Momentum& Work Force and Power&Circular Motion
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Collisions between balls - explain using Newton Laws
ball A applies a force to ball B
ball B must apply an equal and opposite force to ball A
This force opposes motion of ball A
ball A decelerates due to N2
there is then a resultant force on B accelerate B
the force act on balls are equal, so the change in momentum must be equal for both spheres
parachute and terminal velocity six markers
as parachute opens, upward force increases
velocity first decreases at a constant rate as drag is greater than weight
drag is decreasing, and eventually drag balances the weight
so no acceleration, resultant force is zero, terminal velocity is reached
why does a man in a train with support not lean back
man pulls back on the support
N3, support exerts an equal but opposite force on the man
the force is a resultant force on man
due to N1 man accelerates
with the same acceleration as the train
why the man lean back in a train ?
N1 resultant force = 0
friction between the floor and feet accelerates with the train
but the man continues travelling at the original speed so lean backward
Describe an experimental technique by which you could determine accurately the speeds of the trolleys after they separate
use 2 light gates, which display the time for trolley to pass the one gate to the other
measure the length between the two light gates using a meter rule
speed = length between the two light gates/time taken to pass
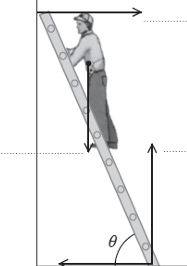
A person is standing on a ladder. Use the principle of moments to explain why the system is stable in the position shown but will topple over if theta becomes too large.
the ladder is stable because forces/moments are in equilibrium
when in equilibrium the clockwise momentum of the normal contact force at the wall is equal to the moment of the weight
taking moment about bottom of ladder
if theta is large enough, center of gravity is to the right of the bottom of the ladder
moment of weight is now clockwise
no anticlockwise moments, so total clockwise moments bigger than total anticlockwise moments
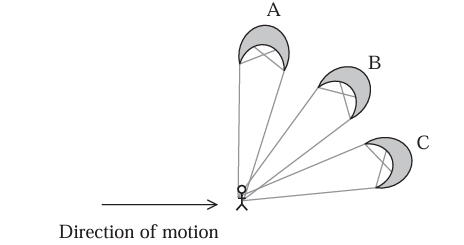
State and explain which position of the kite would supply the most power to the surfer.
horizontal component of the tension in the line produces the forward force acting on the surfer
as the angle to horizontal decreases work done increases
power transferred to surfer = work done/time has increased so the power increases
Explain why there is a maximum safe speed for a train travelling on a curved track
For train to travel on curved track, this requires centripetal force acting towards the centre
the centripetal force is provided by the reaction/friction force
F = mv2/r
when speed is at maximum, exceeds the maximum value of reaction force then train leaves the track