Quiz 6 - Animal Reproduction
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
How is CIDR applied?
Insert the CIDR applicator into the vagina at an upward angle of about 30 degrees. This is done to avoid sticking the CIDR applicator into the bladder opening.
–The wings of the CIDR are folded in and the blue applicator placed in the vaginal vault. The wings are released to hold CIDR in place in the vagina next to the cervix when the applicator is removed.
What hormone does the CIDR have?
progestin → progesterone
What feed contains progestin and is given to feedlot heifers?
melengesterol acetate (MGA)
What is MGA typically used for?
to suppress estrous cycle in heifers, can be used for estrus synchronization
How should melengesterol acetate (MGA) be fed?
»Generally, each pound of MGA supplement contains 200 mg of MGA mixed primarily with soybean hulls
»The supplement should be mixed with ground corn so that each heifer receives 0.5 mg of MGA per day
How many days is melengesterol acetate (MGA) fed?
»Feed the MGA daily for 14 days
•Do not skip any days and provide the feed in the morning each day.
What factors play a role in what estrus synchronization protocol a producer should use?
•Facilities
•Labor
•Time
•Money.
Which four protocols have high labor and time requirements?
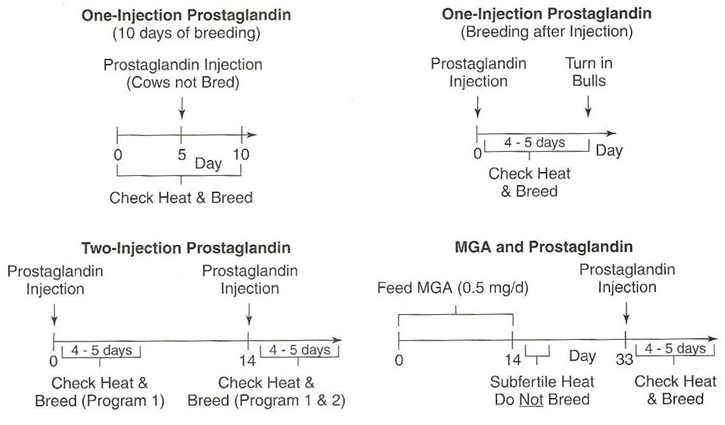
For cattle, what do you do on day 0 of the co-synch + CIDR protocol?
»Give injection of GnRH to stimulate females to ovulate the oocyte from the follicle if a follicle is growing on the ovary
•Ovulation will cause the female to enter the luteal phase
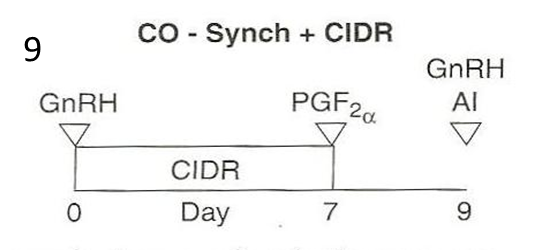
»Insert CIDR into the vagina to suppress estrus for 7 days using the progestin (i.e. synthetic progesterone) on the CIDR
•The progestin on the CIDR suppresses estrus by inhibiting the release of GnRH and LH and FSH through the negative feedback loop
Why is 7 days better than 5 days for keeping the CIDR in?
7 days is how long it takes CL to mature and become receptive/responsive to PGF2alpha
Why can’t we choose who we give GnRH to to save cost?
no matter where they are in their cycle (if you have time to watch them no need for estrus synchronization protocol just breed when they come in heat)
For cattle, what do you do on day 7 of the co-synch + CIDR protocol?
»Remove CIDR
»Give injection of prostaglandin (i.e. PGF2α) to remove the CL and transition her into follicular phase
•Seven days after the GnRH injection is how long it takes for the CL to mature and be responsive to the PGF2α.
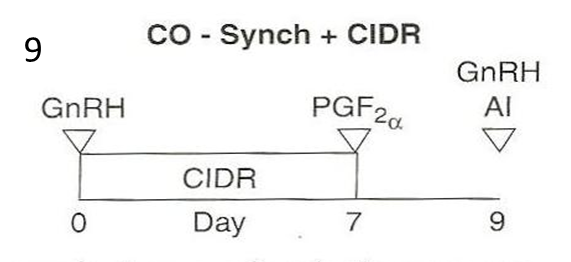
For cattle, what do you do on day 9 of the co-synch + CIDR protocol?
–Day 9 (i.e. 48 to 72 hrs after PGF2α injection):
»Give injection of GnRH to stimulate females to ovulate the oocyte so the oocyte can be fertilized by a sperm cell (takes a couple hours)
»Perform AI
•AI can be done immediately before or after the GnRH shot.
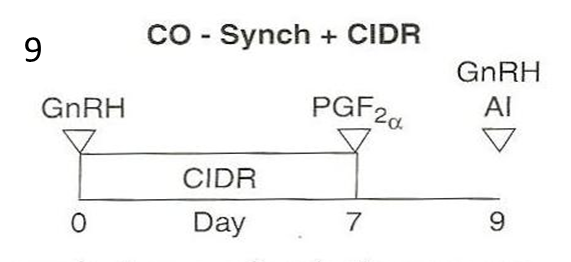
What is co-synch + CIDR protocol also called?
–This is called a ‘timed AI’ protocol because the AI is timed to be performed 48 to 72 hours after the PGF2α injection regardless of whether the female shows estrus or not
saves time and labor
»Some producers do watch for estrus and AI 12 hrs after estrus is observed
For cattle, what do you do on day 0 of the synch protocol?
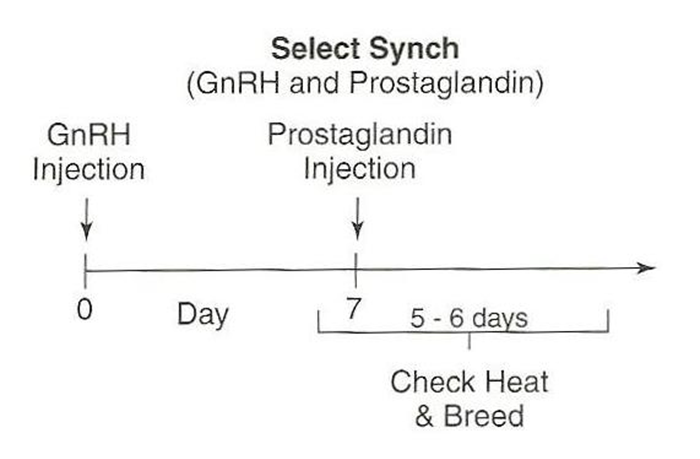
–Use GnRH to stimulate females to ovulate the oocyte, then wait 7 days for the CL to form
For cattle, what do you do on day 7 of the synch protocol?
•Day 7:
–Use prostaglandin to remove the CL
•Days 5, 6, 7+:
–Check for estrus and AI 12 hours after finding in estrus.
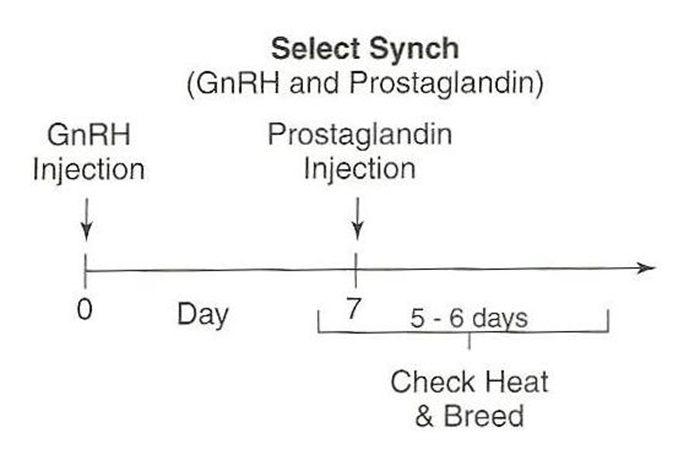
What is an advantage of Select synch protocol?
Not using CIDR saves on cost (advantage)
Can’t do timed AI on which means more time and labor (disadvantage) (is $15 CIDR worth the time and labor needed without it?)
For cattle, what do you do on day 0-14 of the MGA Select protocol?
–Feed MGA to heifers
»Each heifer needs to consume 0.5 mg per day
»This can be challenging when heifers are fed as a group because it is nearly impossible to make sure each heifer consumes 0.5 mg.
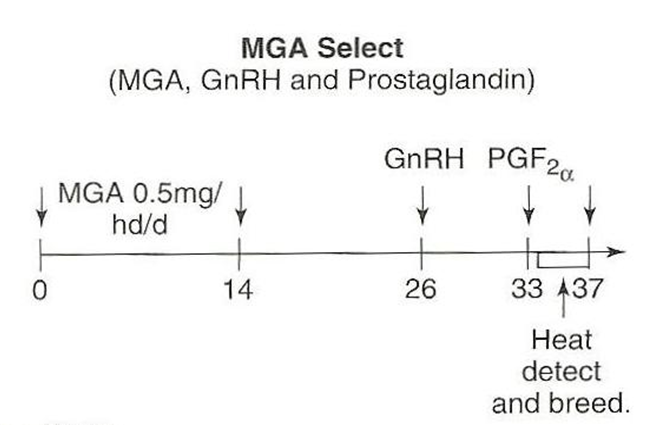
For cattle, what do you do on day 14-25 of the MGA Select protocol?
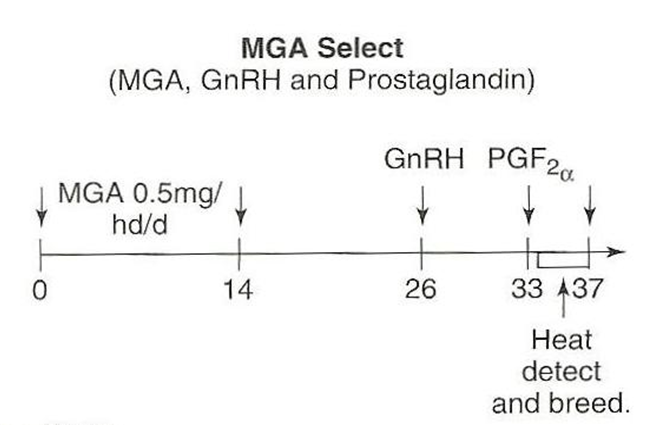
–During this 12 day period, the negative feedback of the progestin wears off and a new group of follicles will begin to grow
–Heifers may show estrus between day 14 and day 21
»Do not breed at this estrus, this estrus is usually subfertile
»A new CL will form after this subfertile estrus if the heifer shows estrus.
For cattle, what do you do on day 26, 33, and 33-37 of the MGA Select protocol?
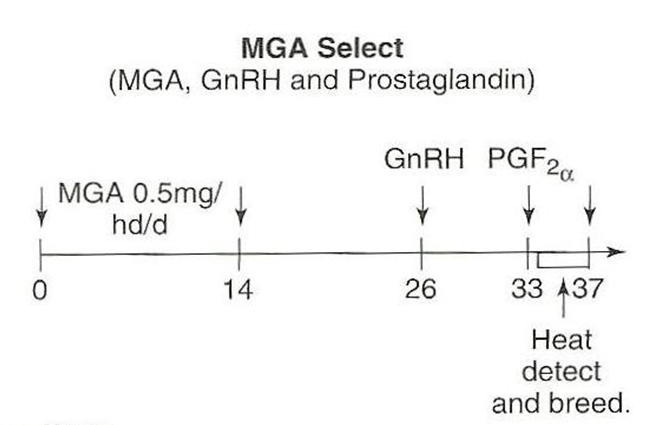
•Day 26:
–Use GnRH to stimulate ovulation of the dominant follicles and allow formation of a CL
•Day 33
–Use prostaglandin to remove CL
•Day 33 to day 37
Check for estrus and AI 12 hours after finding in estrus
Best on heifers because it primes hypothalamic gonadal axis
For swine, is natural or artificial estrus synchronization used more frequently?
–Natural estrus synchronization
•Sows will begin to show estrous cycles and estrus 2 to 10 days after the piglets are weaned
–85% of sows will show estrus 4 to 7 days after weaning
–This is assuming a 21 to 24 day lactation; if lactation lasts longer than 24 days then the sow may begin estrous cycles while the pigs are still consuming milk from the sow
–Artificial estrus synchronization
•Use of hormones to stimulate estrous cycles and/or synchronize estrus in gilts and sows.
For swine, what can be used for artificial estrus synchronization that has progestin in it and can be fed?
matrix
What is matrix?
is a liquid feed additive that is approved by the FDA to suppress estrous cycles in cycling gilts and sows
•Therefore Matrix mimics the effect of progesterone (progestin)
»Research has demonstrated that Matrix can be used to synchronize estrus in swine females, especially gilts
When is the matrix not effective?
»Matrix only works if the gilt or sow is cycling
•In other words, if the gilt has not yet achieved puberty or if the sow is not showing consistent estrous cycles, then Matrix will not work.
Directions for feeding matrix to swine
•Matrix is added to the feed as a top-dress feed additive
•In other words, first give the feed to the female and then immediately apply the Matrix liquid onto the top of the feed so that the female will consume the Matrix with the feed
•Matrix should be fed to the female for 14 straight days
•It is recommended that females be fed individually to make sure that each female consumes the correct amount of Matrix
•Approximately 85% of females will be in estrus within 4 to 9 days after the Matrix feeding period has ended
What is used on swine to synchronize weaned sows for a timed insemination?
»OvuGel is a gel that contains GnRH
•The GnRH stimulates the LH surge to trigger ovulation 40 to 48 hours after the OvuGel has been administered
How is ovugel administered?
injected into the vagina of the weaned sow close to the cervix to allow the absorption of the GnRH into the bloodstream of the weaned sow.
Directions for using ovugel on sows
»Directions (note: timing is very important):
•Day 0 is the day of weaning
•The OvuGel is administered in the morning on day 4 after weaning
•Sows should be inseminated on day 5 about 24 hours after administering OvuGel on day 4 after weaning
What is used on sows to stimulate estrous cycles in •non-cycling gilts and non-cycling sows?
•PG600 is a liquid solution that contains FSH and LH
•PG600 is injected into the gilt or sow to stimulate the estrous cycle by triggering the growth of new follicles through the action of FSH and LH
not very effective at synchronizing females
Why is prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) not used to synchronize estrus in swine?
»PGF2α is not used to synchronize estrus in swine because the CLs of swine are not responsive to PGF2α until approximately day 14 of the estrous cycle, which is when PGF2α would normally be released by the uterus of female swine
•Therefore, there is no purpose to try and use PGF2α to synchronize estrus in swine.
Explain the photoperiod effect in equine for natural synchronization?
•Reproductive activity is stimulated in the spring by an increasing photoperiod (i.e. daylight)
•This is why horses are called ‘long-day’ seasonal breeders
•Generally, horses need to be exposed to 15 to 16 hours of light per day to stimulate reproductive activity
•Conversely, periods of short light exposure (i.e. < 10 hours per day) inhibit reproductive activity.
–Why is artificial lighting used in the horse industry to stimulate horse reproductive activity?
»In order to do this, the mare is exposed to supplemental lighting each day to stimulate reproductive activity.
–When is artificial lighting started in equine?
»Most female horses will exhibit estrous cycles and estrus approximately 60 to 90 days after the artificial lighting regimen has started
•Artificial lighting should begin in late November or early December.
Explain a ‘foal heat’ in equine
•The mare will show estrus about 5-12 days after foaling
•Since the female horse has a long gestational period (approximately 11.2 months) in order to produce a foal every year she must be bred within approximately 25 days from giving birth.
What is used as synthetic progesterone (progestin) for artificial synchronization in equine?
regu-mate
•approved by the FDA to suppress estrous cycles in female horses
•Research has demonstrated that Regu-Mate can be used to synchronize estrus in mares
directions for administering Regu-mate
•Directions: feed Regu-Mate for up to 15 consecutive days to keep the female from entering estrus
•When Regu-Mate feeding is stopped, the mare will come into estrus within 4 to 5 days
What is used to remove CL for artificial synchronization in equine?
•Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α)
•Removes the CL and allows the growth of a new follicle which causes the female horse to show estrus
•The horse CL is responsive to PGF2α by 7 days after the CL has formed
Two brand names for PGF 2 alpha products in equine
lutalyse and estrumate
Explain the photoperiod effect in sheep/goats for natural synchronization?
•Reproductive activity is stimulated in the fall by a decreasing photoperiod (i.e daylight)
•This is why sheep and goats are called ‘short-day’ seasonal breeders
What progestins can be used to synchronize estrus by suppressing the estrous cycle in sheep/goats?
•Feeding MGA
•CIDR inserted into vaginal vault
What PGF 2 alpha can be used to synchronize estrus cycle in sheep/goats?
•Estrumate or Lutalyse can be used to synchronize estrus using prostaglandin F2α (PGF)
•The CLs of the ewe and/or doe are responsive to PGF approximately 5 to 7 days following ovulation and CL formation
What is most common protocol for sheep/goats?
•The two-injection PGF protocol is the most commonly used to synchronize estrus in sheep and/or goats
•Two injections of PGF 11 days apart will cause the female to show estrus approximately 30 to 36 hours after the second PGF injection.
What hormone is released from pineal gland that effect sheep/goats breeding?
•Melatonin is the hormone released from the pineal gland
•Sheep and goats are ‘short-day’ seasonal breeders, therefore, as the day length decreases (i.e. shortens), the release of natural melatonin increases, causing sheep and goats to begin estrous cycles
•Artificial sources of melatonin can be given to sheep and goats for 1 to 3 months outside of the normal breeding season to induce and synchronize estrus
What is purpose of embryo transfer?
–to increase the number of offspring that a specific mating pair can produce from one mating
•In other words, embryo transfer is a way to multiply the number of progeny produced from the mating of one male and one female
What is largest benefit of using ET?
that you can mate genetically superior males and females and get multiple genetically superior offspring from the single mating.
Explain the Ram/buck effect
•The ewe/doe will show heat when exposed to a ram or buck.
gestation length in equine
11.2 mo
Why do breeders what their foal to be as close to Jan 1st at possible?
b/c some breed associations give Jan 1st birth day to every foal born within year, so breeders want the foal to be able to grow the biggest and fastest
What’s overall purpose of embryo transfer (ET)?
to increase the number of offspring that a specific mating pair can produce from one mating
What species is ET performed on more commonly?
cattle
Summary of ET
•accomplished by either naturally or artificially inseminating a female with sperm from a male, collecting the embryos from this mating and then transferring the embryo(s) to a recipient female(s)
–Each recipient female will only take care of gestating and lactating the offspring, in other words, the recipient female does not contribute any genetic material to the embryo.
Steps of ET
1.Superovulation of the donor female
2.Insemination (natural or artificial) of the donor female
3.Non-surgical collection (i.e. flushing) of the pre-implantation embryos from the donor female
4.Grading and freezing of the pre-implantation embryos for transfer to a recipient female
5.Synchronization of the recipient female estrous cycle with the age of the embryo
6.Transfer of the embryos into the recipient female.
What happens during first step of ET → superovulation?
–given a sequence of injections of gonadatropins (i.e. follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)) to stimulate the development of multiple follicles on the ovaries
What species have best response to superovulation?
single-offspring species
How much does superovulation increase ovulation rate?
5-10 times
How many ooctyes on average do cattle produce during superovulation?
8-10 oocytes
When is the donor female insemination during step 2?
–either naturally or artificially approximately 12 hours after she shows estrus
– most common method of insemination of donor females is artificial insemination (AI)
»Usually the donor female will be AI’ed twice, with 12 to 24 hours between inseminations, to ensure that viable sperm are present in the oviduct at the time when the oocytes are ovulated.
what is called when the embryo ‘non-surgically’ collected during step 3?
flushing
When does flushing occur in step 3?
»Day 7 is the most common day to collect the embryos
•Generally speaking, day 7 embryos are at the morula or pre-hatched blastocyst stages
•The morula and pre-hatched blastocyst stages are best because embryos in these stages are easier to evaluate with a microscope after being flushed from the uterus.
Day 7 when embryo has hatched from zona pellucida
What tool is used for flushing?
foley catheter
What is the foley catheter?
»2-way catheter that has one channel for inflation of a balloon at the end of the catheter plus an additional channel for the inflow and outflow of flushing medium (i.e. fluid)
How is the foley catheter used to flush the embryos out?
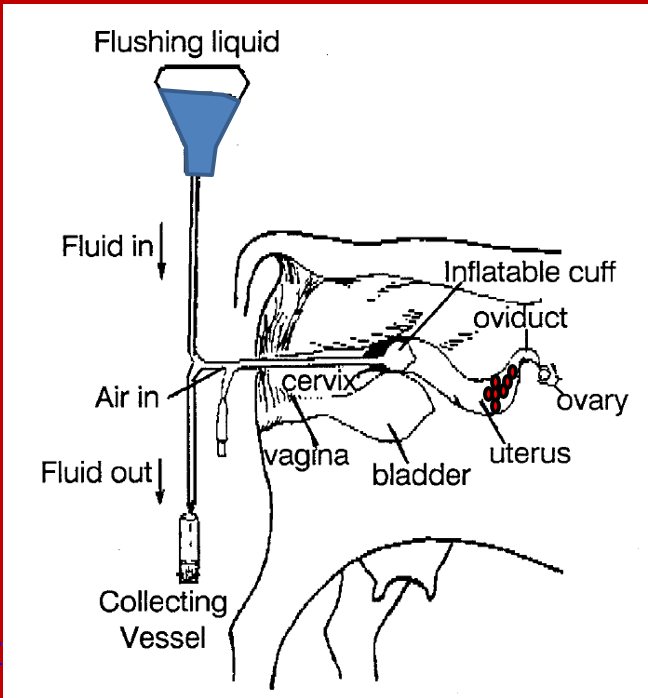
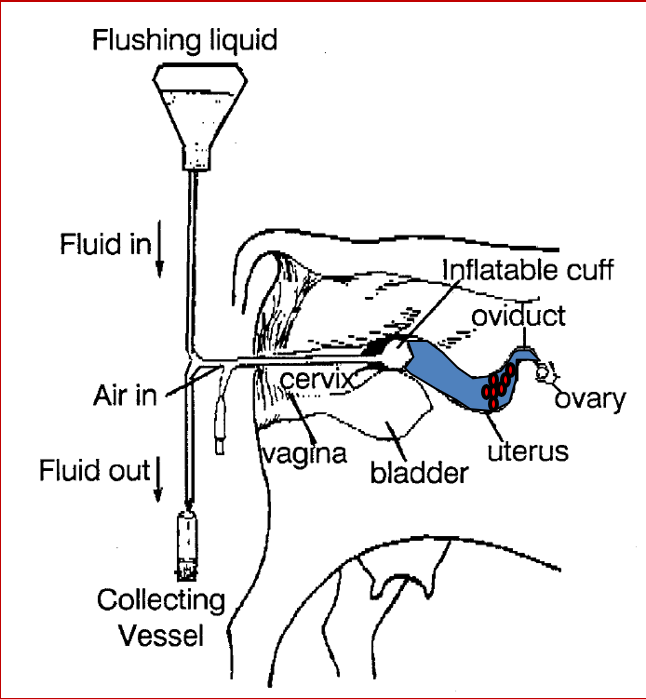
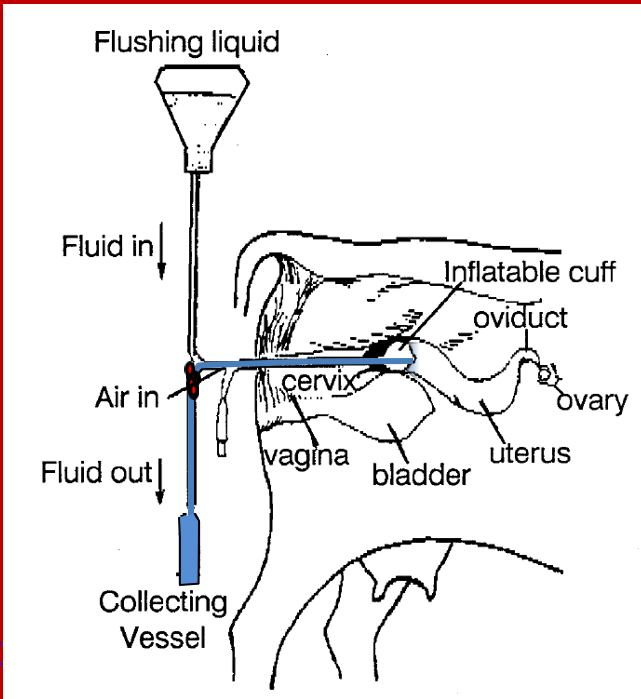
»Th Foley catheter is inserted through vagina, cervix, and into one of the uterine horn
•Once the Foley catheter is positioned in one of the uterine horns, the balloon at the tip of the Foley catheter is inflated
•The inflated balloon will seal off the anterior portion of the uterine horn, which prevents fluid from leaking out of the uterus as flushing media is added to the uterine horn to recover the embryos.
»The Foley catheter is inserted through the vagina, cervix, and into one of the uterine horns
•A small amount (i.e. 100 to 300 mLs) of fluid is then ‘flushed’ through the Foley catheter into the uterine horn
•The ET technician then gently massages the uterine horn so that the embryos become suspended in the fluid
•Next, the ET technician flushes the fluid from the uterine horn and collects the fluid and embryos in a collection vial
•This process is repeated 2 to 3 times per uterine horn.
How many viable embryos are obtained from donor cow when flushing?
5-7 embryos
How are the embryos graded during step 4 of ET?
–evaluated by stage of embryonic development and assigned a grade of 1 to 4 based on the morphological appearance of the embryo
1.Excellent
Embryos with few or no recognizable imperfections, such as poor cell compaction or variation in cell size
Usually, only embryos with a grade of 1 are used for ET
2.Fair
Embryos that show disarrangement, like a small embryonic mass with irregular shape or a large number of extruded and/or dead cells. Usually 1 to 2 days of delayed development
3.Poor
Embryos with signs of cellular degeneration, like a small ICM and several extruded cells
Development has been delayed by more than 2 days
4.Dead or Degenerating
Embryos contain mostly dead cells and very few live cells
Tiny ICM that is disorganized in appearance
Not worth transferring.
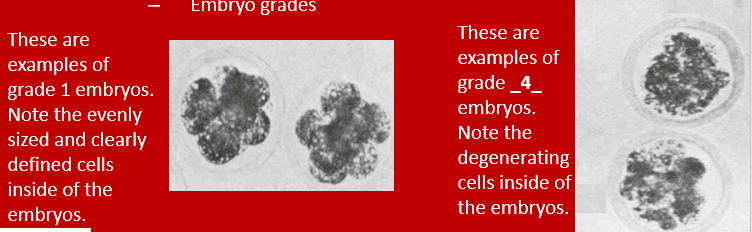
What are two methods that embryos can be transferred in step 4?
–Embryos can be transferred on the same day as they are collected or the embryos can be frozen
–It is most common to freeze the embryos because it requires a great deal of labor and time management to coordinate the estrous cycles of the recipient females with the donor female on the same day.
When freezing embryos in step 4?
–Grade 1 embryos selected for freezing are mixed with special freezing media that contains chemicals called ‘_cryoprotectants_’ (e.g. glycerol and ethylene glycol)
–The embryos and freezing media are then put into straws and frozen in liquid nitrogen
What do cryoprotectants do when freezing embryos?
»The cryoprotectants dehydrate cells of the embryo and protect the cells of the embryo during the freezing and thawing process
In step 5, what is critical?
that the estrous cycle of the recipient female be the same day as when the embryos were collected (i.e. flushed) from the donor female
»Remember that generally the embryos are collected on the 7th day of the estrous cycle (i.e. estrus = day 0)
–In order to coordinate the day of the estrous cycle with the age of the embryo, the recipient female can either be watched for a natural estrus or she can be estrus synchronized.
What are steps for transferring the embryos into the recipient female in step 6 of ET?
1.The ovaries of the recipient female are palpated or ultrasounded to determine which ovary has a CL
»The embryos will be deposited in the uterine horn that has the ovary with the CL; this helps increase the chances for a successful ET
2.The straw containing the embryo is thawed and then the embryo is transferred into the proper uterine horn of the recipient female using a special ET transfer rod
»The embryo is deposited about 1/3 of the way up into the uterine horn
How many embryos are implanted for single bearing species?
most commonly one embryo
How many embryos are implanted for litter bearing species?
15-20 embryos
What is the name of the estrus synchronization product that is a feed additive approved by the FDA to suppress estrous cycles in cycling female horses? In addition, what hormone does this product use to suppress the estrous cycle?
Product name: Regu-Mate; Hormone: Progestin (i.e. synthetic progesterone)
In which livestock species is natural estrus synchronization accomplished by reproductive activity being stimulated in the fall by a decreasing photoperiod (i.e. daylight)?
sheep and goats
PG600 is a liquid solution used in the swine industry to stimulate the estrous cycle in noncycling gilts and non-cycling sows. PG600 contains what two gonadotropin hormones?
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
____is a liquid feed additive that is approved by the FDA to suppress estrous cycles in cycling gilts and sows. This product mimics the effect of progesterone
matrix
On day 0 and day 9 of the CO-Sync + CIDR estrus synchronization protocol, GnRH (i.e. gonadotropin releasing hormone) is given to the female animal to cause the LH (i.e. luteinizing hormone) surge, which will cause ___ to occur
ovulation
the name the hormone that stimulates reproductive activity in sheep and goats. This hormone increases in sheep and goats in response to the decrease in day-light length.
melatonin
overall purpose of ____ transfer (ET) is to increase the number of offspring that a specific mating pair can produce from one mating.
embryo
Why is prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) not used to synchronize estrus in swine?
PGF2α is not used to synchronize estrus in swine because the CLs of swine are not responsive to PGF2α until approximately day 14 of the estrous cycle, which is when PGF2α would normally be released by the uterus of female swine. Therefore, there is no purpose to try and use PGF2α to synchronize estrus in swine.
Look at the MGA Select estrus synchronization protocol shown below. What is occurring from day 14 to 25 in regards to the effects of MGA (i.e. melengesterol acetate)?
From day 14 to 25, during this 12 day period, the negative feedback of the progestin from the MGA wears off and a new group of follicles will begin to grow. Heifers may show estrus between day 14 and day 21. Do not breed at this estrus, this estrus is usually subfertile. A new CL will form after this subfertile estrus if the heifer shows estrus.
OvuGel is a product used in female swine to synchronize estrus. Please explain how OvuGel synchronizes estrus in swine.
OvuGel is a gel that contains GnRH. The GnRH stimulates the LH surge to trigger ovulation 40 to 48 hours after the OvuGel has been administered. OvuGel is used to synchronize weaned sows for a timed insemination.
Why is artificial lighting used in the horse industry to stimulate horse reproductive activity?
Some horse breeds and race horses are given a birth date of January 1 in the USA, regardless when the birth date of the horse actually is during the year. Therefore, female horses need to be bred around mid-February so the foal is born on or shortly after January 1 the following year. Gestation in the horse is approximately 11.2 months. In order to do this, the mare is exposed to supplemental lighting each day starting in late November or early December to stimulate reproductive activity.
. This question is worth two points and partial credit may be given. Natural estrus synchronization is used more than artificial estrus synchronization in the swine industry. Please explain natural estrus synchronization in swine.
With natural estrus synchronization in swine, sows will begin to show estrous cycles and estrus 2 to 10 days after the piglets are weaned; 85% of sows will show estrus 4 to 7 days after weaning. This is assuming a 21 to 24 day lactation; if lactation lasts longer than 24 days then the sow may begin estrous cycles while the pigs are still consuming milk from the sow.
This question is worth two points and partial credit may be given. Please look at the figure below of the CO – Synch + CIDR protocol that was shown and discussed in class lecture. What is the purpose of the CIDR and why is the CIDR used for the length of time that it is?
The purpose of the CIDR is to suppress estrus for 7 days using the progestin on the CIDR. The progestin is synthetic progesterone and mimics the effect of progesterone. The CIDR is in the vaginal vault of the bovine female for 7 days to allow the corpus luteum (CL) to mature and be responsive to the PGF2α injection given at day 7.