Exam 2 Pearson Questions
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
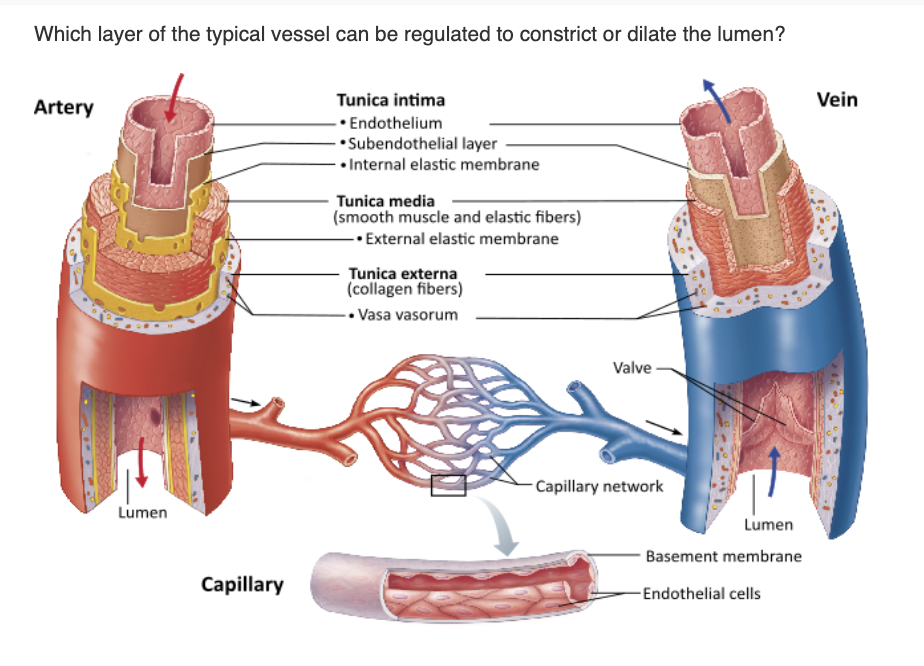
tunica media |
tunica externa |
vasa vasorum |
tunica intima |
tunica media
Arteries always carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart.
True |
False |
False
Which of the following form successively larger vessels that carry blood toward the heart?
arteries |
capillaries |
veins |
venules |
veins
Which of the following is true regarding veins?
Veins have valves; arteries do not. |
Veins carry blood away from the heart, while arteries carry blood to the heart. |
Veins have smaller-diameter lumens compared to arteries. |
Veins are more muscular than arteries. |
Veins have valves; arteries do not. |
Factors that aid venous return include all EXCEPT ________.
pressure changes in the thorax |
activity of skeletal muscles |
venous valves |
urinary output |
urinary output |
An increase in blood viscosity will cause an increase in total peripheral resistance.
True |
False |
True
Which of the following would decrease total peripheral resistance to blood flow?
decreasing the hematocrit |
vasoconstriction |
atherosclerosis |
increasing blood vessel length |
decreasing the hematocrit |
Which of the following is the most significant source of blood flow resistance?
total blood vessel length |
blood vessel diameter |
blood vessels type |
blood viscosity |
blood vessel diameter |
Which of the following is NOT an important source of resistance to blood flow?
vessel diameter |
blood viscosity |
vessel length |
total blood volume |
total blood volume |
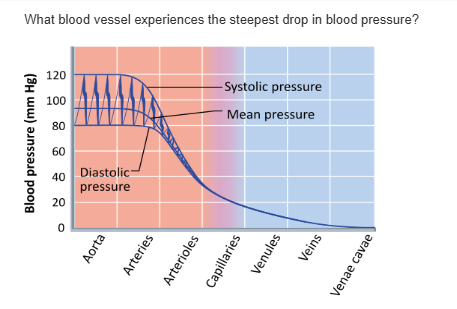
arteries |
capillaries |
venules |
arterioles |
arterioles |
The pulse pressure is ________.
systolic pressure minus diastolic pressure |
systolic pressure plus diastolic pressure |
systolic pressure divided by diastolic pressure |
diastolic pressure plus 1/3 (systolic pressure plus diastolic pressure) |
systolic pressure minus diastolic pressure

__ shock is due to large-scale blood loss
Hypovolemic shock
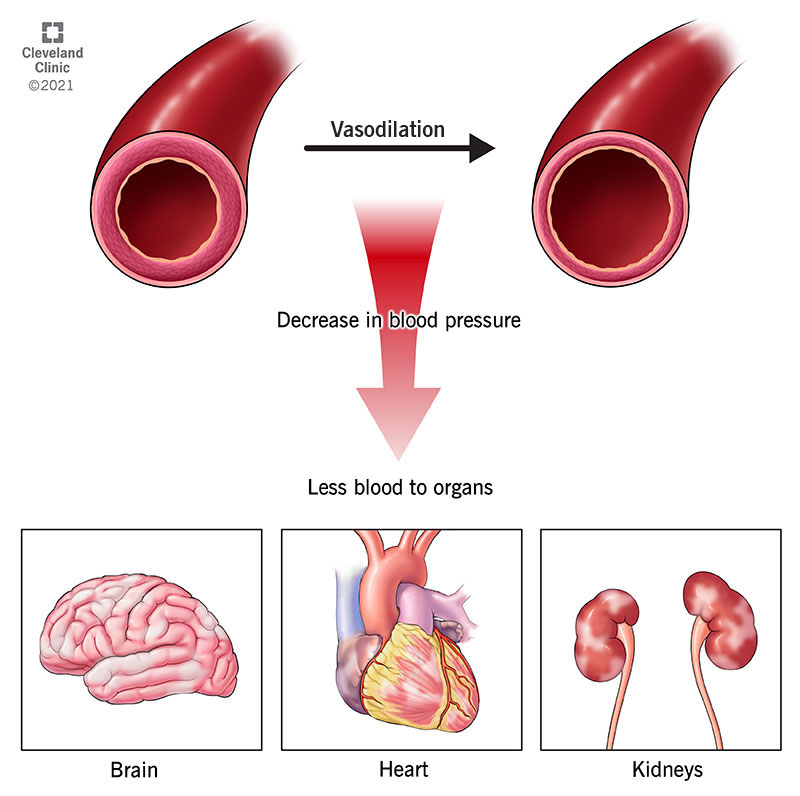
__ shock is when you have normal blood volume but poor circulation due to extreme vasodilation.
Vascular shock
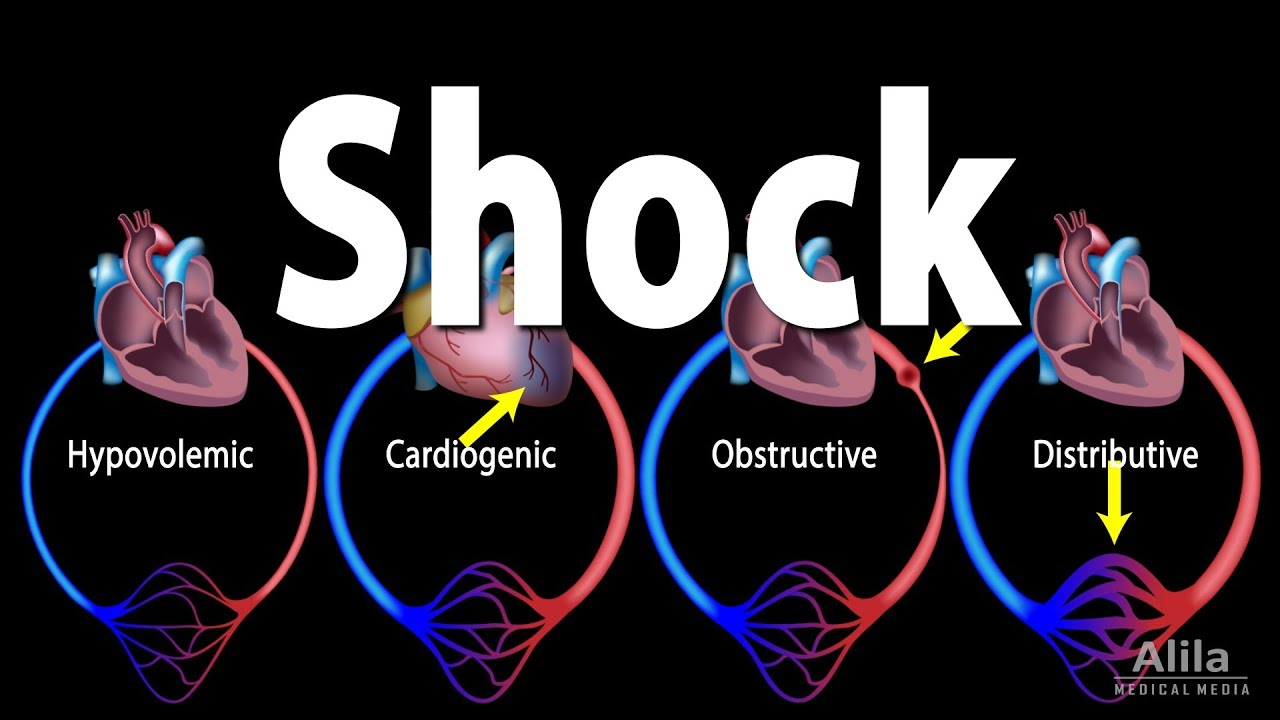
__ shock is due to inadequate blood flow to meet tissue needs
Circulatory
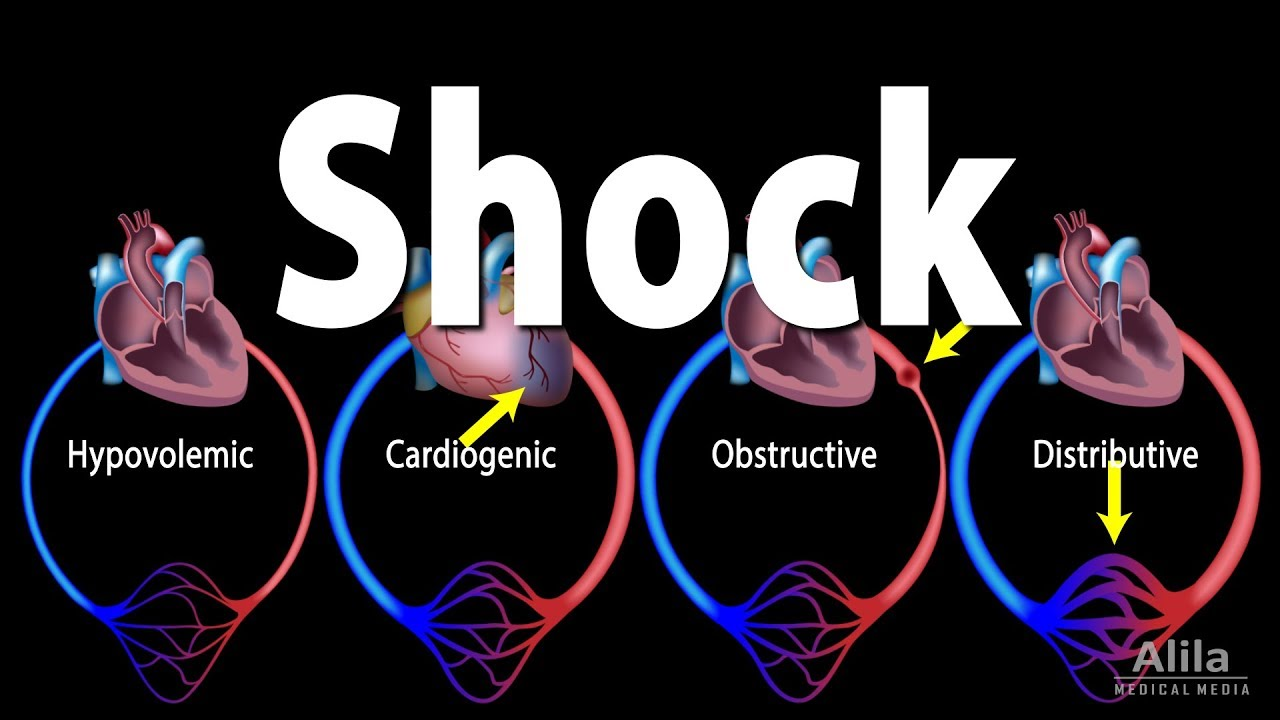
__ shock are results from heart inability to sustain adequate circulation due to myocardial damage.
Cardiogenic shock
Select the correct statement about blood flow.
It is greatest where resistance is highest. |
It is relatively constant through all body organs. |
It is measured in mm Hg. |
Blood flow through the entire vascular system is proportional to cardiac output. |
Blood flow through the entire vascular system is proportional to cardiac output. |
The baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and aortic arch are sensitive to which of the following?
a decrease in oxygen levels |
an increase in oxygen levels |
a decrease in carbon dioxide |
changes in arterial pressure |
changes in arterial pressure |
Where are the sensors for the arterial baroreceptor reflex located?
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems |
carotid sinus and aortic arch |
cardiovascular centers in the medulla oblongata |
carotid sinus and aortic arch |
If blood pressure is increased at the arterial baroreceptors, what would happen with the activity level of the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) and sympathetic nervous system (SNS)?
increased PNS and SNS activity |
decreased PNS activity and increased SNS activity |
increased PNS activity and decreased SNS activity |
increased PNS activity and decreased SNS activity |
Which of the following would cause vasodilation of arterioles?
View Available Hint(s)for Part C
decreased activity of the sympathetic nervous system |
increased activity of the parasympathetic nervous system |
increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system |
decreased activity of the parasympathetic nervous system |
decreased activity of the sympathetic nervous system |
Stimulation of the adrenal medulla would result in which of the following?
View Available Hint(s)for Part D
an increase in heart rate and contractility |
a decrease in blood pressure |
a decrease in cardiac output |
vasodilation of arteries |
an increase in heart rate and contractility |
A decrease in blood pressure at the arterial baroreceptors would result in which of the following?
View Available Hint(s)for Part E
a decrease in heart rate |
an increase in heart contractility |
a decrease in cardiac output |
vasodilation of arterioles |
an increase in heart contractility |
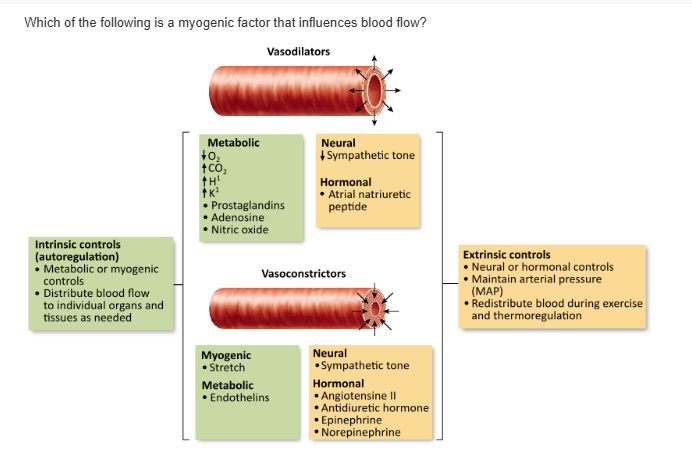
sympathetic tone |
stretch of vascular smooth muscle |
epinephrine from the adrenal medulla |
atrial natriuretic peptide |
stretch of vascular smooth muscle
Which of the following organs would experience decreased blood flow during exercise?
kidneys |
skeletal muscles |
brain |
skin |
kidneys
Blood flow to the skin ________.
is controlled mainly by decreasing pH |
increases when environmental temperature rises |
increases when body temperature drops so that the skin does not freeze |
is not an important source of nutrients and oxygen for skin cells |
increases when environmental temperature rises
Where in the body would you find low oxygen levels causing vasoconstriction and high levels causing vasodilation?
lungs |
liver |
heart |
kidney |
lungs |
Which of the following statements describes the significance of blood pressure changes as blood reaches the capillary beds?
Blood pressure increases as it reaches the capillary beds because capillaries need a higher blood pressure for filtration activities. |
Blood pressure drops as it reaches the capillary beds because high pressure would rupture them. |
Blood pressure drops as it reaches the capillary beds because capillaries depend on the lower pressure to prevent fluid exchange between the capillaries and interstitial space. |
Blood pressure does not change as blood flows from arteries into capillaries. |
Blood pressure drops as it reaches the capillary beds because high pressure would rupture them.
In the capillaries, hydrostatic pressure (HP) is exerted by __________.
View Available Hint(s)for Part A
proteins in the blood |
blood pressure |
blood pressure
The net hydrostatic pressure (HP) is the hydrostatic pressure in the __________ minus hydrostatic pressure in the __________.
View Available Hint(s)for Part B
capillary; interstitial fluid |
interstitial fluid; capillary |
capillary; interstitial fluid
Which of the following would reflect the typical net hydrostatic pressure (HP) at the arterial end of the capillary?
View Available Hint(s)for Part C
1 mm Hg |
12 mm Hg |
34 mm Hg |
34 mm Hg |
The colloid osmotic pressure in the capillary is caused by __________.
View Available Hint(s)for Part D
proteins in the blood |
blood pressure |
proteins in the blood |
Which net pressure draws fluid into the capillary?
View Available Hint(s)for Part E
net osmotic pressure |
net hydrostatic pressure |
net osmotic pressure |
Reabsorption of fluid into the capillary takes place at the arterial end or venous end of the capillary?
View Available Hint(s)for Part F
arterial |
venous |
venous
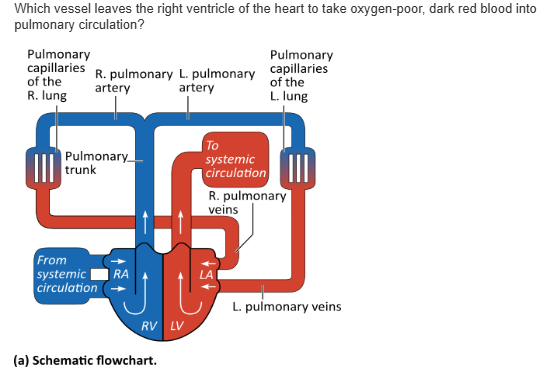
superior vena cava |
aorta |
pulmonary trunk |
pulmonary vein |
pulmonary trunk |
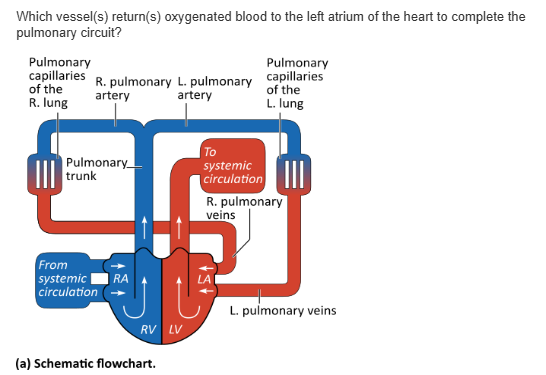
inferior vena cava |
pulmonary vein |
pulmonary arteries |
pulmonary trunk |
pulmonary vein
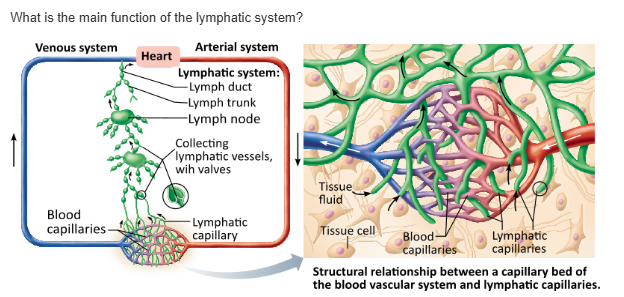
The lymphatic system makes blood cells through a process known as hematopoiesis. |
The lymphatic system returns leaked fluid and plasma proteins that escape from the bloodstream to the blood. |
The lymphatic system produces high fluid pressures to assist in lymph motion. |
The lymphatic system transports blood and lymph throughout the body. |
The lymphatic system returns leaked fluid and plasma proteins that escape from the bloodstream to the blood. |
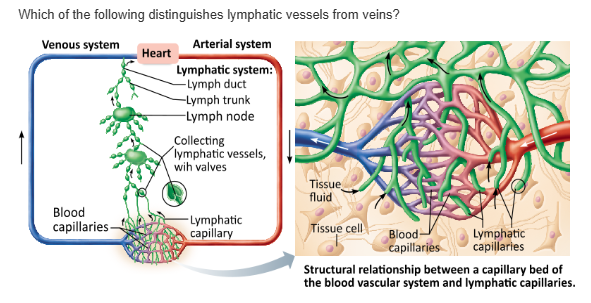
lymphatic vessels lack the three tunics present in veins. |
lymphatic vessels transport fluids toward the heart. |
lymphatic vessels have valves, while veins do not. |
lymphatic vessels collect larger materials |
lymphatic vessels collect larger materials |
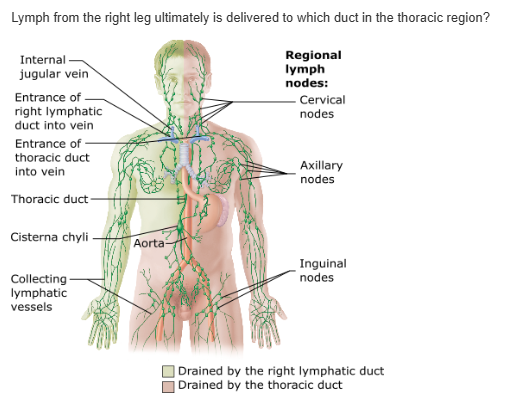
jugular trunk |
right lymphatic duct |
subclavian trunk |
thoracic duct |
thoracic duct |
Select the correct statement about lymph transport.
Lymph transport is only necessary when illness causes tissue swelling. |
Lymph transport is faster than that occurring in veins. |
Lymph transport depends on the movement of adjacent tissues, such as skeletal muscles. |
Under normal conditions, lymph vessels are very high-pressure conduits. |
Lymph transport depends on the movement of adjacent tissues, such as skeletal muscles. |
The lymphatic capillaries function to absorb the excess protein-containing interstitial fluid and return it to the bloodstream.
True |
False |
True |
Digested fats are absorbed from the small intestine by a special set of lymphatic capillaries called lacteals.
True |
False |
True |
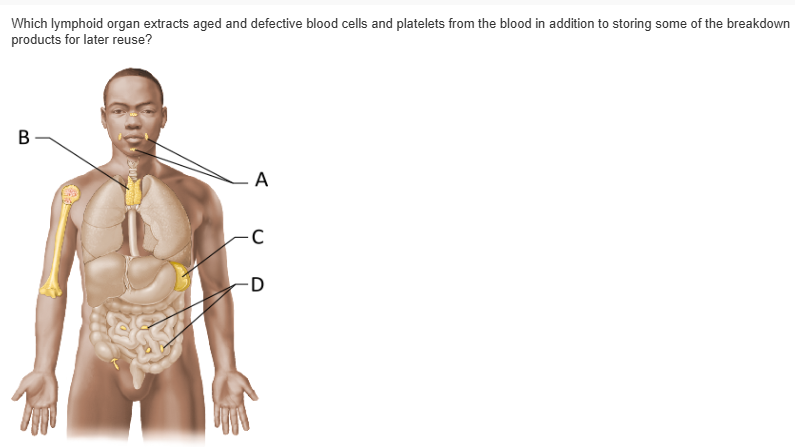
A |
B |
C |
D |
C
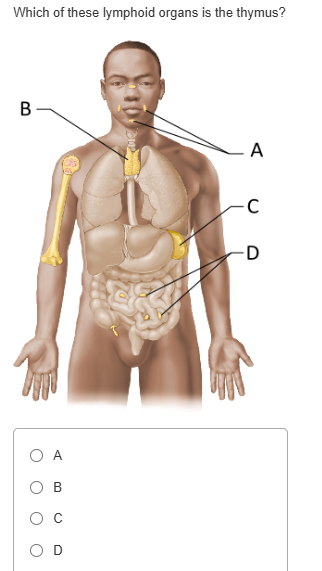
B
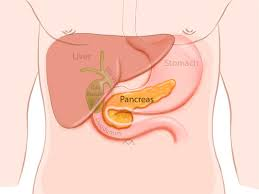
Which of the following would NOT be classified as a lymphoid organ?
pancreas |
tonsils |
spleen |
Peyer's patches of the intestine |
pancreas |
Which of the following is a role of lymph nodes?
They filter lymph. |
They produce red blood cells. |
They produce lymph. |
They return lymph to circulation. |
They filter lymph. |
Flow of lymph through a lymph node is slowed due to ________.
fewer efferent vessels draining it compared to many afferent vessels feeding it |
the presence of lymphocytes and macrophages |
mini-valves |
the viscous nature of lymph |
fewer efferent vessels draining it compared to many afferent vessels feeding it |
Functions of the spleen include all of those below EXCEPT ________.
storage of iron |
removal of old or defective blood cells from the blood |
storage of blood platelets |
forming crypts that trap bacteria |
forming crypts that trap bacteria |
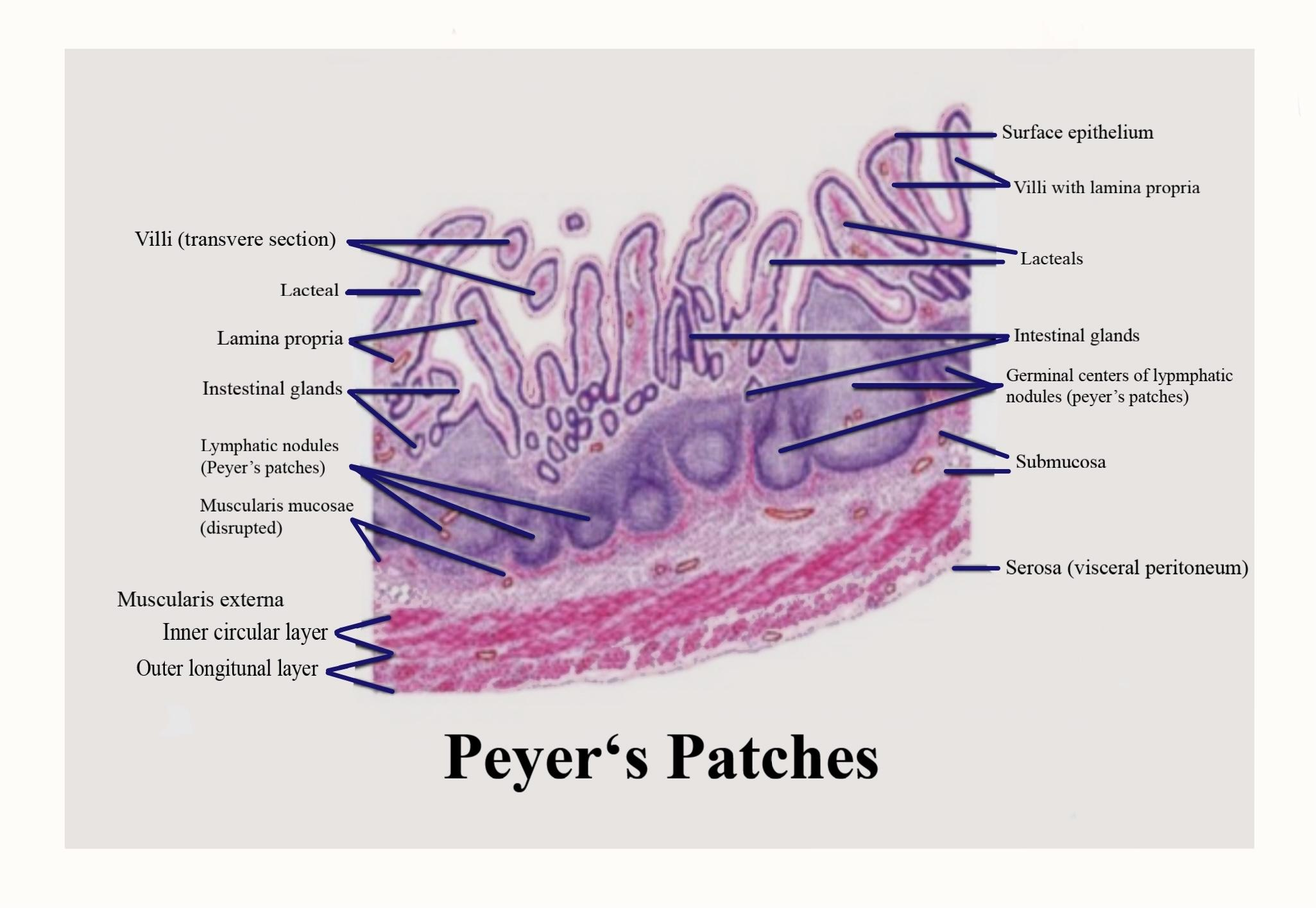
Which of the following lymphoid organs is NOT matched with its function?
spleen: remove old red blood cells |
thymus: site of T cell maturation |
bone marrow: form lymphocytes |
Peyer's patches: site of B cell maturation |
Peyer's patches: site of B cell maturation
The thymus functions strictly in maturation of B cells.
True |
False |
False ❌
The thymus is responsible for the maturation of T cells, not B cells.
B cells mature in the bone marrow.
The thymus is the only lymphoid organ that does NOT ________.
have a cortex and medulla |
have lymphocytes |
produce hormones |
directly fight antigens |
directly fight antigens
Which of the following provides a first line of defense against pathogens?
antimicrobial proteins |
complement |
inflammation |
skin and mucous membranes |
skin and mucous membranes
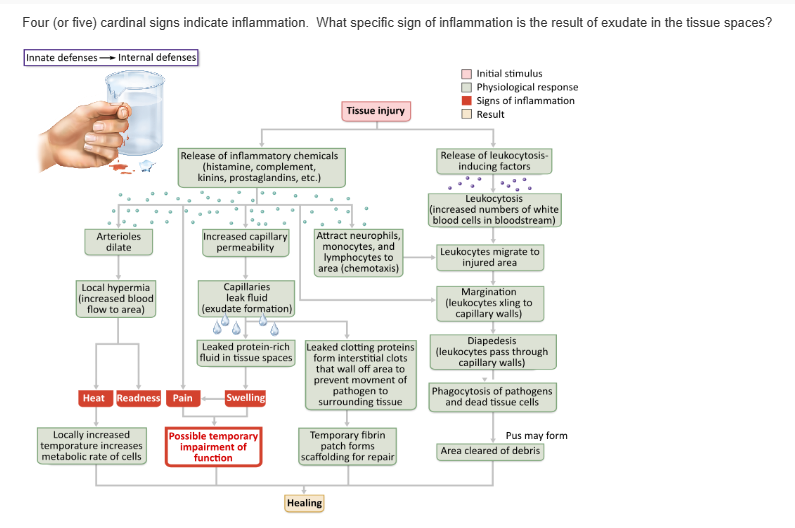
heat |
edema (swelling) |
pain |
impaired function |
edema (swelling) |
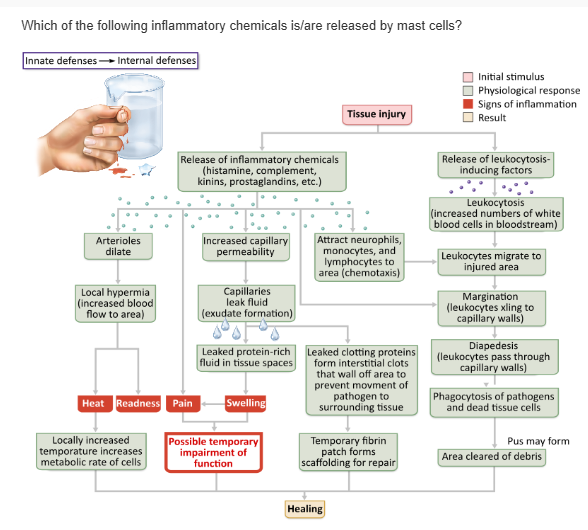
complement |
kinins |
prostaglandins |
histamine |
histamine |
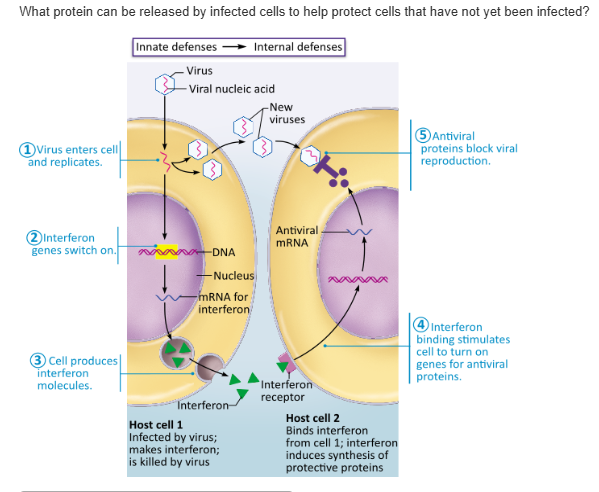
interferon |
complement |
opsonins |
pyrogens |
interferon |
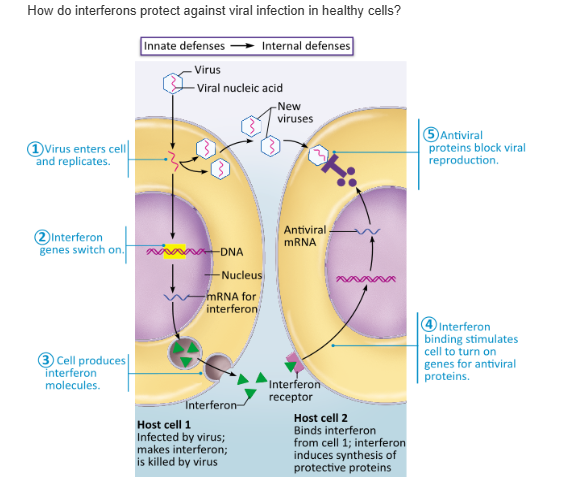
Interferons perform opsonization to coat microorganisms. |
Interferons activate complement. |
Interferons encourage the production of antiviral proteins. |
Interferons promote fever, or an abnormally high body temperature |
Interferons encourage the production of antiviral proteins.
Which of the following phases involves white blood cells leaving capillaries?
leukocytosis |
chemotaxis |
diapedesis |
margination |
diapedesis |
Which of the following is an effect of complement activation?
opsonization |
tissue repair |
fever |
T cell activation |
opsonization
Inflammation ________.
brings more leukocytes to the site of infection |
is caused by bacterial activity to enhance the spread of disease |
slows the healing process with swelling that can impair bodily function |
is caused by viral activity to enhance the spread of the disease |
brings more leukocytes to the site of infection
All but one of the following occurs during the inflammatory response. Select the example below that does NOT describe the process of inflammation.
Inflammation increases capillary permeability. |
Vasoconstriction prevents excessive blood loss due to injury. |
Release of prostaglandins results in pain. |
Chemotaxis draws leucocytes to the site of injury. |
Vasoconstriction prevents excessive blood loss due to injury.
Which of the following is NOT a role of activated complement?
insertion of MAC and cell lysis |
enhancement of inflammation |
prevention of immediate hypersensitivity reactions |
opsonization |
prevention of immediate hypersensitivity reactions
Complement proteins and antibodies coat a microorganism and provide binding sites, enabling macrophages and neutrophils to phagocytize the organism. This phenomenon is termed ________.
agglutination |
opsonization |
chemotaxis |
diapedesis |
opsonization |
Soluble proteins secreted by plasma cells are called antibodies.
True |
False |
True
__ T cell slows or stops the immune response
Regulatory T Cell
__ T cell; it's absence results in no immune response
Helper T cell
__ T cell kills cancer cells and virus infected body cells
Cytotoxic
__ cell enables quick and efficient response to secondary exposure to antigen
Memory cell
__ cell forms antibody producing cells
B cell
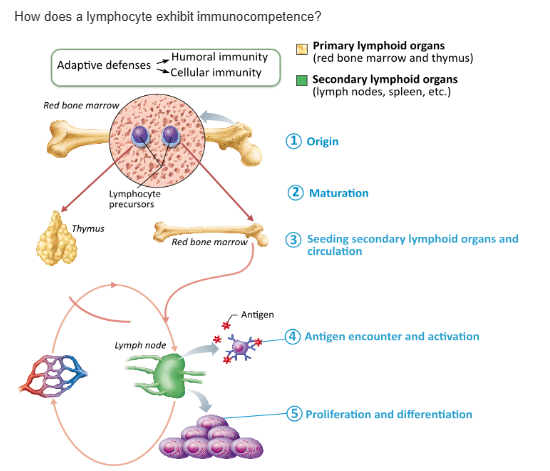
by rapidly proliferating to form an army of cells exactly like themselves and bearing the same antigen-specific receptors |
by being relatively unresponsive to self-antigens so that they do not attack the body's own cells |
by being able to recognize their one specific antigen |
by recognizing self-antigen |
by being able to recognize their one specific antigen |