Uplearn radioactivity
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
When an unstable nucleus decays, radiation is emitted.
Identify all the different types of radiation that can be emitted by unstable nuclei.
gamma
alpha
beta
Identify the symbol used for beta radiation
β
Identify the type of particles that beta negative radiation, β- emits
electrons
Identify the type of particles that beta positive radiation, β+emits.
positrons
Identify the force that causes beta radiation
Weak nuclear force
Identify all the quantities that are conserved during a beta decay
electric charge
nucleon number
n a β- decay, the structure of the nucleus changes and particles are emitted.
Identify the process that takes place in a β- decay
A neutron converts into a proton, and emits an electron and an electron antineutrino
Identify the correct equation for β- decay
This is represented with the following decay equation:
∘∘ 01n→11p+ 0-1e+ve-
In a β+ decay, the structure of the nucleus changes and particles are emitted. Identify the process that takes place in a β+decay.
a proton converts into a neutron, and emits a positron and an electron neutrino
Identify the correct equation for β+ decay.
∘∘ 11p→10n+ 0+1e+ve
Identify the equation for β- decay in terms of quarks and leptons.
∘∘ d→u+0-1e+ve-
Identify the equation for β+ decay in terms of quarks
s:
∘∘ u→d+0+1e+ve
What do we call an atom that loses or gains one or more electron?
Ion
symbol for an alpha particle?
α
In terms of the atomic mass unit, u,what is the mass of an alpha particle?
The nucleon number is 4, so the mass is approximately 4 u.
What is the difference between a beta minus and a beta positive particle?
Beta minus is an electron, charge -e, beta positive is a positron, charge +e
Which of the following is the symbol for gamma radiation?
γ
What is the mass and charge of a gamma particle?
0
What is the range of alpha particles in air?
Several cm
Which of the following will stop alpha particles?
A sheet of paper
A few mm of aluminium
A few cm of lead
Which of the following will stop beta particles?
A few mm of aluminium
A few cm of lead
Which of the following will stop gamma radiation?
Several m of concrete
Several cm of lead
When alpha emission occurs, what will the change in the proton and nucleon numbers of the parent nucleus be?
proton number= -2
nucleon number= -4
Which of the following equation correctly represents alpha decay?
AzX—>A-4z-2Y+42 α
Beta negative decay occurs when:
Radioactive nuclei have too many neutrons for stability
Which of the following equation correctly represents beta negative decay?
AzX—>Az+1Y+0-1β+νe-
Beta positive decay occurs when:
Radioactive nuclei have too many protons for stability
Which of the following equation correctly represents beta positive decay?
AzX—>Az-1Y+0+1β+νe
Gamma decay occurs when:
A nucleus has too much energy, often after alpha or beta decay
Which of the following is the correct equation for when a gamma photon is emitted from a nucleus
AzX→Az X+γ
exponential decay?
A value decreases by the same factor in equal time intervals
Which of the following notations can be used to represent exponential decay?
e-x
Identify the correct statement about the relationship between the number of decayed particles ΔN and both the time interval Δt and the number of undecayed particles N
ΔN is proportional to both N and Δt.
Identify the correct statement about the relationship between the rate of nuclear decay, ΔN/Δt, and the number of undecayed particles N
ΔN/Δt is proportional to −N
definition of the decay constant, λ
λ is the probability that a given nucleus will decay per unit time
The number of undecayed nuclei remaining in a sample depends on the number originally present, No, the decay constant, λ, and the time, t. The equation connecting these terms is:
N=Noe-λt
Which of the following graphs shows the correct shape for the equation N=Noe−λt
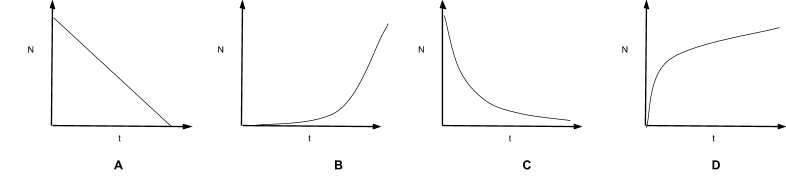
C
The diagram shows the exponential decay curves for three materials. Which one will have the largest decay constant λ?
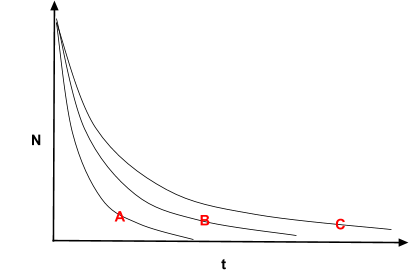
A
definition of the half life of radioactive nuclei
The average time taken for half of a radioactive sample to decay
A radioactive sample has a half life of 15s.
How much time will it take before we expect a sample to decrease to an 8th of its initial value.
3×15=45s
The graph below shows the decay constant for different elements as a function of their half life.
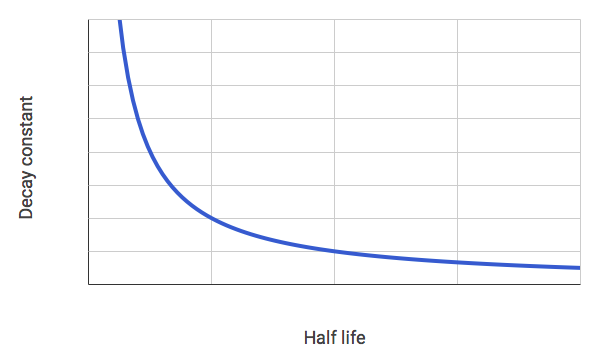
Identify the correct statement about the relationship between the decay constant, λ and the half life, t1/2
The decay constant is inversely proportional to the half life
Identify the option(s) below that correspond to the carbon isotope(s) that can be used in carbon dating
carbon-12
carbon-14
Identify the option below that gives the correct equation for the formation of carbon-14 radioisotope in the upper atmosphere
147N+10n—>146C+11p
How do Carbon-12 and carbon-14 enter all living organisms?
through green plants
Identify the option corresponding to the value that is closest to the half-life of carbon-14
5750 years
One limitation with carbon dating is that the atmospheric ratio of carbon-12:carbon-14 isotopes is not necessarily constant. Identify the all the options below that can alter the carbon-12:carbon-14 atmospheric ratio
Emissions from fossil fuels
Volcano eruptions
Deforestation
Identify the option below that shows the item whose age could be reliably determined using carbon dating
A set of early human remains from roughly 10,000 years ago
Beta negative decay
A neutron decays into a proton, releasing an electron and an electron antineutrino
Beta positive decay
A proton decays into a neutron, releasing a positron and an electron neutrino
Alpha particle
two protons and two neutrons:
5lA1.png)
Random nuclear decay
We can’t predict when any particular nuclei will decay, and each nucleus within a sample has an equal probability of decay per unit time. All nuclear decays are random
Spontaneous nuclear decay
The decay of a particular nucleus is not affected by other nuclei in the sample or by external factors such as pressure or heat. All nuclear decays are spontaneous
Activity
the rate of nuclei decay, measured in becquerels. 1 becquerel is 1 decay per second
Decay constant
λ, is the probability that a nucleus decays per unit time
Carbon-14
Most carbon in the atmosphere is carbon-12, but there is a small amount of carbon-14 created by cosmic rays. Carbon-14 has a half-life of ~5700 years