Chapter 2-Cell Chemistry and Bioenergetics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
How to Read the Periodic Table

Covalent Bonds
- form when two atoms come in close contact and SHARE one or more of their outer-shell electrons
- atoms joined by two or more ________ cannot rotate freely around the bond axis
Weak Non-covalent Bonds
- have less than 1/20 the strength of a strong covalent bond
- have a cumulative strength effect
H Bonds
- strongest when the three atoms lie in a straight line
- form when an H atom is "sandwiched" between two electron-attracting atoms (usually O or N)
Hydrophilic
dissolve readily in water
Ionic
bond that generates two oppositely charged ions
Polar
molecules with uneven distribution of electron density, resulting in a partially positive and another partially negative end (dipole moment)
Hydrophobic
- nonpolar bonds are usually insoluble in water
- water molecules are not attracted to these molecules, therefore don't surround them
- repulse from water
Electrostatic Attractions
- occur between fully charged groups (ionic) and between partially charged groups (polar)
- weak in water
- inorganic ions also cluster around charged groups and further weaken these attractions
Acids
substances that release H ions (protons) into solutions
Weak Acids
do not completely dissociate, ie -COOH
Bases
substances that reduce the number of H ions in solution
- some combine directly with H ions, ie NH3 + H = NH4
- some reduce the number of H ions indirectly by producing OH ie NaOH = Na + OH-
Weak Bases
partially associated with H ions, ie -NH2
Condensation
- loss of water in a reaction
- energetically unfavorable
Hydrolysis
- gains water
- water breaks down larger molecules into smaller subunits
- energetically favorable
Sugars
are the small organic building blocks for polysaccharides, glycogen, and starch (in plants)
Fatty Acids
are the small organic building blocks for fats and membranes
Amino Acids
are the small organic building blocks for proteins
Nucleotides
are the small organic building blocks for nucleic acids
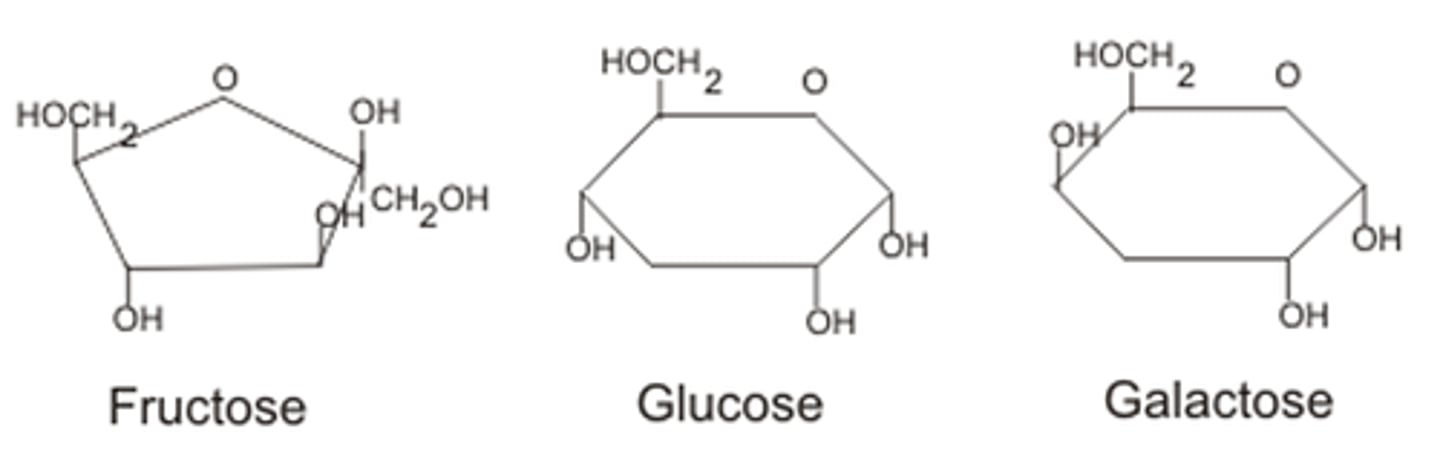
Monosaccharides
- A ___________ is a simple sugar and the most basic unit of carbohydrates
-he building blocks for more complex sugars
- general formula of (CH2O)n, where n can be 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8 and have two or more hydroxyl groups
- contain either an aldehyde group and are called aldoses or a ketone group and are called ketoses
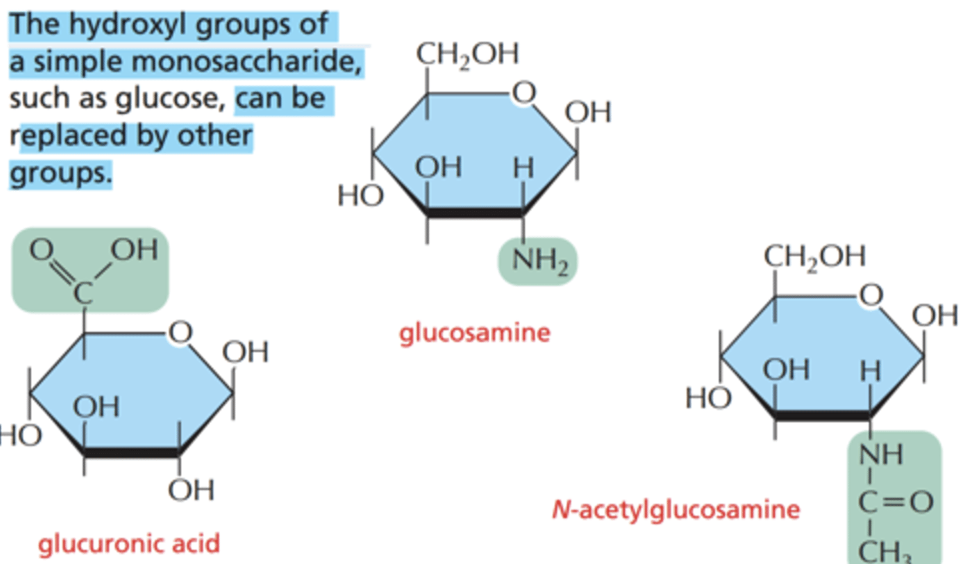
Sugar derivatives
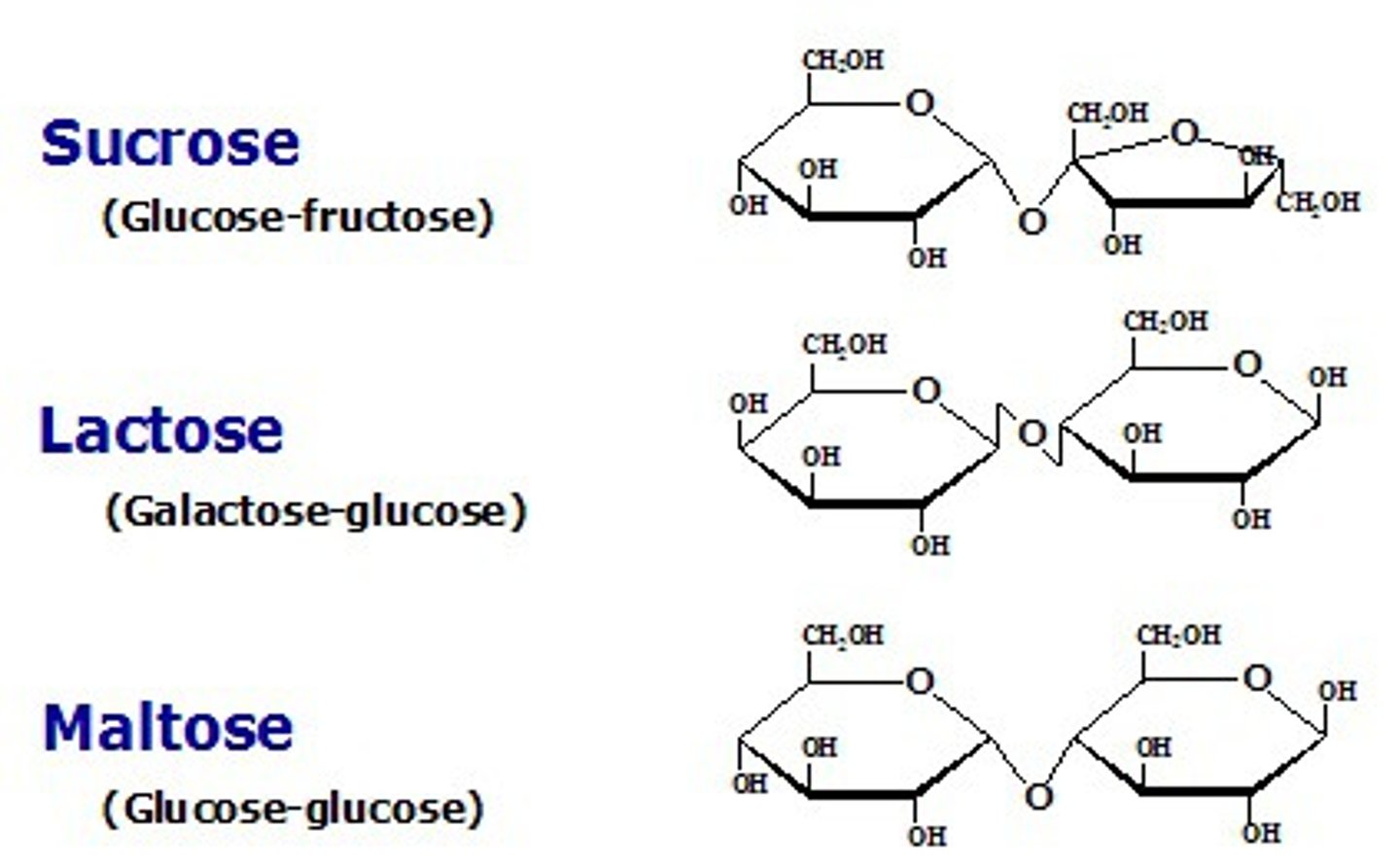
Disaccharides
- the carbon that carries the aldehyde or ketone can react with any hydroxyl group on a second sugar molecule
- three common ________ - maltose (glucose + glucose), lactose (galactose + glucose), sucrose (glucose + fructose)
Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides
simple repeated sugar subunits create large linear and branched molecules, short chains are _______________, longer chains are _________________
Nucleotide
consists of:
- an N-containing base (either pyrimidines or purines)
- a 5 C sugar (2 kinds of pentoses are used: B-D-ribose [used in ribonucleic acid (RNA)] and B-D-2-deoxyribose [used in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)]
- one or more phosphate groups (normally joined to the C5 hydroxyl or the deoxy/ribose sugar) and gives the nucleotide a negative charge
![<p>consists of:</p><p>- an N-containing base (either pyrimidines or purines)</p><p>- a 5 C sugar (2 kinds of pentoses are used: B-D-ribose [used in ribonucleic acid (RNA)] and B-D-2-deoxyribose [used in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)]</p><p>- one or more phosphate groups (normally joined to the C5 hydroxyl or the deoxy/ribose sugar) and gives the nucleotide a negative charge</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/60f01a36-4322-4f1c-ab25-ea7b603bf3a0.jpg)
Pyrimidine
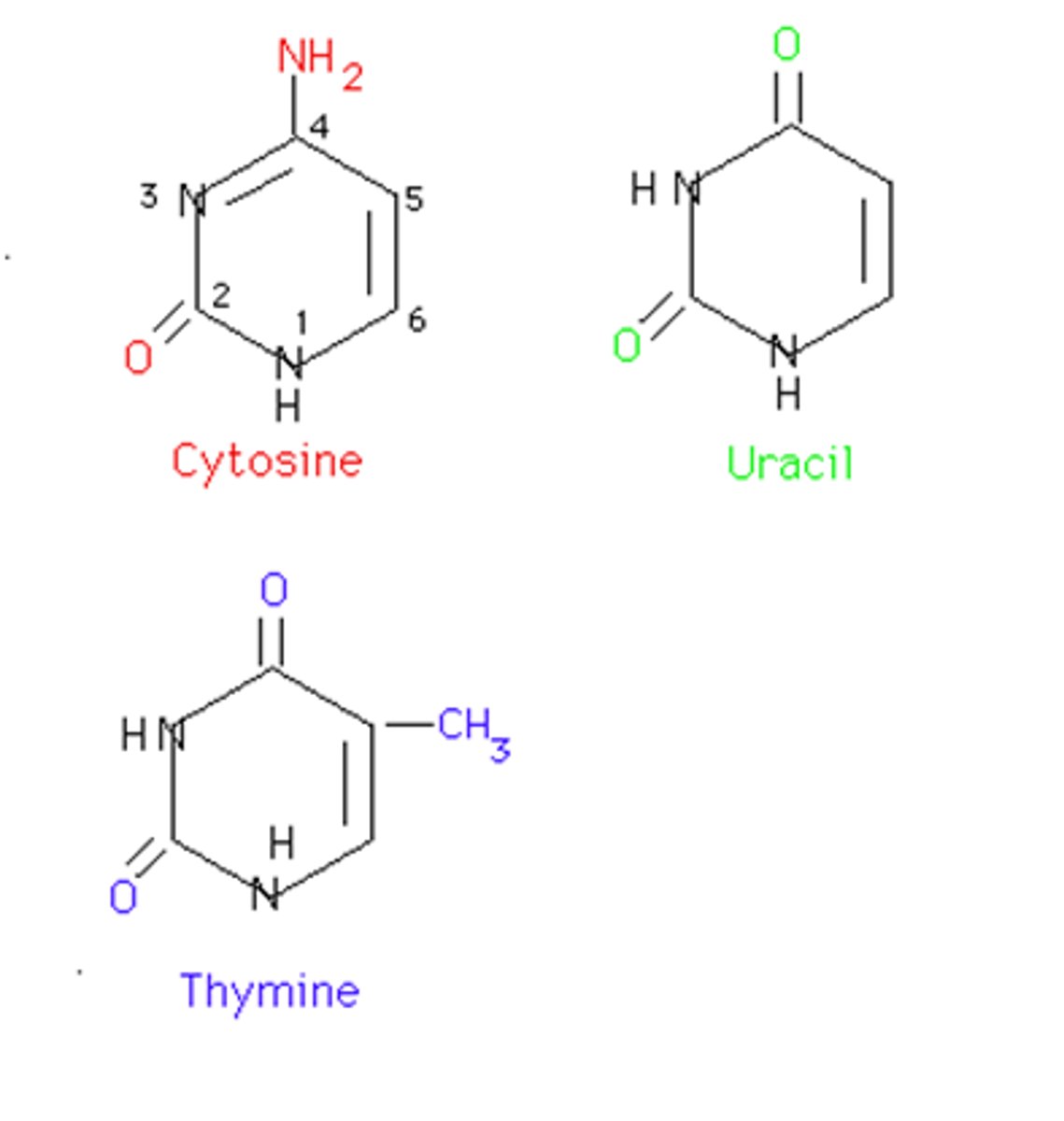
Purine
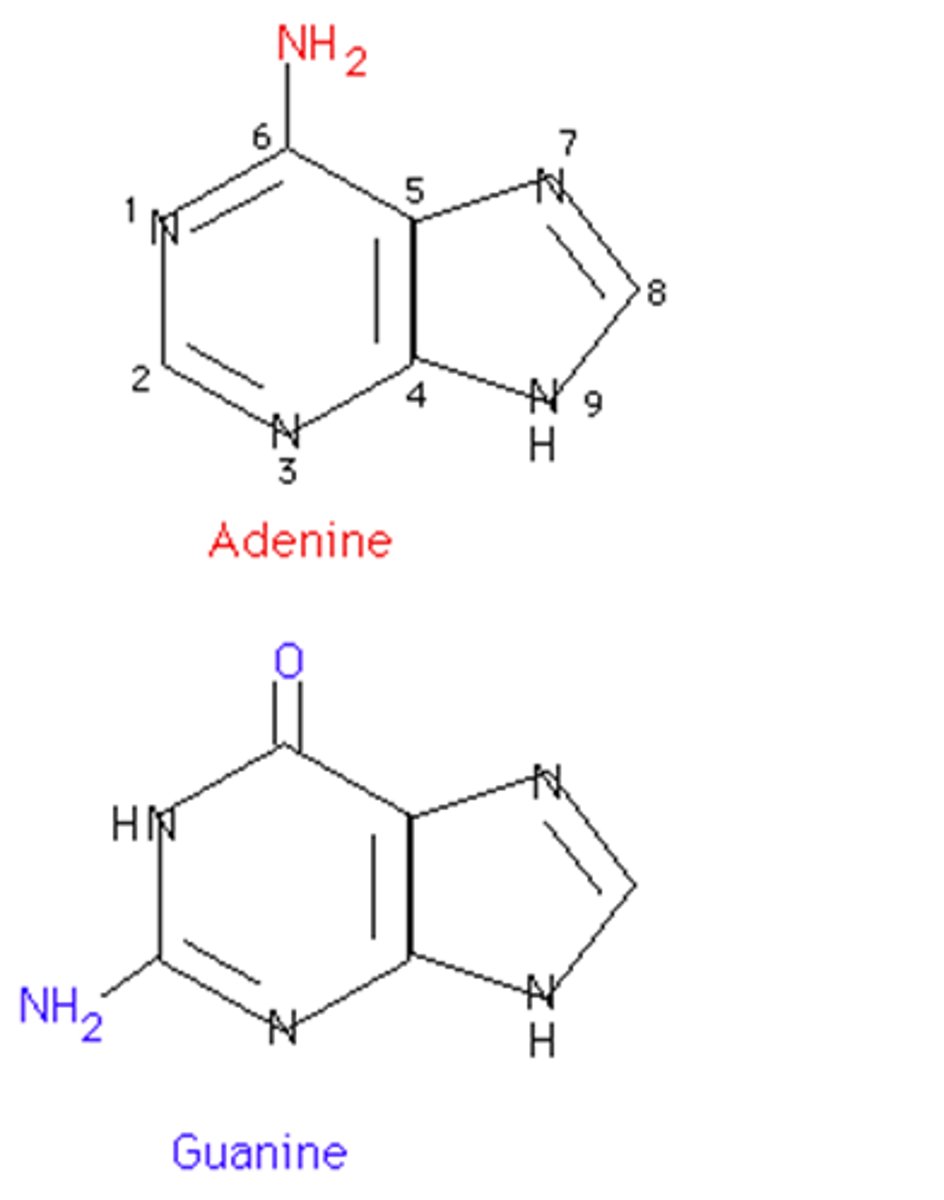
Nucleic Acids
nucleotides are joined together by PHOSPHODIESTER BONDS between the 5' and 3' C atoms of adjacent sugar rings
Nucleotides and the Functions of Their Derivatives
- di- and triphosphates carry chemical energy in their phosphoanhydride bonds, ie ATP
- combine with other groups to form coenzymes, ie CoA
- used as small intracellular signaling molecules in the cell, ie cAMP
Fatty Acids
- have a CARBOXYL GROUP at one end and a long hydrocarbon tail at the other
- unsaturated: one or more double bonds in their HC tail
- saturated: no double bonds
- stored in cells as an energy reserve through an ester linkage to GLYCEROL to for triacylglycerols
- have polar heads, hydrophobic tails
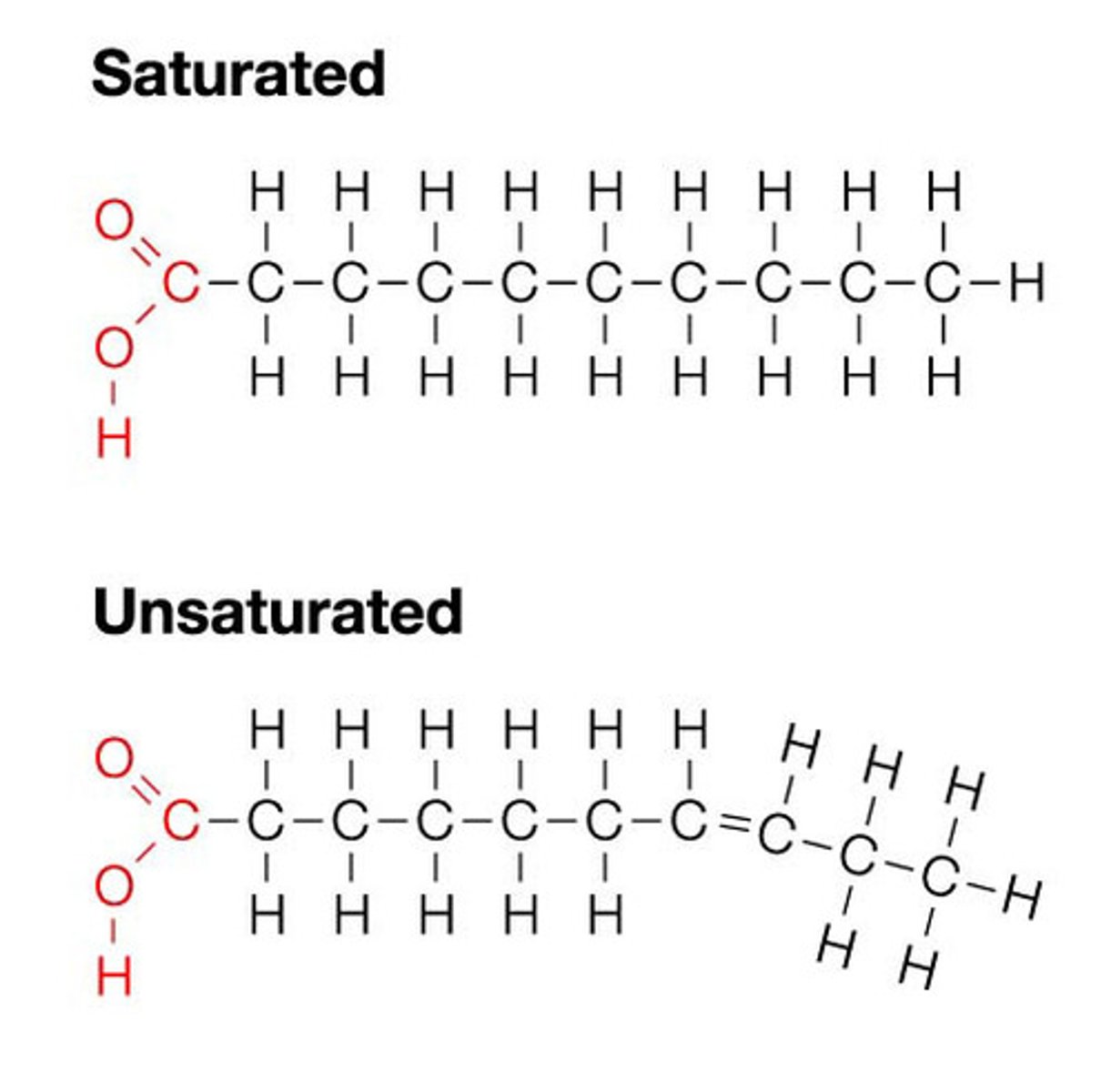
Carboxyl Groups
- if free, the ________ of a fatty acid will ionize
- most often are linked to other groups to form either esters or amides
Phospholipids
- major constituents of cell membranes
- two of the -OH groups in glycerol are linked to __________, third -OH group is linked to phosphoric acid
- phosphate linked to one of a variety of small polar groups, ie choline
Micelles and Liposomes
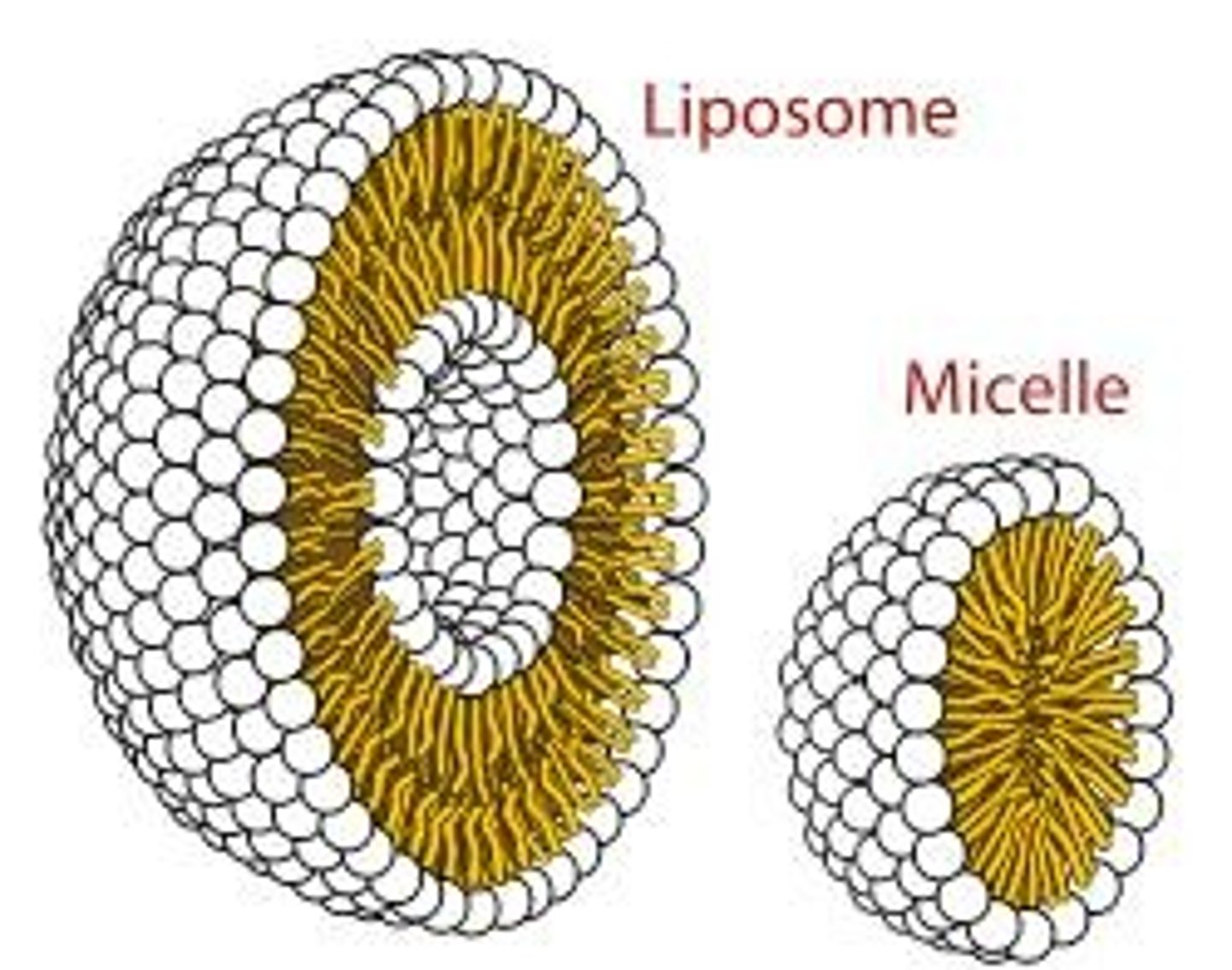
Nature of Soluble or Luminal Proteins vs Membrane Proteins?
soluble or luminal proteins are typically hydrophilic and exist in aqueous environments, while membrane proteins are largely hydrophobic
Triacylglycerols
form large, spherical fat droplets in the cell cytoplasm
Phospholipids and Glycolipids
form self-sealing lipid bilayers, which are the basis for all cell membranes
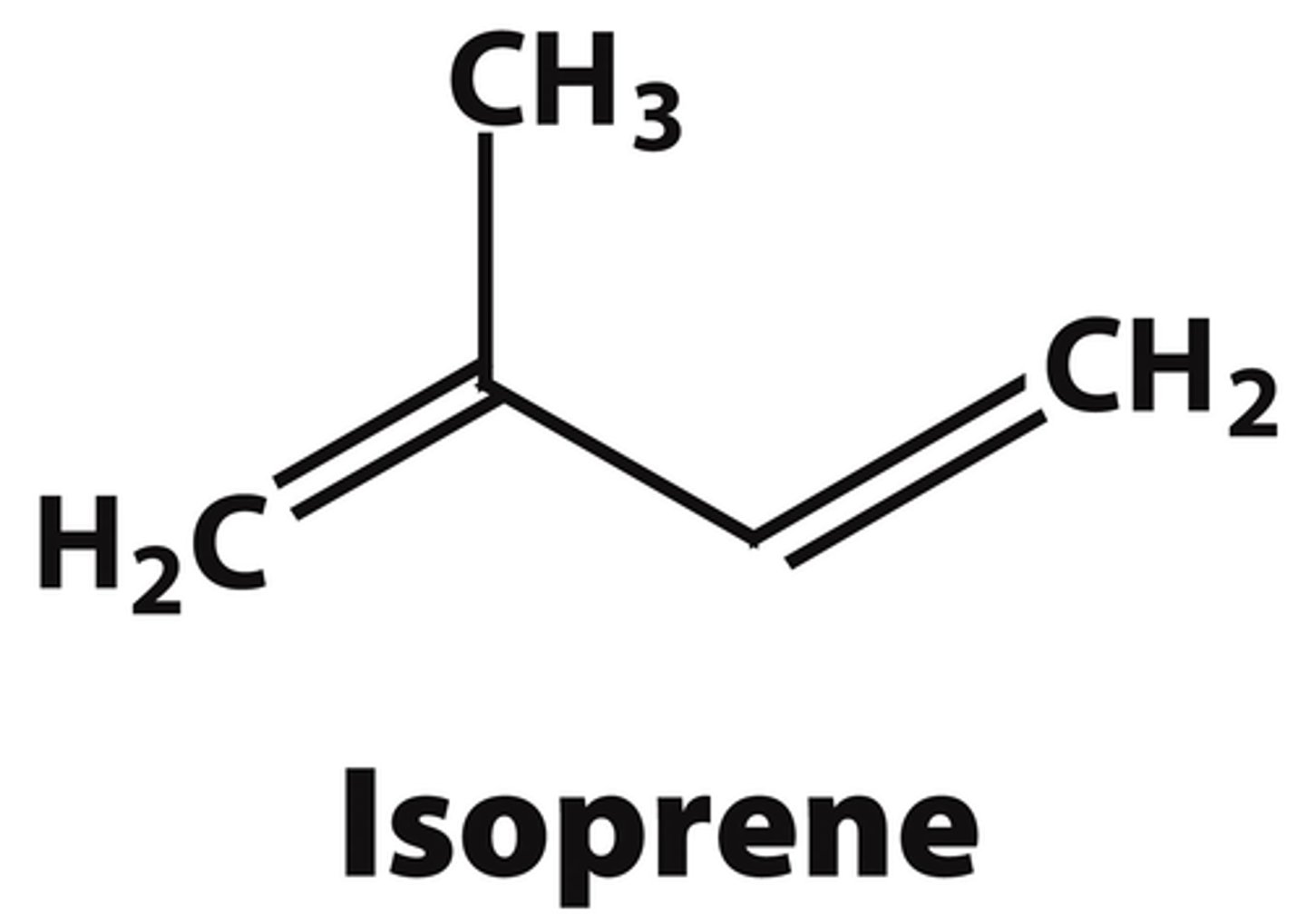
Lipids
water-insoluble molecules that are soluble in organic solvents, common lipids include steroids and polyisoprenoids, both made from isoprene units
Isoprene
Cholesterol
(steroid) found in many cell membranes
Testosterone
(steroid) male sex hormone
glycolipids
composed of two long HC tails and one or more sugars (no phosphate)
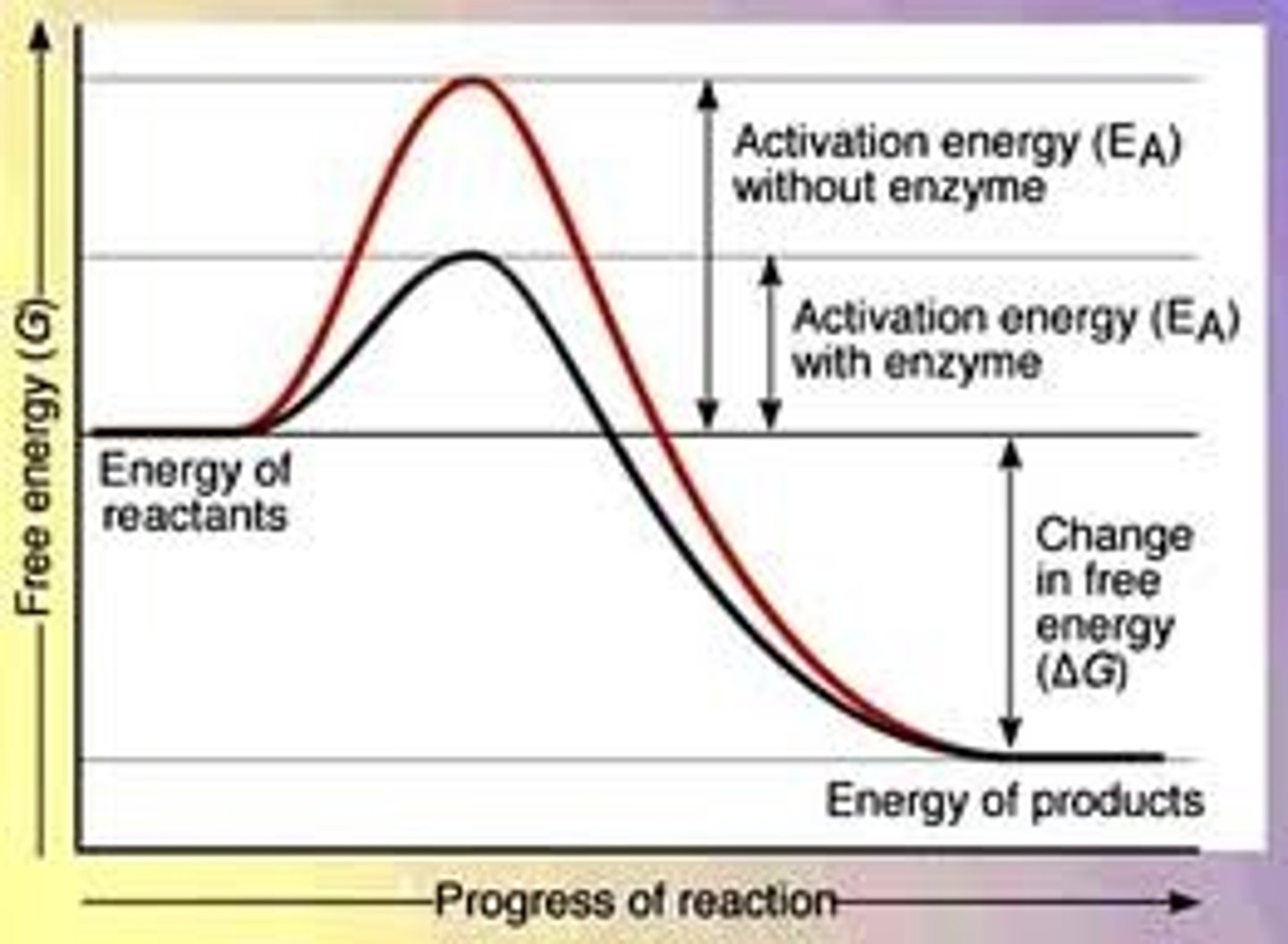
Catalysis and the Use of Energy By Cells
- ΔG determines whether a rxn occurs spontaneously
- enzymes do not affect free energy, only lower activation energy during a rxn
- the formation of an activated cell is due to an energetically unfavorable rxn
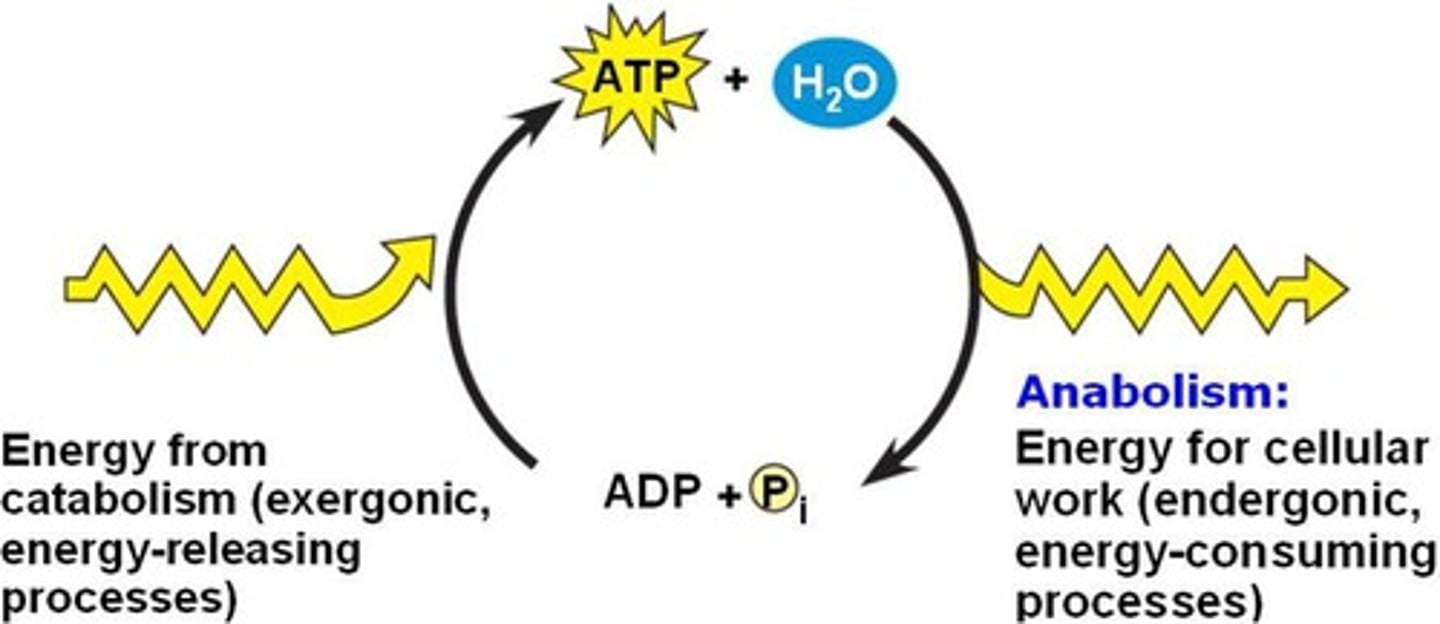
- ATP is the most widely used activated carrier molecule
- ATP joins two molecules together and drives anabolic rxns
Catabolic Pathways
- rxn that breaks down complex molecules into simpler ones, heat is lost
- exergonic
Anabolic Pathways
- process that synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones, they require energy, and it usually comes from ATP
- endergonic
Activation Energy
ATP Cycle
Molecular Interactions, Binding, Folding
- molecules are 3D via their folding and interactions
- molecular interations are driven by gibbs free energy
- molecules will interact, bind, and fold in order to reach their lowest state of free energy (lowest G)