APHG Unit 2 Vocab Review
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Population distribution
The pattern in which humans are spread out on Earth’s surface
Arable land
Land suitable for cultivation
Carrying capacity
The number of people a particular environment or Earth as a whole can support on a sustainable basis
metacity
A city with more than 20 million residents
megacity
A city with more than 10 million residents
ecumene
The portion of Earth’s surface with permanent human settlement
Population density
The average number of people per unit of land area
Rate of natural increase
The difference between the number of births and deaths in a given year, when expressed as a percentage of total population
Crude birth rate
The average number of births per 1000 people; the traditional way of measuring birth rates
Crude death rate
The number of deaths per year per 1000 people
Total fertility rate
The average number of children born per woman during her reproductive lifetime, considered to be from 15 to 49 years of age
Replacement level fertility
The average number of children needed to replace both parents and stabilize population over time
Life expectancy
The number of years a person can expect to live from birth
Dependency ratio
The number of dependents in a population that each 100 working-age people (ages 15 to 64 years) must support
Sex ratio
The ratio of the number of men to number of women in a population
Doubling time
The number of years it takes for a population to double in size
Overpopulation
Occurs when the human population exceeds the food supply
Pronatalist policies
Designed to boost fertility rates and ultimately population growth
Anti Natalist policies
Designed to stop population growth by reducing fertility rates
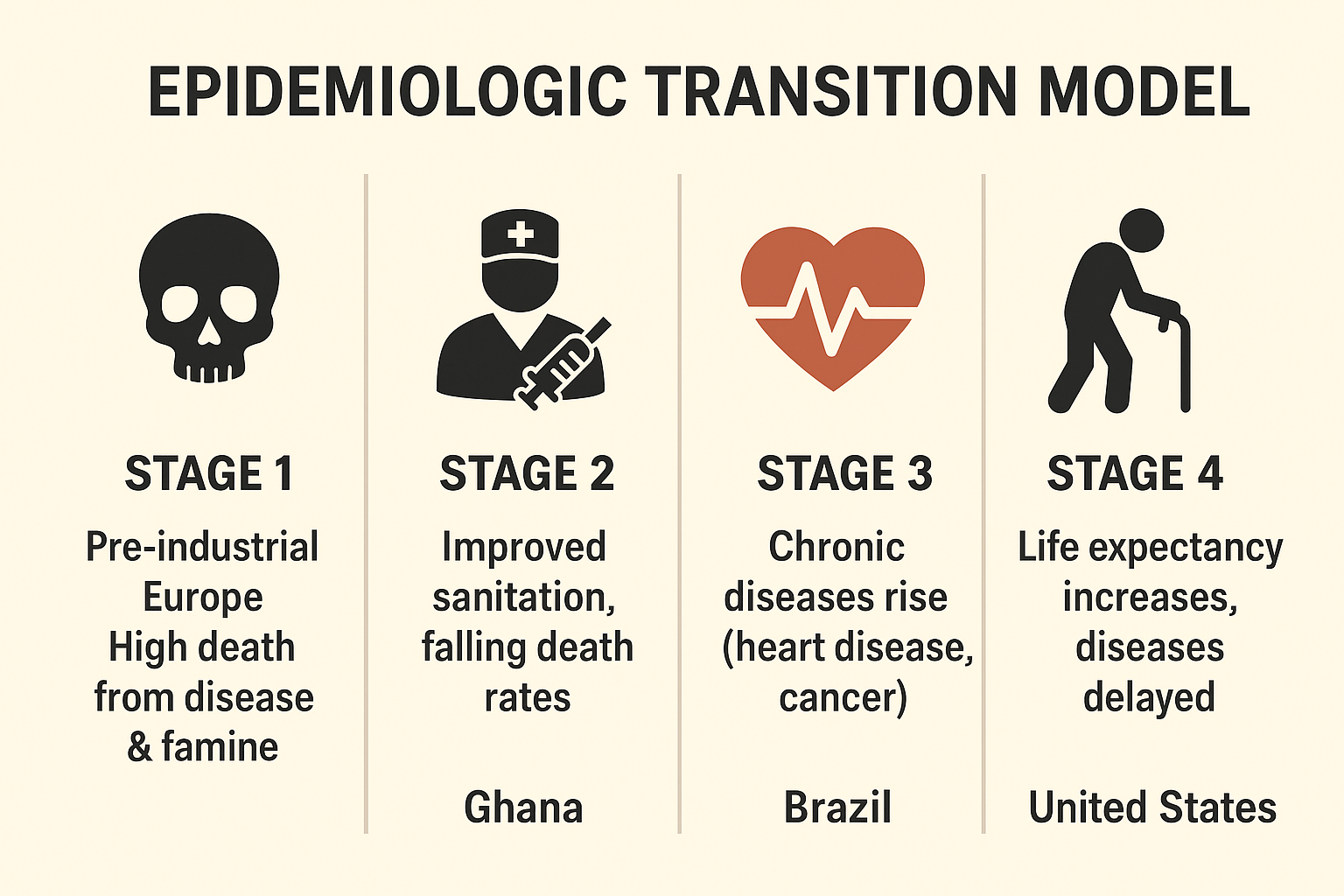
Epidemiological Transition Theory
Seeks to explain how changes in health services and living standards affect patterns of disease
migration
The long-term or permanent relocation of individuals, families, or entire communities from one place to another
Net migration
The difference between the number of in-migrants and out-migrants
Brain Drain
A phenomenon where a country or a place loses young, more educated, and skilled people through migration
Push factors
Factors that cause people to be dissatisfied with their present locales and want to move somewhere else
Pull factors
The attributes of other places that make them appealing to potential migrants
refugees
A person who leaves their country because of persecution based on race, ethnicity, religion, nationality, or political opinion
Internally displaced persons
Someone who remains within his or her country’s borders despite being persecuted by their home country
Asylum Seekers
Transhumance
A phenomenon where herders and their livestock move seasonally between their summer and winter pastures
Step Migration
Migration carried out in a series of stages, usually from nearby to bigger and more distant places
Chain Migration
The process by which some people’s migration to a new place leads their family members, friends, and others to move to the same place
Guest Workers
A person with temporary permission to work in another country
Intervening Obstacles
A complication that potential migrants will need to overcome to reach their destination
Intervening Opportunities
A nearby attractive locale where migrants may decide to settle instead of going to the intended destination farther away
Thomas Malthus’s Theory
-Population grows exponentially but food production increases linearly
-The world’s rate of population increase is far outrunning the development of supplies
*he was incorrect*
Neo Malthusian Theory
Malthus couldn’t predict how bad it would be b/c poor countries have the most rapid growth
-food production isn’t the only thing being affected by overpopulation (energy, etc)
Critics of Malthus
Say that the world’s food population is expanding, not fixed and that technology will change outcomes
-larger population will stimulate the economy
Arithmetic density (Total population / Total land area)
A general measure of how populated an area is, but doesn't account for the usability of the land
Physiological density (Total population / Arable (farmable) land)
Physiological density measures the number of people per unit area of arable land and indicates how many people a region's agricultural resources must support
Agricultural Density
The number of farmers per unit of farmland, which can indicate the level of agricultural efficiency