9.8.25 Eicosanoids (Gardner)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
eicosanoids
chemically diverse
act as autocoids (signaling molecules that function in an autocrine or paracrine fashion)
arachidonic acid derived
act in autocrine or paracrine fashion; function through G protein linked receptors
numerous subtypes
prostaglandins → includes prostacyclin and thromboxane
leukotrienes
lipoxins
epoxyeicosatrienoic acids
hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids
hepoxilins
biochemical effects
gluconeogenesis → creates glucose from non-carb precursors
lipolysis → breakdown of triglycerides into FFA
glycogenolysis → breakdown of stored glycogen to glucose
slowed heart rate
increase/decrease neuronal electrical activity
vision
increase/decrease muscle contraction
increase/decrease blood psi
arachidonic acid metabolism
synthesized from linoleic acid
arachidonic acid → esterfied to membrane phospholipids
e.g. phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanoliamine
predominantly released by phospholipase A2 (rate determining step)
released from membrane phospholipids thru ^
secretory or cytosolic (2 forms of PLA2)
stimulated by cytokines and growth factors
inhibited by lipocortins
arachidonic acid and esterification to membrane phospholipids pathway
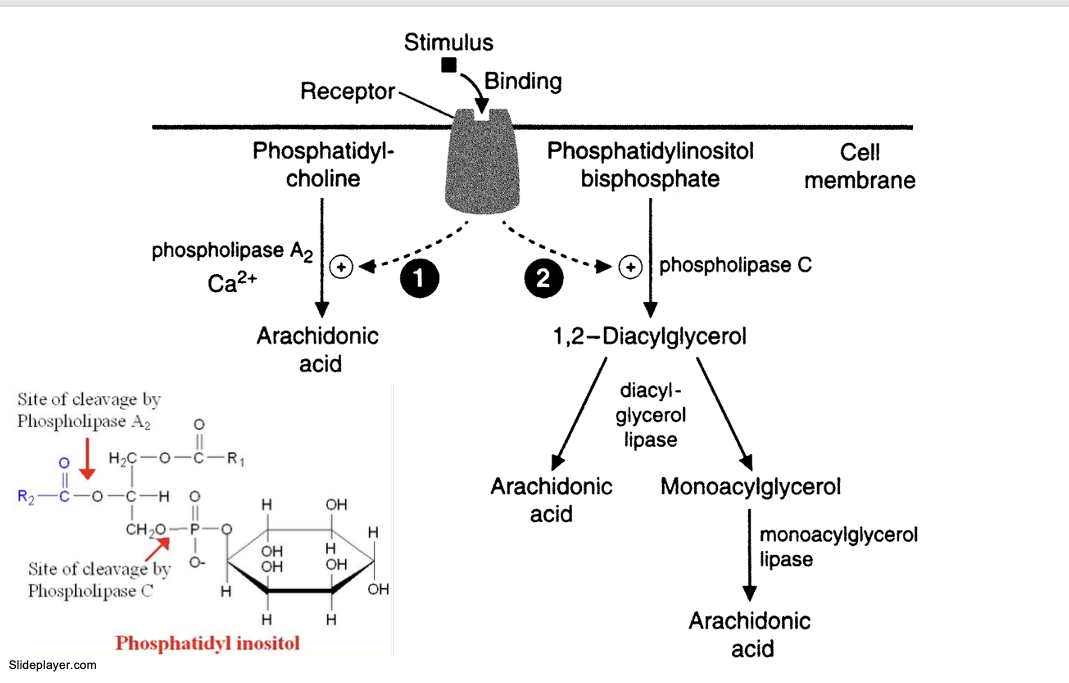
stimulus binds to receptor
PLA2 pathway
PLA2 acts on phosphatidylcholine and frees arachidonic acid
PLC pathway
PLC hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) into 2 pathways
PLC → 1,2-diacylglycerol
→ arachidonic acid thru diacylglycerol lipase
→ monoacylglycerol thru diacylglycerol lipase → arachidonic acid thru monozcylglycerol lipase
eicosanoid biosynthesis + receptors
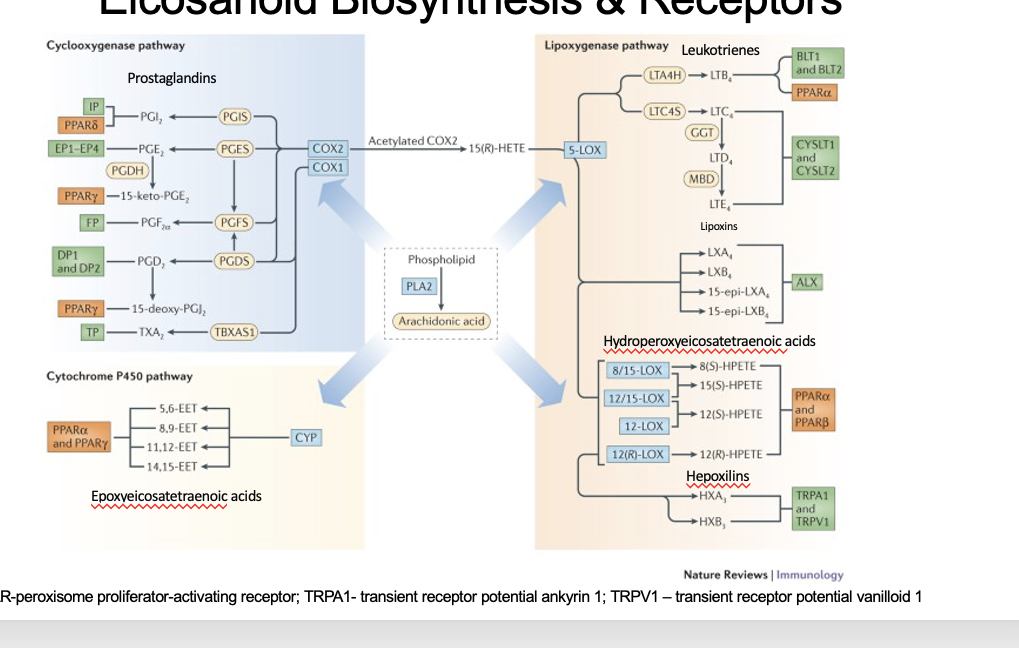
arachidonic acid is cleaved from phospholipid thru PLA2
arachidonic acid goes through 3 different pathways
cyclooxygenase pathway
enzymes = COX2/COX1 → prostaglandins
cytochrome P450 pathway
enzymes = CYP → epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid
lipooxygenase pathway
enzymes
5-LOX → leukotrienes
8/15 LOX; 12/15 LOX; 12 LOX; 12(R)-LOX → hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids
prostanoids
prostaglandins, prostacycline and thromboxanes
modulators of adenylyl cyclase activity (controls platelet aggregation and inhibit the effect of anti-diuretic hormone)
plays a role in inflammatory responses, pain, CV and renal functions, pregnancy (F type prostaglandins → labor)
NSAIDs or w3 PUFAs inhibit synthesis
synthesized via cyclo-oxygenase pathways
COX1
COX2
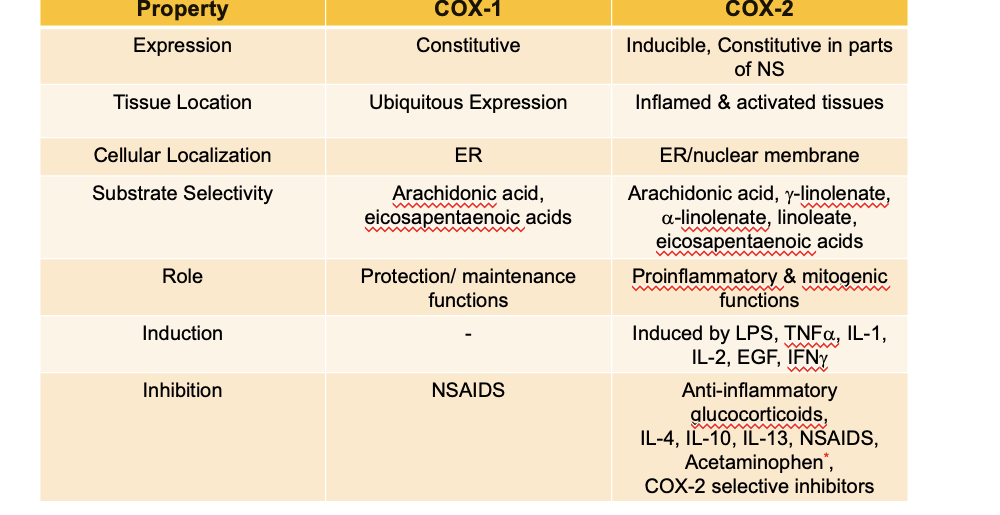
comparison of COX enzymes
expression
COX1 → constitutive (continually expressed under normal conditions)
COX2 → inducible, constitutive in parts of NS
tissue location
COX1 → ubiquitous expression (everywhere)
COX2 → inflamed + activated tissues
cellular localization
COX1 → ER
COX2 → ER/nuclear membrane
substrate selectivity
COX1 → arachidonic acid, eicosapentaenoic acids
COX2 → arachidonic acid, g-linolenate,a-linolenate-linoleate, eicosapentaenoic acid
role
COX1 → protection/maintenance functions
COX2 → pro-inflammatory + mitogenic functions (undergo mitosis)
induction
COX1 → N/A
COX2 → induced by LPS, TNFa, IL-1, IL-2, EGF, IFNg
inhibition
COX1 → NSAIDs
COX2 → anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids, IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, NSAIDS, acetaminophen, COX-2 selective inhibitors
acetaminophen does NOT directly inhibit COX-2. its a co-substrate so it shunts away some of the ability of COX2 to make eicosanoids
prostanoid synthesis
arachidonic acid is cleaved from phospholipid by PLA2
arachidonic acid → PGG2
enzyme = COX1 and 2
cyclooxygenase rxn
PGG2 → PGH2
enzyme = COX1 and 2
peroxidase rxn
PGH2 becomes hella prostanoids
→ PGF2α thru PGF synthase
→ PGD2 thru PGD synthase
→ PGE2 thru PGE synthase
→ PGI2 thru prostacyclin synthase
→ TXA2 thru tromboxane synthase
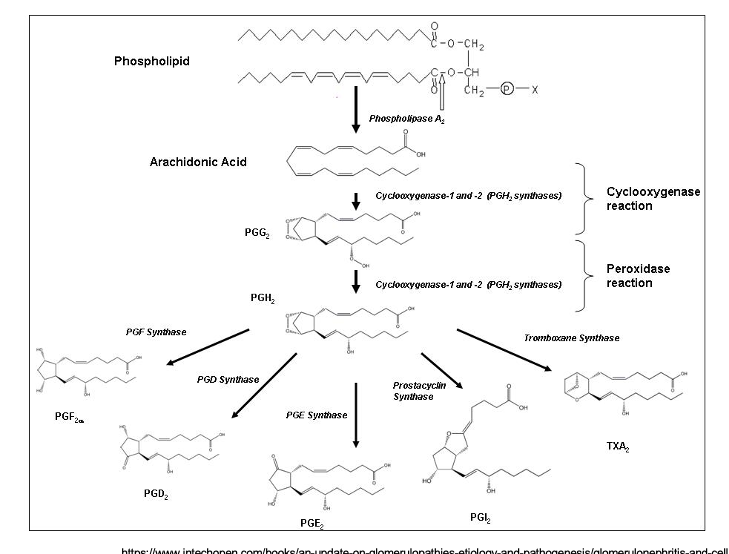
prostanoid production
anadamide (AEA)
FAAH/NAAA breaks down AEA → arachidonic acid and ethanolamine which goes thru COX-2 pathway
can be directly metabolized by COX-2 but creates a different PGH2 from AA
PGE2 → anti-inflam
PGF2 → pro-inflam
2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
MAGL/ABHD6 breaks down 2-AG → arachidonic acid and glycerol which goes thru COX-2 pathway
can be directly metabolized by COX-2 but creates a different PGH2 from AA
PGE2 → pro-inflam
PGD2 → anti-inflam
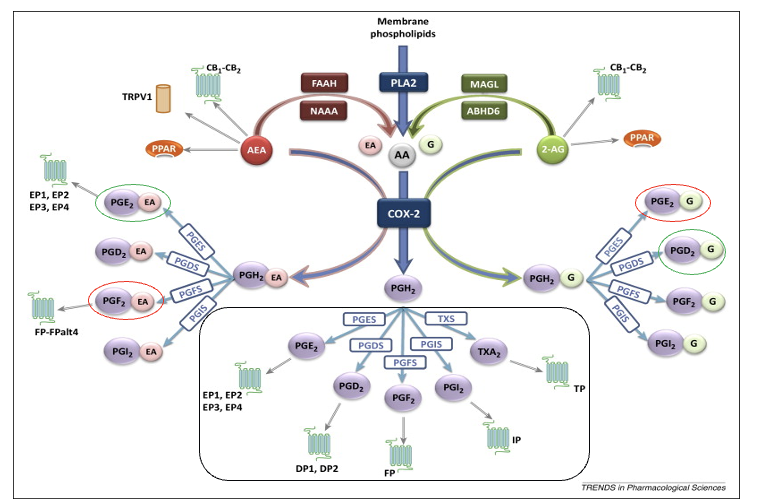
prostaglandins
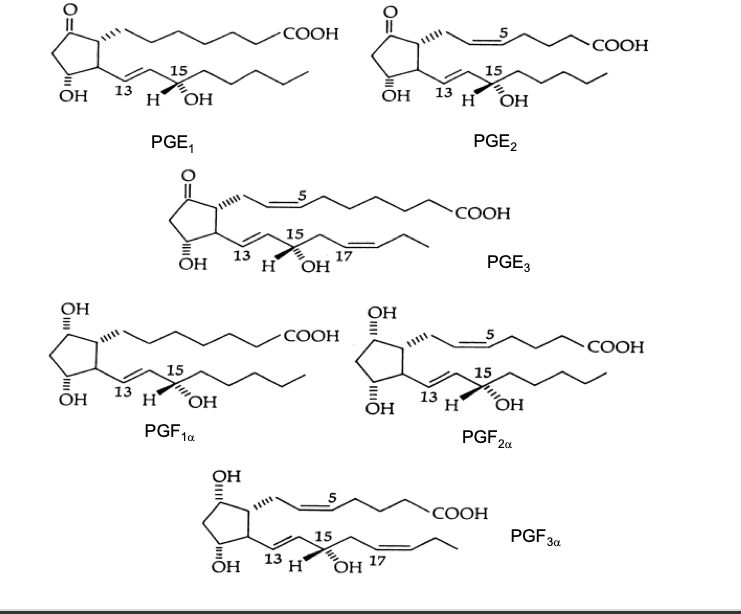
prostaglandins all have a cyclopentane ring
letter code is based upon ring modifications (e.g. hydroxyl or keto groups)
the subscript refers to the # of double bonds in the 2 side chains
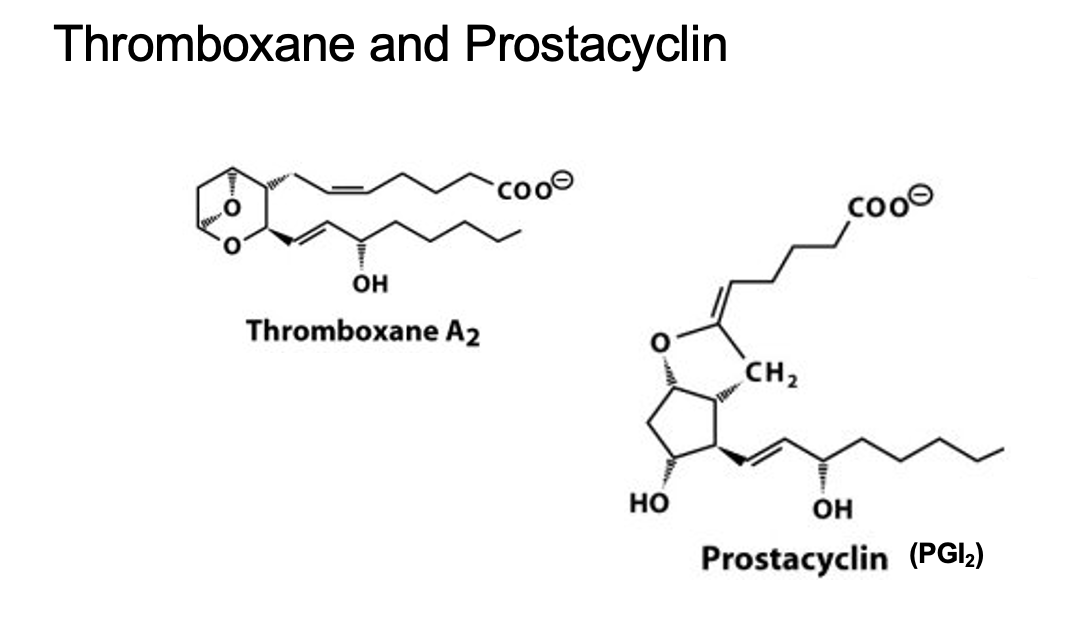
thromboxane and prostacyclin
thromboxane
6 membered ring
prostacyclin
only I Ietter code
prostanoid receptors
receptors located on cell surface
pharmacologic specificity determined by receptor density and type on different cells
all G protein coupled
multiple isoforms of receptors identified in humans via differential mRNA splicing
EP3 (I,II,III,IV,V,VI,e,f)
FP (A,B)
TP (α,β)
prostanoid receptor signaling
IP/EP2/EP4/DP1
coupled to Gαs → increases adenylyl cyclase → increases cAMP → biological effects
TP/FP/EP
TP → Gα12/13 → activates rhoGEF → rho activation → biological effects
TP → Gα16 → activates PLC15-a-hydroxy PGDH

→ increase Ca2+ → biological effects
TP/FP/EP → Gαq → activates PLC-β → increase Ca2+ - >biological effects
EP3
couples to Gαi → increase Ca2+ → biological effects
but can also → inhibit adenylyl cyclase → decrease cAMP
DP2/CR H2
couples to Gαi → increase Ca2+ → biological effects
but can also → inhibit adenylyl cyclase → decrease cAMP
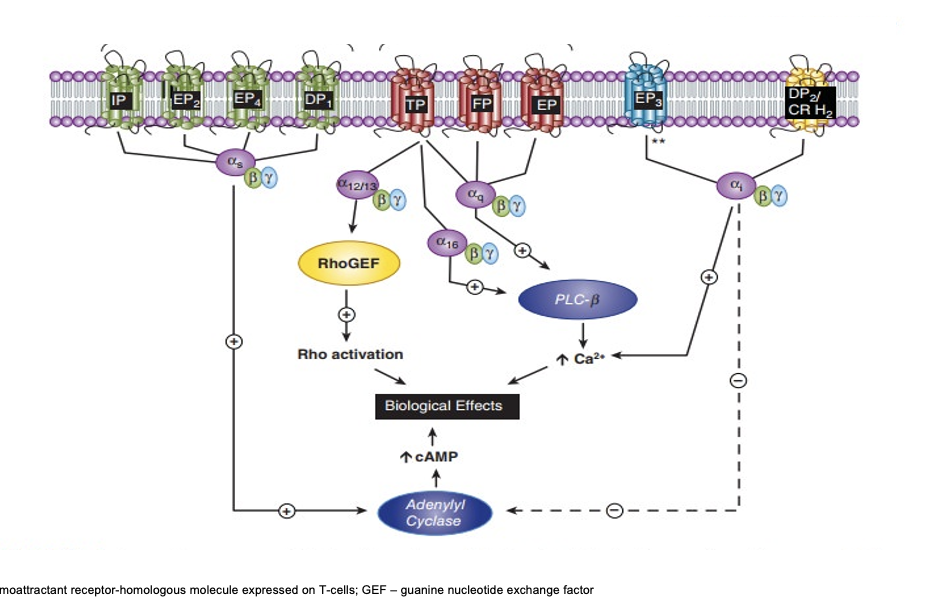
prostanoid signaling
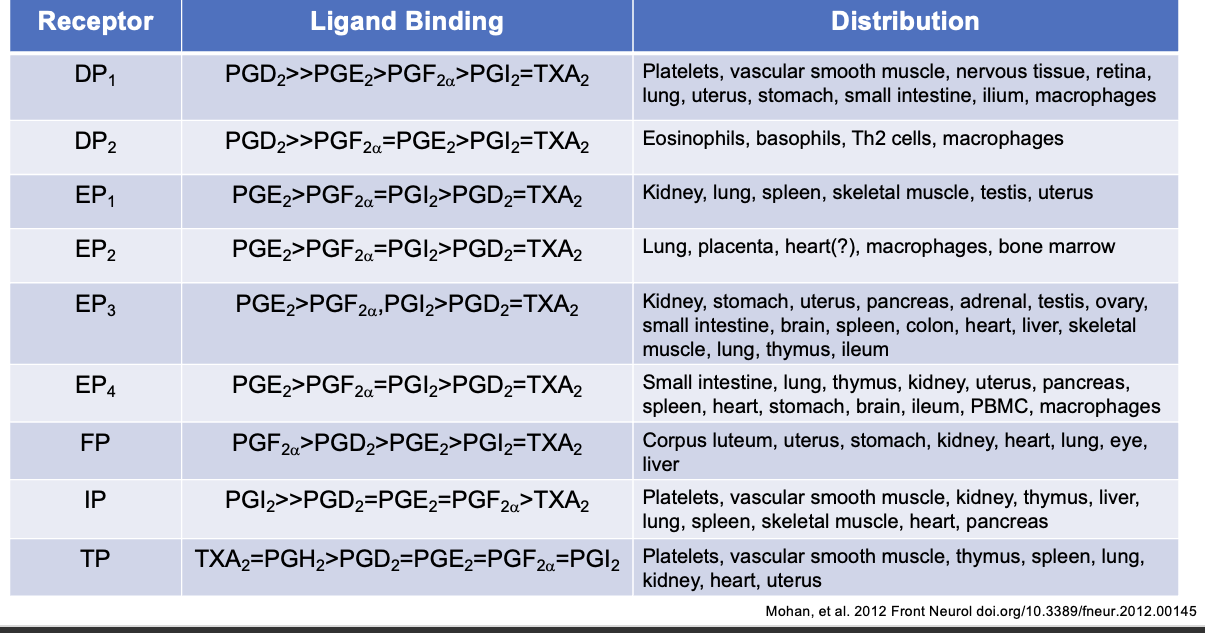
prostanoid functions
PGH2 → precursor to all other PGs
PGD2 → bronchoconstriction, sleep control, inhibits platelet aggregation
PGE2 → vasodilation, bronchodilation, hyperalgesia, fever, diuresis (excessive urine), immunomodulation
PGF2α → smooth muscle contraction, bronchoconstriction, abortion (give birth)
TxA2 → vasoconstriction, control of vascular tone, platelet activation
PGI2 → vasodilation, control of vascular tone, inhibits platelet aggregation
prostanoid inactiavtion
half life → seconds to minutes
major sites → liver and lungs
hydroxylation by 15-a-hydroxy PGDH and reduction by 13-PG reductase
oxidation of OH group at C15 to keto group
reduction of C13 and C14 to dihydroxy derivatives
β-oxidation → results in loss of 2 carbons
ω-hydroxylation → dicarboxylic acid derivatives
excreted in urine
leukotrienes
produced by leukocytes
100-1000x more potent than histamine in causing bronchoconstriction
component of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A → acronym for slow reacting substance)
produced via 5-lipoxgenase pathway
leukotriene synthesis
intracellular
arachidonic acid → 5-HPETE
thru 5-lipoxygenase
5-HPETE → LTA4
thru 5-lipoxygenase
LTA4 → LTC4
conjugated with GSH using LTC4 synthase
alternate pathway: LTA4 → LTB4 thru hydrolase
extracellular
LTC4 → LTD4
glutamate is removed
LTD4 → LTE4
glycine is removed
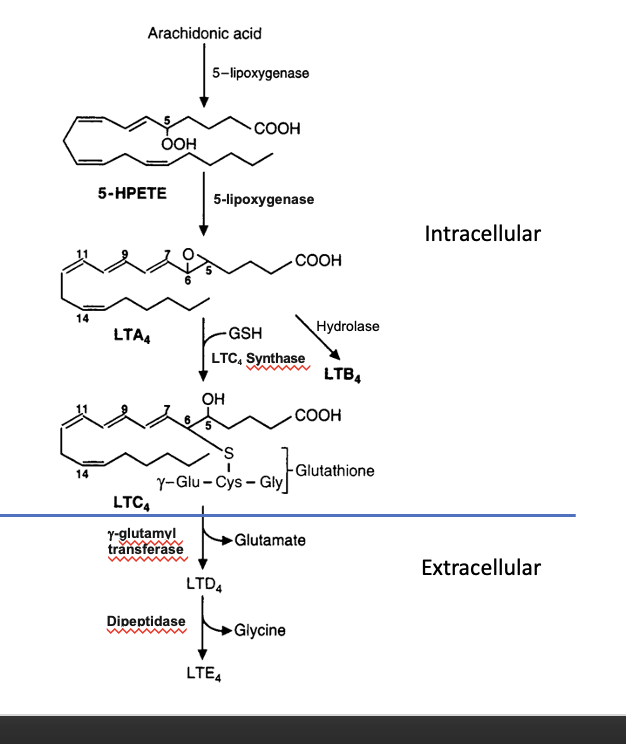
leukotriene signaling
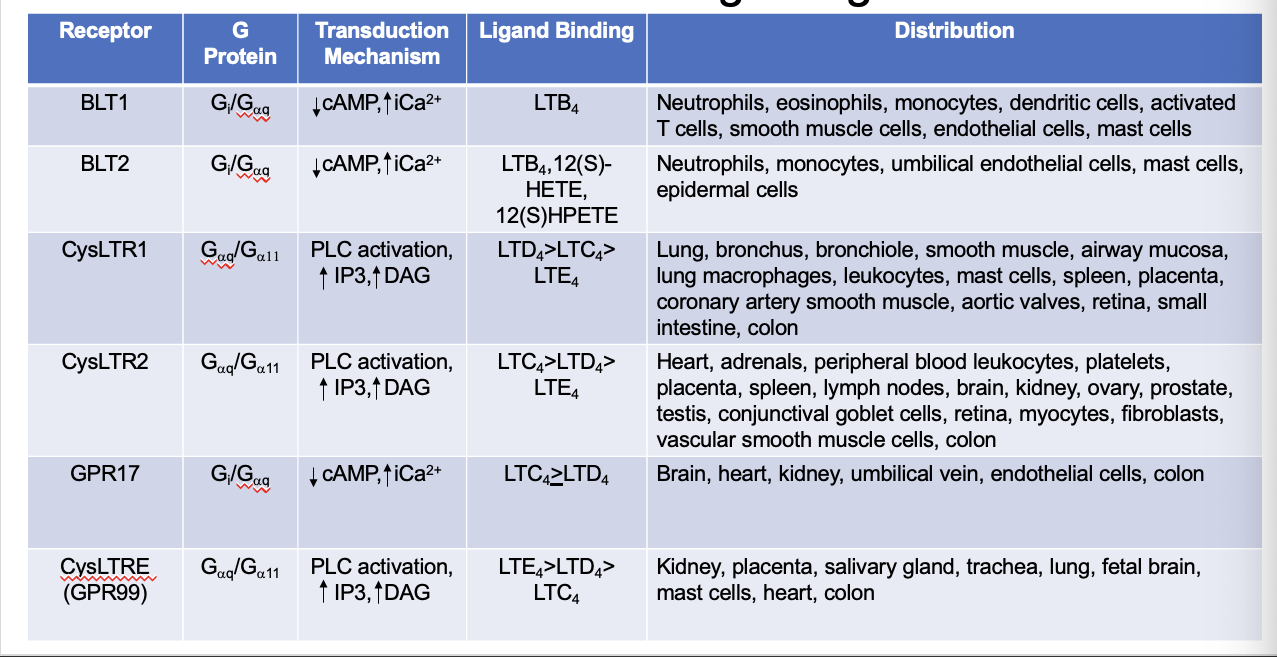
leukotriene functions
LTA4 → gives rise to all other LTs
LTB4 → neutrophil activation, chemotatic, plasma exudation (extravasation of fluids)
LTC4/LTD4 → bronchoconstriction, vasoconstriction, decrease coronary blood flow, decrease cardiac contractility, plasma exudation, promote endothelial and mesangial cell proliferation, activation of transcription factors, cytokine release
LTE4 → mucin release
HETEs → release Ca2+ stores and promote cell proliferation
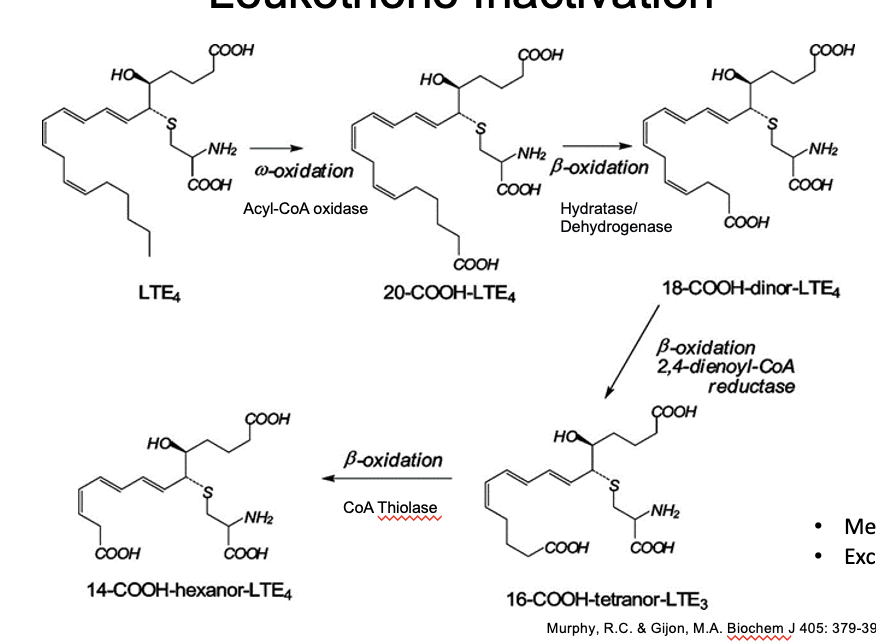
leukotriene inactivation
LTE → 20-COOH-LTE4
ω-oxidation
thru acyl-coA oxidative
20-COOH-LTE4 → 18-COOH-dinor-LTE4
β-oxidation
thru hydratase/dehydrogenase
18-COOH-dinor-LTE4 → 16-COOH-tetranor-LTE3
β-oxidation
thru 2,4-dienoyl-coA reductase
16-COOH-tetranor-LTE3 → 14-COOH-hexanor-LTE4
β-oxidation
thru coA thiolase
metabolized in the liver
excreted in the urine
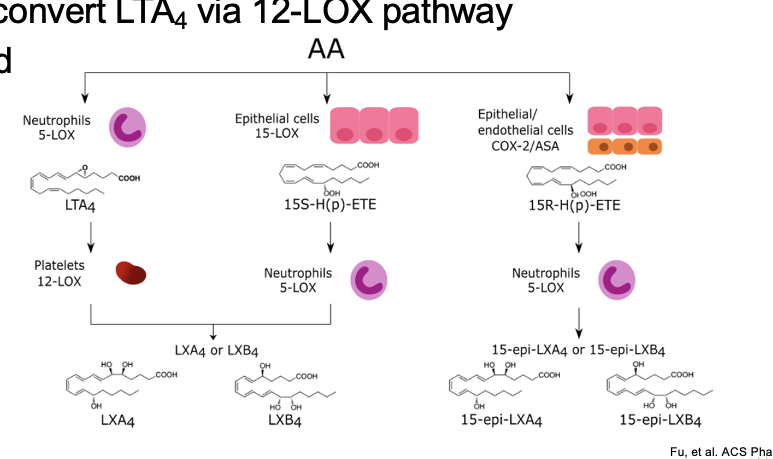
lipoxins
produced via 5-LOX alone or a combo of 15-LOX pathway + 5-LOX followed by conversion by hydrolase
platelets convert LTA4 via 12-LOX pathway
short lived
diagram
1st pathway
AA → LTA4
thru neutrophils 5-LOX
LTA4 → LXA4 or LXB4
thru platelets 12-LOX
2nd pathway
AA → 15S-H(p)-ETE
thru epithelial cells 15-LOX
15S-H(p)-ETE → LXA4 or LXB4
thru neutrophils 5-LOX
3rd ptahway
AA → 15R-H(p)-ETE
thru epithelial/endothelial cells COX-2/ASA (aspirin; partially inhibits COX-2)
15R-H(p)-ETE → 15-epi-LXA4 or 15-epi-LXB4
thru neutrophils 5-LOX
lipoxin functions
act as negative regulators of inflammation and leukotriene action
LXA2 receptors present on neutrophils, monocytes, T cells, lung, spleen, blood vessels, Gi protein-coupled receptor
inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis (mvmt toward site of inflammation), adhesion, transmigration
inhibit eosinophil recruitment
stimulate vasodilation by stimulating production of PGI2 and PGE2
inhibit LTC4 + LTD4 stimulated vasoconstriction
inhibit LTB4 stimulated inflammatory effects
inhibit function of NK cells and T cell secretion
mediate resolution of inflammatory response
stimulates uptake and clearance of apoptotic neutrophils by macrophages
increases non-phlogistic (non-inflammatory) activation of monocytes
eicosanoid involvement in pathophysiology
asthma → bronchoconstriction → driven by LTC4/D4/E4
inflammatory bowel disease → increase LTB4
rheumatoid arthritis (autoimmune disease) → up-regulation of COX2 and PGE2
glomerulonephritis → increase LTB4, C4, D4
cancer → many cancers express COX-2, PGE2, promotes tumor growth
CV disease → TxA2 mediates thrombosis in MCI, LT production
inflammation → LTs, PGE2, LXA2, TxA2, PGI2, PGD2 → involved in vasoconstriction (TxA2), vasodilation, edema, chemotaxis, pain, vascular permeability, fever
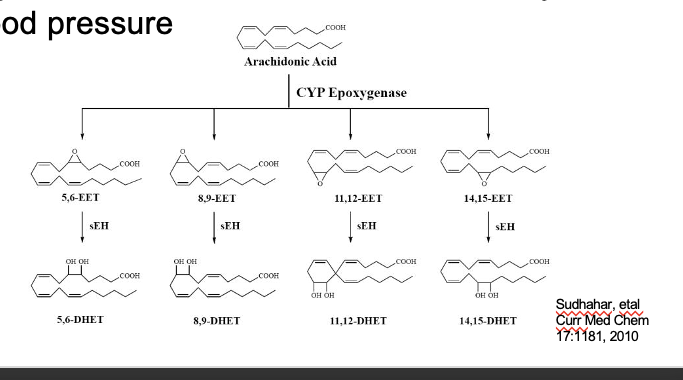
epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EETs)
produced via cytochrome P450 epoxygenase
occurs in CV endothelium and smooth muscle cells, ascending loop of henle, vascular endothelium in the kidney, brain astrocytes, airway and parenchymal lung tissue and other tissues lacking cycooxygenase and lipoxygenase
acts as paracrine factor regulating local vascular tone, anti-inflammatory
can act as vasodilator, lower blood psi
diagram
AA → 5,6 EET/8,9-EET/11,12-EET/14,15-EET
thru CYP epoxygenase
EET → DHET (essentially inactive form)
thru sEH (soluble exposide hydrolase)