pre cal midterm review
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
hyperbola definition
a set of all points in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference from F1 and F2 is equal
parabola definition
set of all points are equidistance from a focus to a directrix
ellipse definition
set of all points where sum of each of the distances from focal points is d
circle definition
all points in a plane that are fixed distance from a fixed point
equation of a circle
(x-h)²+(y-k)²=r²
horizantal hyperbola equation
(x-h)²/a² - (y-k)²/b² =1
verticl hyperbola equation
(y-k)²/a² - (h-k)²/b² =1
horizantl parabola equaiton
(y-k)²=4p(x-h)
vertical parabola equation
(x-h)²=4p(y-k)
horizantal ellipse equaiton
(x-h)²/a² + (y-k)²/b²=1
verical ellipse eqution
(x-h)²/b² + (y-k)²/a²=1
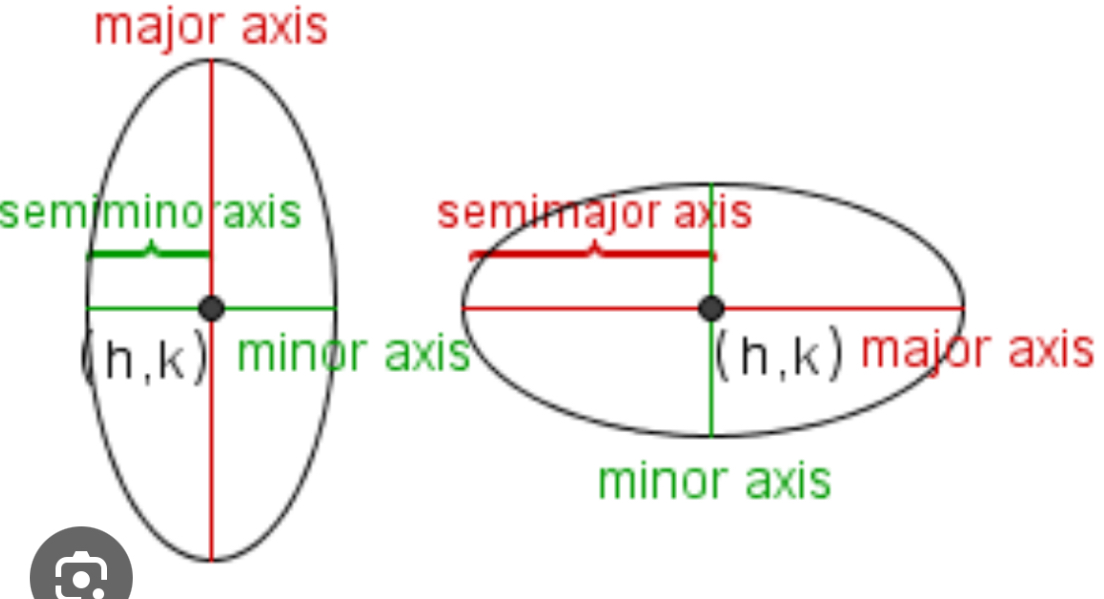
which one is a vertical ellipse?
on the left
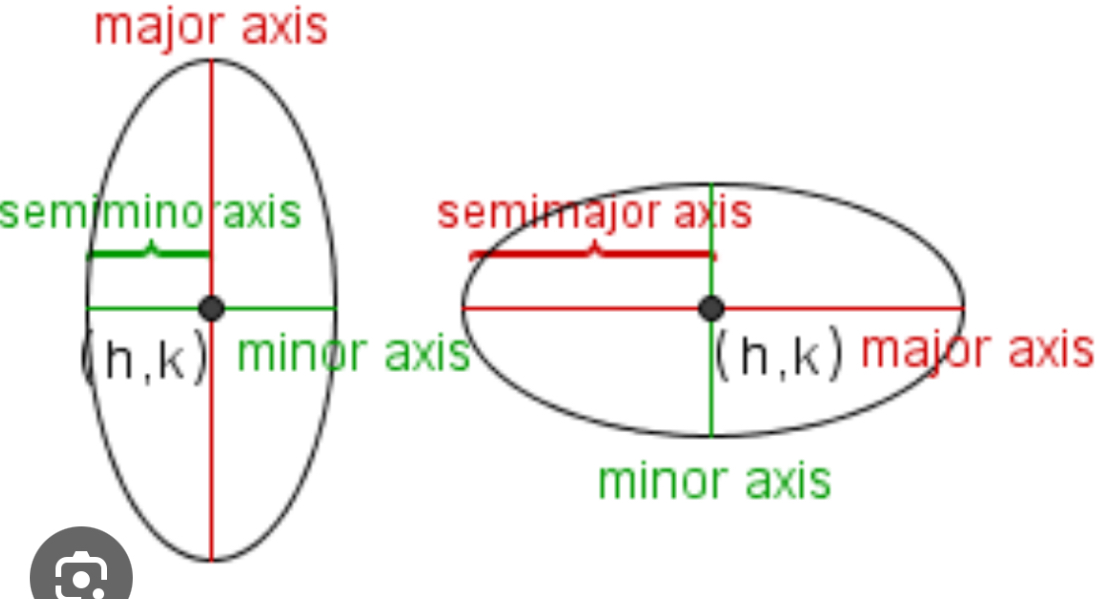
which one is a horizontal ellipse?
one on the right
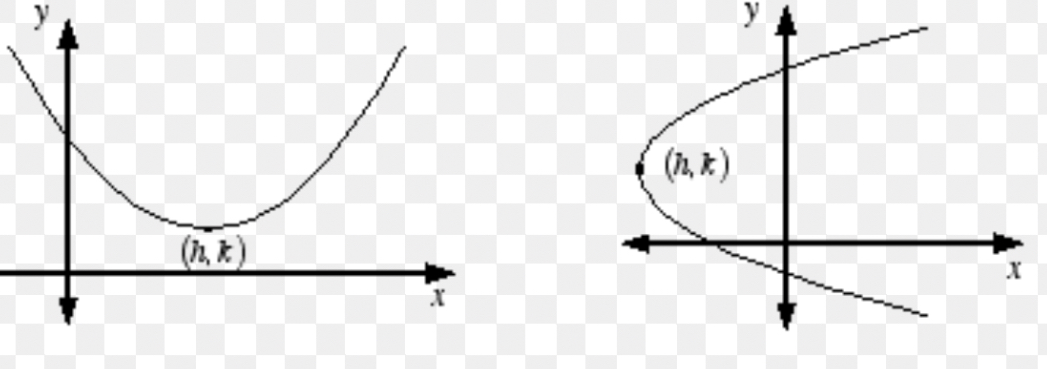
which one is a vertical parabola
one on the left
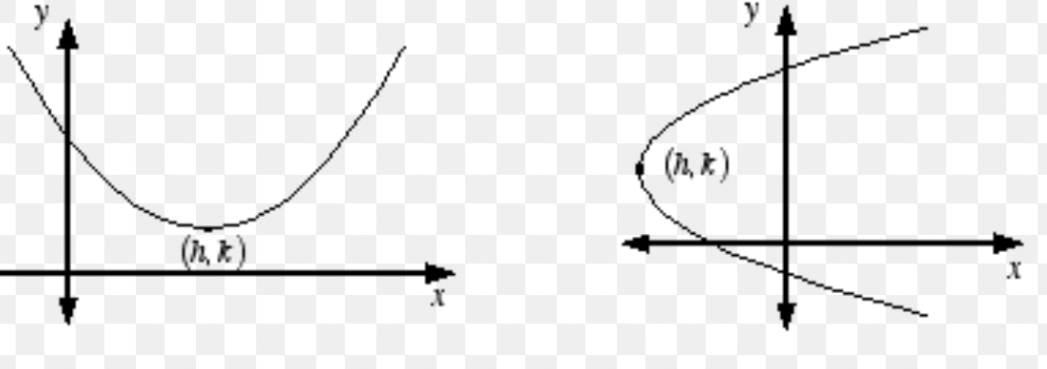
which one is a horizontal parabola
one on the right
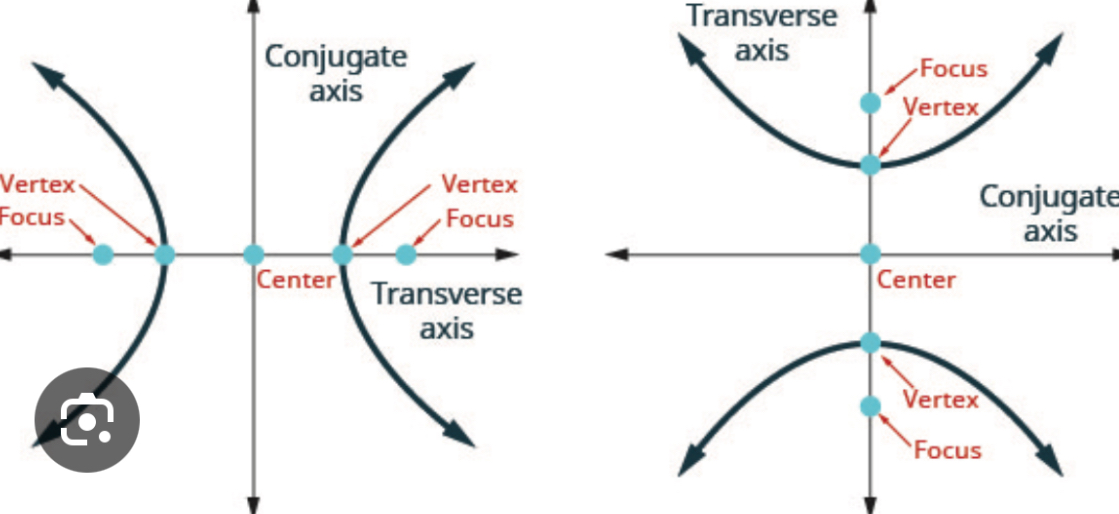
which one is a vertical hyperbola
one on the right
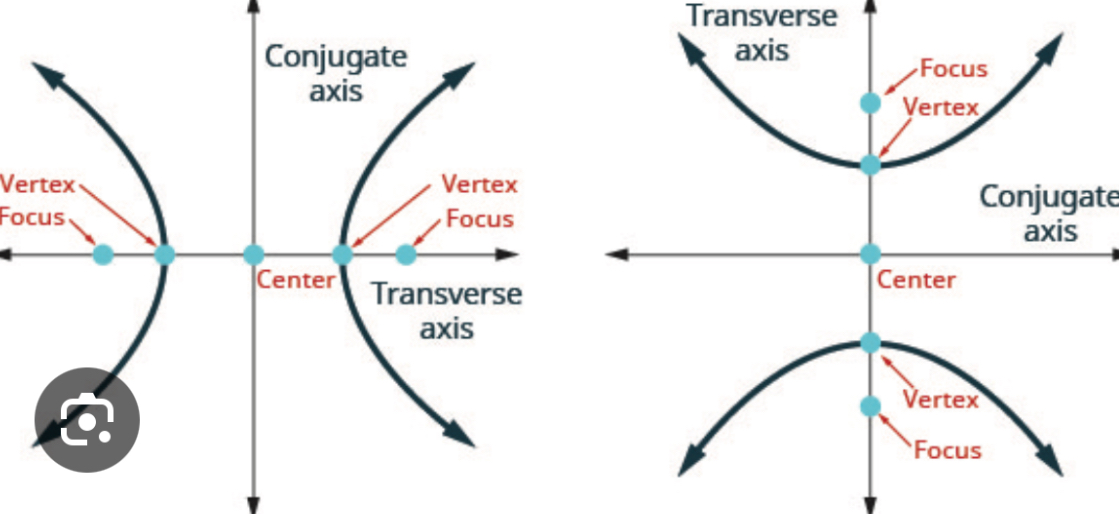
which one is a horizontal hyperbola
one on the left
what is the lacey’s rectum equal to?
4p and the focal diameter
what is p
the distance from the vertex to the focus
what is the directrix equation
x or y = h or k -p
what is the focus point for a horizontal parabola
(h+p,k)
what is the focus point for a vertical parabola
(h, k+p)
is 4p= a negative number
the parabola is facing downwards(vertical) or to the left(horizontal)
what are the vertices of a horizontal hyperbola
(h+-a,k)
what are the vertices of a vertical hyperbola
(h,k+-a)
what is c
the distance from the central to a focus point
what is the foci of a vertical hyperbola
(h,k+-c)
what are hr dock of a horizontal hyperbola
(h+-c,k)
what is eccentricity equal to
c/a
what is the ep major of a horizontal ellipse parallel to
the x axis
what is the ep minor of a horizontal ellipse parallel to
the y axis
what is the ep major of a vertical ellipse parallel to
the y axis
what is the ep minor of a vertical ellipse parallel to
the x axis
what is c²=a² - b² used for
ellipses
what is c²=a²+b² used for
hyperbolas
locus definition of a circle
the locus of all points in a plane that are a fixed, constant distance from a central point
locus definition of an ellipse
the locus of points in a plane where the sum of the distances from any point on the curve to two fixed points (foci) is a constant
locus definition of a parabola
the locus of all points that are equidistant from a fixed point (the focus) and a fixed line (the directrix)
locus definition of a hyperbola
the locus of points where the absolute difference of the distances from two fixed points (foci) is a constant
log function form
y=log (x+b)
a
half life formula
N(t)=N (1/2) ^t/t1/2
o
general conics equation
𝐴𝑥2+𝐵𝑥𝑦+𝐶𝑦2+𝐷𝑥+𝐸𝑦+𝐹=0
bijective function
both surjective and injective (every y value is used and every y value correspond to a singualar x value)
injective/ one to one function
every y - value corresponds with a singular x value, ex.lisd students to their chromebooks (everyone has there own but just 1)
surjective
every y value is used, even if an x value leads to 2 y values, ex. at a resturaunt 3 friends order different things but two friends order the same thing
domain for polynomial funtions
all real numbers
domain for rational function (fraction)
excludes factors that make the denominator 0
domain for square root function
excludes factor the make the number under the square root negative
domain for composite functions
find each components' domain restrictions and find the intersecction
why would a graph not have an inverse function?
the y values might repeat (in the original function) so in the inverse function it would make the x values repeat, making it not a function
sum-sum funcitons
linear
sum - constant 2nd difference functions
quadratic
product - product functions
power
sum -product funcctions
expoential
product - sum functions
logarithmic
on a graph a filled in dot means
greater/less than or equal to
on a graph an open dot means
greater/less than
if a value is greater than 1 and is in parenthesis/absolute value bars/under the root with x the graph has a
horizantal compression of the value touching x
if a value is less than 1 and is in parenthesis/absolute value bars/under the root with x the graph has a
horizantal stretch of the reciprocal of the value
if a value is greater than 1 and is in front of the parenthesis/absolute value bars/ root with x the graph has a
vertical stretch of the value
if a value is less than 1 and is in front of the parenthesis/absolute value bars/root with x the graph has a
verticl compression of the value
log(M) + log(N) also =
log(MN)
log(M) - log(N) also =
log(M/N)
log(M)^N also =
Nlog(M)
when something is raised to a fraction
power/root (raise to power of numerator then take the root of the denominator)
e =
2.7
exponential growth rate
A(t)=P(1+r)^t
compound growth rate
A(t)=P(1+r/n)^nt
compounded continuously
A(t)=Pe^rt
in the equation y=a•b^kt if b is greater than 1
it’s a growth model
in the equation y=a•b^kt if b is between 0 and 1
it’s a decay model
if your given a growth/decay model with a numerator above the a•b^kt that number is
the carrying capacity of the model
log N = x can also be written as
a
a^x=N