CH 11: the Prokaryotes: Domains, Bacteria, and Archaea
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Highlight the bacteria and then tell why they fit into one of the categories such as phylum, class, etc. highleighed term memsn she said to know it.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
the Prokaryotes: Domains, Bacteria, and Archaea
•One circular chromosome, not in a membrane
•No histones
•Lack organelles
•Peptidoglycan cell walls
•Binary fission
Phylum- Proteobacteria
Class -a (alpha) Proteobacteria
•Human pathogens:
•Bartonella- human pathogen
•B. hensela Cat-scratch disease
•Brucella (obligate paracites) Brucellosis- by contact with animals
The a (alpha) Proteobacteria
Obligate intracellular parasites:(produce only in a mamalian cell)
• Ehrlichia. Tick-borne, ehrlichiosis
•Rickettsia. Arthropod-borne, spotted fevers, by insect bites
R. prowazekii Epidemic typhus (transmitted by lice)
R. typhi Endemic murine typhus (by rat fleas)
R. rickettsii Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever(by ticks)
The a (alpha) Proteobacteria
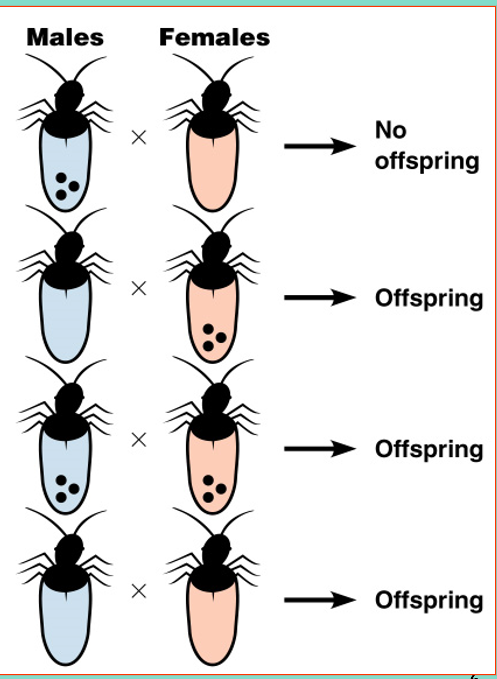
•Wolbachia. Live in insects and other animals
most popular in the bacteria world since it effects insects- spread fast
The a (alpha) Proteobacteria
•Caulobacter. Stalked bacteria found in lakes
•Hyphomicrobium. Budding bacteria found in lakes
budding releases genetic material to other cell and the cell that receives it is not similar to the parent cell
The a (alpha) Proteobacteria
•Nitrobacter and Nitrosomonas
•Chemoautotrophic:
Oxidize nitrogen for energy
Fix CO2
Nitrobacter. NH4+ to NO2–
Nitrosomonas. NO2– to NO3
The a (alpha) Proteobacteria
•Nitrogen-fixing bacteria:
Azospirillum
Grow in soil, using nutrients excreted by plants
Fix nitrogen
Rhizobium
Fix nitrogen in the roots of plants
nitrogen in the soil- crop rotation
The b (beta) Proteobacteria
•Thiobacillus
Chemoautotrophic, oxidize sulfur: H2S to SO42–
The b (beta) Proteobacteria
•Neisseria
Chemoheterotrophic, diplococci
Inhabit mucous membranes of mammals
N. meningitidis
N. gonorrhoeae
•Spirillum
Chemoheterotrophic, helical spirochetes
In fresh water
The b (beta) Proteobacteria
•Bordetella
Chemoheterotrophic, rods, whooping cough
B. pertussis
•Burkholderia. Nosocomial infections, grow in disinfectants, contaminate drugs equipment and durgs in hospitals
•Zoogloea. Slimy masses in aerobic sewage-treatment processes
The g (gamma) Proteobacteria
•Pseudomonas
Opportunistic pathogens
Metabolically diverse
Polar flagella
•Azotobacter and Azomonas- Nitrogen fixing
•Moraxella -Conjunctivitis-inflammation of membrane the covers the eye and lines the eyelids
•The g (gamma) Proteobacteria
•Order-Enterobacteriales (enterics):
Peritrichous flagella, facultatively anaerobic
Enterobacter\
Erwinia
Escherichia
Klebsiella
Proteus
Salmonella
Serratia- on catheters
Shigella
Yersinia
The g (gamma) Proteobacteria
•Pasteurella
Cause pneumonia and septicemia, transmitted by dog and cat bites
•Haemophilus- in mucous
Require X (heme) and V (NAD+, NADP+) factors
The e (epsilon) Proteobacteria
•Campylobacter
One polar flagellum
Gastroenteritis
The e (epsilon) Proteobacteria
•Helicobacter pylori
Multiple flagella
Peptic ulcers
may be associated with some stomach cancers
cyanobacteria
•Nonproteobacteria, gram-negative
•Oxygenic photosynthesis
•Gliding motility
•Fix nitrogen
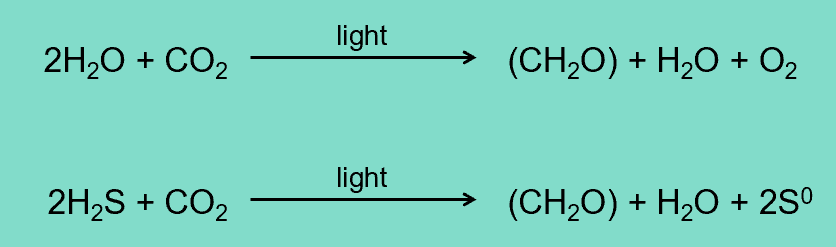
Purple and Green Photosynthetic Bacteria
•Anoxygenic (not producing oxygen) photosynthesis
•Purple and green sulfur bacteria
Phylum- Chlamydia
•Transmit to human by interpersonal contact or by respiratory routes
•C. trachomatis
Trachoma-blindness in human
STD, urethritis
•C. pneumoniae
•C. psittaci
Causes respiratory disease psittacosis (ornithosis)
Phylum-Spirochaetes
•Coiled morphology, endoflagella (axial filamets)
•Borrelia (Lyme disease-transmitted by ticks or lice
•Leptospira (from water – urine of dogs, rats and swine)
•Treponema (Treponema pallidum- cause of syphilis)
Phylum- Fusobacteria
•Fusobacterium
Found in mouth and intestine
May be involved in dental diseases
Phylum Firmicutes order Clostridiales
•Low G + C Gram positive bacteria
•Clostridium
Endospore-producing
Obligate anaerobes
Order-Bacillales
Bacillus
Endospore-producing rods
Staphylococcus
Clusters of Cocci
Order-Lactobacillales
•Generally aerotolerant anaerobes, lack an electron-transport chain
Lactobacillus
Streptococcus
Enterococcus
Listeria
Order-Mycoplasmatales
•Wall-less, pleomorphic
•Lack a cell wall
•0.1 - 0.25 µm
M. pneumoniae
Domain Archaea
•Hyperthermophiles
Pyrodictium
Sulfolobus
•Methanogens
Methanobacterium
•Extreme halophiles
2000 m deep in the ocean
Halobacterium
Microbial Diversity
•PCR indicates up to 10,000 bacteria/gm of soil. Many bacteria have not been identified or characterized because they:
Haven't been cultured
Need special nutrients
Are part of complex food chains requiring the products of other bacteria
Need to be cultured to understand their metabolism and ecological role