Orbit Intro, Congenital Deformities, Cranio-Orbital Defects
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
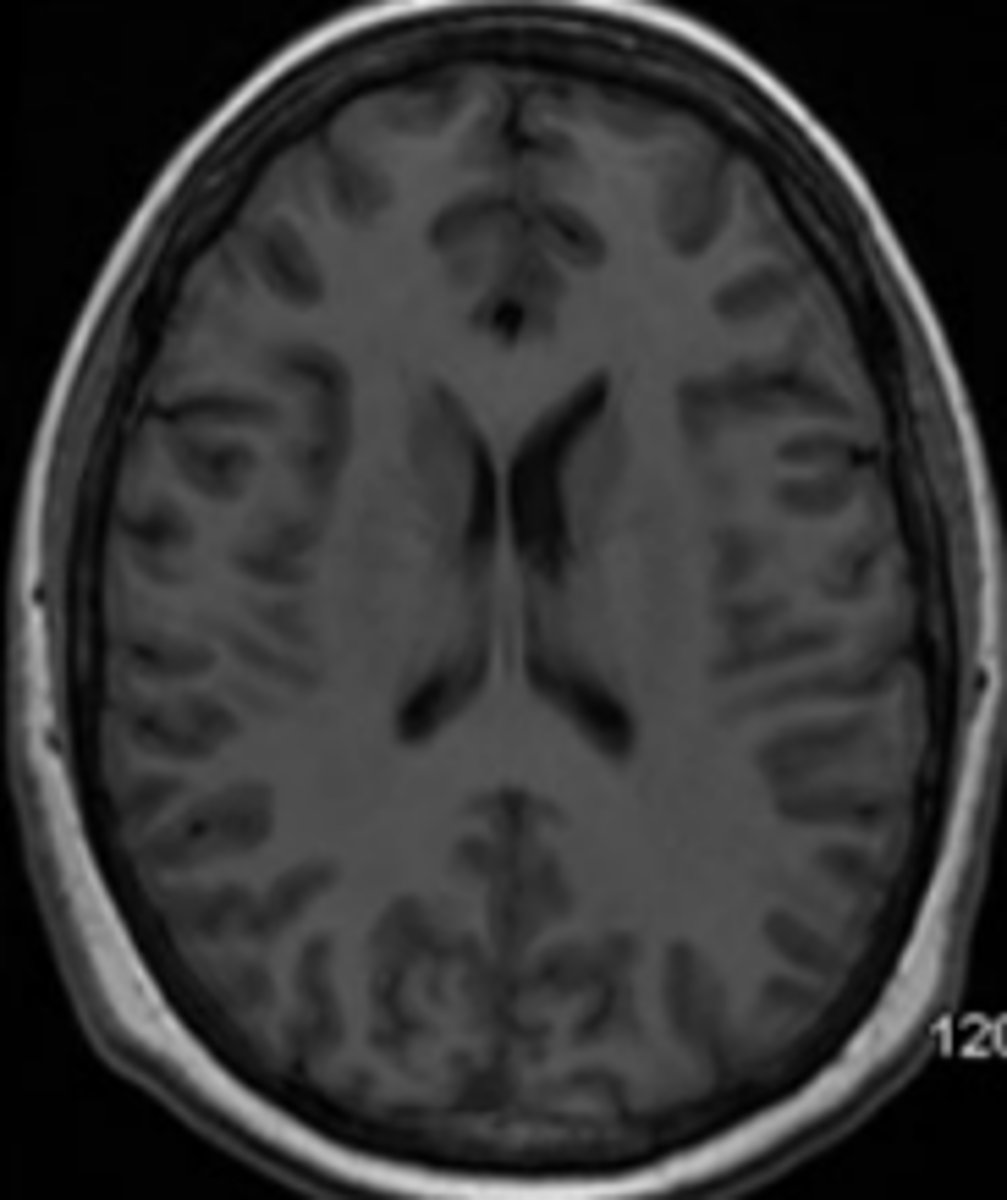
Axial
imaging plane that is along the horizontal plane.
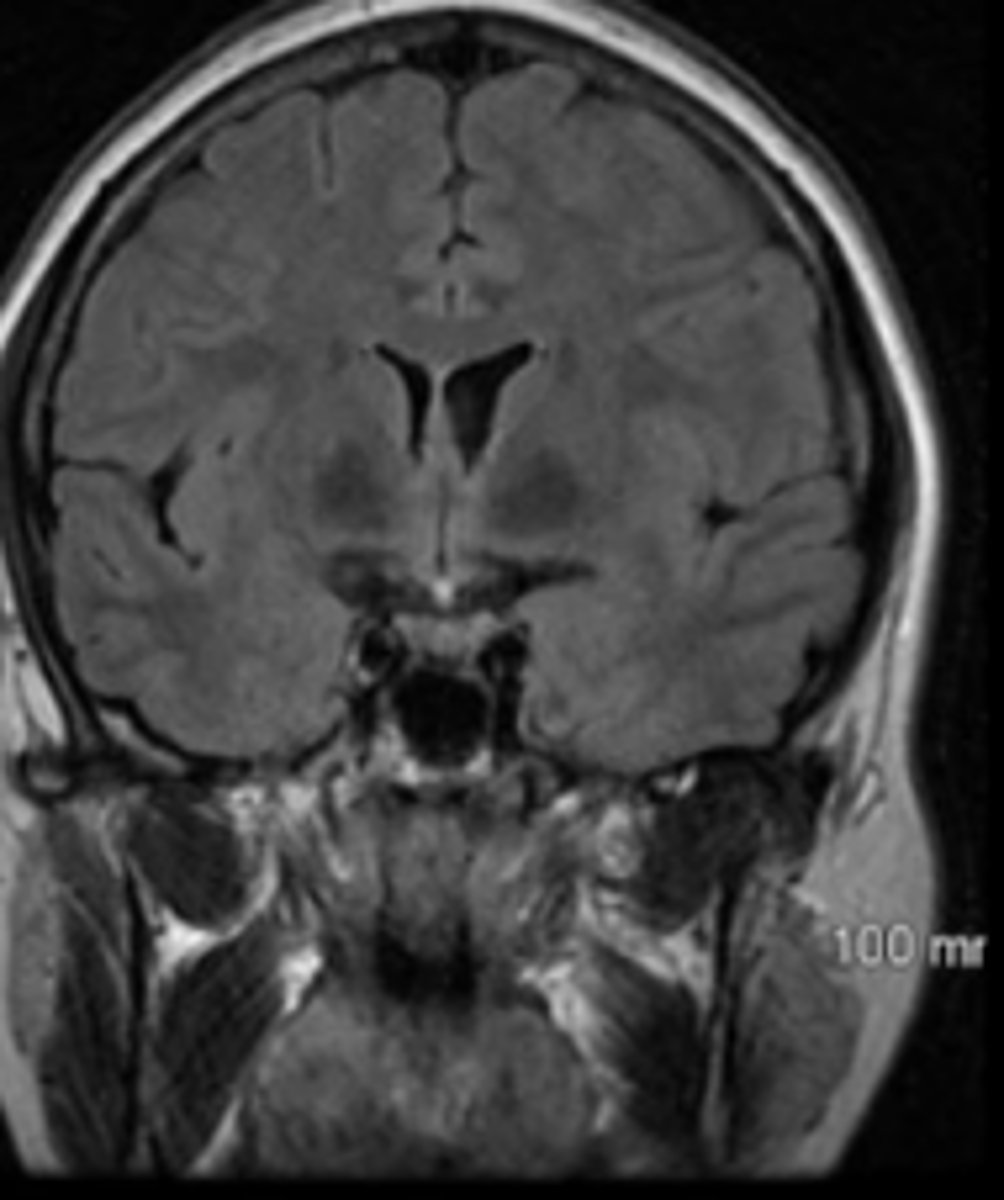
Coronal
imaging plane that is along the vertical plane, separating the body from front to back
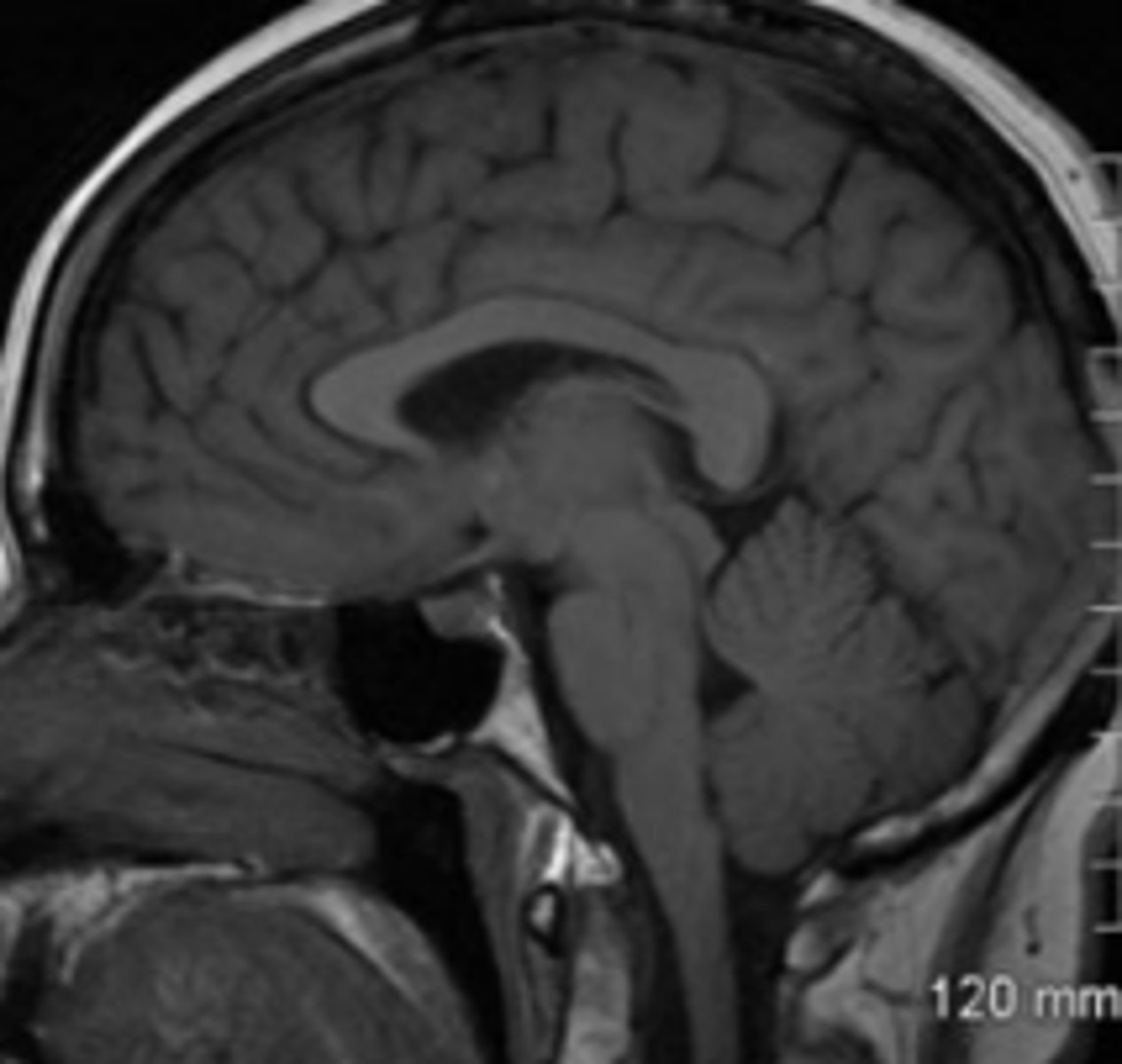
Sagittal
imaging plane that is along the vertical plane, separating the body from left to right
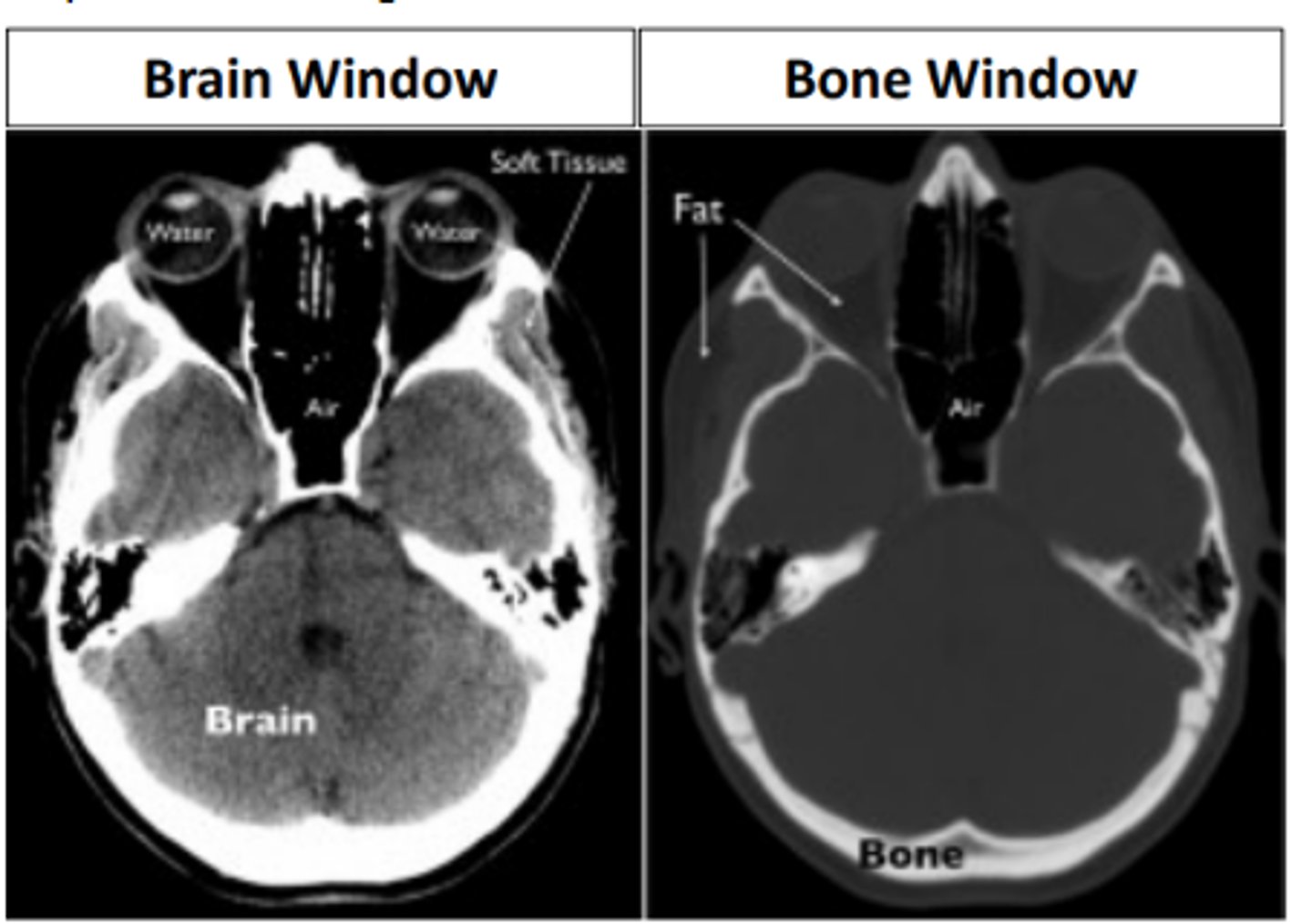
Computed tomography (CT)
a scan which is a series of X-rays taken at different angles to create cross sectional images. Has the ability to image a wide variety of structures including bone, soft tissues, tumors, vasculature, etc.
Fast
High detail (thin slices)
Cost effective
Less sensitive to movements
four Benefits of CT Scan
radiation exposure
reaction to contrast dye
fetal exposure
not sensitive to inflammation of meninges
four Disadvantages of CT Scan
dense
White areas of a CT scan represent ____ tissue such as bone or metal
less dense
Grey areas of a CT scan represent less dense tissue such as fat or water
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
a scan which uses magnetic and radio waves for detailed 3D imaging of the body. Has the ability to image a wide variety of structures including bone, soft tissues, organs, etc. Avoid in cases of metallic foreign bodies.
No radiation
High detail
Low risk of allergy
3 Benefits of MRI Scan
cannot use w implantable devices
cannot use in nursing women
slow
costly
fetal exposure
difficulty differentiating tumors and edema
six Disadvantages of MRI Scan
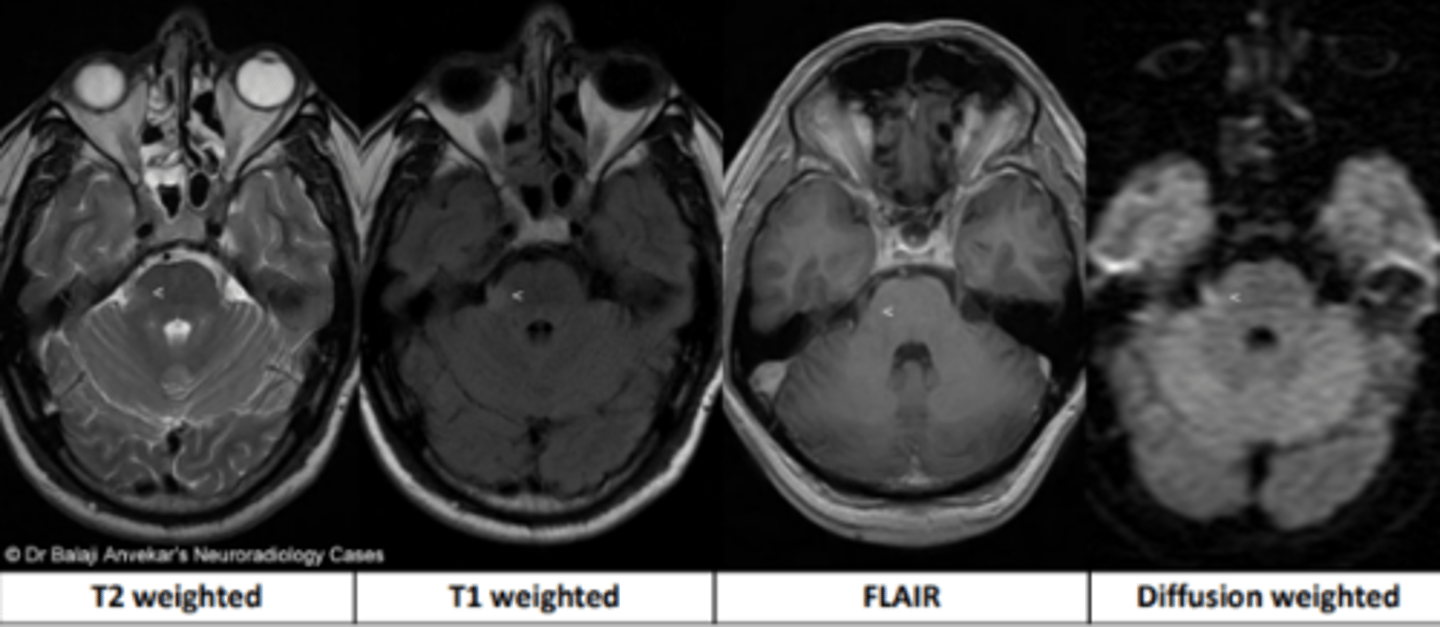
T1
MRI sequence that highlights locations of fat using gadolinium for contrast.
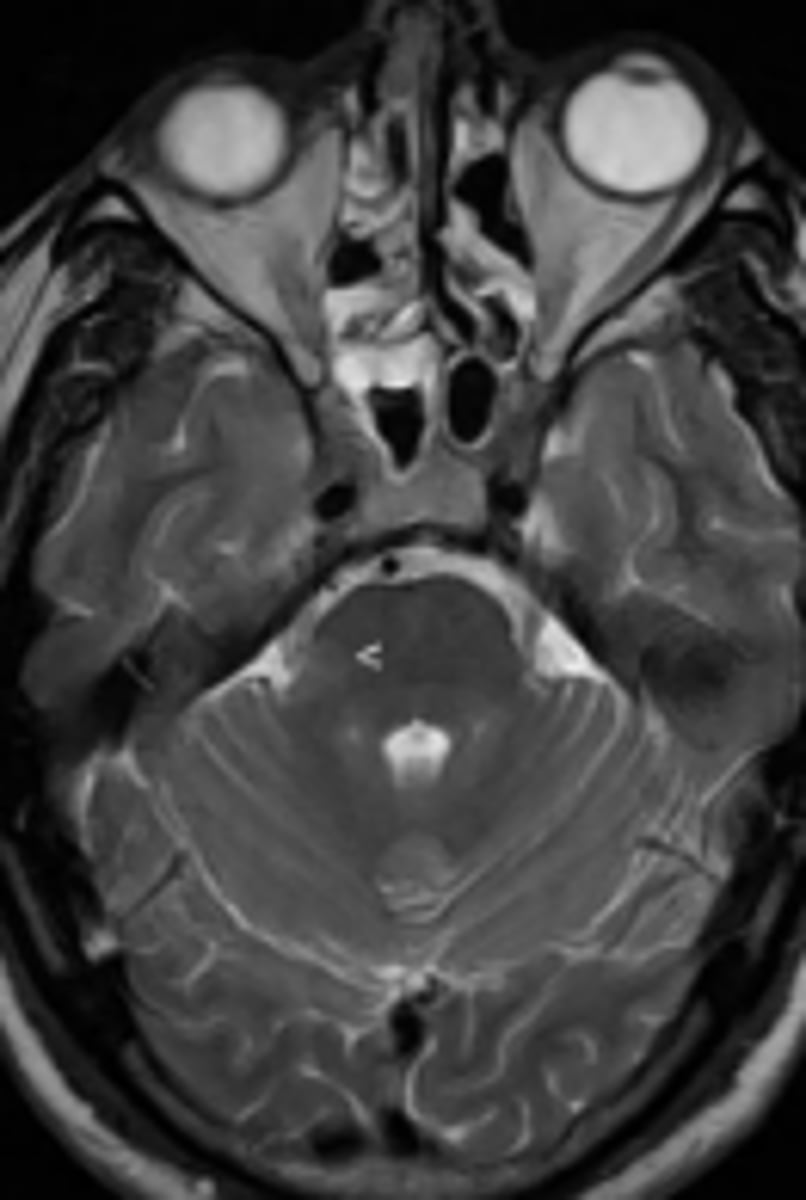
T2
MRI sequence that highlights locations of water.
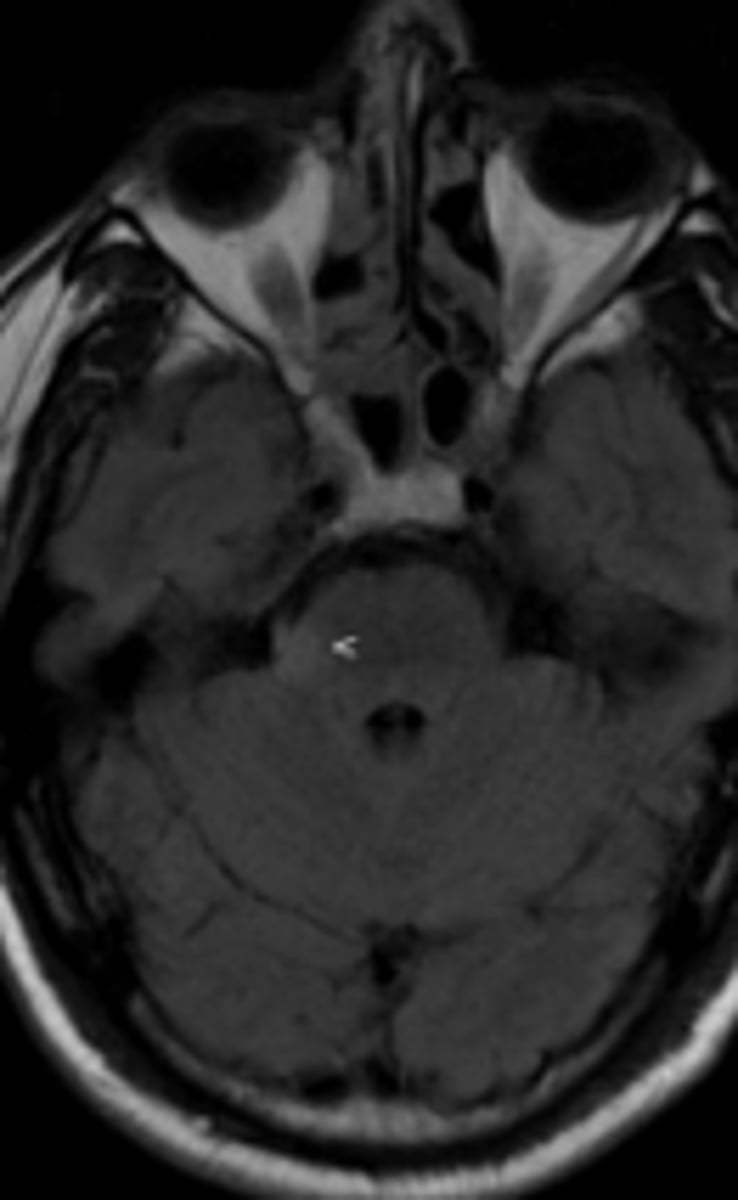
FLAIR
MRI sequence that is similar to T2, but suppresses free water as seen in normal cerebrospinal fluid
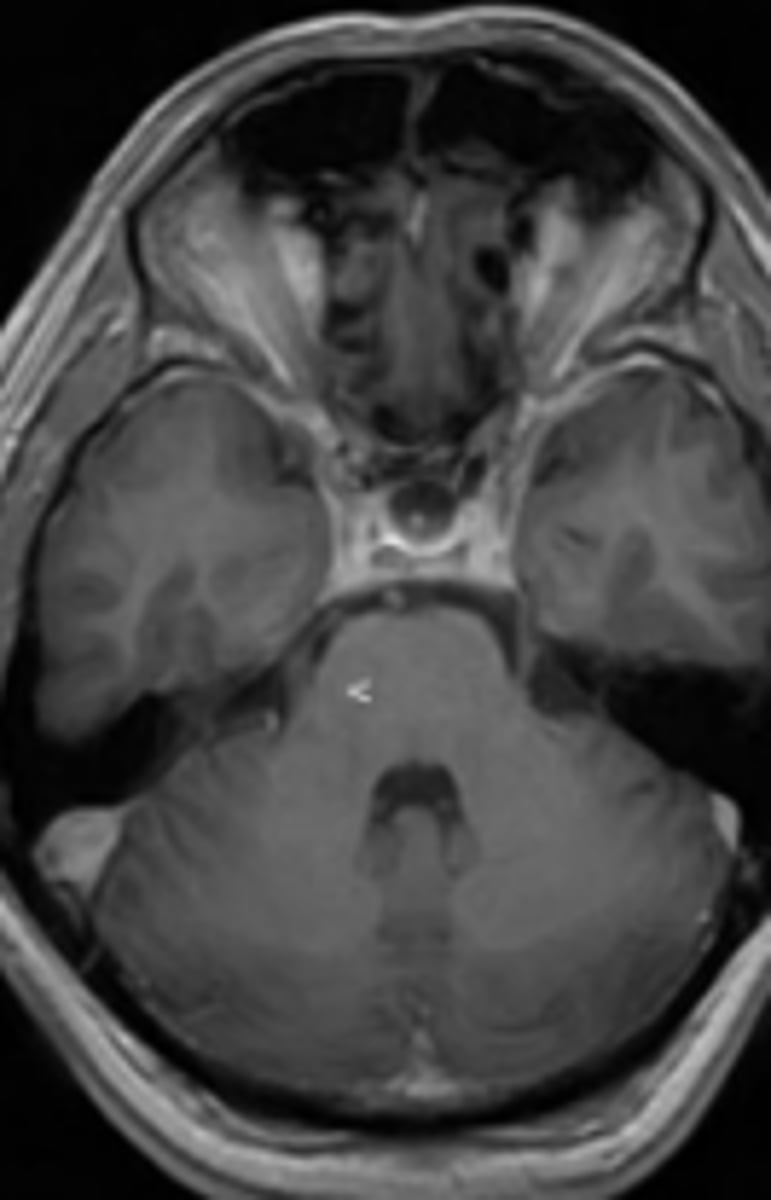
Diffusion
MRI sequence used for tumor characterization and cerebral ischemia
Anophthalmos
a rare, complete failure of optic vesicle development occurring week 1-3 of embryological development. Can result in the disruption of development of other ocular structures including the orbit, lacrimal gland, lids, etc.
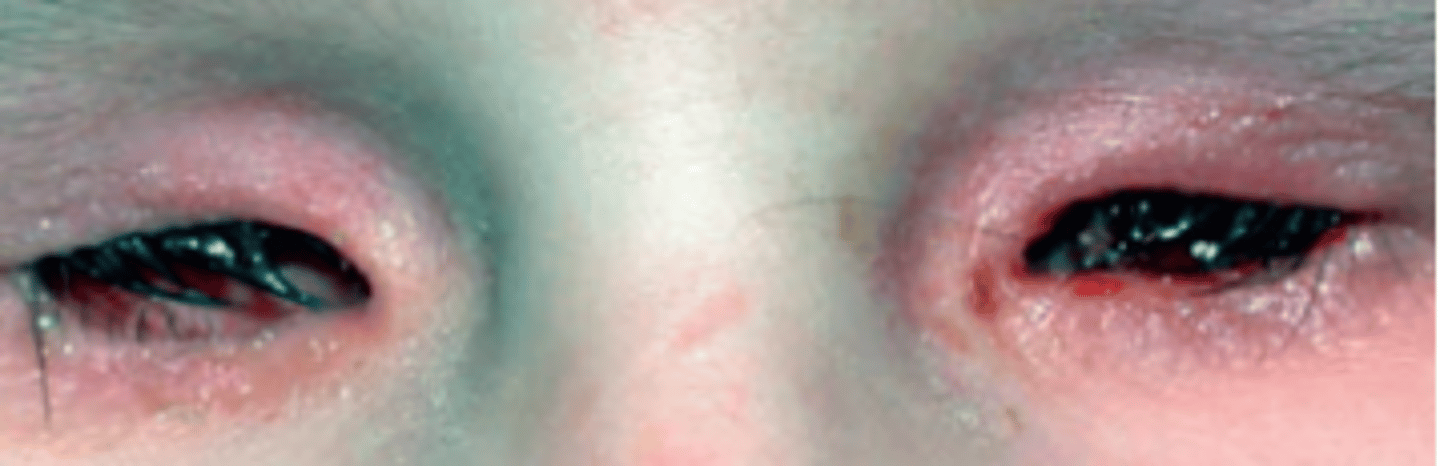
Microphthalmos
an arrest of ocular growth (unilateral or bilateral) leading to total axial length 2+ standard deviations below the age similar controls. Results from a developmental problem of the globe at any stage of growth of the optic vesicle after week 4 of embryological development.
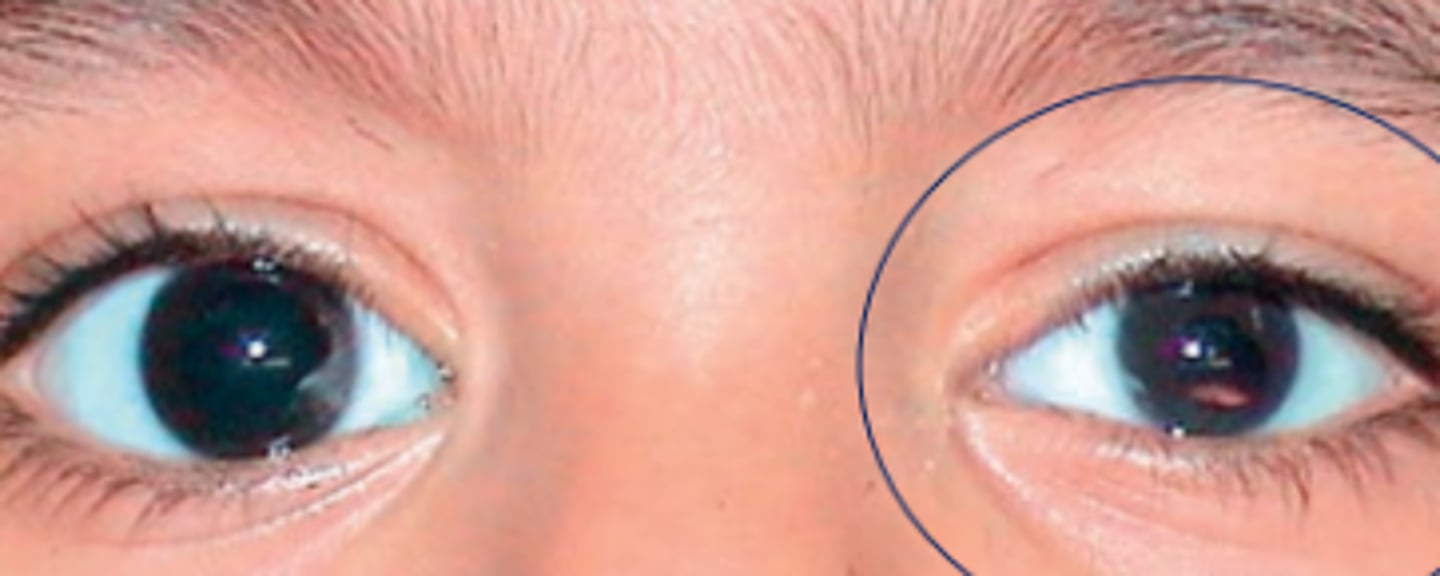
Simple
form of microphthalmos occurring without other ocular malformations
Complex
form of microphthalmos occurring with a coloboma, usually of the iris.
Cystic
form of microphthalmos occurring with a cyst.
Hypertelorism
an abnormally large pupillary distance.
Hypotelorism
an abnormally small pupillary distance.
Craniosynostosis
premature fusion of one (more common) or more of the cranial sutures resulting in malformation of the head shape. Can occur independently or as part of a syndrome.
12-18
Cranial sutures will normally fused around ____ months of age
Misshapen head
impaired brain development
increased intracranial pressure
orbital deformities
four complications of craniosynostosis.
Scaphocephaly (MOST COMMON)
premature sagittal suture fusion resulting in the elongation of the skull in the anterior-posterior direction leading to a bossing of the forehead. Is more common in boys (4:1)
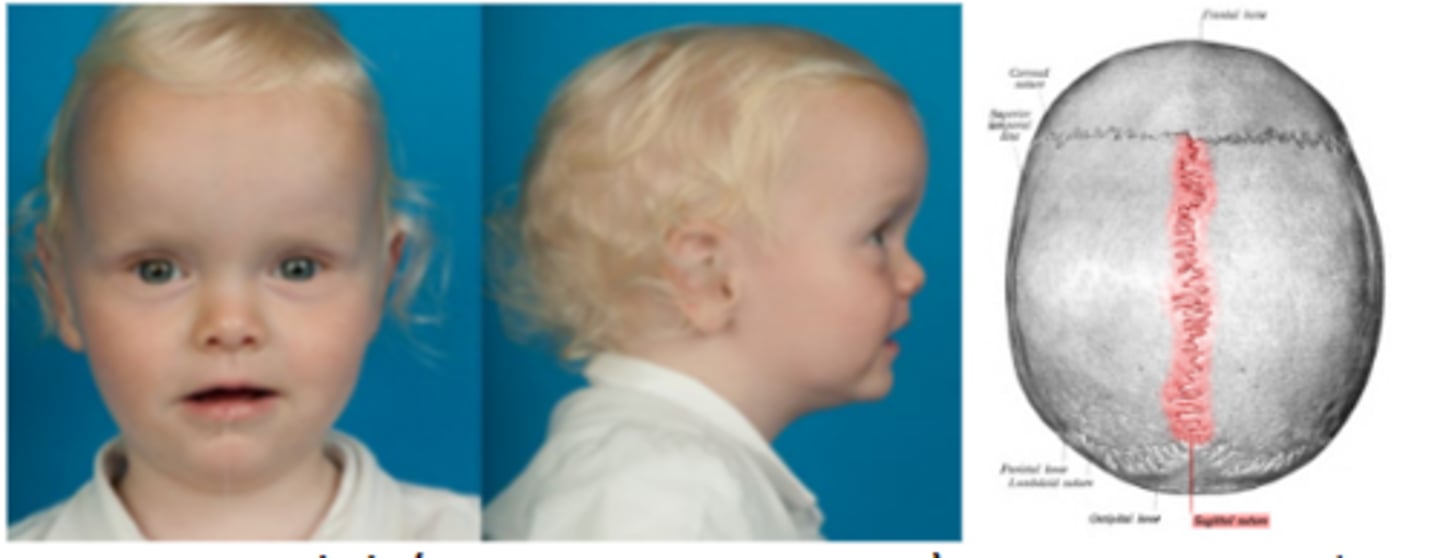
Trigonocephaly (SECOND MOST COMMON)
premature metopic (frontal) suture fusion resulting in a high, retreating, triangular forehead. Is also associated with hypotelorism due to migration of the eyes following cranium growth.
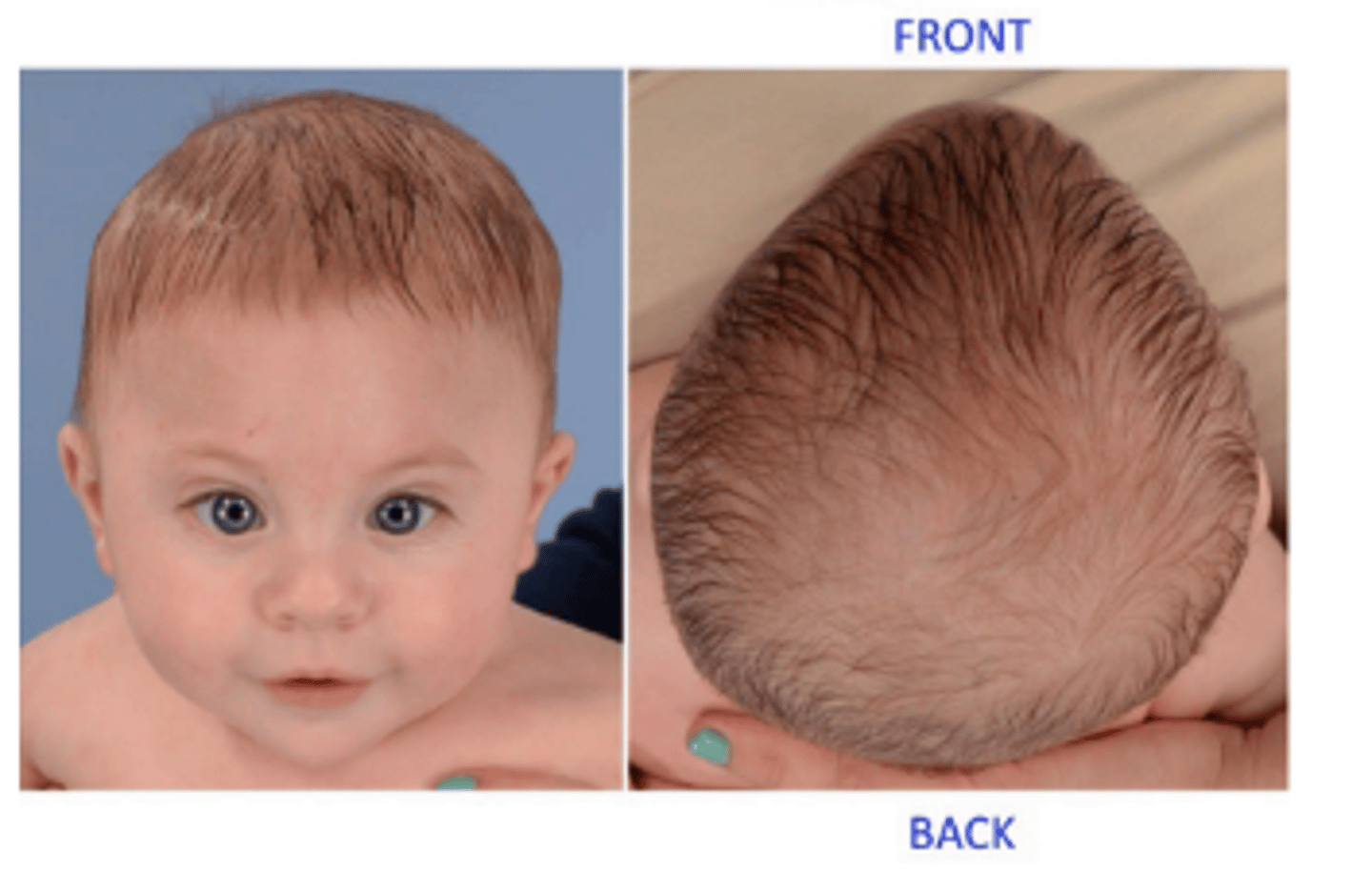
Brachycephaly
premature fusion of the coronal sutures resulting in the shortening of the skull in the anterior-posterior direction.
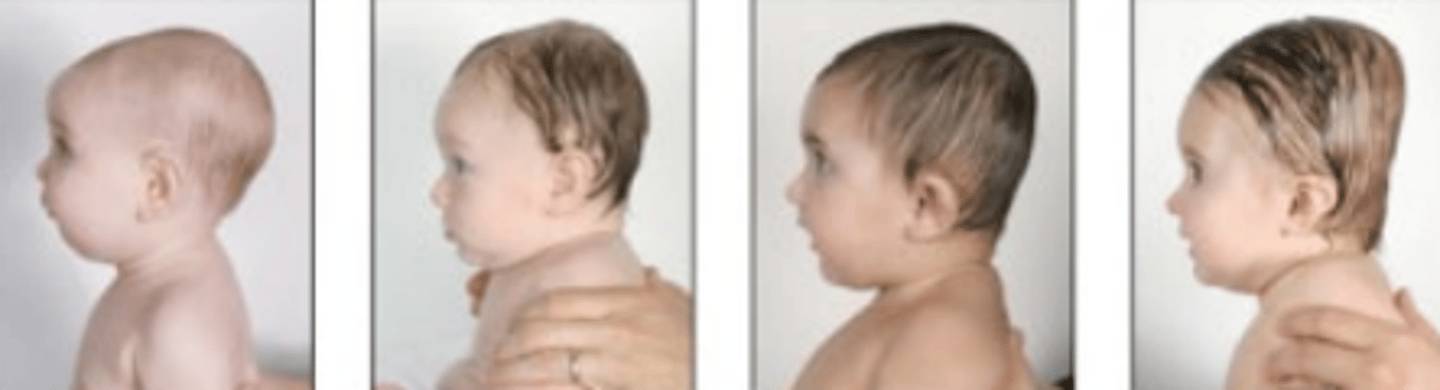
Plagiocephaly
premature unilateral fusion of all cranial sutures on a single side of the head resulting in a flattening of one side of the skull producing a rhomboid shape.
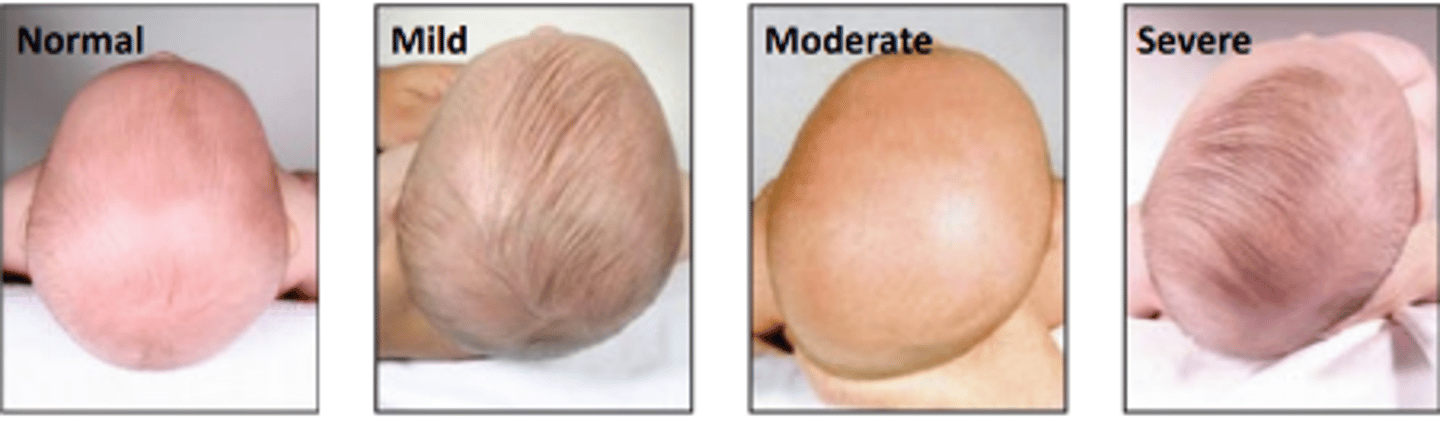
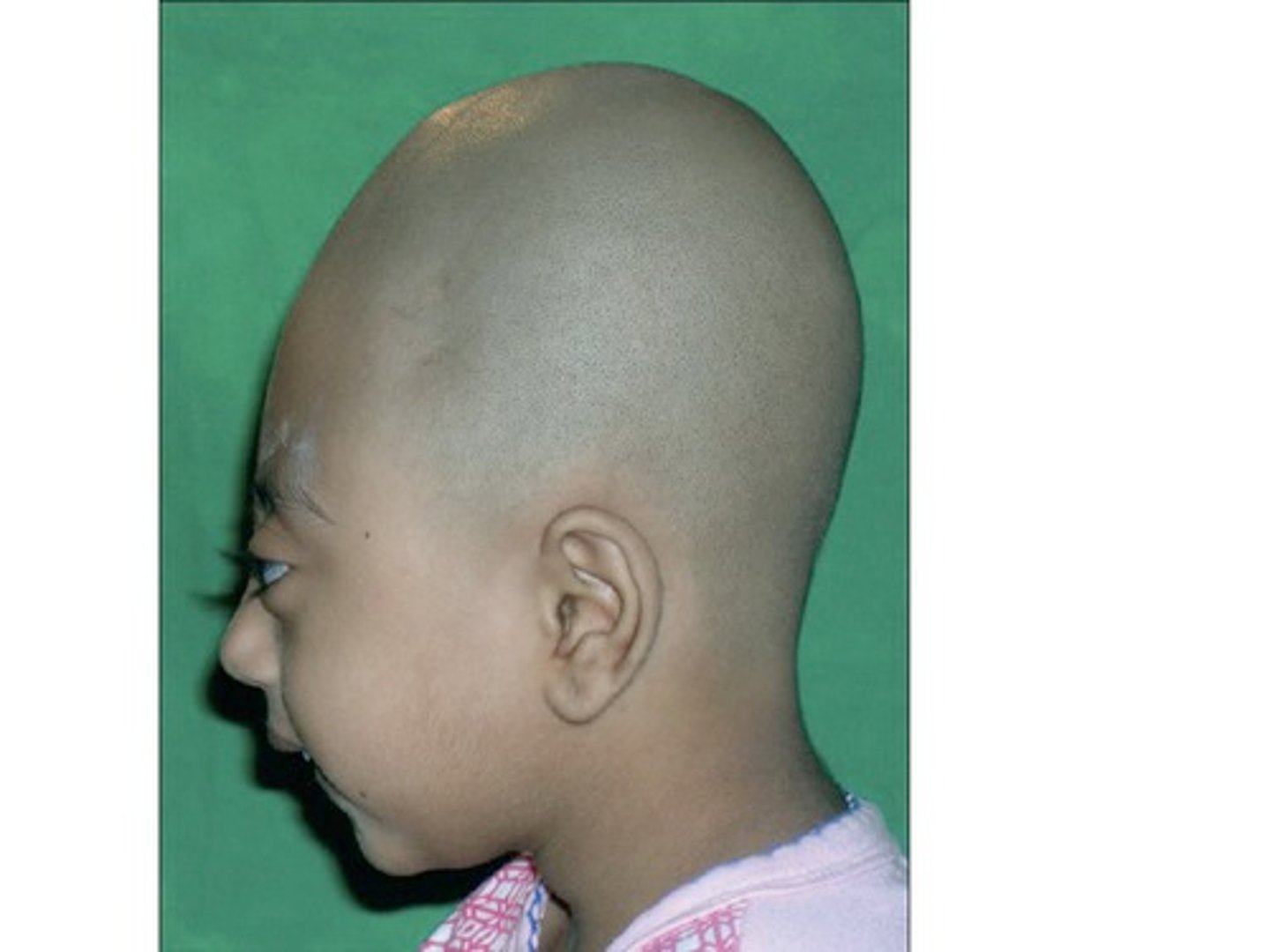
Oxycephaly
Premature fusion of all cranial sutures resulting in a cone shaped skull. Is the most severe form of craniosynostosis.
Orbital dystopia
a vertical misalignment of the orbit which can be congenital (craniosynostosis) or acquired via trauma or mass of the orbit.
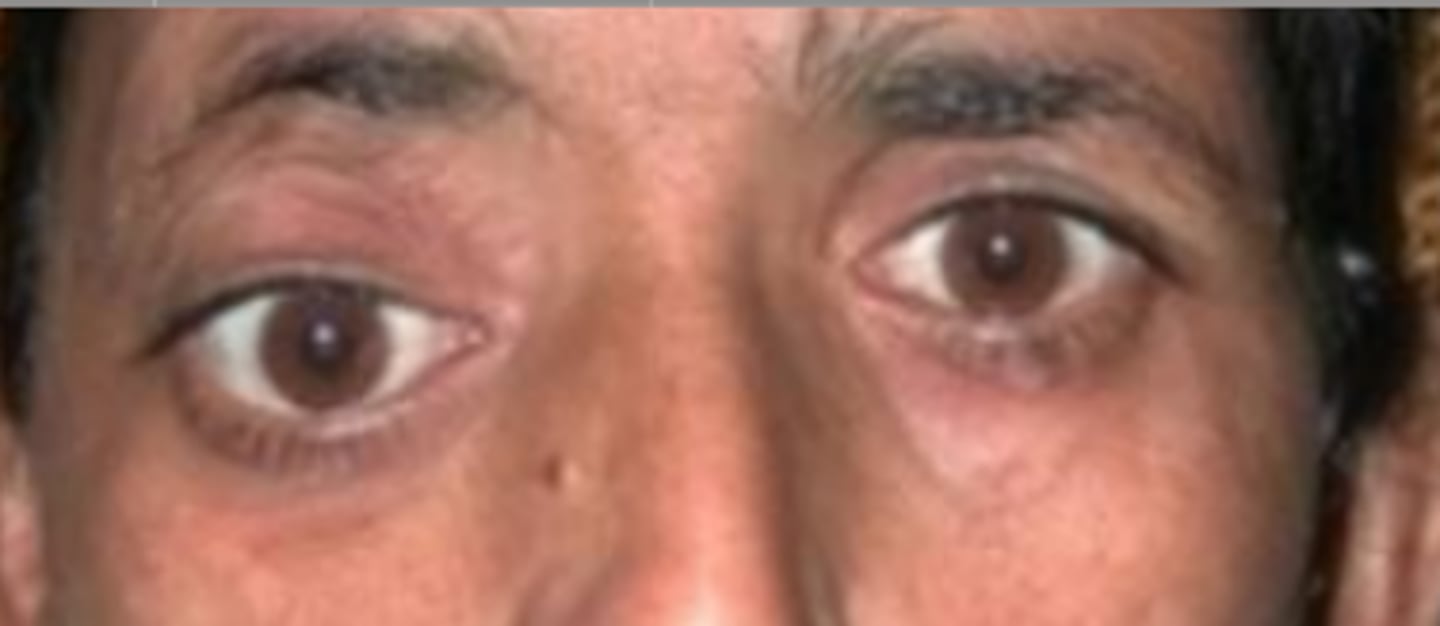
11-24 mm
normal range of exophthalmos
18 mm
average Asian exophthalmos value
20 mm
average Caucasian exophthalmos value
24 mm
average African American exophthalmos value
2
Any difference of exophthalmos values between the two eyes greater than ___ mm should be investigated
Couzon's disease
the most common cranio-facial syndrome occurring due to mutation of the fibroblast growth factor gene (FGFR2) or by spontaneous mutation 50% of the time. Begins in the first year and completes by the 2nd to 3rd year. Involves brachycephaly, underdevelopment of the maxillary and zygomatic bones, wide cranium, hearing loss, and V shaped palate. Characteristic "frog like face".
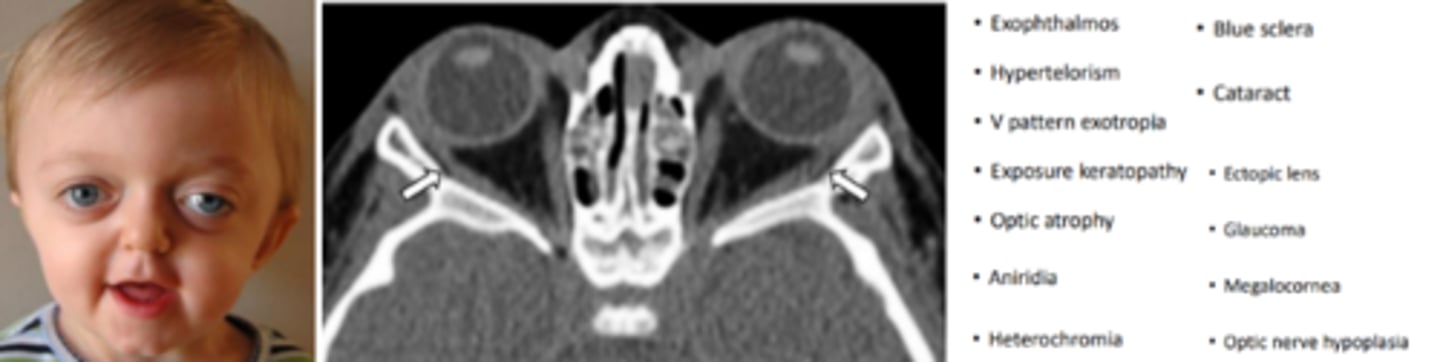
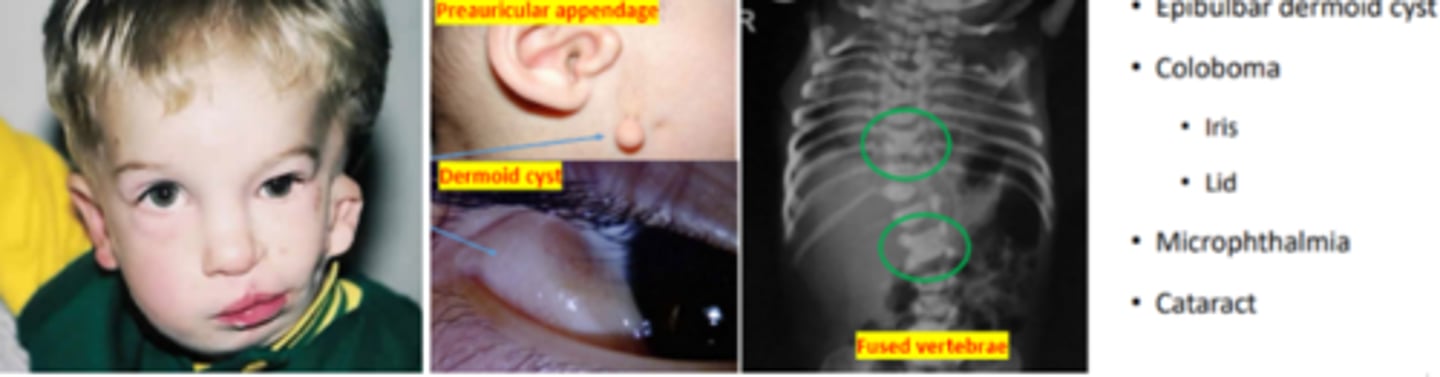
Goldenhar syndrome (oculo auricular vertebral dysplasia)
syndrome involving malformation of the ear, eye, and vertebra. Is the second most common cranio-facial syndrome. Appears as a triad of craniofacial microsomia, spinal abnormalities, and ocular dermoid cyst. Is more common in males (3:2).
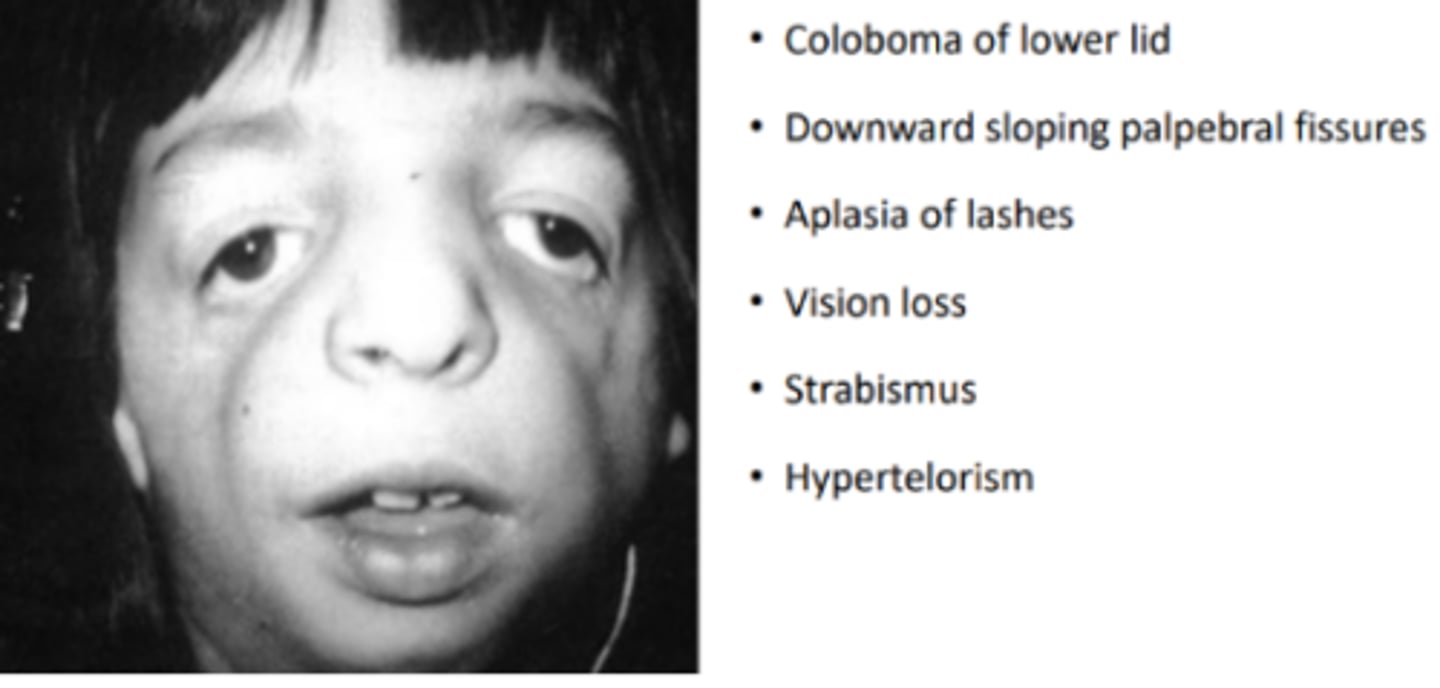
Mandibulofacial dystoses (Franceschetti syndrome, Treacher Collins syndrome)
a craniofacial syndrome caused by an autosomal dominant mutation of the TCOF1 gene resulting in hypoplasia of the zygomatic, maxillary, and mandibular bones. Is also commonly associated with underdevelopment of the ear and hearing, cleft palate, and airway problems. May or may not have impaired intelligence.
Hallerman Streiff syndrome (Oculomandibulodyscephaly)
a rare craniofacial syndrome caused by spontaneous or autosomal recessive mutation. Results in a "bird face" and other facial abnormalities.

Apert's syndrome
craniofacial syndrome involving brachycephaly, oxycephaly, high cleft palate, organ anomalies, mental handicap, and syndactyly.

Supportive therapy, strabismic therapy, epilation
three ocular treatments of cranio-facial syndromes
Meningocele
a rare, congenital neural tube defect resulting in meninges and CSF protruding through the orbit usually through a bony defect, and sometimes through a natural opening. Can be anterior or posterior variety.
Encephalocele
a rare, congenital neural tube defect resulting in a sac like protrusion of the meninges, CSF, and grey matter through an opening in the skull. Can be anterior or posterior variety. Is more common in females than in males. The more neural tissue that is herniated, the worse the prognosis of the condition is.
Mucocele
an acquired defect involving erosion of the orbital wall caused by mucoid secretions and epithelial debris seen in infection, trauma, allergy, or tumor. Ocular signs include proptosis, periocular edema, diplopia, and epiphora.
Cyclopia/synophthalmia
a rare failure of the prosencephalon to divide the orbits into two separate cavities. The paired ocular structures then become one central orbit where the nose is often missing. Incompatible with life.