AP Psych- Sleep Quiz
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
nREM1
During this stage of sleep individuals experience a drowsy interval between waking and sleeping, characterized by brief, hallucinatory dream like experiences known as a hypnagogic state.
REM
Most vivid dreams occur in this stage.
nREM3
Dreams occurring in this stage are typically shorter, less emotional and less visual.
nREM3
Sleep terrors may occur in this stage.
nREM2
Sudden brief muscular contractions may occur in these two stages as muscles relax.
nREM2
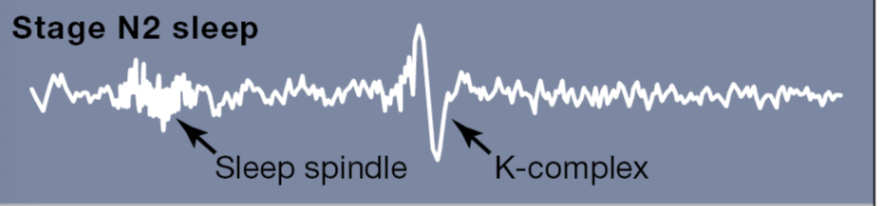
During this stage EEGs reveal K complexes and sleep spindles.
REM
This sleep stage can be characterized by an increase in blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing.
REM
Stage showing loss of muscle tone and an inability to move voluntary muscles.
nREM2
The body tends to stop in this stage between nREM3 and REM, and vice versa.
nREM3
Sleep walking is only possible in this stage.
All but most coherent: REM
Sleep talking occurs in this stage
REM
This sleep stage features saw-tooth “beta-like” waves.
nREM1
Theta waves predominate this stage.
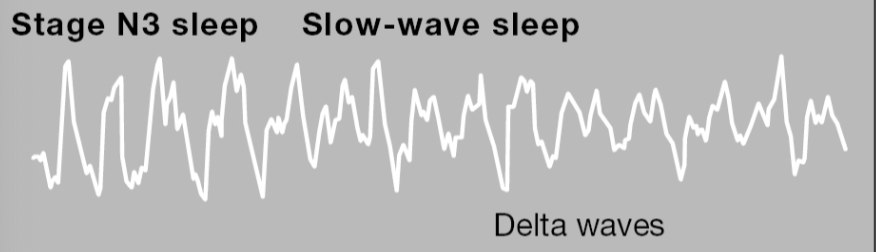
nREM3
As the sleep cycle repeats throughout the night time, this stage DECREASES most.
REM
As the sleep cycle repeats throughout the night time, this stage INCREASES most.
nREM2
On average, you spend the largest portion of the night in this stage.
Alpha Waves
just before sleep
Theta Waves
nREM1 (and some nREM2)
Theta→Delta
nREM2
Delta
nREM3-4
Beta-like
REM
Consciousness
awareness of yourself and your external environment
Circadian rhythms
Daily autonomous cycle of bodily processes (sleeping/digestion)
Suprchiasmatic Nucleus
The part of the hypothalamus that regulates the circadian rhythms and CONTROLS MELATONIN
Jet Lag
body’s internal clock has trouble adjusting when you travel across time zones
Shift Work
biological clock of an individual is often altered during night shifts (consistent overnight shifts)
How many minutes do the cycles of sleep take in total?
60-90 mins (you should have 5-6 cycles a night)
Hypnagogic sensations:
Occur in nREM1
trippy, drowsy, dreamy
myoclonic jerks: muscle spasms/body shakes
What happens during nREM2?
Sleep spindles (thalamus shutting down and not processing stimuli)
K-complexes (hippocampus beginning to process for consolidation)
What happens during nREM3-4
Hardest to wake up, sleep movement, very slow brain waves
What happens during REM
also called paradoxical sleep (contradicting state of active mind vs sleeping body)
vivid dreams
rapid eye movement
REM Rebound
After REM deprivation, your body will undergo much more REM and skips through processes to get there
sleep revenge
spend all day working and finish work late and since you deserve fun time you end up staying up even later
Information Processing/Consolidation Theory
dreams are how we transfer info from hippocampus to cerebral cortex
Activation Synthesis Theory
Dreams are random neural firings in the brain that the brain tries to make sense of
Physiological Function Theory
Dreams are a way of keeping neural pathways stimulated/preserved while sleeping
Cognitive Development Theory
Dreams help people solve problems/process info and represents a person’s experiences
Insomnia
can’t fall asleep
or you can fall asleep but then you wake up and can’t fall asleep for another 30-45 mins
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
act out dreams, talk, scream
Somnambulism
move around in sleep in nREM3/sleep walk
Narcolepsy
brain can’t control when to sleep
fall asleep involuntarily at random times
Sleep Apnea
stop breathing at night
brain forces you to wake up
Sleep spindles
thalamus shutting down and not processing stimuli
K-complexes
hippocampus getting ready for memory consolidation