Urinary physiology 2: How do nephrons work?
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What substances are reabsorbed in the proximal tubule of the nephron?
Na, Cl, glucose, amino acids, peptides, metabolites, urea, water
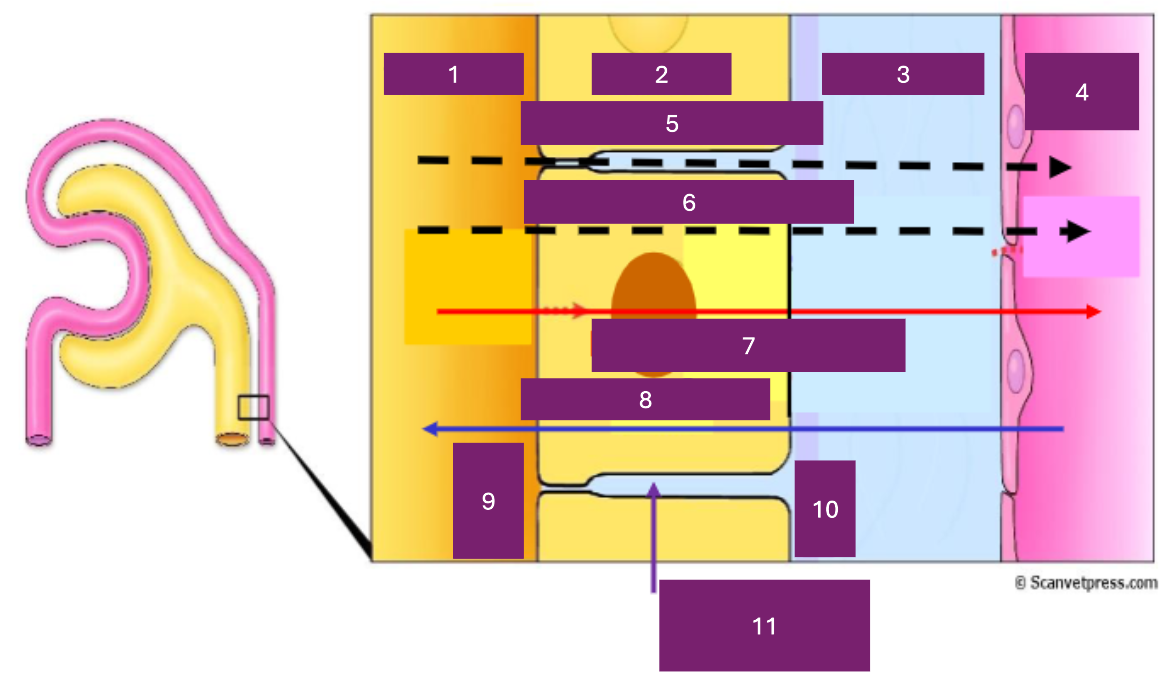
Name 1
tubular lumen
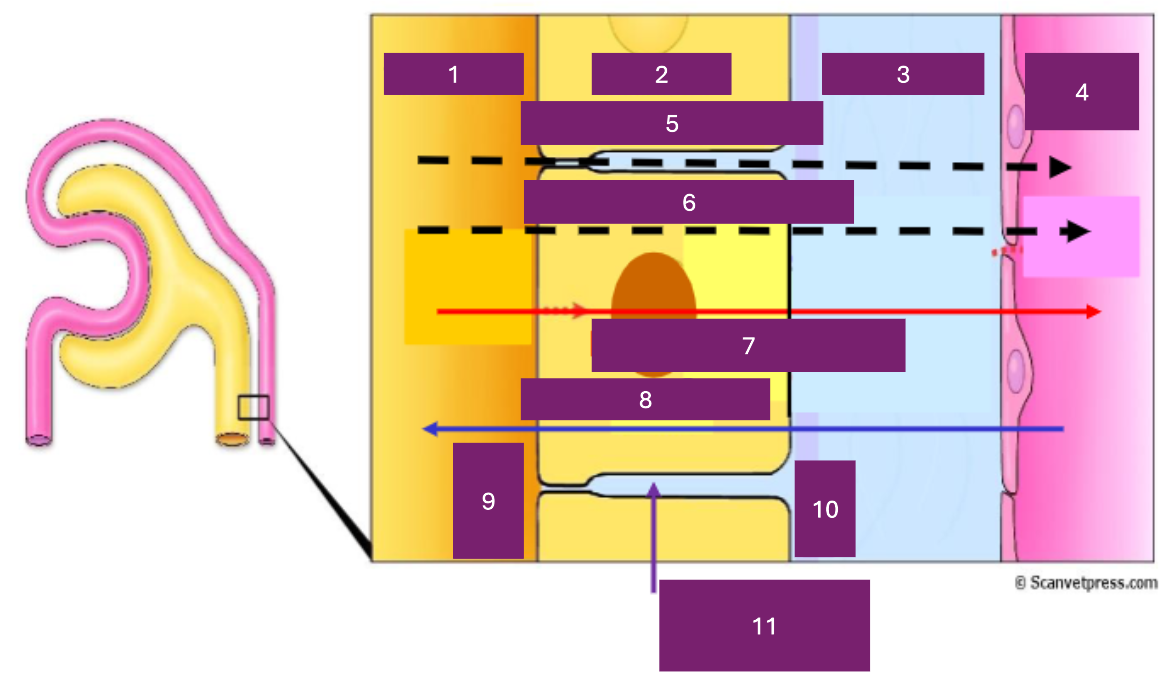
Name 2
tubular cell
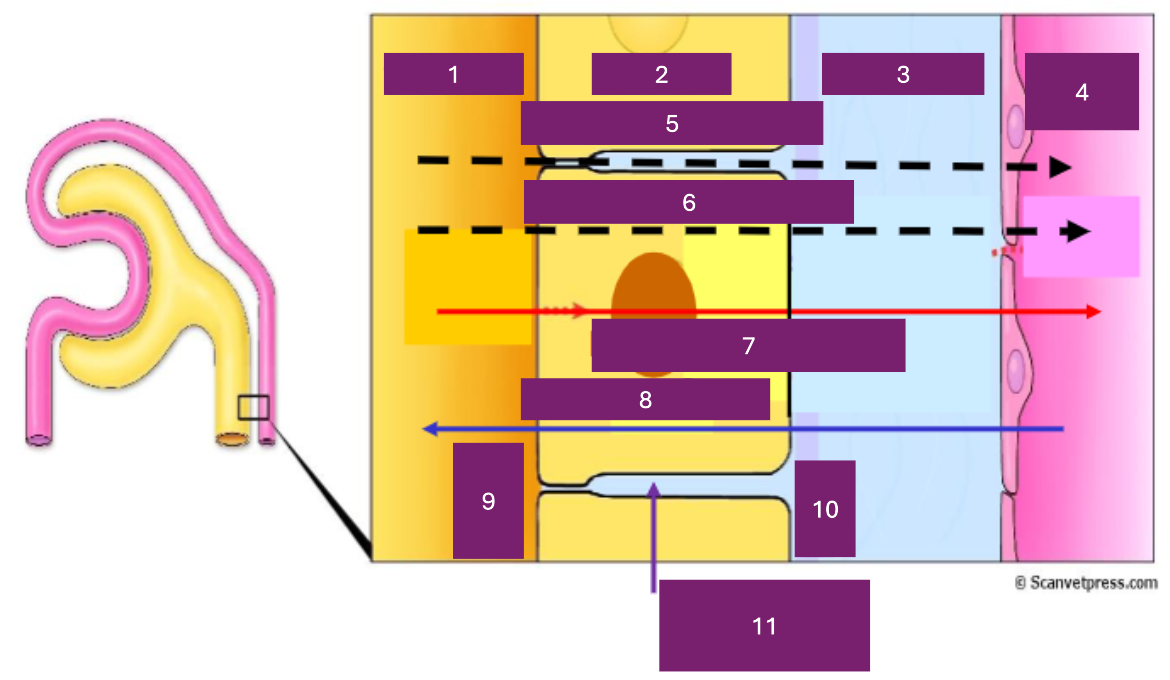
Name 3
interstitial fluid
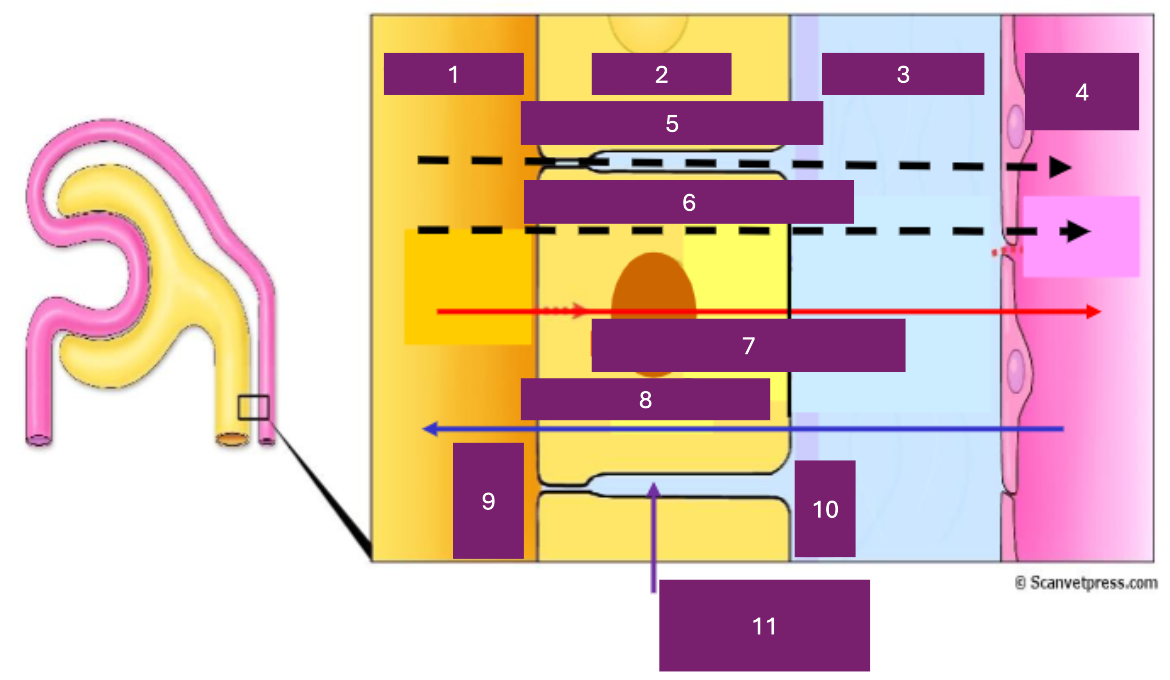
Name 4
capillary lumen
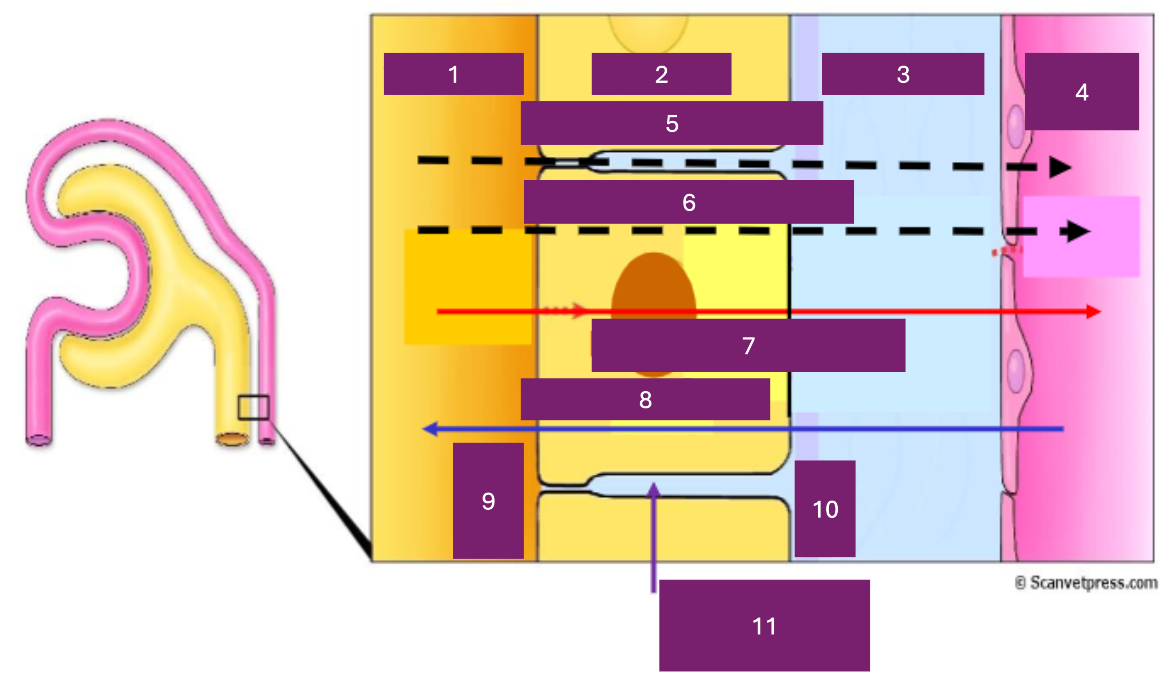
Name 5
Paracellular
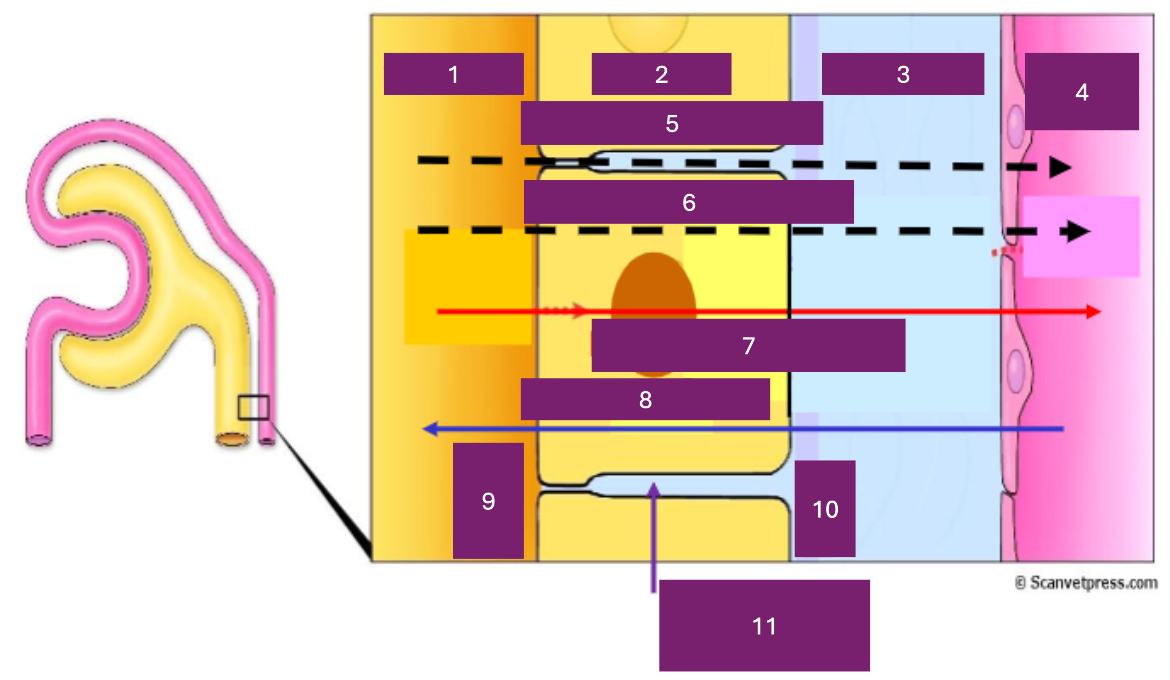
Name 6
transcellular
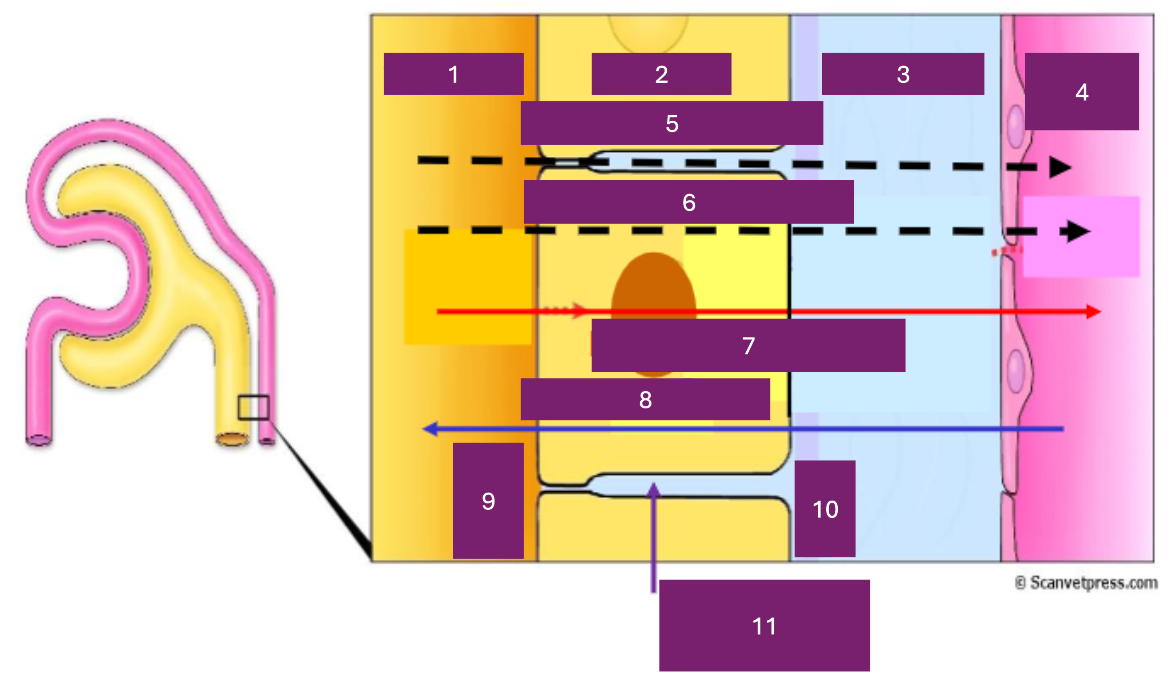
Name 7
reabsorption
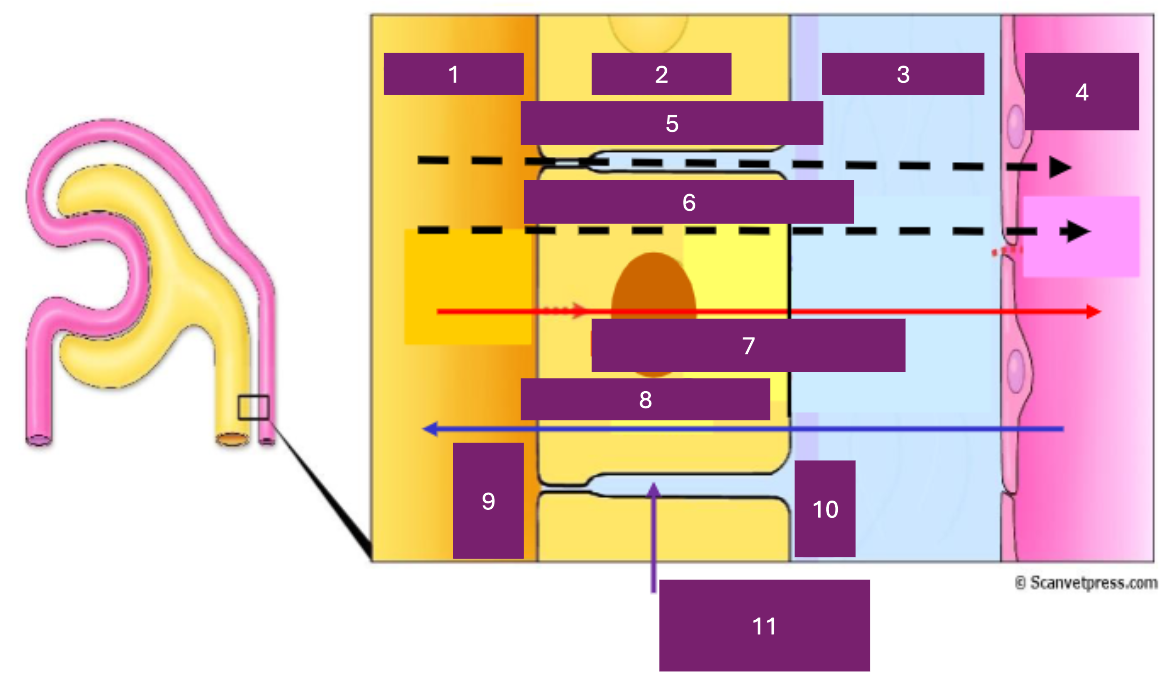
Name 8
secretion
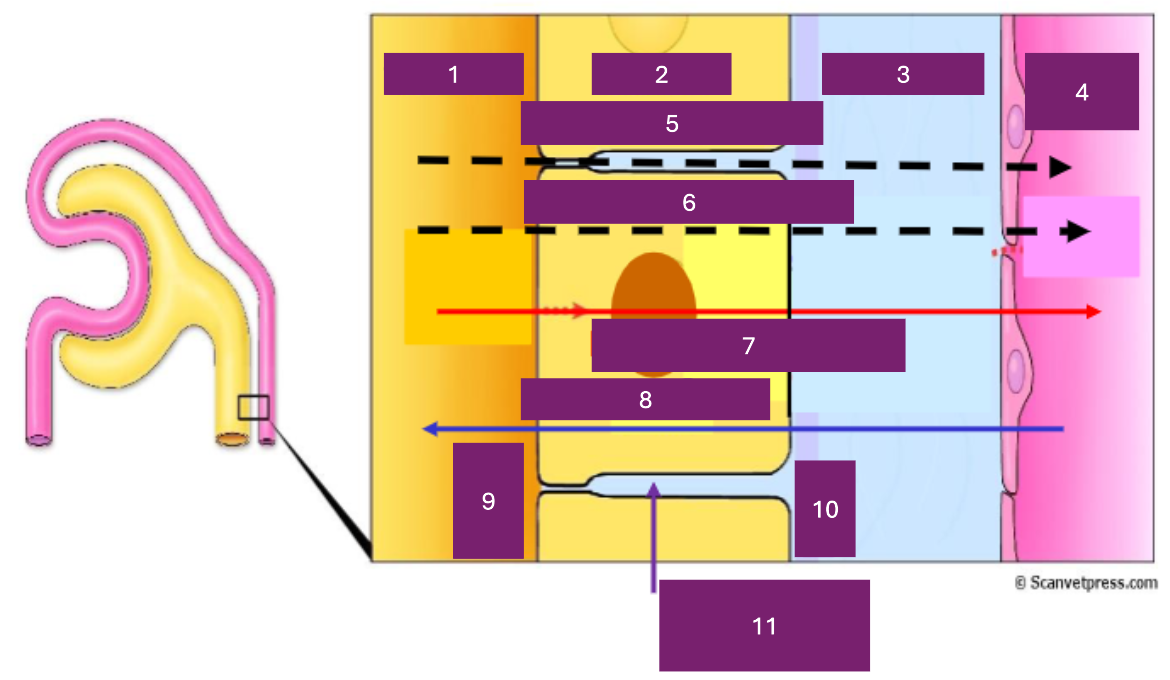
Name 9
apical
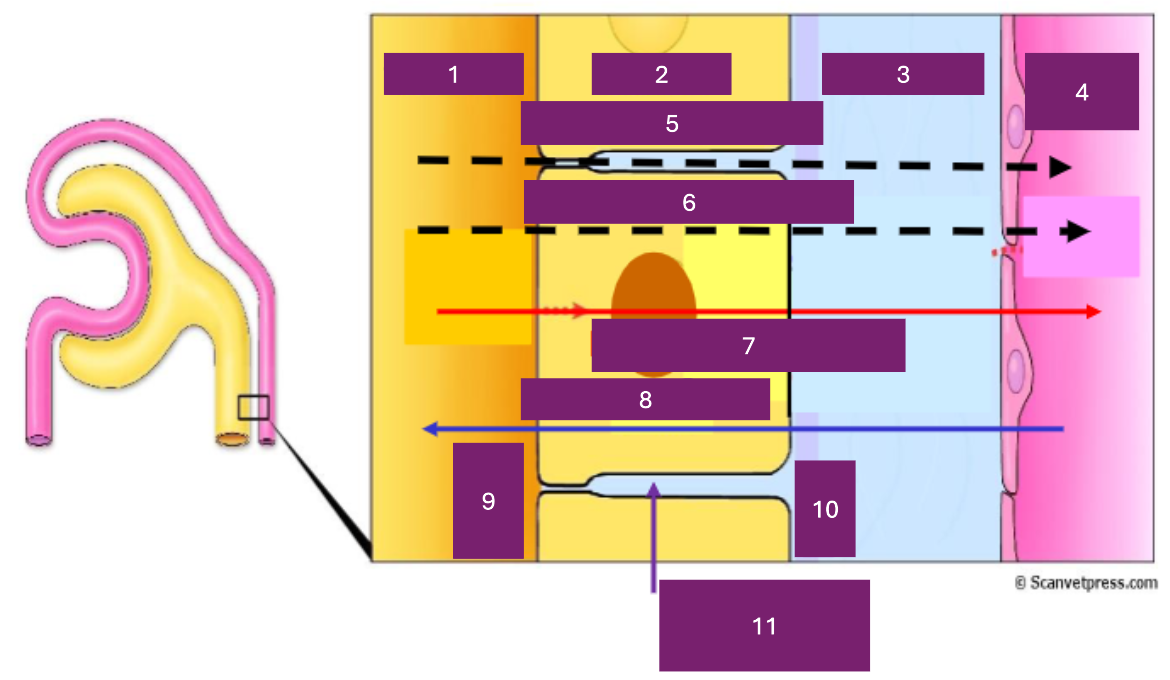
Name 10
basal
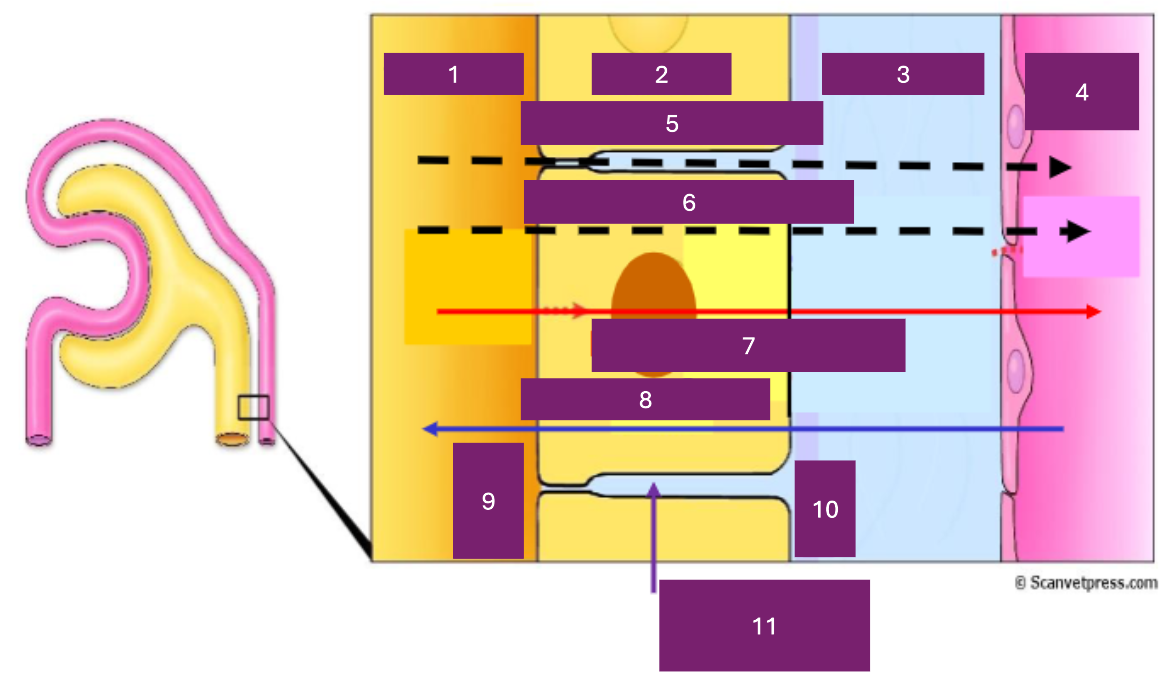
Name 11
basolateral space
Where is secretion (into the proximal tubule) from
capillary to tubular fluid
Name the 2 types of transport mechanisms
active, passive
Name the 2 types of active transport
primary and secondary AT
Active transport
metabolic energy required
passive transport
no metabolic energy required
primary active transport
coupled to ATP hydrolysis
secondary active transport
relies on Na gradient set up by Na+K+ATPase
How is the proximal tubule adapted for reabsorption?
located immediately after glomerulus
convoluted
peritubular blood has high oncotic pressure
tubule cells
How are tubule cells (in the proximal convoluted tubule) adapted for reabsorption?
brush border on apical surface
infoldings of basal membrane
many mitochondria
carriers/transporters for different solutes
tight junctions to reduce paracellular reabsorption
Which portion of the nephron does most transport occur in?
proximal tubule
Brush border (proximal tubule)
lots of infoldings on membrane
What does the brush border increase?
surface area
Antiport
counter transport
symport
co-transport
What transport mechanism is most reabsorption in the proximal tubule by?
secondary active transport
What drives movement of ions across the apical membrane?
sodium gradient
What enzyme is reabsorption in proximal tubule in basal and basolateral membranes driven by?
ATPase
Does reabsorption of glucose occur with or against the concentration gradient of glucose?
against conc grad
What is the reabsorption of glucose dependent on?
Na+ gradient
Where is almost all of filtered glucose resbsorbed?
proximal tubule
How much of filtered water is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule?
60-70%
Is reabsorption of water active or passive?
passive (osmosis)
Does the osmolarity of tubular fluid change in the proximal tubule?
NO
Where does variable reabsorption of water occur?
from the collecting duct
What is the osmotic effect in the proximal tubule aided by?
build up of solutes in clefts (basolateral spaces) between tubule cells
What drug affects cAMP?
aspirin
What drug affects bile salts?
penicillin
What drug affects prostaglandins?
several diuretics
What drugs affect adrenaline?
morphine
What drug affects noradrenaline?
isoprenaline
What drugs affect dopamine?
amiloride and atropine
What is the permeability of water like in the distal tubule?
low and constant
What gets reabsorbed in the distal tubule?
Na+ and Cl-
What is Na+ and Cl- reabsorbed via in the distal tubule?
NaCl symporter in apical membrane
What is the NaCl symporter in the apical membrane driven by? (distal tubule)
Na+K+ATPase in basal membrane
What is the normal osmolarity of the plasma of a dog?
290 mOsmol/L
What is the urine of a dog that had one bowl of water (500ml) in a day like?
less, more concentrated
What is the urine of a dog that has drunk lots of water (1.5L) in a day like?
more, dilute
What are the mechanisms that allow urine to be concentrated to an osmolarity higher than that of plasma?
generate osmotic grad in medulla
anatomical arrangement of LOH and CD
max urine conc directly proportional to length of LOH
What is the maximum urine concentration directly proportional to?
length of LOH
What are the features of the descending limb? (what it’s permeable to)
permeable to water
What are the features of the thin ascending limb? (what is is permeable/impermeable to)
impermeable to water
permeable to Na+ & urea
What are the features of the thick ascending limb? (what is is permeable/impermeable to)
impermeable to water & urea
Na+ and Cl- actively removed
What is high osmolarity in the medulla created by?
countercurrent multiplier
What is the name of the vessels that supply blood to the medulla?
vasa recta
What does counter current blood flow in vasa recta prevent?
‘wash out’ of salts in the medulla
Where does the collecting limb run in relation to the ascending limb?
parallel to AL of LOH with flow in opposite direction
What causes increased permeability of water in the collecting duct?
ADH (vasopressin)
How does water move out of the collecting duct?
by osmosis due to hyperosmotic medulla
What are the cortical and medullary sections of the collecting duct impermeable to?
water, urea and NaCl
When does permeability of water in the collecting duct increase?
in presence of ADH
When is permeability of the collecting duct to urea increased?
in medullary section by ADH
What percentage of urea is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule?
50%
In what part of the nephron does urea conc increase?
Loop of Henle
Why does tubular urea concentration increase in the cortical collecting duct?
removal of water
What receptors detect change in plasma osmolarity?
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus
What does excess fluid do to blood fluid osmolarity?
lowers it
What lowers blood fluid osmolarity?
excess fluid
What does fluid deprivation do to body fluid osmolarity?
increases it
What increases blood fluid osmolarity?
fluid deprivation
What does increase in osmolarity do? (ADH)
increases circulating levels of ADH
What does increasing circulating levels of ADH do?
increase water reabsorption
What does ADH act on?
collecting duct
What does ADH do to the collecting duct?
inserts aquaporin channels
Where does ADH insert aquaporin channels?
apical membrane