BIOPSYCH: Major structures of the brain
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Nucleus
Cluster of neurons in the central nervous system
Tracts
Bundle of nerve fibers (axons)
Peduncle
Stem-like connector
Gyrus
A ridge on the cerebral cortex
1. Forebrain
2. Midbrain
3. Hindbrain
Main divisions of the brain
1. Prosencephalon (Forward brain)
2. Diencephalon (Between-brain)
3. Telencephalon (End-brain)
What consists the forebrain?
Mesencephalon (Middle brain)
What consists the midbrain?
1. Rhombencephalon (Parallelogram-brain)
2.Metencepalon (Afterbrain)
3. Myelencephalon (Marrow-brain)
What consists the hindbrain?
Thalamus, hypothalamus
What are the major structures of diencephalon?
Cerebral cortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia
What are the major structures of telencephalon?
Tectum, tegmentum, superior colliculus, inferior colliculus, substantia nigra
What are the major structures of mesencephalon?
Hindbrain
- Both the myelencephalon and the metencephalon form the hindbrain
- Consists of the medulla, pons, and cerebellum
- Located at the posterior portion of the brain
Brainstem
It is made up by the hindbrain structures, the midbrain and other central structures of the brain
Myelencephalon
- Sometimes called the medulla or medulla oblongata
- Basic life support
- Situation between the pons and the brainstem
- Composed largely of tracts carrying signals between the rest of the brain and the body
- Contains the reticular formation
Reticular formation
Plays a role in arousal, attention, movement, maintenance of muscle tone, various cardiac, respiratory, and circulatory reflexes
1. Parvocellular Reticular nuclei (Lateral zone)
2. Gigantocellular reticular nuclei (Medial zone)
3. Raphe nuclei (Median)
4. Somatic motor control
Division of the reticular formation
Parvocellular Reticular nuclei (Lateral zone)
Division of the reticular formation that regulate exhalation
Gigantocellular reticular nuclei (Medial zone)
Division of the reticular formation that is responsible for motor coordination
Raphe nuclei (Median)
Division of the reticular formation where serotonin (5-HT) is synthesized which affects mood regulation
Somatic motor control
Division of the reticular formation that is responsible for tone, balance, and posture during body movements.
Relays eye and ear signals to the cerebellum so that the cerebellum can integrate visual, auditory and motor coordination
Medullary pyramids
Bundle of fibers (Pyramid tracts) that decussate and continue down the spinal cord on the contralateral side
1. Corticospinal tract
2. Corticobulbar tract
Two kinds of pyramidal tracts
Olivary bodies
- Medullary olives or Olives
- Pair of prominent oval structures that contain the olivary nuclei
Cerebral
Learning
Cerebellar
Learned/Muscle memory
1. Inferior Olivary nucleus
2. Superior Olivary nucleus
What consists olivary bodies?
Inferior Olivary nucleus
Part of the olivo-cerebellar system and is mainly involved in cerebellar motor-learning and function
Superior Olivary nucleus
Part of the pons and part of the auditory system, aiding in the perception of sound
Metencephalon
Houses many ascending and descending tracts and parts of the reticular formation
Bridge
What does Latin pons mean?
Pons
- Regulation of breathing (pneumotaxic center) and involved in the transmission of to and from other areas of the brain (Cerebrum to the cerebellum)
- Lies on each side of the medulla (ventral and anterior)
- Along with the medulla, contains the reticular formation and raphe system
1. Descending portion
2. Ascending portion
Portions of the reticular formation
Descending portion
Portion of the reticular formation that control the motor areas of the spinal cord
Ascending portion
Portion of the reticular formation that sends output to much of the cerebral cortex and selectively increasing arousal and attention
Raphe system
Sends axons to much of the forebrain, modifying the brain's readiness to respond to stimuli
Cerebellum
- Coordinate muscle movements, posture, and integrate sensory formation from the inner ear and proprioception in the muscles and joints
- Helps regulate motor movement, balance and coordination
- Important for shifting attention between auditory and visual stimuli
Proprioception
Sense of one's position and strength of effort
Compress brain size as it contains a large size of information
What is the purpose of the folds in the brain?
Tectum
- Roof of the midbrain
- Responsible for auditory and visual reflexes
Superior colliculus and inferior colliculus
Located on each side of the tectum and processes sensory information
Hill
Meaning of colliculi
Tegmentum
The intermediate level of the midbrain containing nuclei for cranial nerves and part of the reticular formation
Tegmentum
Floor of the midbrain
Substantia nigra
Gives rise to the dopamine-containing pathway facilitating readiness for movement
1. Tectum
2. Tegmentum (contains superior colliculus and inferior colliculus)
Divisions of mesencephalon
Superior colliculus
Responsible for visual
Inferior colliculus
Responsible for auditory
1. Periaqueductal gray
2. Substantia nigra
3. Red nucleus
Colorful structures of the tegmentum
Periaqueductal gray
A colorful structure of Tegmentum with a gray matter situated around the cerebral aqueduct. It mediates the analgesic effect of opiate drugs and acts as pain-receiver
Substantia nigra
A part of the tegmentum's colorful structure that is responsible for eye-movement, motor planning, reward-seeking, learning, and addiction and mediated by the striatum
Red nucleus
A part of the tegmentum's colorful structures that is vestigial in primate brains and is responsible for motor coordination (crawling in babies and arm swinging in walking)
Vestigial
A part that is evolutionary present but with unknown function; An evolutionary remnant
Diencephalon
Thalamus + Hypothalamus
Thalamus
A large, two-lobed structure that constitutes the top of the brain stem that both sit on each side of the third ventricle. A sensory "way-station" and is composed of many different pairs of nuclei which project to the cortex
Massa intermedia
Joins both lobes
Lamina
Screen/Surface
Internal capsule
Fibers (Corticospinal tracts) that join the telencephalon to the diencephalon. It carries motor information from the motor cortex downward.
Sensory relay nuclei
Most understood thalamic nuclei that receives signals from sensory receptors, process them, and then transmit them to appropriate areas of sensory cortex
Lateral geniculate nuclei, medial geniculate nuclei, and the ventral posterior nuclei
Relay stations in the visual, auditory, and somatosensory systems
Hypothalamus
Below the anterior thalamus where all senses get terminated and regulated sleeping, eating, and sexual behavior and hormones released by the pituitary gland
Hyperthyroidism
Release too much thyroid hormones that can cause anxiety like symptoms
Hypothyroidism
Release too few thyroid hormones that can cause depression like symptoms
Optic chiasm
It is where the nerves from the eyes decussate
Mamillary bodies
Spherical nuclei which has a role in recollective memory
Limbic system and the basal ganglia
Circuit of midline structures that circle thalamus
Fight, flight, feeding, and sexual intercourse
Four F's of behavior
Basal forebrain
Comprised of several structures that lie on the dorsal surface of the forebrain and contains the nucleus basalis
Nucleus basalis
Receives input from the hypothalamus and basal ganglia that sends axons that release acetylcholine to the cerebral cortex
and is responsible for arousal, wakefulness, and attention
Amygdala
Enhances emotional memory and does not store memory; Emotional memory and fear
Cingulate cortex
Linking motivational outcomes to behavior; Important for schizophrenia and depression
Fornix
Function is not entirely sure but correlates well with recall memory
Septum pellucidum
Anatomical barrier yet real function remains unclear, however it is associated with motivation, emotion, drives, and aggression. This part includes the olfactory bulb, hypothalamus, amygdala, and cingulate gyrus of the cerebral cortex.
Hippocampus
A large structure located between the thalamus and cerebral cortex and is critical for storing certain types of memory
Basal ganglia
Plays a role in the performance of voluntary motor responses
Putamen
Responsible for planning, learning (Reinforcement learning, implicit learning, category learning, hate circuit (with insula)) and execution, motor preparation, specifying of amplitudes of movement, and movement sequences
Globus pallidus
Regulates movement at the subconscious level
Pallidoctomy
Damage is cause in order to reduce involuntary muscle tremors
Central canal, ventricles
Parts of the canal system
Central canal
A fluid-filled channel in the center of the spinal cord
Ventricles
Four-fluid filled cavities within the brain containing cerebrospinal fluid
Telencephalon
Largest division of the human brain and mediates the brains most complex functions
as it initiates voluntary movements, interprets sensory input, and mediates complex cognitive processes such as learning, speaking, and problem solving
Cerebral cortex
The most prominent part of the mammalian brain and consists of the cellular layers on the outer surface of the cerebral hemisphere and is more highly developed in humans than other species
Corpus callosum and anterior commissure
Two halves of the cerebral cortex
Frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobes, and occipital lobe
Four lobes of the brain
Fissures
Large furrows in the brain
Longitudinal fissure
Divides both (cerebral) hemisphere
Cerebral commissures
Connect both hemisphere
Corpus callosum
Largest commissure
Sulci
Small furrows
Gyri
Ridges between fissures and sulci
Precentral gyri, postcentral gyri, and the superior temporal gyri
Largest gyri
Neocortex (New cortex)
Six layers of recent evolution
Pyramidal and stellate
Two types of cells which abound from cortices I to VI
Hippocampus
Memory specifically for spatial locations
1. Contains up to six distinct laminae (layers) that are parallel to the surface of the cortex
2. Cells of the cortex are also divided into columns that lie perpendicular to the laminae
3. Divided into four lobes: Occipital, parietal, temporal and frontal
Organization of the cerebral cortex
Postcentral gyrus
Analyze sensations of the body
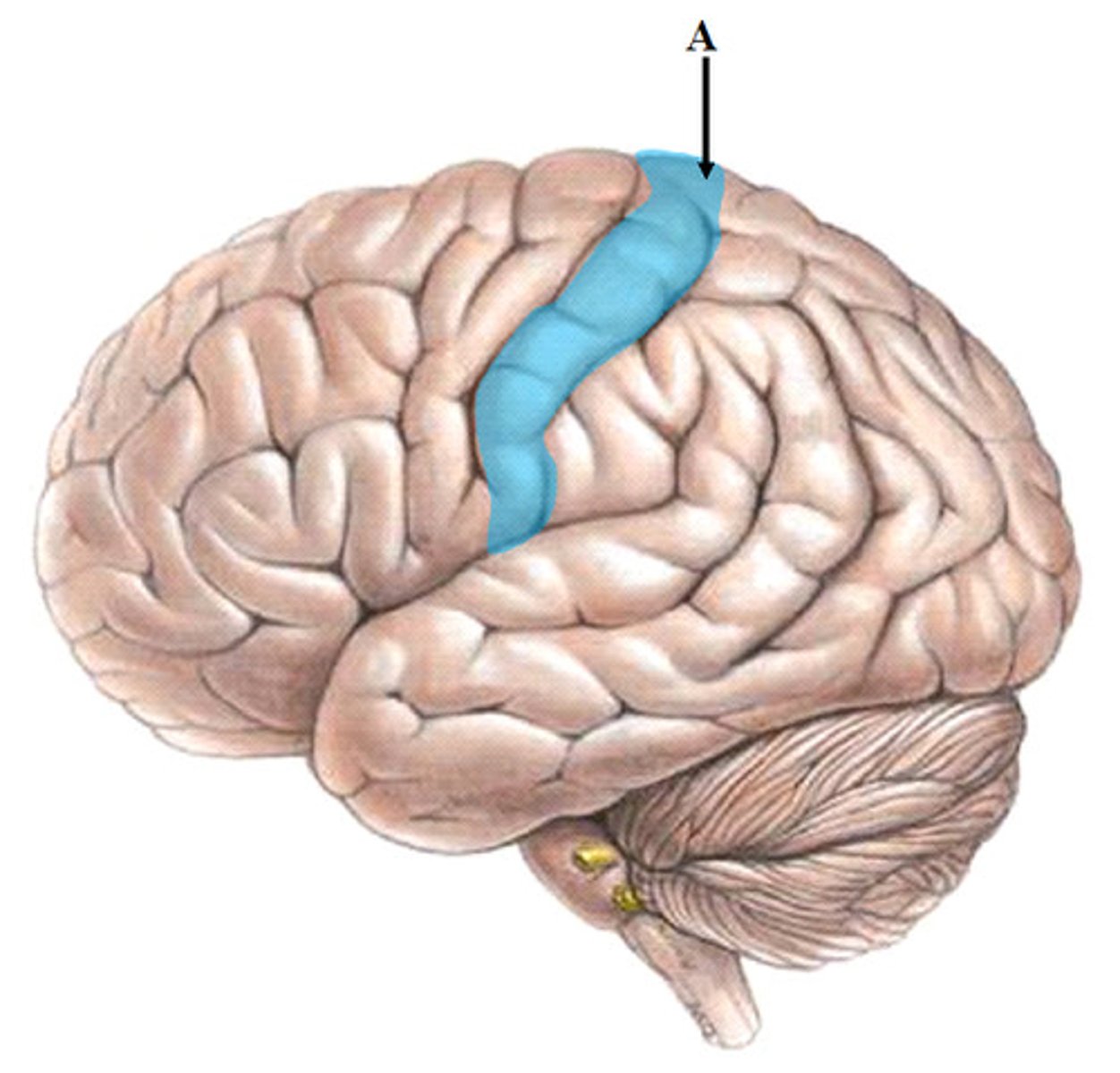
Precentral gyrus
Motor function
Gyrus rectus/orbital gyri
Function is unclear and is viewed as primitive development but is linked with personality and hypersexuality with men
Inferior frontal gyrus
Speech production
Superior temporal gyrus
Auditory processing and social cognition