24-Metabolism of Acylglycerols & Sphingolipids
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What constitutes the majority of lipids in the body?
Acylglycerols
What are the major lipids in the body?
Triacylglycerols
What are the main lipids of cell membranes?
Phospholipids and sphingolipids
Dipalmitoyl Lecithin
Lung surfactant
Where are glycosphingolipids located?
On cell surfaces with oligosaccharide chains facing outward
What must happen to triacylglycerols before further catabolism?
They must be hydrolyzed by a lipase to fatty acids and glycerol
Where does much of the hydrolysis (lipolysis) of triacylglycerols occur?
In adipose tissue
How are free fatty acids transported in the plasma?
They combine with serum albumin
Free fatty acids are uptake into tissues for
catabolism.
What determines the utilization of glycerol in tissues?
The presence of glycerol kinase
What is the common precursor of triacylglycerols and many phosphoglycerols?
Phosphatidate
What is the primary source of glycerol-3-phosphate?
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate, formed by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Formation of sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate
a. From Glycerol
Enzyme:
Reaction:
a. From Glycerol
Enzyme: Glycerol kinase
Reaction: Glycerol + ATP → sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate + ADP
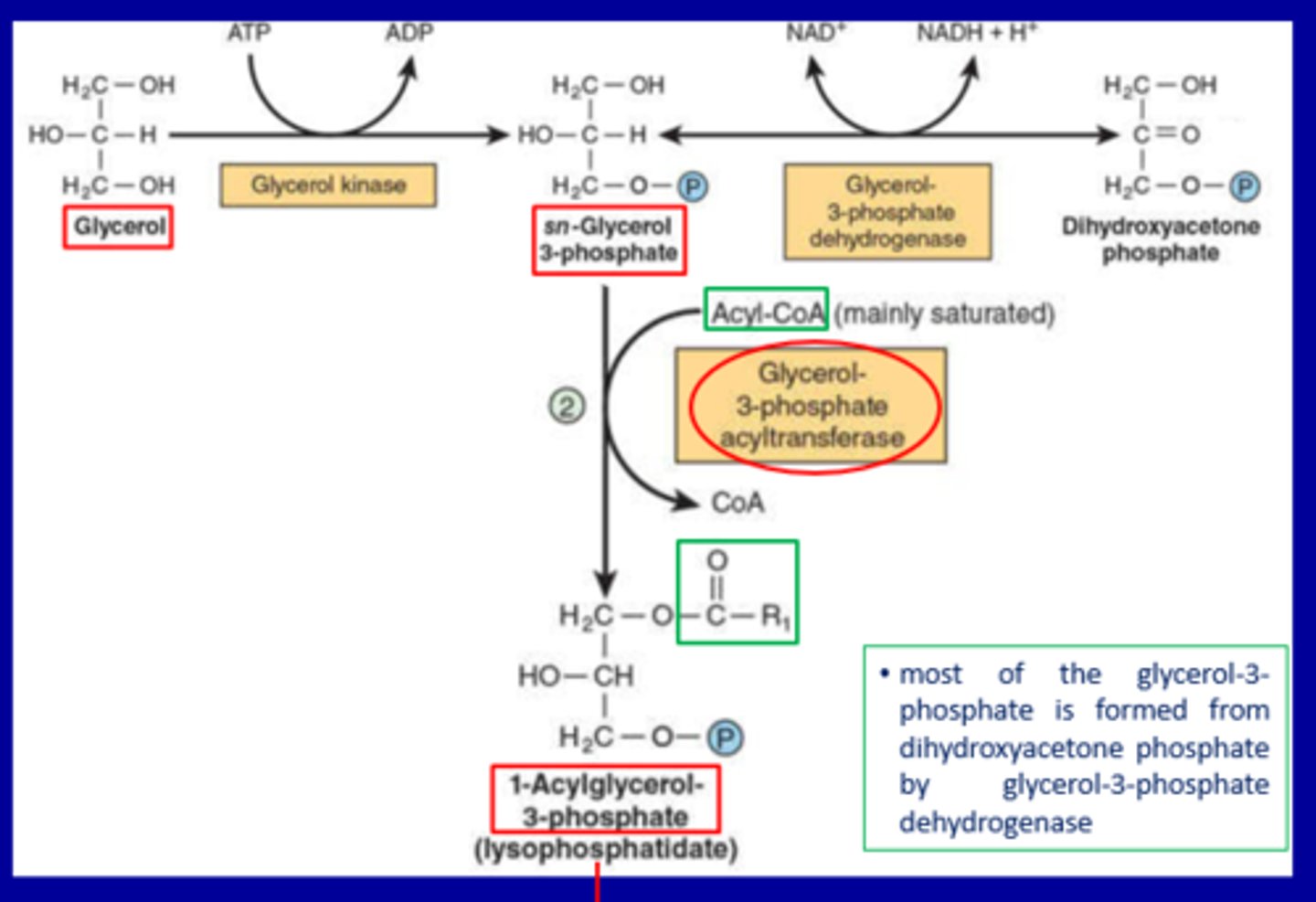
b. From Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate (DHAP)
Enzyme:
Reaction:
Note: This is the primary source of glycerol-3-phosphate (as highlighted in the green box)
Enzyme: Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Reaction:DHAP + NADH + H⁺ → sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate + NAD⁺
2. Formation of Lysophosphatidate
Reactants:
Enzyme:
Product:
Reactants: sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate + Acyl-CoA (mainly saturated)
Enzyme: Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase
Product: 1-Acylglycerol-3-phosphate (lysophosphatidate)
Name one of the acyltransferase enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of triacylglycerols.
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase
Three acyltransferase enzymes to add fatty acid to glycerol:
•glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase
•1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase
•Diacylglycerol acyltransferase
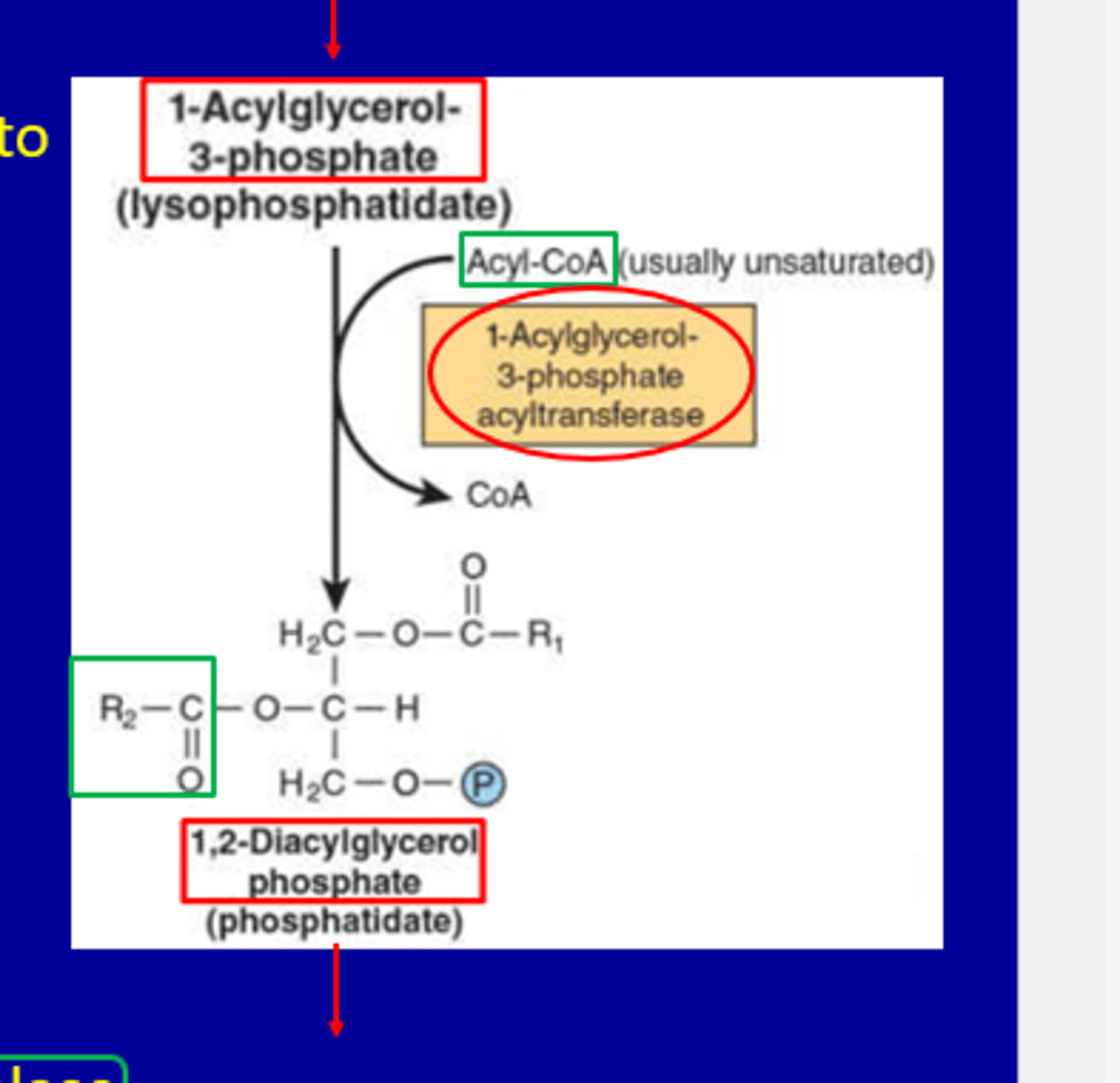
Step: Formation of Phosphatidate
Reactants
Enzyme
Reaction
Reactants
1-Acylglycerol-3-phosphate (lysophosphatidate)
Acyl-CoA
Enzyme
1-Acylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase
Reaction
Adds a second fatty acid (R₂) to the glycerol backbone
What is the role of monoacylglycerol acyltransferase?
It is involved in the monoacylglycerol pathway
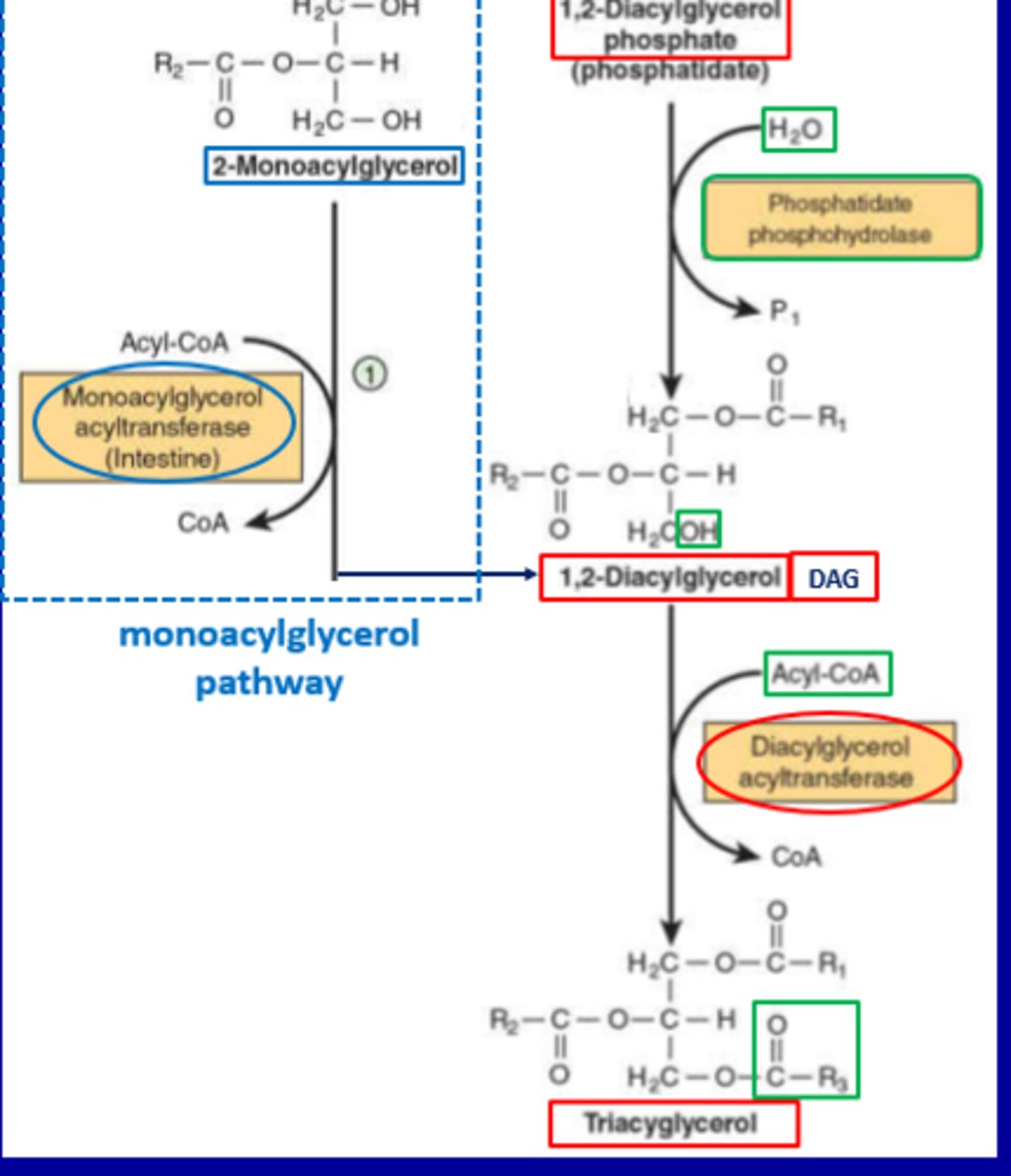
Monoacylglycerol pathway:
1. Formation of Diacylglycerol (DAG) from Monoacylglycerol
Substrate:
Enzyme:
Reactants:
Product:
Substrate: 2-Monoacylglycerol
Enzyme: Monoacylglycerol acyltransferase (active in the intestine)
Reactants: Acyl-CoA + CoA
Product: 1,2-Diacylglycerol (DAG)
Monoacylglycerol pathway:
2. Alternative DAG Formation from Phosphatidate
Substrate:
Enzyme:
Reactants:
Product:
Phosphatidate
Substrate: 1,2-Diacylglycerol phosphate (phosphatidate)
Enzyme: Phosphatidate phosphohydrolase
Reactants: H₂O → releases Pᵢ (inorganic phosphate)
Product: 1,2-Diacylglycerol (DAG)
Monoacylglycerol pathway:
3. Final Step: Triacylglycerol Synthesis
Substrate:
Enzyme:
Reactants:
Product:
Substrate: 1,2-Diacylglycerol
Enzyme: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase
Reactants: Acyl-CoA + CoA
Product: Triacylglycerol (TAG)
What are the two main phospholipids synthesized?
Phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine
Biosynthesis of phospholipids:
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) Pathway
Step 1: Ethanolamine Activation
Ethanolamine + ATP → Phosphoethanolamine Enzyme:
Ethanolamine kinase (EK)
Biosynthesis of phospholipids:
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) Pathway
Step 2: CDP-Ethanolamine Formation
Phosphoethanolamine + CTP → CDP-Ethanolamine + PPi
Enzyme:
CTP:phosphoethanolamine cytidylyltransferase (ECT)
Biosynthesis of phospholipids:
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) Pathway
Step 3: PE Synthesis
CDP-Ethanolamine + Diacylglycerol (DAG) → Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)
Enzyme:
Ethanolamine phosphotransferase (EPT)
Biosynthesis of phospholipids:
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) Pathway
Optional Step: Conversion to PC
Phosphatidylethanolamine + 3CH₃ → Phosphatidylcholine
Enzyme:
PE N-methyltransferase (PEMT)
2. Phosphatidylcholine (PC) Pathway
Step 1: Choline Activation
Choline + ATP → Phosphocholine
Enzyme:
Choline kinase
Step 2: CDP-Choline Formation
Phosphocholine + CTP → CDP-Choline + PPi Enzyme:
CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase
Step 3: PC Synthesis
CDP-Choline + DAG →
Phosphatidylcholine
Additional Note
DAG can also be converted to ______ depending on cellular needs.
triacylglycerol
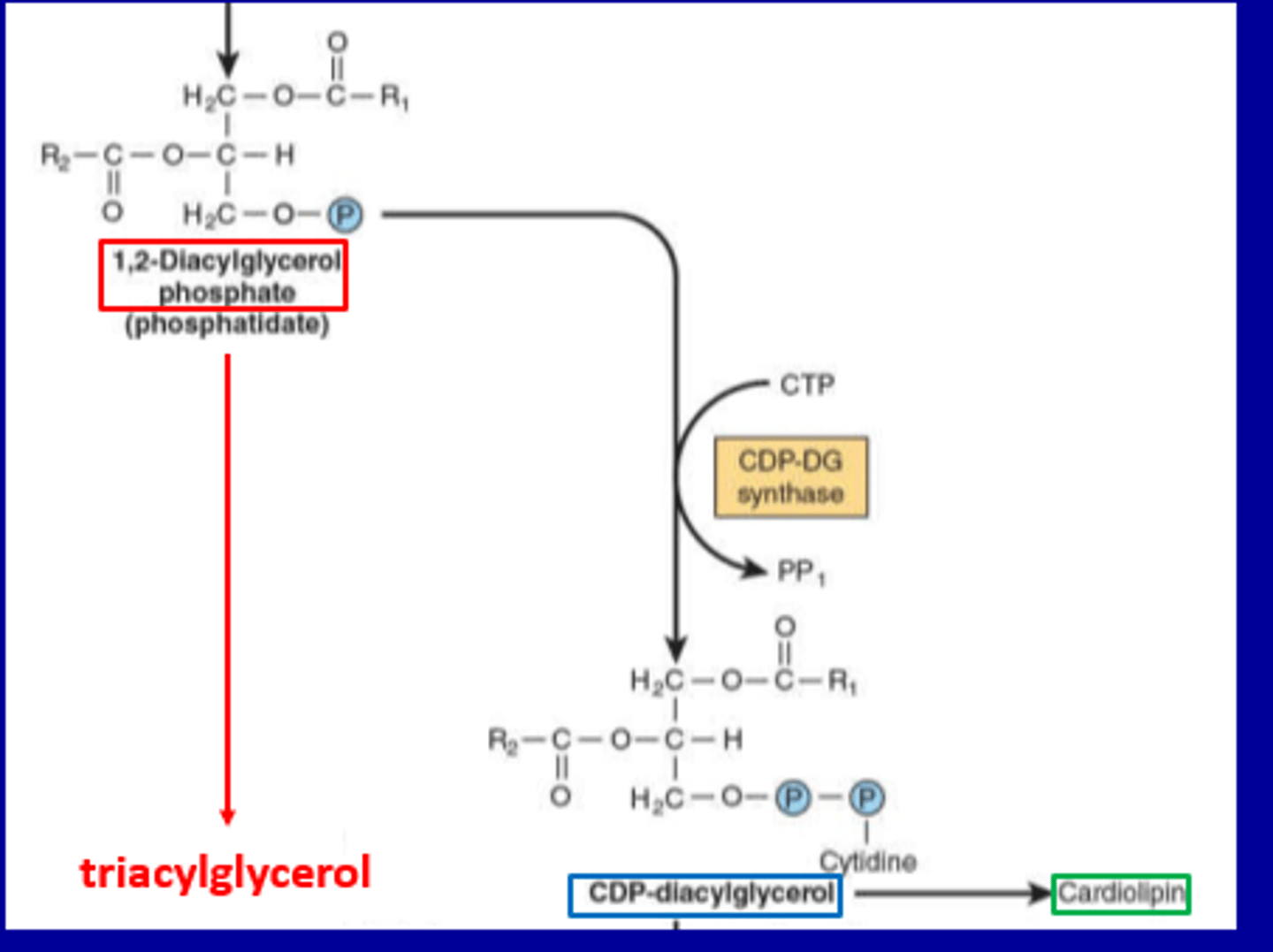
•Synthesis of cardiolipin:
Triacylglycerol (TAG) Synthesis
Phosphatidate is converted to Diacylglycerol (DAG) via phosphatidate phosphohydrolase
DAG then reacts with Acyl-CoA to form Triacylglycerol Enzyme: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase
2. Phospholipid Synthesis via CDP-Diacylglycerol
Phosphatidate reacts with CTP to form CDP-Diacylglycerol
Enzyme: CDP-diacylglycerol synthase
CDP-Diacylglycerol is a precursor for: Cardiolipin (important for mitochondrial membranes)
Other phospholipids like phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylglycerol
(3) Biosynthesis of glycerol ether phospholipids:
Section 1: Formation of Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate
Step 1: Glycerol → sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate
Enzyme: Glycerol kinase
Reaction:Glycerol + ATP → sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate + ADP
Step 2: sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate → Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Enzyme: Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Reaction:NAD⁺ → NADH + H⁺
Section 2: Ether Lipid Pathway
Step 3: Dihydroxyacetone phosphate → 1-Acyldihydroxyacetone phosphate
Enzyme: Acyltransferase
Step 4: 1-Acyldihydroxyacetone phosphate → 1-Alkyldihydroxyacetone phosphate
Enzyme: Synthase
Step 5: 1-Alkyldihydroxyacetone phosphate → 1-Alkylglycerol 3-phosphate
Enzyme: Reductase
Cofactor: NADPH → NADP⁺
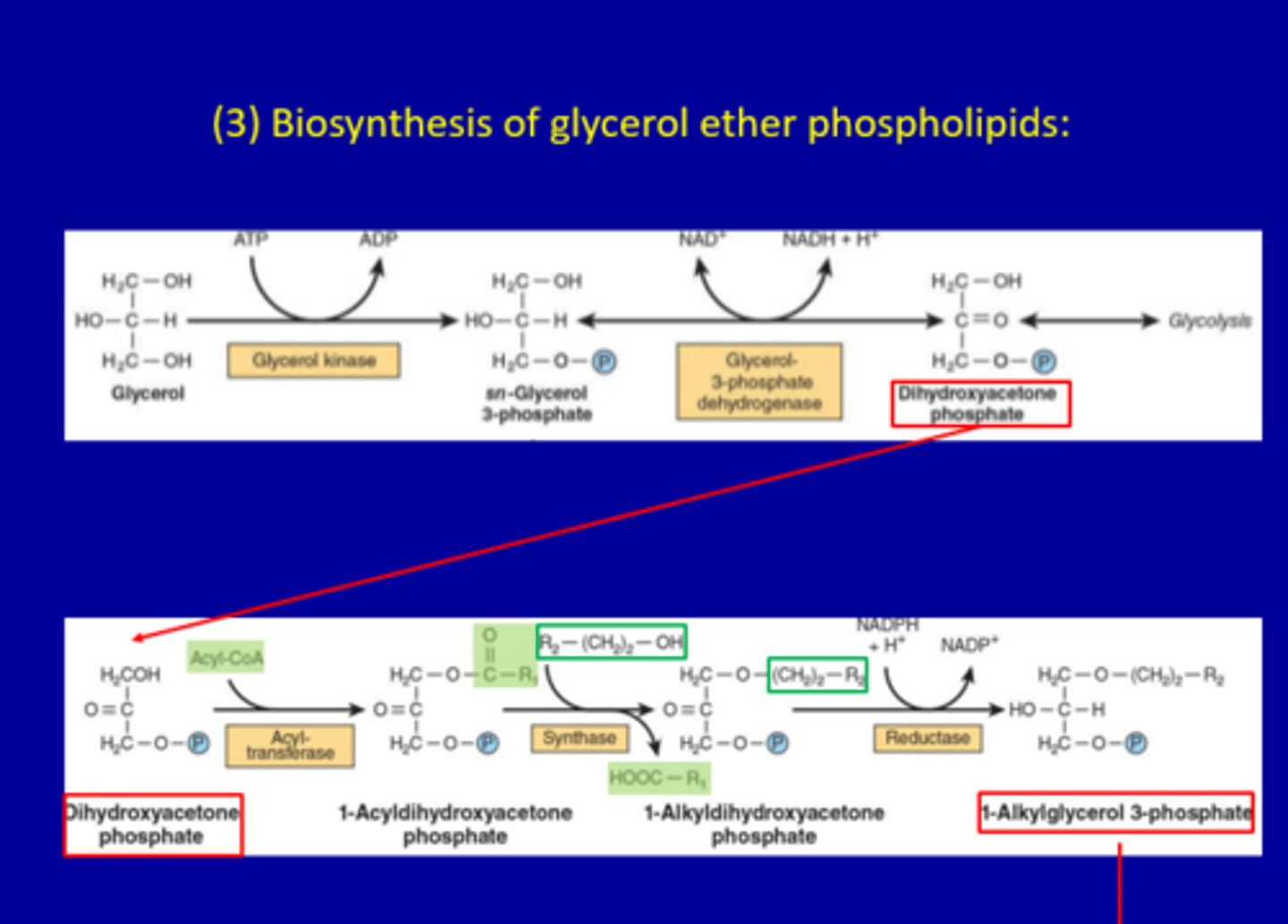
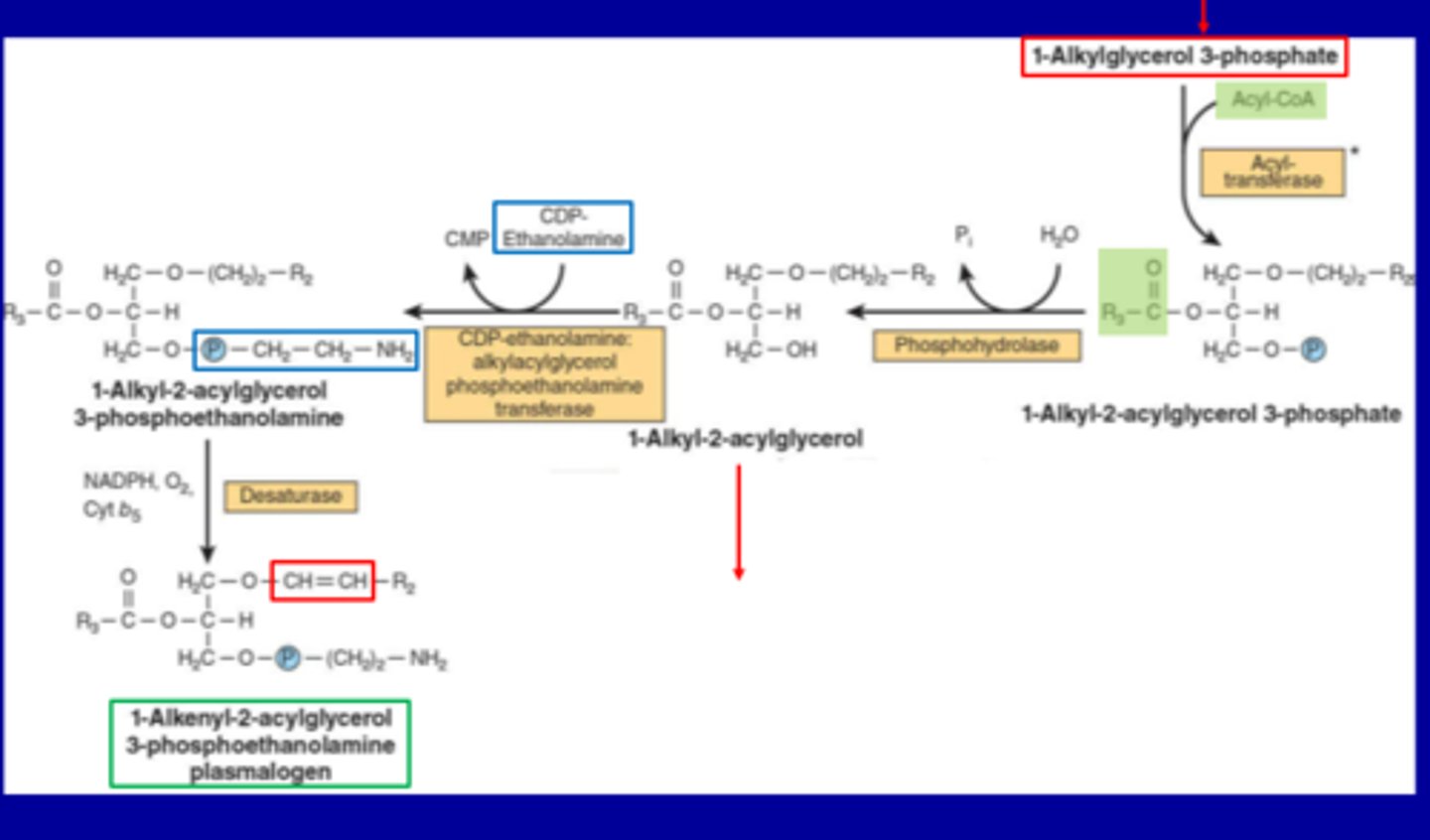
•Synthesis of plasmalogens:
1. Formation of 1-Alkyl-2-acylglycerol
Starting compound: 1-Alkyl-2-acylglycerol 3-phosphate
Enzyme: Phosphohydrolase
Reaction: Removal of phosphate group → 1-Alkyl-2-acylglycerol
2. Addition of Phosphoethanolamine
Reactants: 1-Alkyl-2-acylglycerol CDP-Ethanolamine
Enzyme: CDP-ethanolamine:alkylacylglycerol phosphoethanolamine transferase
Product: 1-Alkyl-2-acylglycerol 3-phosphoethanolamine
3. Desaturation to Form Plasmalogen
Enzyme: Desaturase
Cofactors: NADPH, O₂, Cytochrome b₅
Reaction: Introduces a double bond at the sn-1 ether linkage
Product: 1-Alkenyl-2-acylglycerol 3-phosphoethanolamine plasmalogen
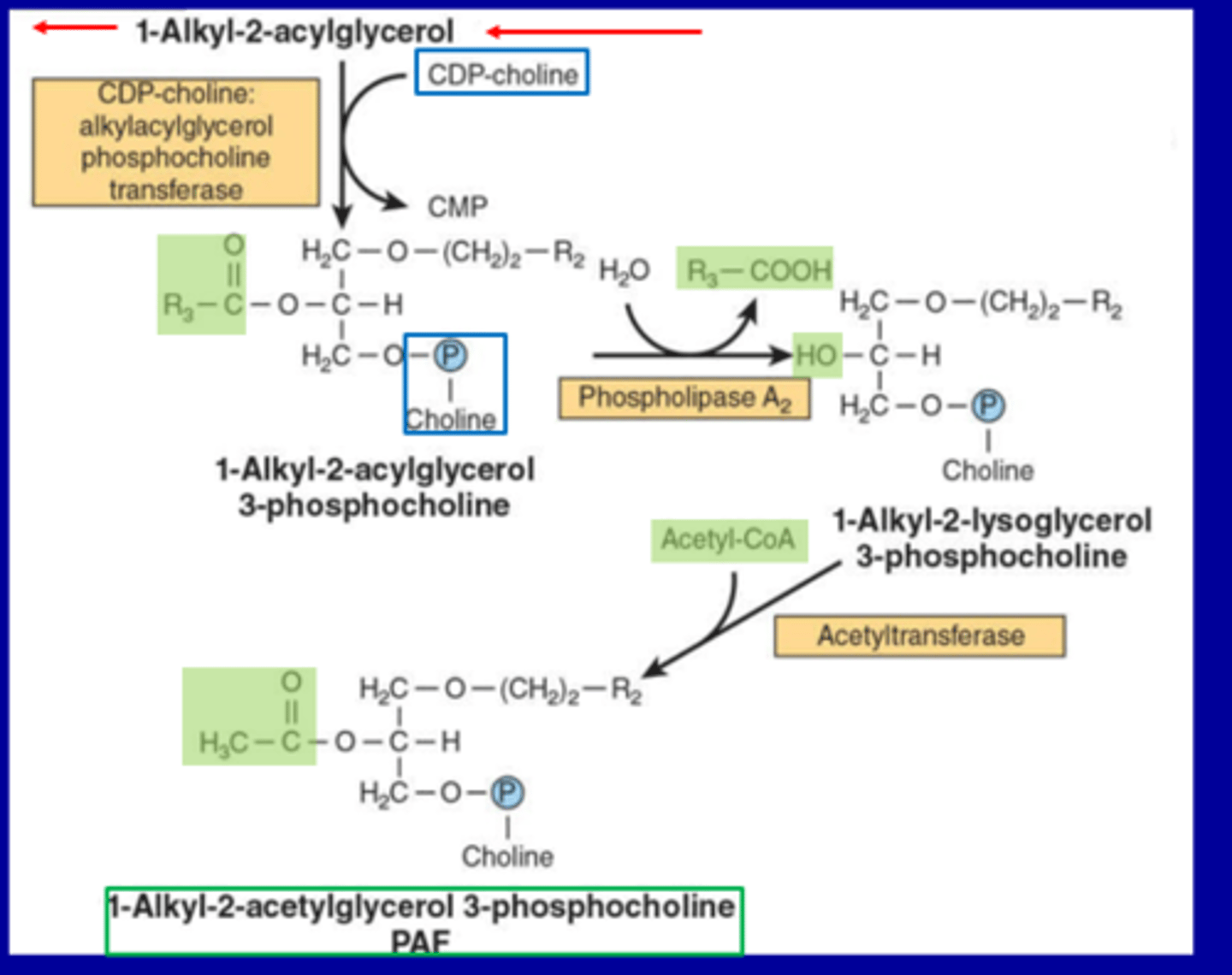
•Synthesis of platelet-activating factor (PAF):
Key Molecules & Reactions
Starting Molecule:
1-Alkyl-2-acylglycerol Structure: Glycerol backbone with an alkyl group at position 1 and an acyl group at position 2.
Step 1: Formation of PAF Precursor
Enzyme: CDP-choline: alkylacylglycerol phosphocholine transferase
Reactants: CDP-choline + 1-Alkyl-2-acylglycerol
Products: 1-Alkyl-2-acylglycerol 3-phosphocholine + CMP
Step 2: Hydrolysis
Enzyme: Phospholipase A₂
Reactants: 1-Alkyl-2-acylglycerol 3-phosphocholine + H₂O
Products: 1-Alkyl-2-lysoglycerol 3-phosphocholine + R₃-COOH
Step 3: Acetylation
Enzyme: Acetyltransferase
Reactants: Acetyl-CoA + 1-Alkyl-2-lysoglycerol 3-phosphocholine
Products: PAF (1-Alkyl-2-acetylglycerol 3-phosphocholine)
Final Product
Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF): A bioactive phospholipid with roles in: Platelet aggregation Inflammation Allergic responses
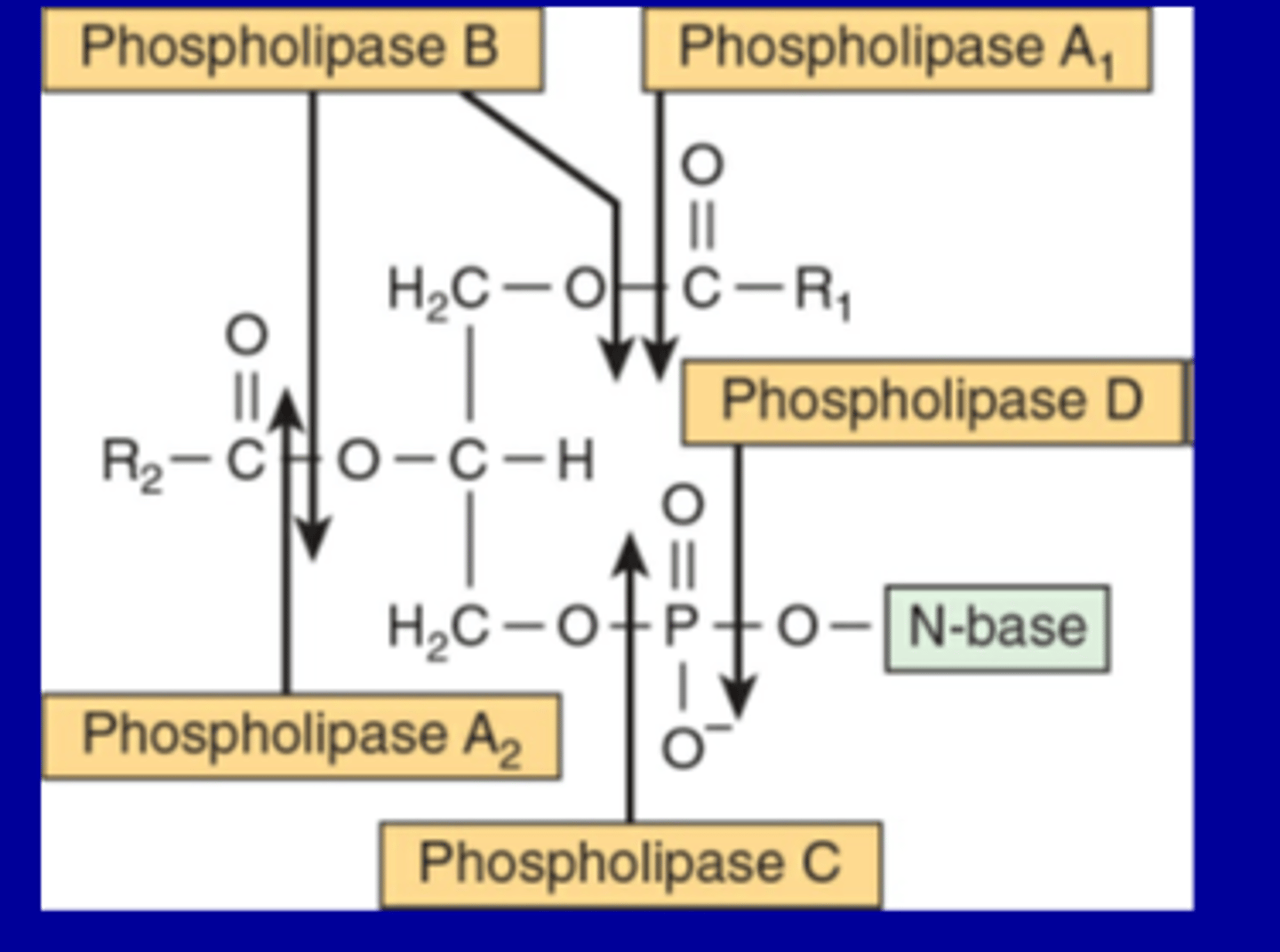
3. Metabolism of phospholipids:
Phospholipase A₁ (PLA₁):
Cleaves the ester bond at the first carbon of glycerol.
Releases the fatty acid at position 1.
Phospholipase A₂ (PLA₂):
Cleaves the ester bond at the second carbon of glycerol.
Releases the fatty acid at position 2.
Important in inflammatory responses (e.g., arachidonic acid release).
Phospholipase B (PLB):
Can act on both positions 1 and 2, removing both fatty acids.
Phospholipase C (PLC):
Cleaves before the phosphate group, releasing diacylglycerol (DAG) and the phosphorylated head group.
Plays a role in signal transduction.
Phospholipase D (PLD):
Cleaves after the phosphate group, releasing phosphatidic acid and the free head group.
Also involved in cell signaling.
4. Sphingolipids synthesis:
•all sphingolipids are formed from
ceramide
From what is ceramide synthesized?
From the amino acid serine in the endoplasmic reticulum
What is ceramide's role in the cell?
It is an important signaling molecule regulating apoptosis, the cell cycle, and cell differentiation
Where is sphingomyelin mainly synthesized?
In the Golgi apparatus
What are gangliosides synthesized from?
Ceramide, activated sugars (e.g., UDPGlc and UDPGal), and a sialic acid (e.g., N-acetylneuraminic acid)
How does the metabolism of phospholipids vary?
Each portion of the phospholipid turns over at a different rate and is attacked by different phospholipases
Synthesis of sphingomyelins:
mainly in the
Golgi apparatus
1. Sphingomyelin Synthesis
Reactants:
Enzyme:
Products:
Reactants: Ceramide
Phosphatidylcholine
Enzyme: Sphingomyelin synthase
Products:
Sphingomyelin (a major component of cell membranes, especially in the myelin sheath)
Diacylglycerol (DAG)
This reaction transfers the phosphocholine head group from phosphatidylcholine to ceramide.
2. Glycosphingolipid Synthesis
Reactants:
Enzyme:
Products:
Reactants:
Ceramide
UDP-Galactose (UDP-Gal)
Enzyme: Galactosyltransferase
Products:
Galactosylceramide (a type of cerebroside)
UDP
Synthesis of gangliosides:
______
•activated sugars
•a sialic acid
Ceramide