investigation 4: diffusion and osmosis
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
part 1: surface area and cells — basic setup
demonstrate relationship between SA and volume and how this ratio affects diffusion rates.
block of agar that has indicator dye that changes colour when pH drops
cut blue agar into 3 different block sizes with diff SA-volume ratios (SA:V)
each block is dropped into a solution & diffuses. Track the time it took to fully diffuse
part 1: surface area and cells — results
larger SA = slowest diffusing time
high SA:V ratio is important for any cell that relies on high diffusion rate.
eg. the linings of ur small intestines and lungs have many folds in order to create the highest SA possible in the smallest amount of space
Part 2: modelling diffusion and osmosis — basic setup
dialysis tubing, selectively permeable to water and some solutes
Part 2: modelling diffusion and osmosis — results
when molarities are equal (eg 1 mol sucrose & 1 M NaCl) and the solution becomes lighter after 30 minutes for example, ionization constant from solute potential equation becomes the deciding factor. NaCl ionizes but sucrose doesn’t (i = 2). Thus water diffuses out of the bag into surrounding NaCl solution
part 3: observing osmosis in living cells — basic setup
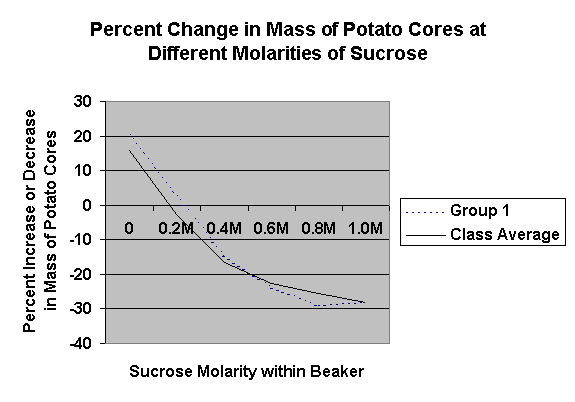
surcose solutions (0 mol to 3 mol) and use potato cores to find out the relative concentrations of these solutions. U can then calculate %change in weight of potato cores & get the water potential of potato tissue
bigger the difference in water potential between a cell and solution, the bigger the movement of water (into our out)
part 3: observing osmosis in living cells — results
arrange change in weight from most negative to positive
very (-) means heavy loss of water
very (+) means heavy water gain (hypotonic), greater the weight, the lower the molarity of the solution
graph %changes in weight and find x intercept which indicates the molarity when there would be no net change in weight.
if water potential of the solution = cell water potential