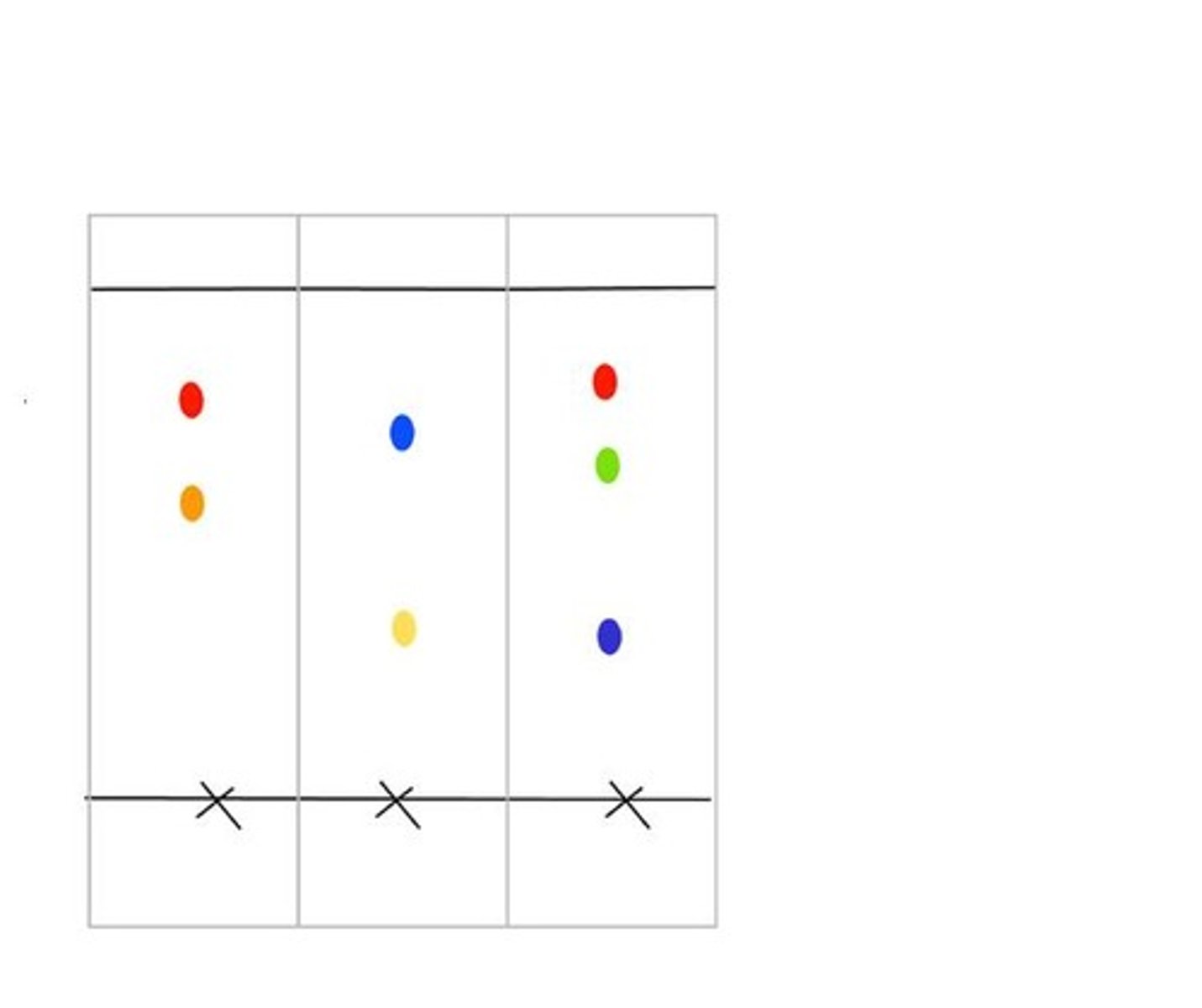
Chromatogram
The chromatography strip at the end of the experiment
Rf formula
distance traveled by spot ÷ distance traveled by solvent

Solvent front
The furthest point reached by the solvent
Rf of the same chemical
Is always the same in the same solvent
Pure substance on chromatogram
Will produce one spot in the same vertical column
Mixtures on a chromatogram
Will produce more than one spot in the same vertical column
A substance moves at different speeds
depending on how attracted it is to the stationary/mobile phase
Identification of chemicals using chromatography
Compare Rf to known substances in a database
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
A type of chromatography that uses a thin layer of powder on a plate as the stationary phase
