Histology: All Tissues
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Neural
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
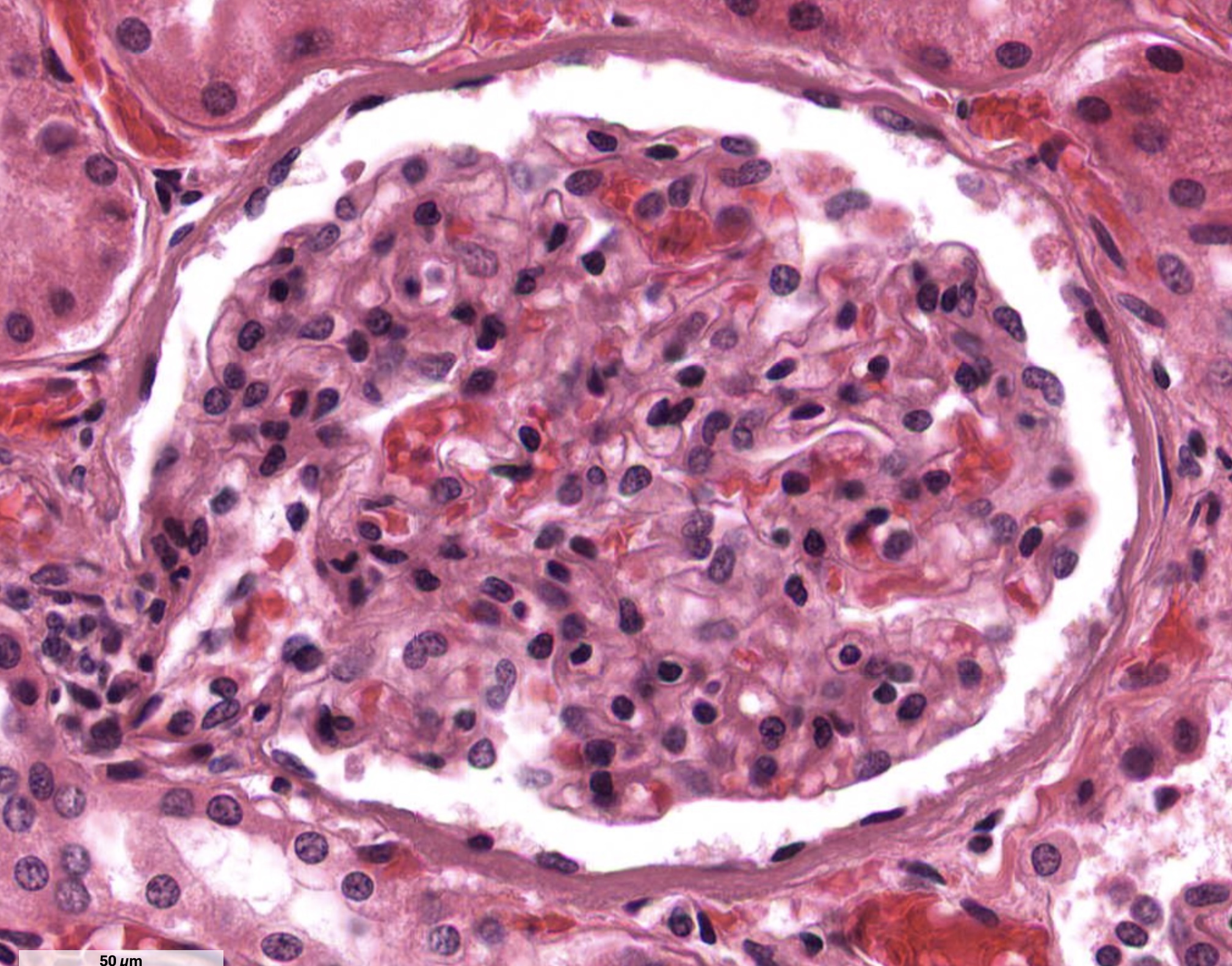
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Location: Lining body cavities
Function: Diffusion
( simple squamous are very thin cells — thinner cells = faster rate of diffusion )
-
Simple Squamous Epithelium
One layer
Flat & squished
Round nuclei (but may look squished)
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
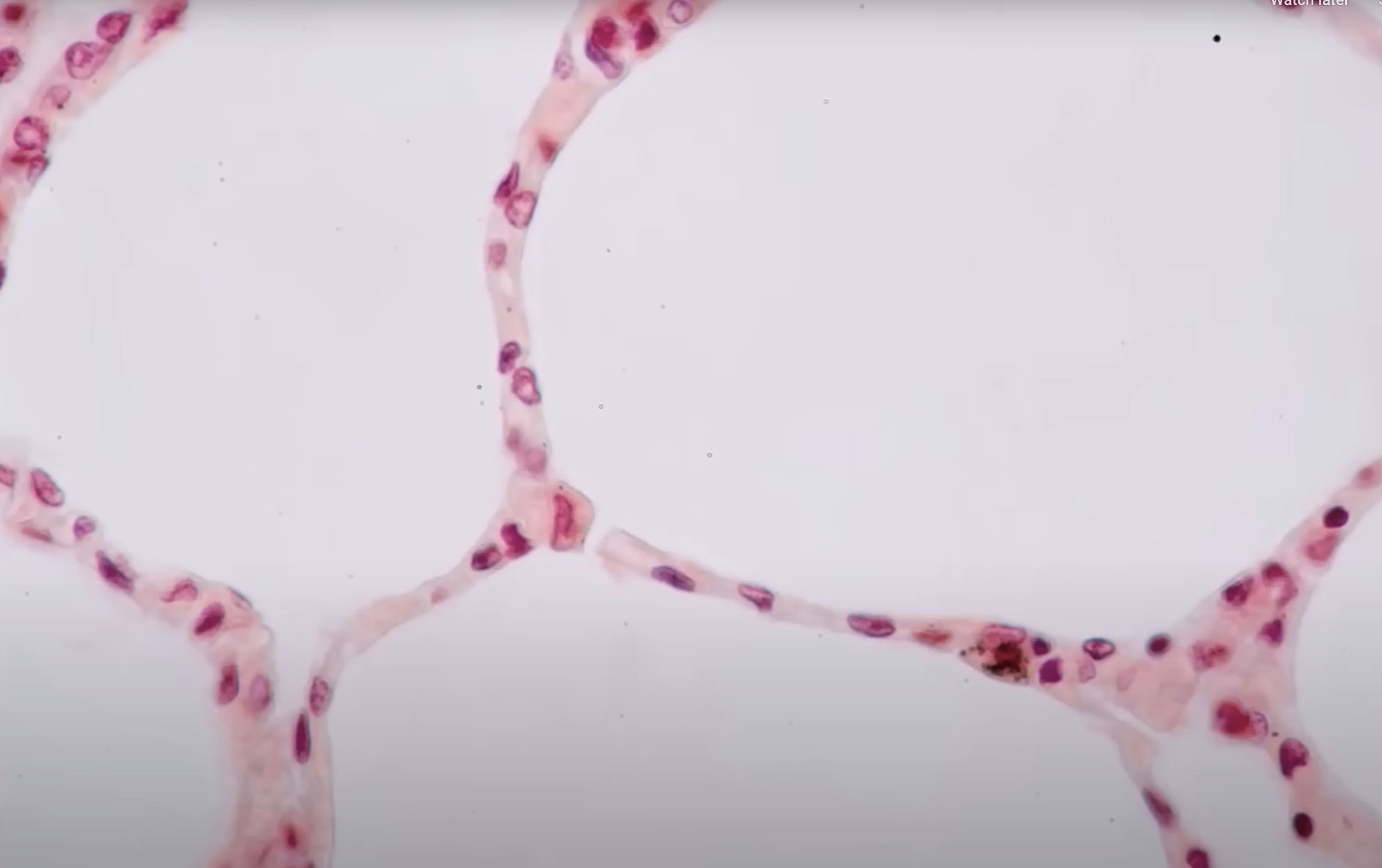
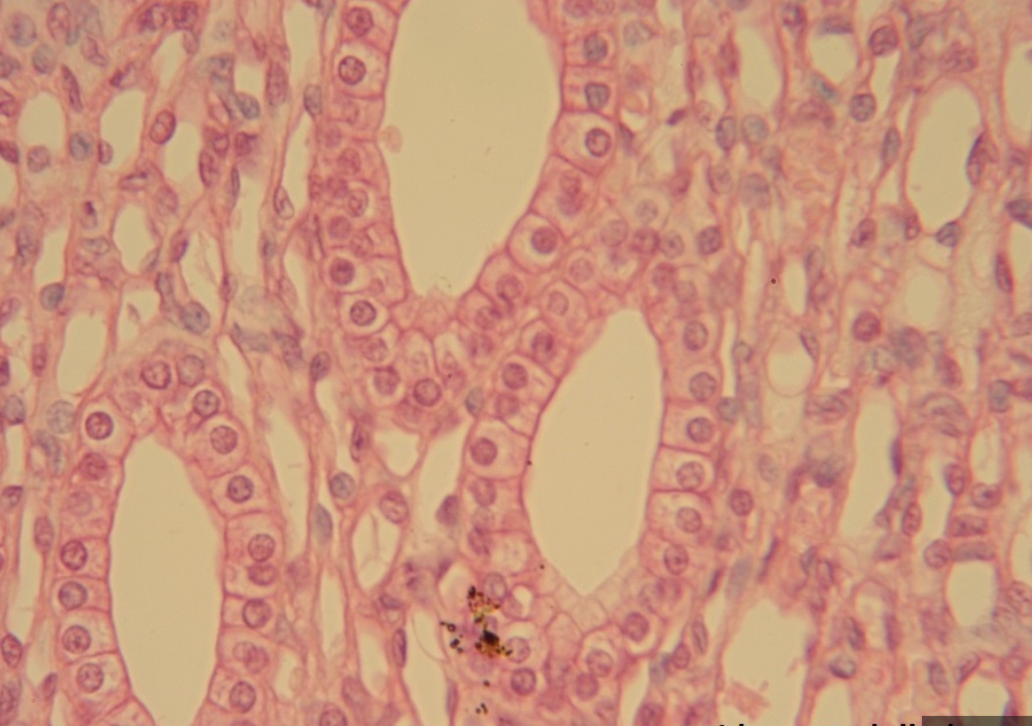
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Location: Thyroid gland
Function: Secretion
-
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
One layer
Boxy with round nuclei
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
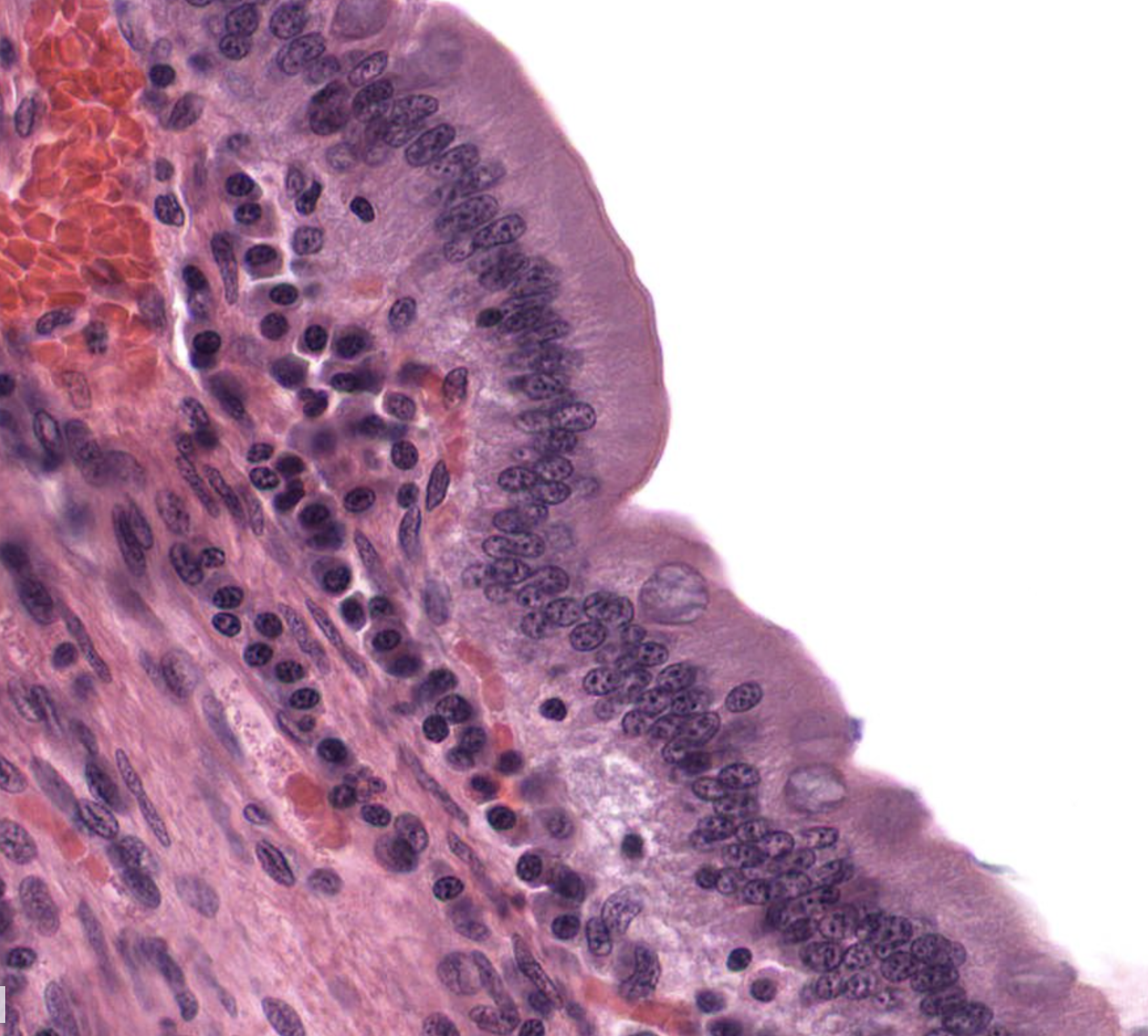
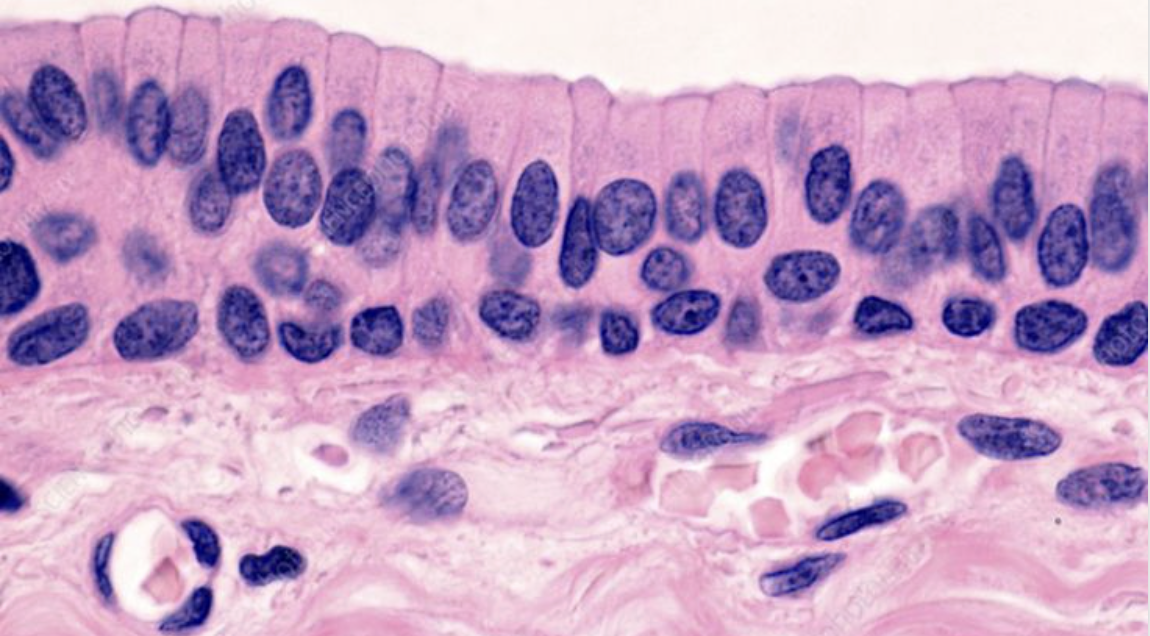
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Location: Intestinal lining
Function: Secretion
-
Simple Columnar Epithelium
One layer
Long like columns, nuclei is elongated (oval-shaped)
Nuclei are somewhat linear
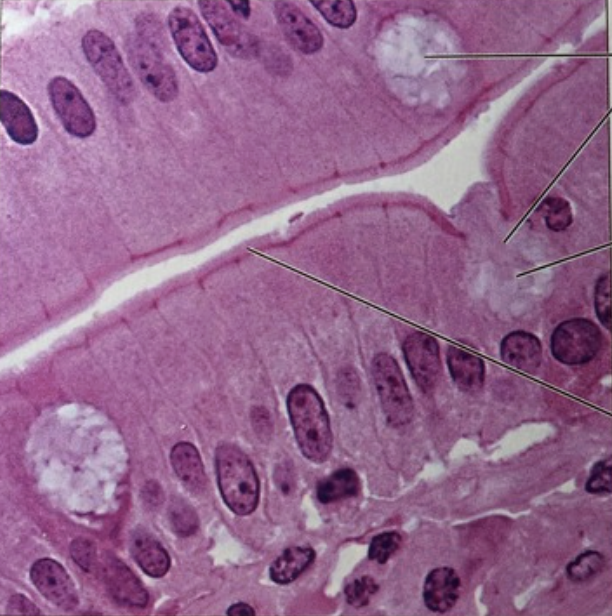
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Simple Columnar Epithelium w/ Microvilli
Location: Intestinal lining
Function: Secretion
-
Microvilli = increases surface area for absorption & secretion
Microvilli has:
Goblet cells = secrete mucus
Can also be: Simple Columnar Epithelium w/ Cilia = moves substances over the apical (exposed) surface of the cells
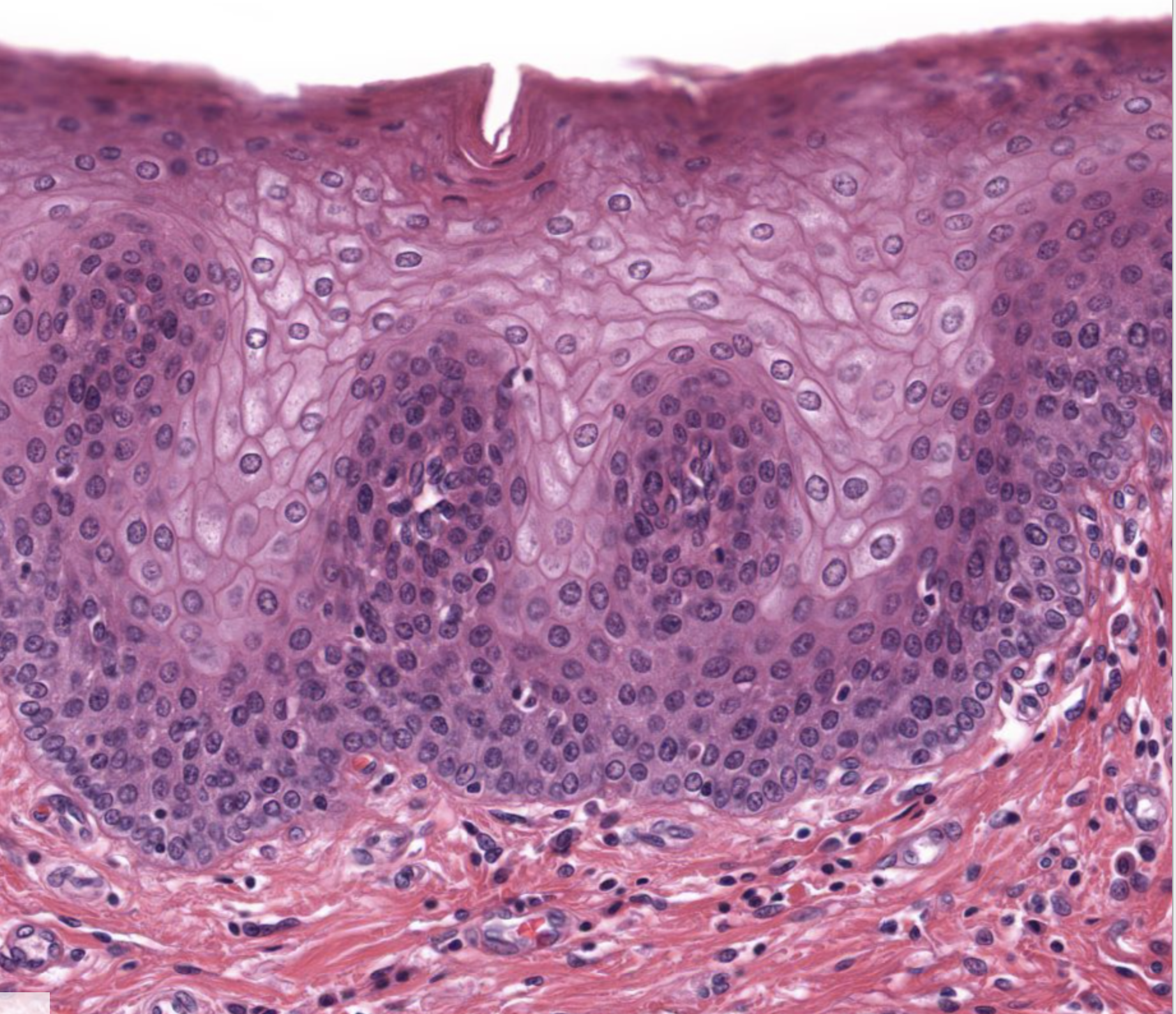
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Location: Surface of skin (dry)
Function: Protection
-
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Many layers
Many nuclei
Apical cells look flat & squished at the top
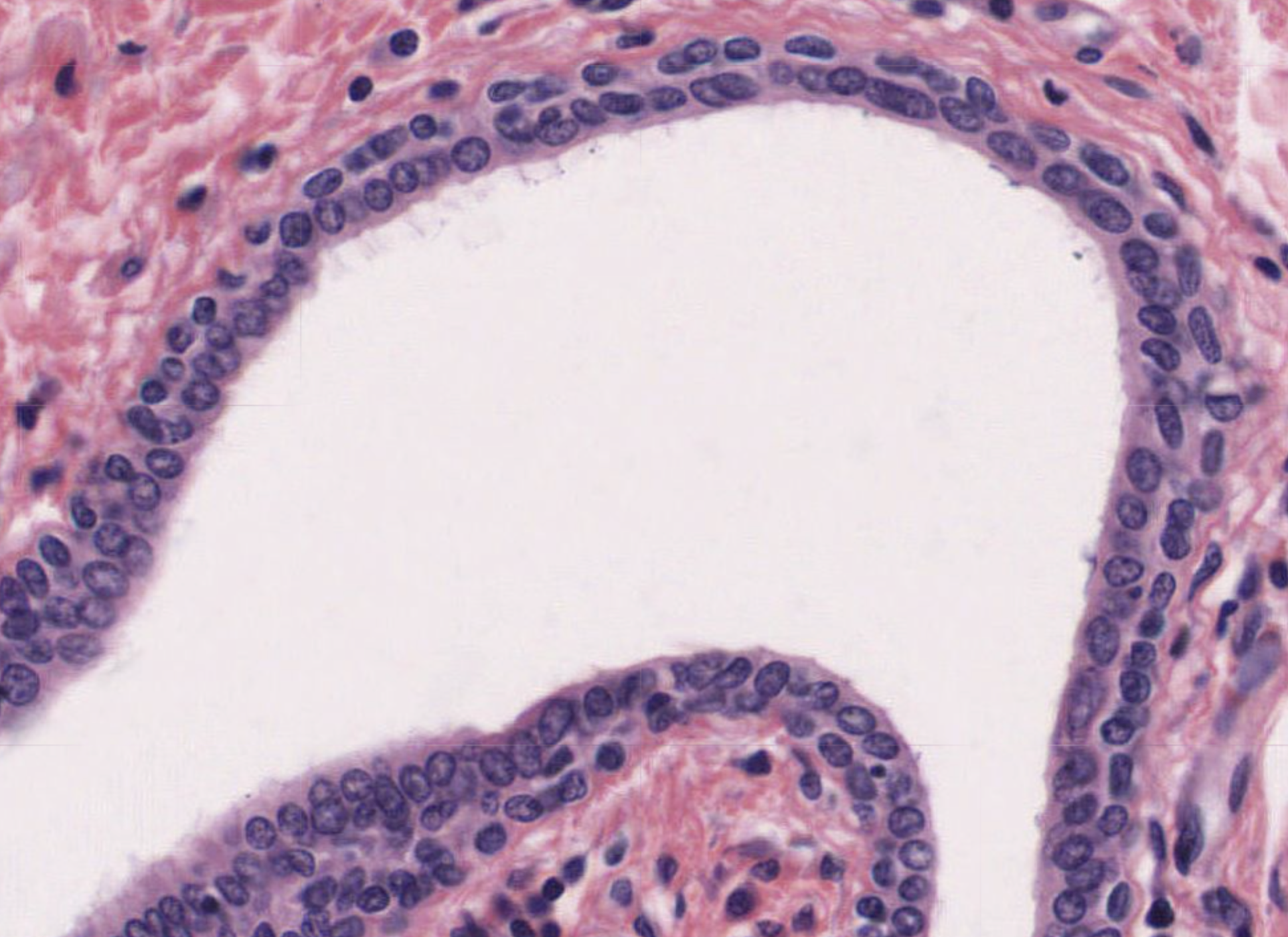
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Location: Lining of some ducts
Function: Protection
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Many layers
Apical cells look boxy with round nuclei
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Location: Male urethra
Function: Protection
-
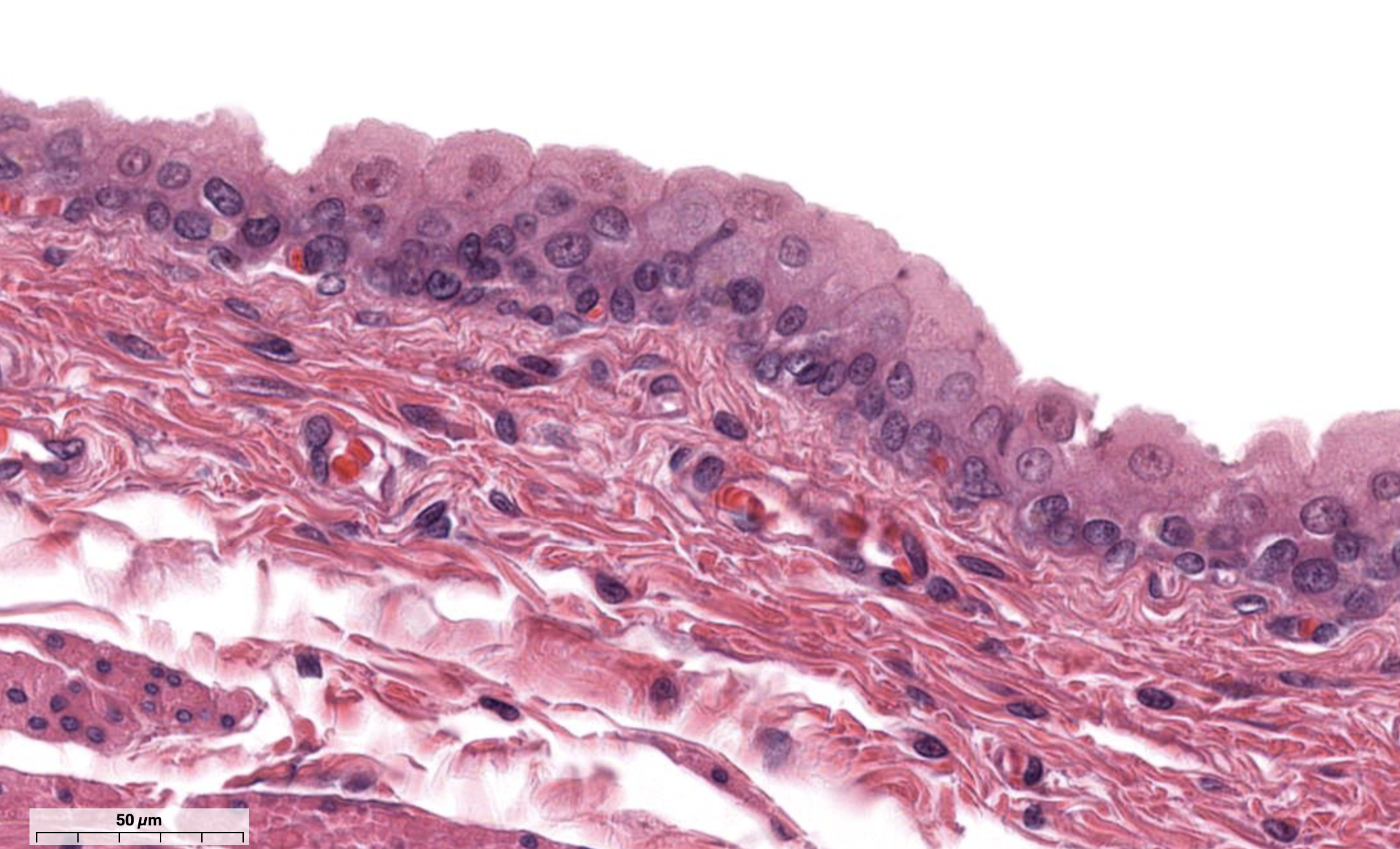
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Many layers
Apical cells look columnar & long, nuclei look elongated
Goblet cells are lighter in image which means they secrete mucus
Nuclei stains darker
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Transitional Epithelium
Location: Urinary bladder
Function: Allows for stretching
-
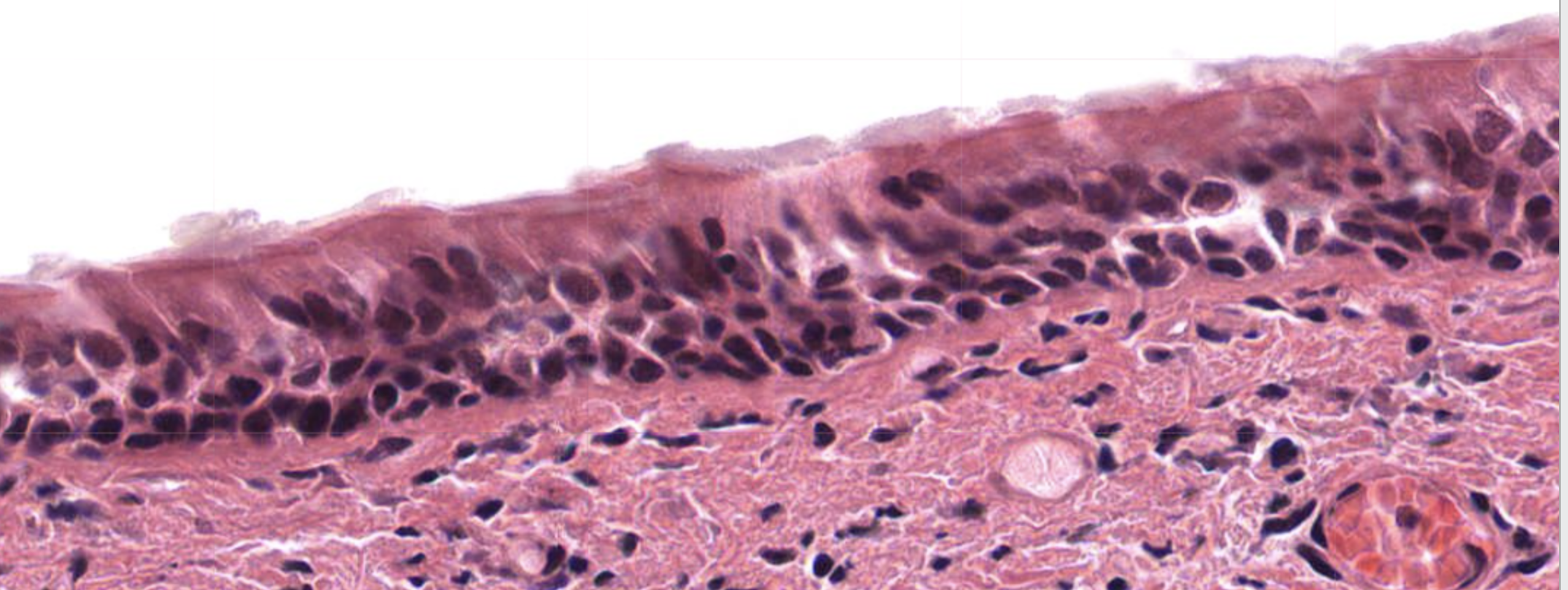
Transitional Epithelium
Dome-shaped cells on top
Many layers (you almost think its "stratified” but look at the umbrella cells on top)
Round nuclei
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Location: Nasal cavity
Function: Protection
→ Pseudo = fake Stratified = layers
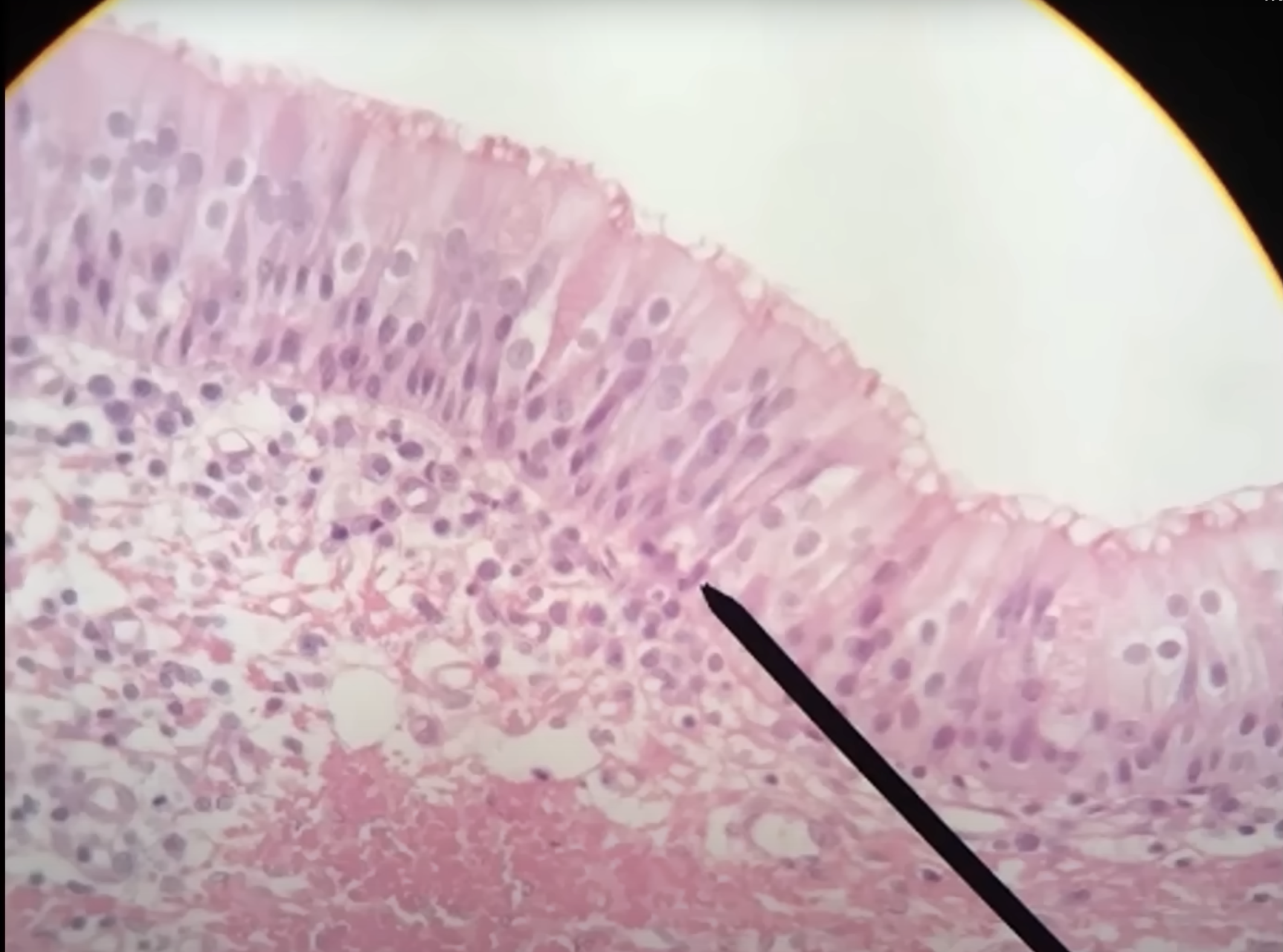
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Nuclei = up & down, squished
Cilia on apical surface (moves substances across apical)
All will have attachment to the basement membrane
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Areolar Connective Tissue
Location: Deep dermis, between muscles
Function: Connects skin to muscle
-
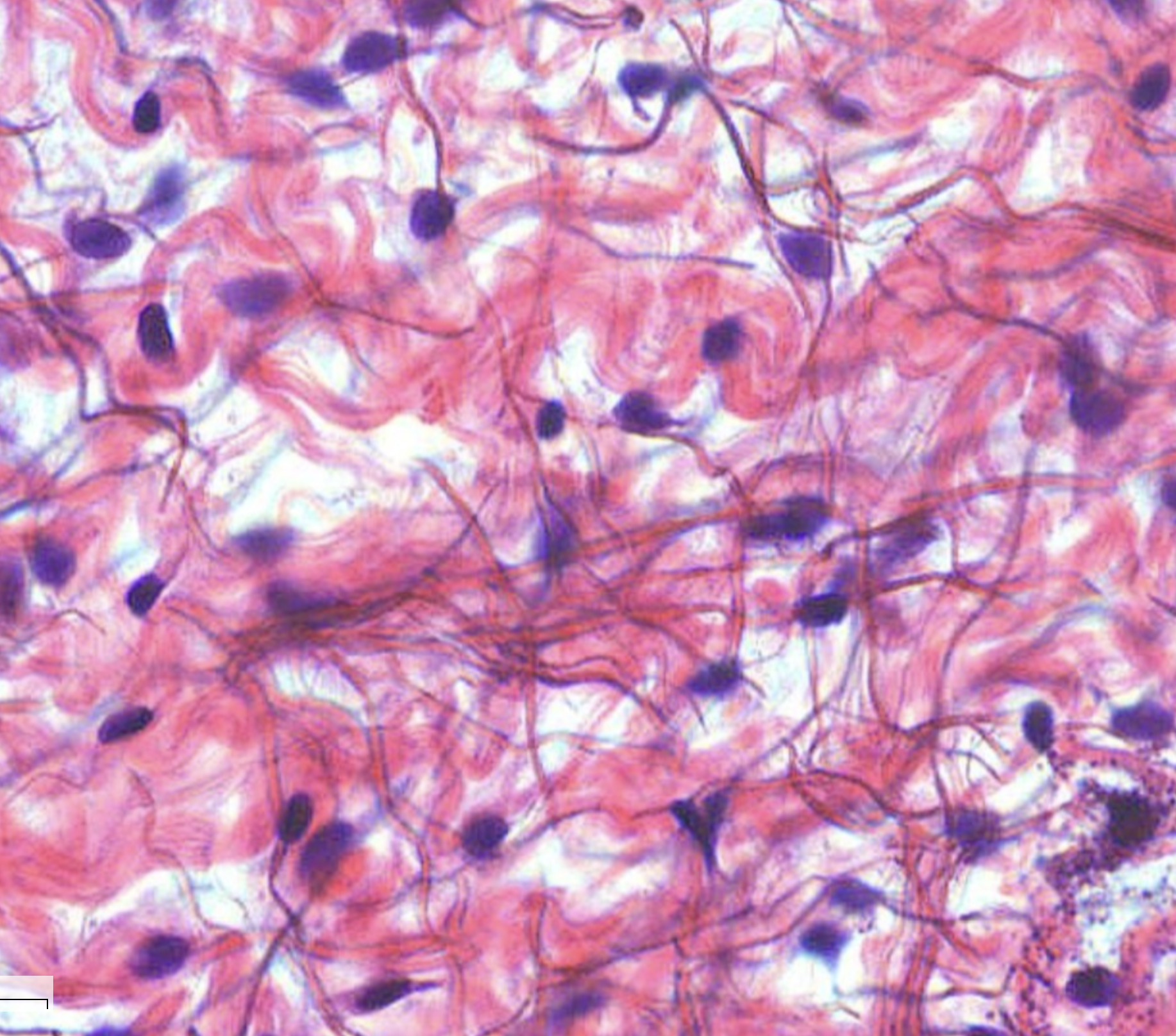
Areolar Connective Tissue
Loose fibers = open framework (seeing lots of space between fiber & cells)
Gel-like matrix w/ 3 fiber types: collagen, elastin, reticular
Can see many types of cells like: mast cells and fibroblasts
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
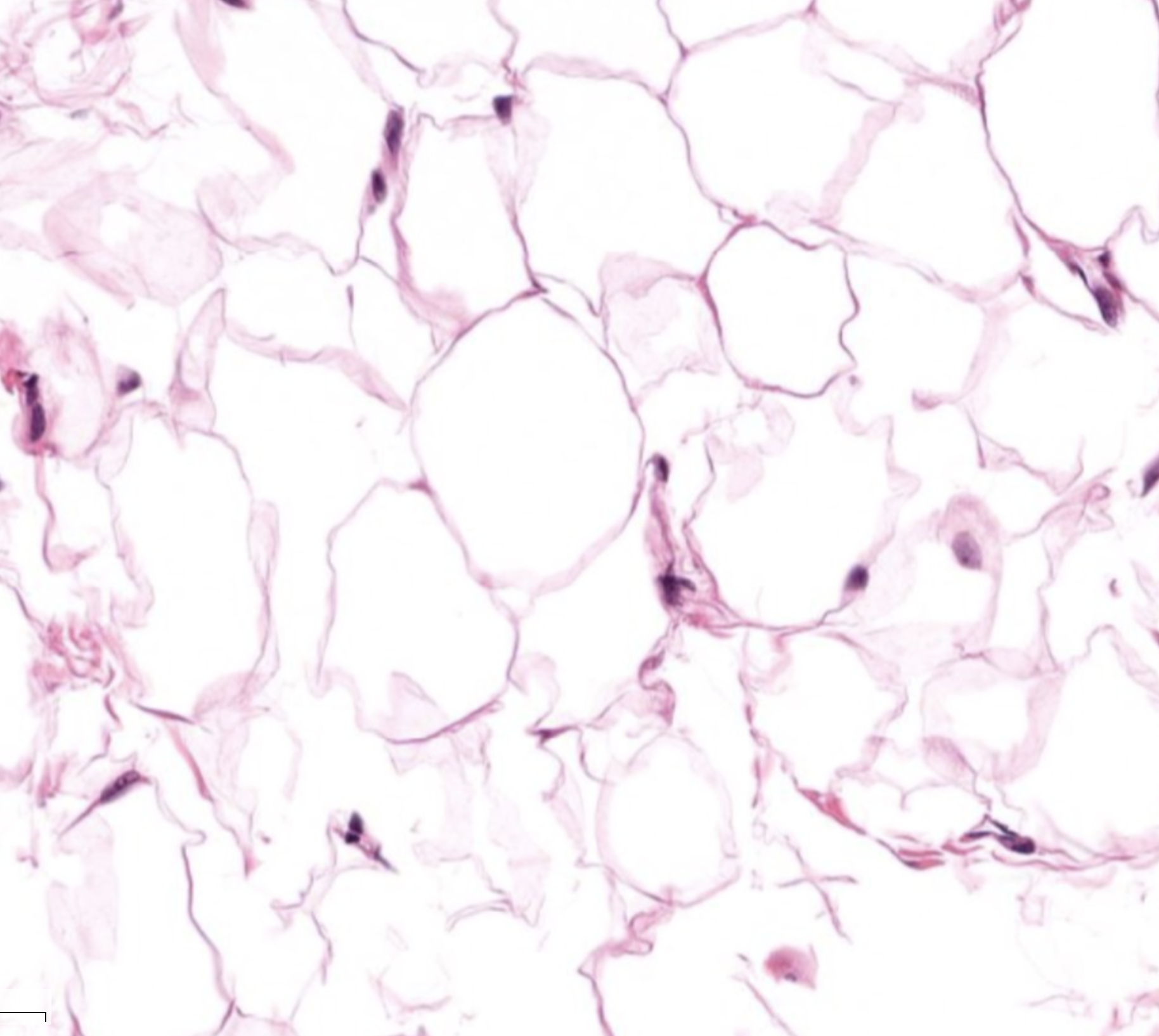
Adipose Connective Tissue
Location: Buttocks
Function: Provides padding and cushion
-
Adipose Connective Tissue
Consists of Adipocytes: filled with white fat
Because of fat, the nucleus is pushed to the side (may look shaped like simple squamous, but look at the nucleus pushed to the side)
Loose fibers = open framework (BUT in adipose tissue you can’t see much fibers or open framework because of the fat)
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
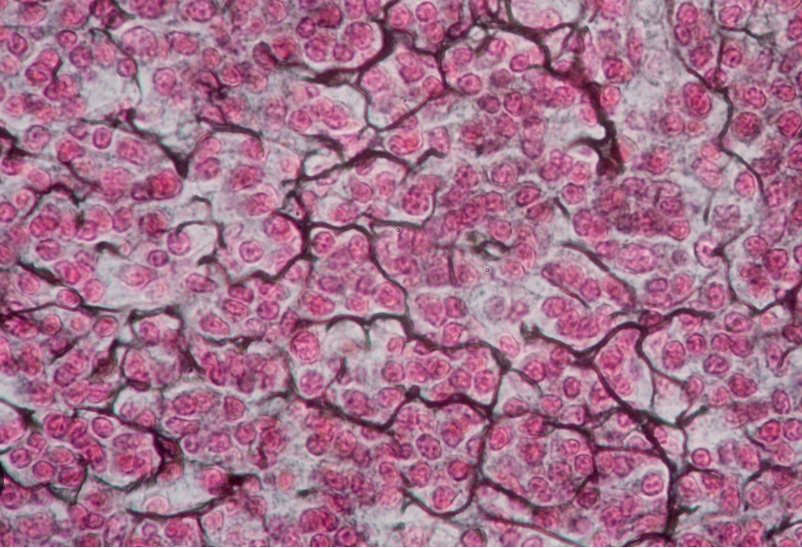
Reticular Connective Tissue
Location: Liver
Function: Provides supporting framework
-
Reticular Connective Tissue
Loose fibers = open framework
See many cells called fibroblasts
Webby branches are reticular fibers w/ many cells & open framework
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Location: Tendon
Function: Conducts pull of muscles
-
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Dense fibers = NO open framework
LOT of collagen fibers densely packed in, adjacent to each other
(Tendon - connective tissue connecting muscle to bone)
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Location: Deep dermis
Function: Provides strength to resist forces applied from many directions
-
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Dense fibers = NO open framework
LOT of collagen fibers going in different directions — which allows your skin to take forces and pressures in different directions
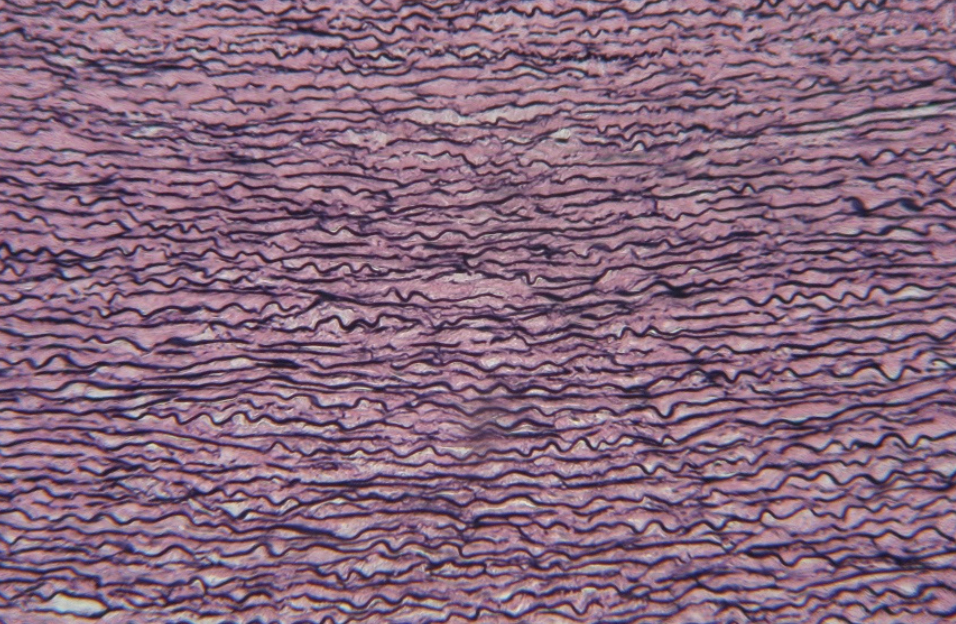
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Elastic Connective Tissue
Location: Between vertebrae of the spinal column
Function: Stabilizes position of vertebrae
-
Elastic Connective Tissue
Dense fibers = NO open framework
Fibers appear in bundles
Contains more elastic fibers than collagen fibers
Elastic fibers are thinner than collagen fibers
Elastic fibers stain darker and are wavy like an elastic band
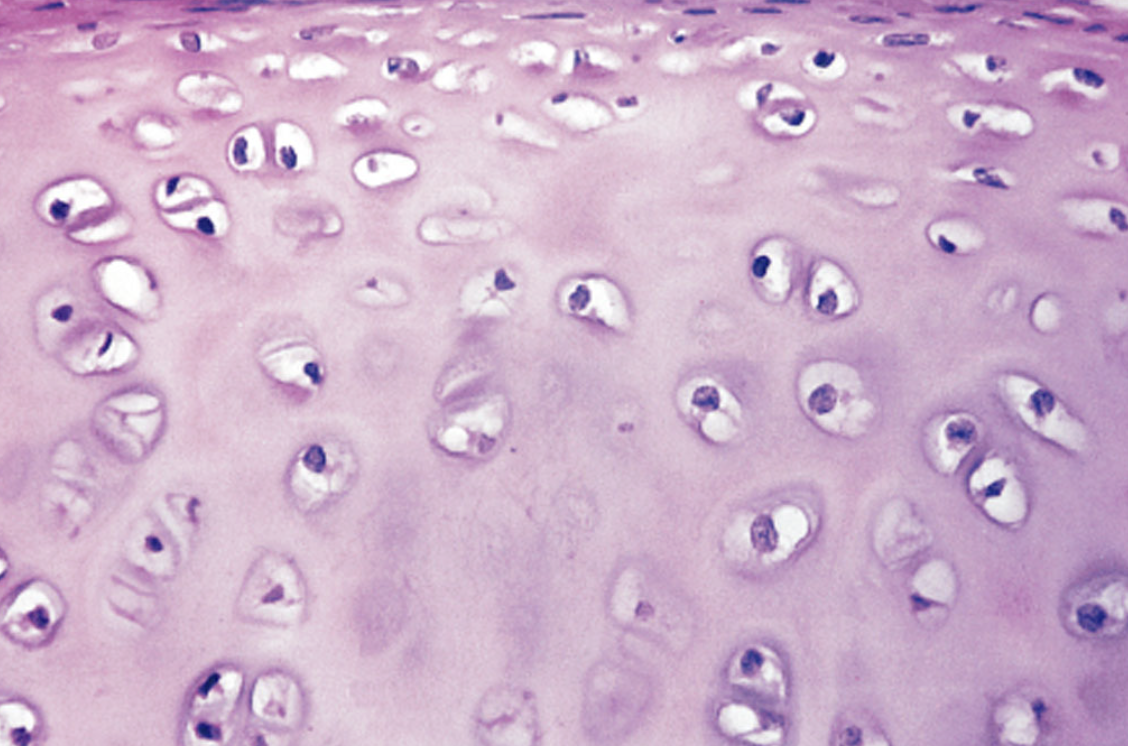
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue
Location: Between bones at the joints
Function: Flexible support
-
Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue
Matrix: looks hazy, glassy
Chondrocytes in lacunae
Nuclei = chondrocytes
Lacuna = white space looking “halo”
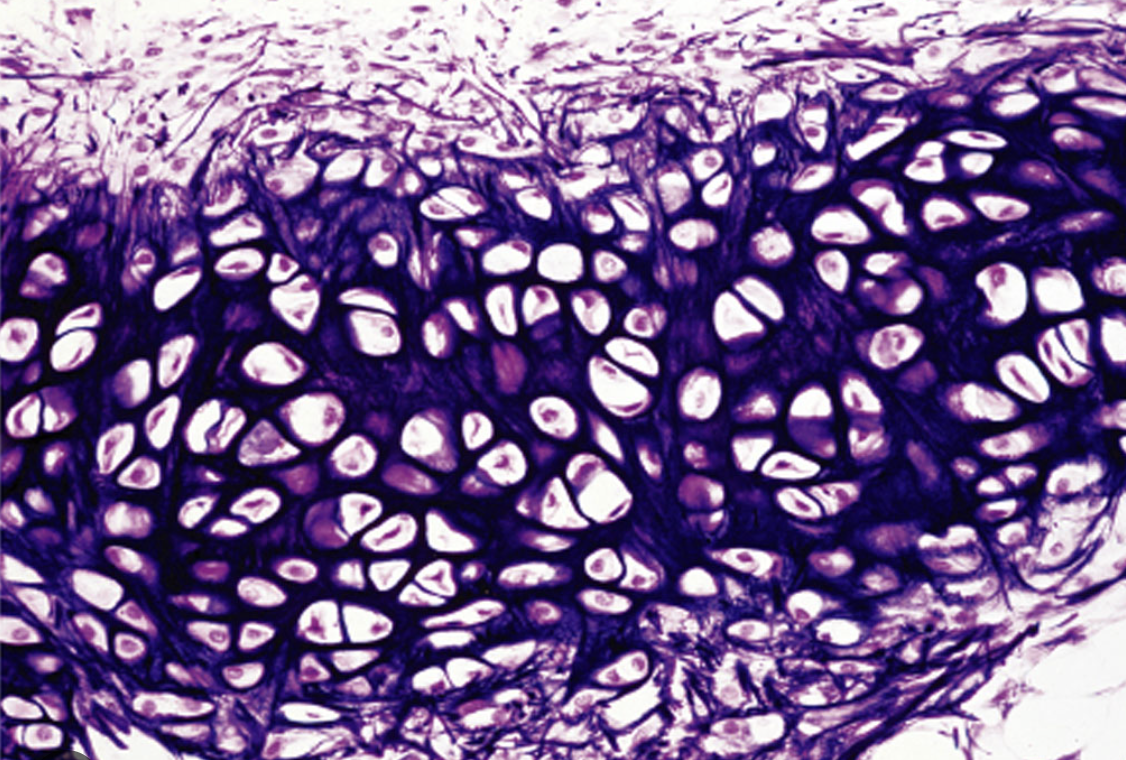
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Elastic Cartilage Connective Tissue
Location: Auricle of the ear
Function: Maintains shape but allows for great flexibility
-
Elastic Cartilage Connective Tissue
Matrix: gel w/ elastic fibers
Elastic fibers stained darker & thinner than collagen
Chondrocytes in lacunae
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue
Location: Knee meniscus
Function: Resists compression (strongest of all cartilage types)
You see fibrocartilage in areas w/ high stress (knee joints) to absorb compressive shocks
-
Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue
Matrix: gel w/ chondrocytes in lacunae lined up in a row
Collagen fibers, unlike hyaline, will stain when looking at fibrocartilage
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
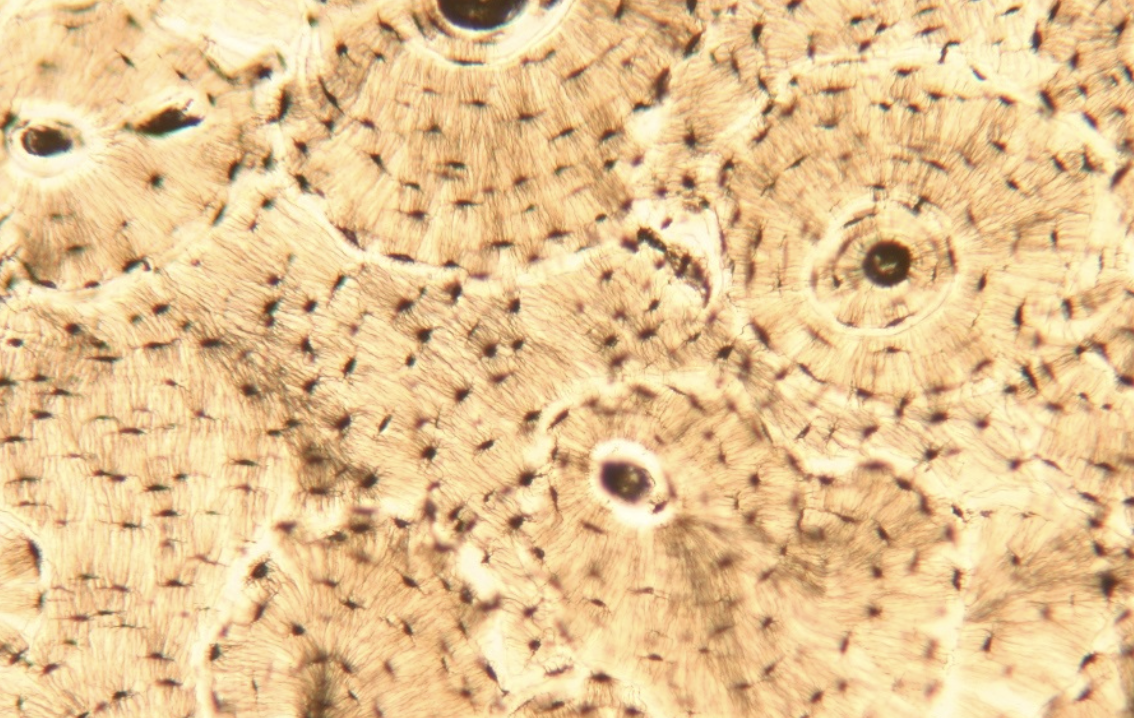
Bone Connective Tissue (Osseous Tissue)
Location: Skeletal system
Function: Support & strength
-
Osseous Tissue (Bone)
Osteons
Lamellae (solid) = matrix
Osteocytes = mature bone cells found within osteons
Has lacunae, calcium salts, central canal, blood vessels
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
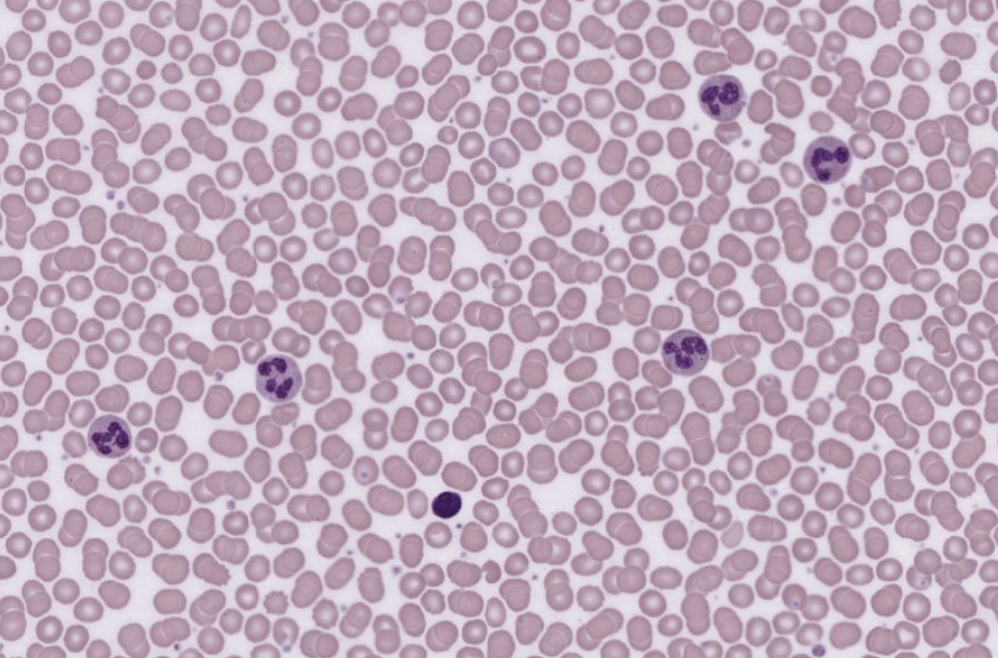
Blood - Fluid Connective Tissue
Location: Blood vessels
Function: Transports substances throughout the body - nutrients, hormones, gases
Blood Tissue
Matrix of Blood = Plasma
RBC’s, WBC’s, Platelets
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
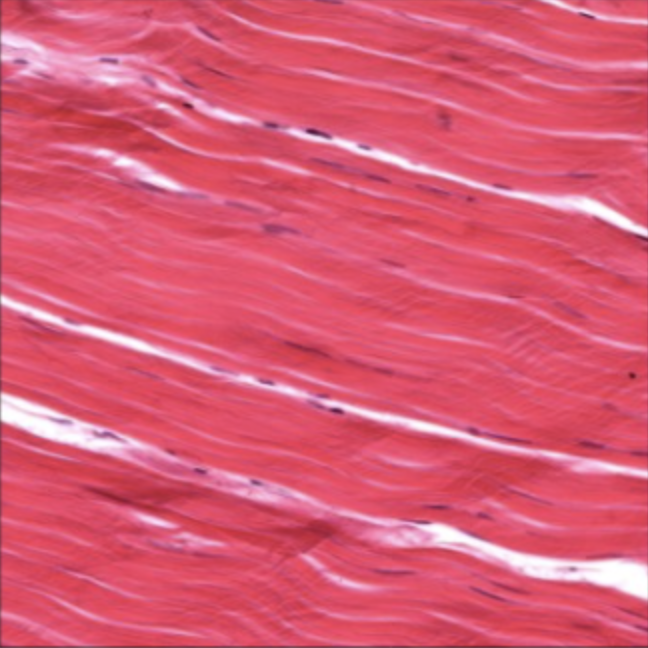
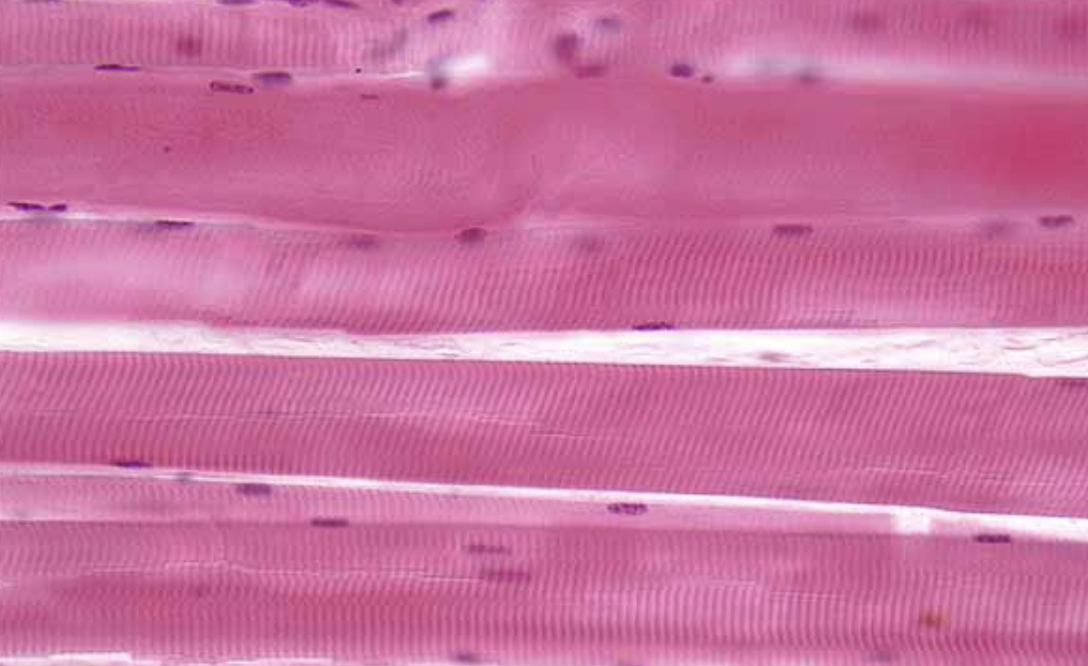
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Location: Combined with connective and neural tissues in skeletal muscle
Function: Moves or stabilizes the position of the skeleton
-
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Has striations, long multi-nucleated cells
Voluntary movement
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
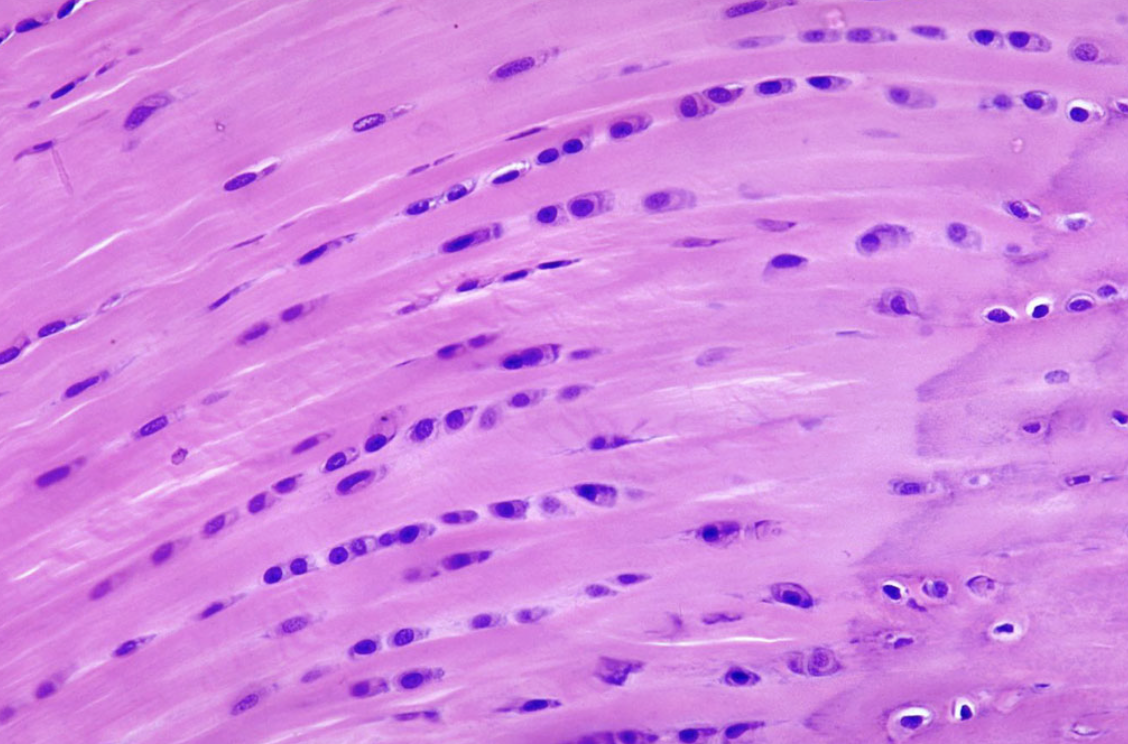
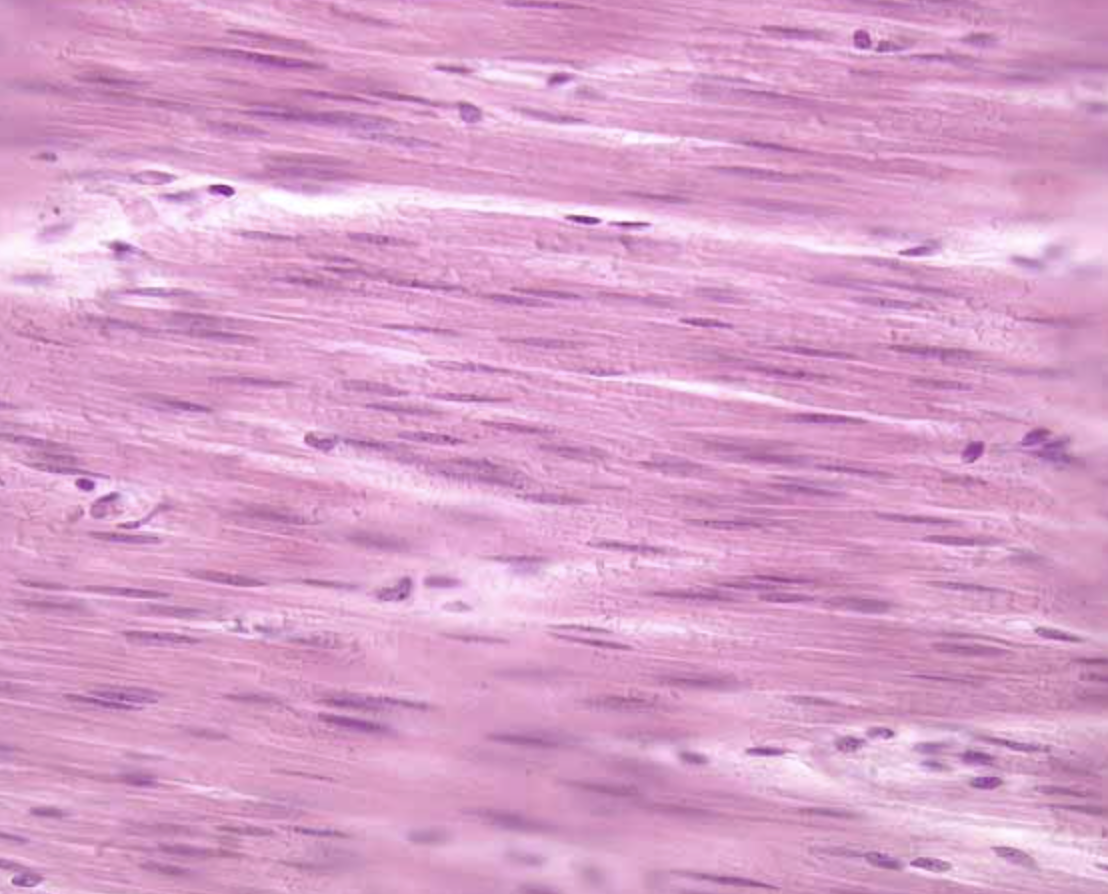
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Location: Walls of blood vessels
Function: Regulates diameter of blood vessels
-
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Nonstriated w/ a single, central nucleus
Cells are short, spindle-shaped
Pay attention to the nuclei
→ Smooth Muscle is most commonly confused w/ dense regular connective and elastic tissue
But on smooth muscle, the nuclei are long and oval-shaped (cigar shaped) and centrally located
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
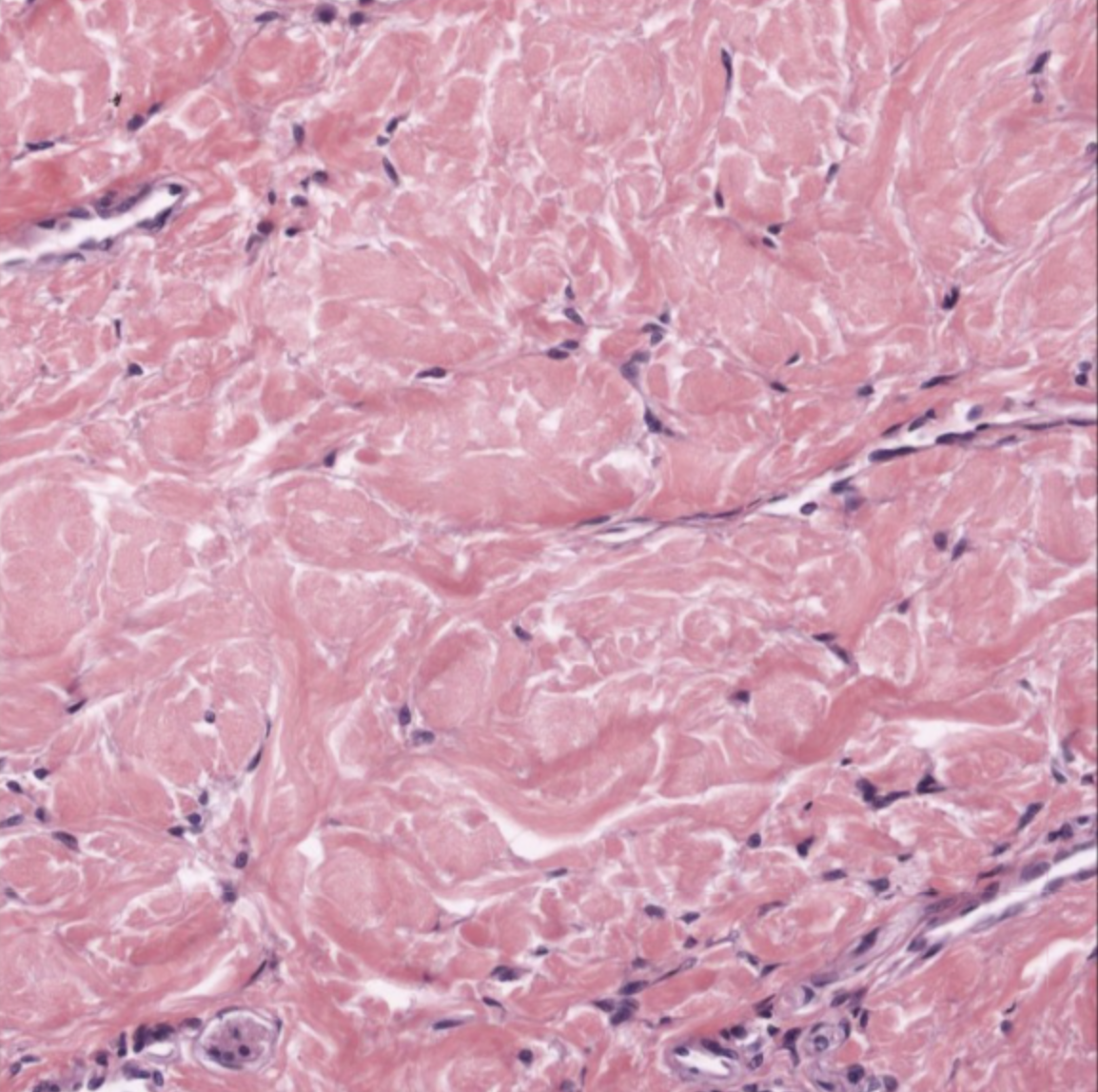
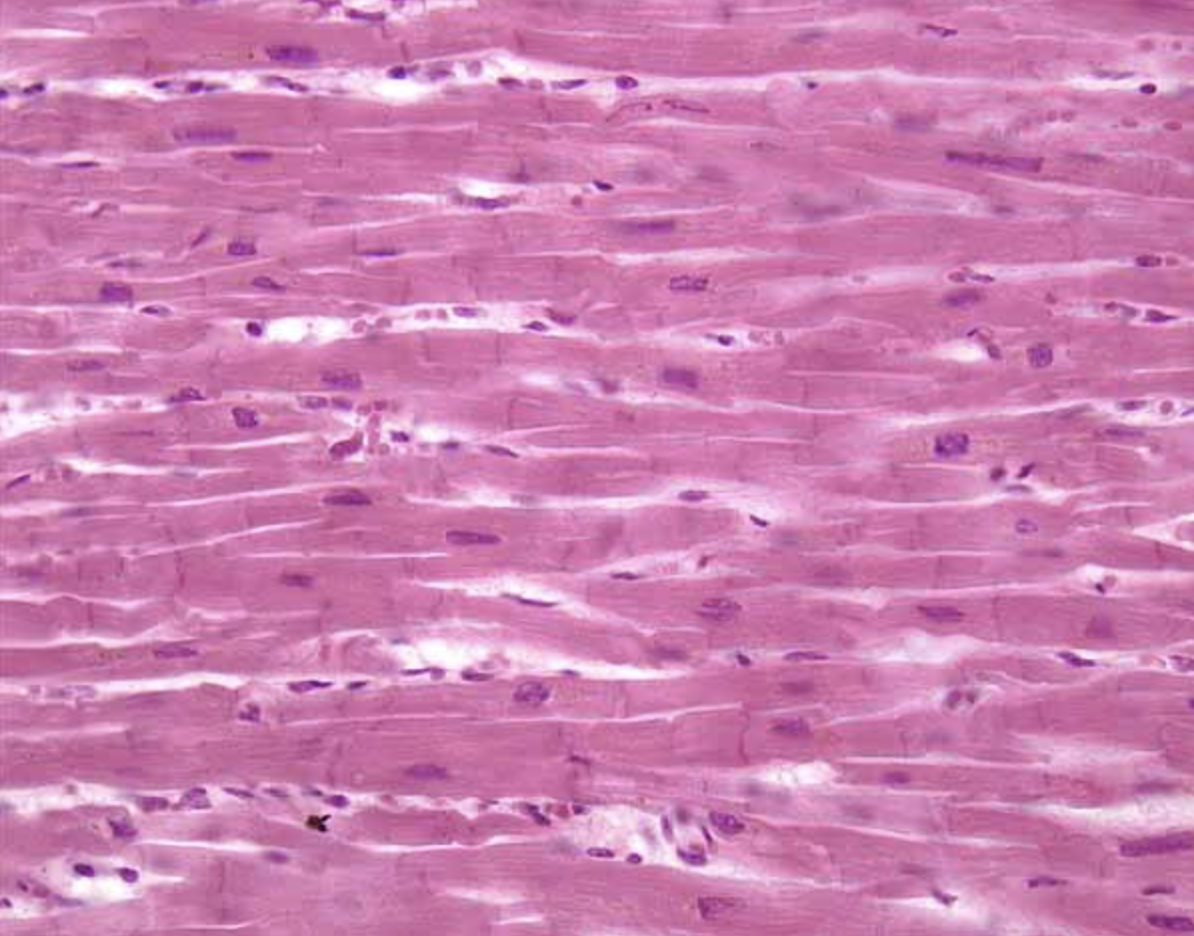
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Location: Heart
Function: Circulates blood
-
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Cells are short, branched, and striated, usually w/ a single nucleus
Cells are interconnected by intercalated discs
On the histology image, pay attention to intercalated discs that are stained darker and found in between cells
What tissue is this?
Where can it be found?
What is its function?
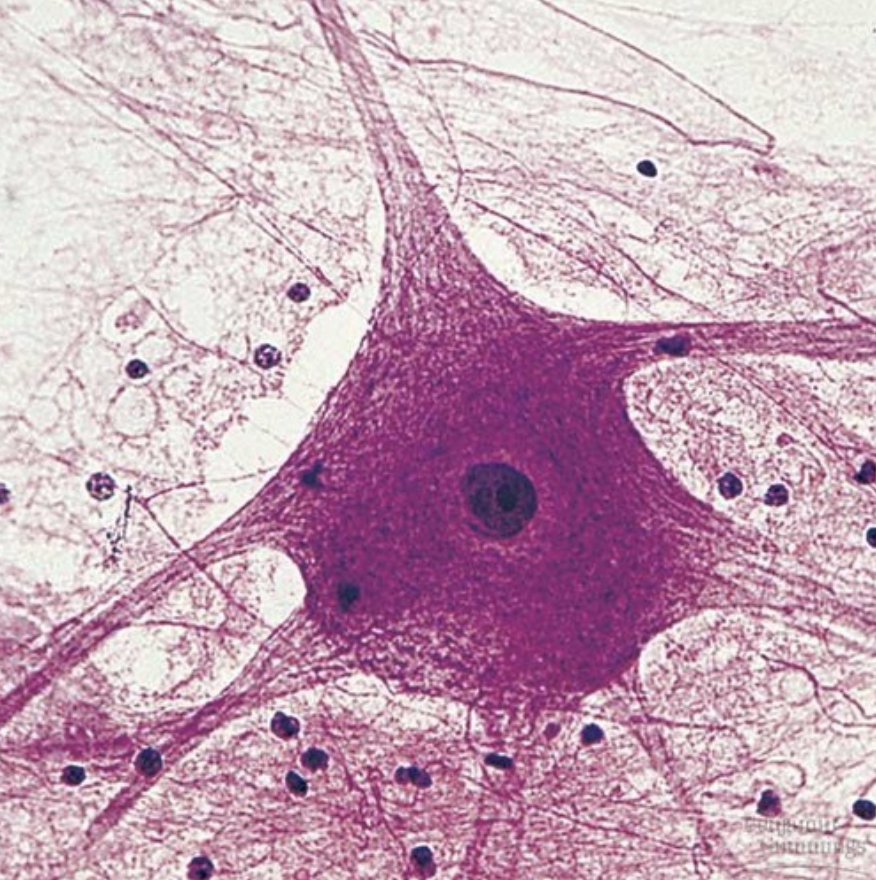
Neural Tissue
Location: Brain & Spinal cord
Function: Conduct electrical signals through the body
Neural Muscle Tissue
Has dendrites, cell body, axon hillock, axon, and axon terminals