Biochemistry Final
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
Exam 1A-1
What is the reason for the existence of the hydrophobic effect?
a. the tendency of water molecules to make a bond with hydrophobic proteins
b. the tendency of polar molecules to self-associate in the presence of an aqueous solution
c. the tendency of nonpolar molecules to self-associate in the presence of an aqueous solution
d. the inability of charged molecules to dissolve in water
e. the property of nucleic acids to dissolve in water
c. the tendency of nonpolar molecules to self-associate in the presence of anaqueous solution
Exam 1A-2
All the following characteristics are found in eukaryotic cells EXCEPT for:
a. Linear chromosome
b. Presence of a nucleus
c. Presence of organelles
d. Circular chromosome
e. DNA base pair range 1 X 10^7 to 5 X 10^9
d. Circular chromosome
Exam 1A-3
Which statement about covalent bonds is INCORRECT?
a. A covalent bond is formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons between adjacent atoms.
b. If more than one electron pair is shared, then a covalent bond becomes stronger.
c. Existence of several resonance structures of nearly equal energies decreases stability of a compound.
d. Some molecules possess several patterns of covalent bonding.
e. The key properties of a bond are length and energy
c. Existence of several resonance structures of nearly equal energies decreases stability of a compound.
Exam 1A-4
What is the direct consequence of the bent shape of a water molecule?
a. Water is highly cohesive.
b. Distribution of charge is asymmetric.
c. Hydrogen atoms possess a net negative charge.
d. The oxygen atom possesses a net positive charge.
e. The water molecule can form hydrogen bonds.
b. Distribution of charge is asymmetric.
Exam 1A-5
What is the concentration of hydroxide ions [OH-] in an aqueous solution with pH 3?
a. 10^-11 M
b. 10^-14 M
c. 10^3 M
d. 10^-3 M
e. 10^11 M
a. 10^-11 M
Exam 1A-6
What is the number of hydrogen bonds formed between A and T nucleotides?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
b. 2
Exam 1A-7
Order the type of interactions by the bond strength from strongest to weakest.
a. hydrogen bonds, covalent bonds, van der Waals interactions
b. covalent bonds, van der Waals interactions, hydrogen bonds
c. van der Waals interactions, covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds
d. covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals interactions
e. hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, electrostatic interactions
d. covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals interactions
Exam 1A-8
For an acid HA that can dissociate into A- and H+, when the pH is equal to pKa, then:
a. the concentration of the protonated HA equals the concentration of the protonated A-
b. the concentration of the deprotonated HA equals the concentration of the deprotonated A-
c. the concentration of the protonated HA equals the concentration of the deprotonated A-
d. the concentration of the protonated HA is greater than the concentration of the deprotonated A-
e. the concentration of the protonated HA is less than the concentration of thedeprotonated A-
c. the concentration of the protonated HA equals the concentration of the deprotonated A-
Exam 1A-9
Buffers are important in biological systems because of their ability to:
a. prevent any changes in pH during exercise
b. resist changes in pH near the pKa of the buffer
c. allow the pH to drop over a wide range
d. resist changes in pH at a value more than its pKa
e. resist changes in pH at a value less than its pKa
b. resist changes in pH near the pKa of the buffer
Exam 1A-10
In a basic solution (pH = 12), what is the ionization state of an amino acid?
a. The amino group is deprotonated; the carboxyl group is protonated.
b. The amino group is deprotonated; the carboxyl group is deprotonated.
c. The amino group is protonated; the carboxyl group is deprotonated.
d. The amino group is protonated; the carboxyl group is protonated.
b. The amino group is deprotonated; the carboxyl group is deprotonated.
Exam 1A-11
Which amino acid has the one-letter abbreviation R?
a. tyrosine
b. arginine
c. alanine
d. valine
e. lysine
b. arginine
Exam 1A-12
The amide bond is a linkage between the:
a. β-amino group of one amino acid and the α-amino group of another amino acid.
b. β-carboxyl group of one amino acid and the β-amino group of another amino acid.
c. δ-carboxyl group of one amino acid and the α-carboxyl group of another amino acid.
d. α-amino group of one amino acid and the ε-amino group of another amino acid.
e. α-carboxyl group of one amino acid and the α-amino group of another amino acid.
e. α-carboxyl group of one amino acid and the α-amino group of another amino acid.
Exam 1A-13
What is the amino-terminal residue and what is the carboxyl-terminal residue in thesequence of amino acids Gly-Tyr-Gly-Phe-Leu?
a. Leucine is N-terminal and glycine is C-terminal.
b. Glycine is N-terminal and leucine is C-terminal.
c. Tyrosine is N-terminal and leucine is C-terminal.
d. Phenylalanine is N-terminal and leucine is C-terminal.
e. There are no N-terminal and C-terminal residues in the sequences of amino acids.
b. Glycine is N-terminal and leucine is C-terminal.
Exam 1A-14
What is the configuration of peptide bonds in proteins?
a. Almost all peptide bonds are in the cis configuration.
b. Almost all peptide bonds are in the trans configuration.
c. Half of all peptide bonds are in the trans configuration and the other half are in the cis configuration.
d. Approximately one third are in the trans configuration and rest are in the cis configuration.
e. Approximately one third are in the cis configuration and rest are in the trans configuration.
b. Almost all peptide bonds are in the trans configuration.
Exam 1A-15
A β sheet is formed by linking two or more β strands lying next to one another through:
a. nitrogen bonds.
b. oxygen bonds.
c. ionic bonds.
d. disulfide bridges.
e. hydrogen bonds.
e. hydrogen bonds.
Exam 1A-16
What disrupts the noncovalent interactions in proteins?
a. guanidinium sulfide
b. β-mercaptoethanol
c. uric acid
d. urea
e. ammonia
d. urea
Exam 1A-17
Which amino acid forms disulfide bonds?
a. histidine
b. methionine
c. proline
d. serine
e. cysteine
b. methionine
Exam 1A-18
What plot type allows one to investigate the likely and ψ angles of the peptide φ backbone?
a. Hill
b. Lineweaver-Burk
c. Hanes-Woolf
d. Ramachandran
e. Michaelis-Menten
d. Ramachandran
Exam 1A-19
The amino acids Tyr, Asn, and Thr:
a. have aromatic rings.
b. are negatively charged at pH = 7.0.
c. are positively charged at pH = 7.0.
d. have double bonds within side chains.
e. are polar.
e. are polar.
Exam 1A-20
What pair of amino acids is positively charged at a neutral pH?
a. Lys, Arg
b. Tyr, Arg
c. Cys, Met
d. Leu, Pro
e. Asp, Glu
a. Lys, Arg
Exam 1A-21
What would be the most likely problem for a patient if prolines are not hydroxylated inpost-translational modification?
a. scurvy
b. sickle cell anemia
c. osteogenesis imperfecta
d. sarcoma
e. thalassemia
a. scurvy
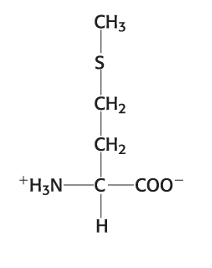
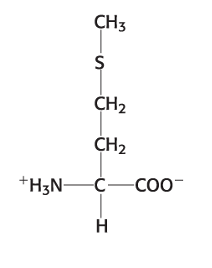
Exam 1A-22
Which amino acid is shown in the picture below?
a. cysteine
b. methionine
c. valine
d. leucine
e. alanine
b. methionine
Exam 1A-23
Which of the following amino acids would be most likely associated with water on the exterior of a protein?
a. phenylalanine
b. glutamine
c. isoleucine
d. tryptophan
e. methionine
b. glutamine
Exam 1A-24
As the partial pressure of carbon dioxide increases, the affinity of oxygen binding to hemoglobin:
a. decreases.
b. increases.
c. stays the same.
d. increases then decreases.
e. decreases then increases-
a. decreases.
Exam 1A-25
What is the difference between the T form and R form of the hemoglobin molecule?
a. The R form of the hemoglobin molecule has a pocket in the center of the tetramer for 2,3-BPG.
b. The R form of the hemoglobin molecule has the oxygen-binding sites free of strain.
c. The T form of the hemoglobin molecule is not constrained by subunit-subunitinteractions.
d. The T form of the hemoglobin molecule is unstable without 2,3-BPG.
e. The R form of the hemoglobin molecule is unstable.
b. The R form of the hemoglobin molecule has the oxygen-binding sites free of strain.
Exam 1A-26
Which model better explains the cooperative binding of oxygen by hemoglobin?
a. concerted model
b. combination of concerned and MWC models
c. sequential model
d. combination of sequential and concerted models
e. Bohr effect
d. combination of sequential and concerted models
Exam 1A-27
What is the functional role of 2,3-BPG?
a. stabilization of the T state of hemoglobin
b. stabilization of the R state of hemoglobin
c. covalent modification of the R state of hemoglobin
d. covalent modification of the T state of hemoglobin
e. saving the equilibrium between the R and T states of hemoglobin
a. stabilization of the T state of hemoglobin
Exam 1A-28
Sickle-cell anemia results in:
a. decreased production of α chains of hemoglobin.
b. increased production of β chains of hemoglobin.
c. loss of the heme group in mutated globins.
d. increased solubility of deoxyhemoglobin.
e. formation of large aggregates of the mutated globins
e. formation of large aggregates of the mutated globins
Exam 1A-29
Oxygen binds to hemoglobin at the:
a. sixth coordination site when the iron is in the ferrous state.
b. fifth coordination site when the iron is in the ferrous state.
c. sixth coordination site when the iron is in the ferric state.
d. fifth coordination site when the iron is in the ferric state.
e. fourth coordination site when the iron is in the ferrousstate.
a. sixth coordination site when the iron is in the ferrous state.
Exam 1A-30
The estrogen receptor would have the highest affinity for:
a. estradiol
b. testosterone
c. bisphenol A
d. tamoxifen
e. Synthetic estrogen
a. estradiol
Exam 1A-31
Myoglobin's binding curve for oxygen will be:
a. sigmoidal
b. linear
c. hyperbolic
d. cooperative
e. logarithmic
c. hyperbolic
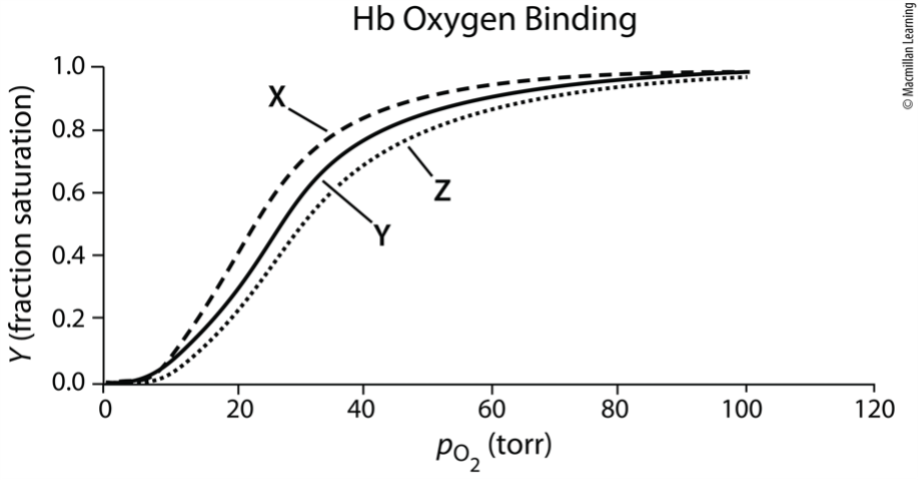
Exam 1A-32
Consider the oxygen-binding profile at three different pH values of 7.6, 7.4, and 7.2.Which statement is MOST accurate?
a. Curve X most likely corresponds to pH 7.2.
b. Curve Z most likely corresponds to pH 7.6.
c. Hb has a higher affinity for oxygen at the pH of curve Z.
d. Curve Y most likely corresponds to pH 7.4.
e. pH has no effect on oxygenation of hemoglobin
d. Curve Y most likely corresponds to pH 7.4.
Exam 1A-33
What method can be used to separate proteins only by their charge?
a. gel-filtration chromatography
b. affinity chromatography
c. gel electrophoresis
d. ion-exchangechromatography
e. dialysis
d. ion-exchangechromatography
Exam 1A-34
The method based on detection of the antibody to a particular antigen that is attached to the plate is:
a. co-immunoprecipitation.
b. indirect ELISA.
c. sandwich ELISA.
d. western blotting.
e. electrophoresis.
b. indirect ELISA.
Exam 1A-35
In SDS-PAGE, the protein mass is inversely proportional to the:
a. velocity of protein migration.
b. frictional coefficient.
c. protein shape.
d. viscosity of the medium.
e. concentration of polyacrylamide
a. velocity of protein migration.
Exam 1A-36
What can be identified with the nuclear Overhauser effect (i.e. NOESY NMR)?
a. pairs of protons in different locations
b. pairs of protons in close locations
c. pairs of electrons in different locations
d. pairs of electrons in close locations
e. exact quantity of electrons in the molecule
b. pairs of protons in close locations
Exam 1A-37
A method that can be used to separate proteins by their sedimentation coefficients is:
a. gel-filtration chromatography.
b. mass spectrometry.
c. dialysis.
d. differential centrifugation.
e. electrophoresis
d. differential centrifugation.
Exam 1A-38
Monoclonal antibodies can be used for all the following except:
a. western blot
b. indirect ELISA
c. co-immunoprecipitation
d. fluorescence microscopy
e. cryoelectron microscopy
e. cryoelectron microscopy
Exam 1A-39
Which type of reaction requires an input of energy to proceed?
a. reversible reaction
b. irreversible reaction
c. catalyzed reaction
d. exergonic reaction
e. endergonic reaction
e. endergonic reaction
Exam 1A-40
The Gibbs free energy of activation is the difference between the:
a. substrate and the transition state.
b. substrate and the product.
c. product and the transition state.
d. substrate and the final state.
e. final and initial states
a. substrate and the transition state.
Exam 1A-41
Choose the CORRECT statement about enzymes.
a. Enzymes shift the equilibrium of a chemical reaction.
b. Enzymes increase the number of products of a chemical reaction.
c. Enzymes increase the rate of a chemical reaction.
d. Enzymes decrease the free energy of reactants.
e. Enzymes decrease the rate of a chemical reaction
c. Enzymes increase the rate of a chemical reaction.
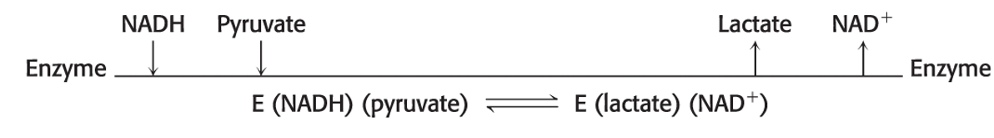
Exam 1A-42
Which type of the multiple substrate reaction is shown?
a. ordered sequential reaction
b. random sequential reaction
c. double-displacement reaction
d. ordered displacement reaction
e. double sequential reaction
a. ordered sequential reaction
Exam 1A-43
The neurotoxin diisopropylphosphofluoridate (DIPF) binds only to a serine amino acidresidue at the active site of acetylcholinesterase to inhibit the enzyme. What type of irreversible inhibitor is it?
a. group-specific
b. affinity label
c. reactive substrate analog
d. suicide
e. mechanism-based
a. group-specific
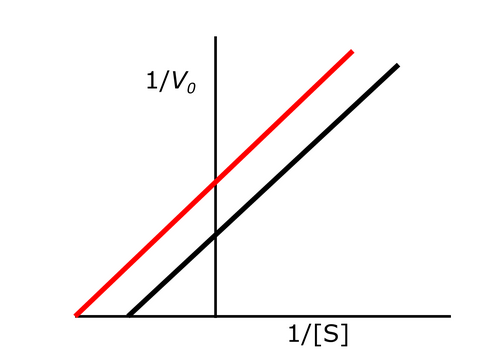
Exam 1A-44
The following Lineweaver Burk plot shows an enzymatic reaction in the presence (left line) or absence (right line) of an inhibitor. What type of inhibitor is represented?
a. Noncompetitive reversible inhibitor
b. Uncompetitive reversible inhibitor
c. Irreversible inhibitor
d. Competitive inhibitor
b. Uncompetitive reversible inhibitor
Exam 1A-45
What can reduce the effect of a competitive inhibitor of an enzyme?
a. increased substrate concentration
b. decreased reaction temperature
c. increased reaction temperature
d. increased coenzymeconcentration
e. increased enzyme concentration
a. increased substrate concentration
Exam 1A-46
What possesses the highest free energy?
a. reactant
b. product
c. transition state
d. final state
e. initial state
c. transition state
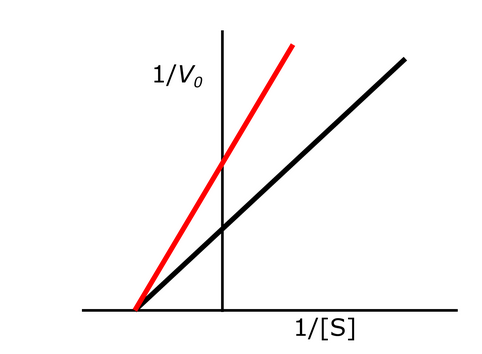
Exam 1A-47
The following Lineweaver Burk plot shows an enzymatic reaction in the presence (left line) or absence (right line) of an inhibitor. What type of inhibitor is represented?
a. Noncompetitive reversible inhibitor
b. Uncompetitive reversible inhibitor
c. Irreversible inhibitor
d. Competitive inhibitor
a. Noncompetitive reversible inhibitor
Exam 1A-48
If a reaction is exergonic at specific reactant concentrations, it is considered:
a. to be at equilibrium.
b. nonspontaneous.
c. spontaneous.
d. irreversible.
e. that ΔG is positive.
c. spontaneous.
Exam 1A-49
Riboflavin is a water-soluble organic substance that is not synthesized by humans. Metabolically, it is chemically converted into a substance called flavin adenine dinucleotide, which is required by succinate dehydrogenase. Which of the following statements is MOST accurate?
a. Riboflavin is a coenzyme.
b. Flavin adenine dinucleotide is a vitamin.
c. Succinate dehydrogenase is a coenzyme.
d. Flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme.
e. Succinate dehydrogenase is a vitamin.
d. Flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme.
Exam 1A-50
For myoglobin, the release of superoxides from the heme is prevented by the interaction of which amino acid with the oxygen?
a. proximal glycine
b. proximal histidine
c. distal glycine
d. distal histidine
e. proximal leucine
d. distal histidine
Exam 2A-1
Which of the following is NOT a catalytic strategy for enzymes?
a. covalent catalysis
b. acid-base reactions
c. approximation of substrates
d. induced fit
e. using metal ions to facilitate catalysis
d. induced fit
Exam 2A-2
What amino acid residue is used to hydrolyze both a peptide bond and ATP?
a. histidine
b. aspartate
c. glycine
d. tryptophan
e. serine
e. serine
Exam 2A-3
Which catalytic strategy is NOT used by carbonic anhydrase?
a. covalent catalysis
b. general acid-base catalysis
c. catalysis by approximation
d. metal ion catalysis
a. covalent catalysis
Exam 2A-4
Proteases cleave peptide bonds in a reaction which:
a. is thermodynamically unfavorable
b. is zinc ion dependent
c. is thermodynamically favorable
d. is kinetically fast
e. involves the formation of hydrogen bonds with a substrate intermediate
c. is thermodynamically favorable
Exam 2A-5
The resistance of the peptide bond to hydrolysis is because:
a. the carbonyl carbon is more electrophilic and more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
b. the carbonyl carbon is less electrophilic and more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
c. the carbonyl carbon is less electrophilic and less susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
d. the carbonyl carbon is more electrophilic and less susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
c. the carbonyl carbon is less electrophilic and less susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
Exam 2A-6
Chymotrypsin is sensitive to chemical modification by DIPF or nerve agents like sarin due to:
a. blocking of His57 from hydrogen bonding to Aps102
b. bonding to the Ser195 residue
c. interfering with the deacylation of the enzyme
d. preventing release of the carboxylic acid component of the cleaved protein
e. stabilizing the tetrahedral intermediate
b. bonding to the Ser195 residue
Exam 2A-7
What metal ion is frequently found in enzyme active sites that act on phosphate-containing substrates?
a. Zn 2+
b. Mg 2+
c. Cu 2+
d. Fe 2+
e. Ni 2+
b. Mg 2+
Exam 2A-8
Binding of ATP causes:
a. a decrease in myosin head affinity for actin filaments.
b. an increase in myosin head affinity for actin filaments.
c. no change in myosin head affinity for actin filaments.
d. cross-linking of the myosin head and actin filaments.
e. complete removal of affinity between actin and myosin.
a. a decrease in myosin head affinity for actin filaments.
Exam 2A-9
Once Zn 2+ binds a molecule of water, the next step needed for the enzyme carbonic anhydrase to carry out its catalysis is:
a. positioning of CO2 in the active site
b. the oxygen of water attacks the carbon of CO2
c. buffer facilitates protonation of water-bound Zn 2+
d. Zn 2+ facilitates protonation of the bound hydroxide ion
e. Deprotonation of Zn 2+-bound water
e. Deprotonation of Zn 2+-bound water
Exam 2A-10
His64 in carbonic anhydrase II acts as a proton shuttle. Which statement aboutproton shuttles is true?
a. The rate of proton diffusion limits the rate of deprotonation of the zinc-boundwater molecule.
b. In the presence of buffer, the rate of deprotonation of the zinc-bound water molecule is increasing.
c. The rate of protonation of the zinc-bound hydroxide ion limits the rate of proton diffusion.
d. The buffer is involved in the reaction because the rate of proton diffusion is higherthan the rate of CO2 hydration.
e. In the presence of buffer, the rate of deprotonation of the zinc-bound water moleculeis decreasing.
b. In the presence of buffer, the rate of deprotonation of the zinc-bound water molecule is increasing.
Exam 2A-11
Which step in the interaction between myosin and actin allows for the reorientation (i.e. movement) of the lever portion of myosin to physically move the actin filament relative to the myosin?
a. addition of ATP to the binding site on myosin
b. hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pi
c. attachment to the actin filament
d. release of Pi
e. release of ADP
d. release of Pi
Exam 2A-12
The first step of the cascade for the activation of zymogens in digestion requires:
a. breakdown of trypsinogen by enteropeptidase
b. breakdown of chymotrypsinogen by trypsin
c. breakdown of prolipase by trypsin
d. breakdown of chymotrypsinogen by enteropeptidase
e. breakdown of procarboxypeptidase by trypsin
a. breakdown of trypsinogen by enteropeptidase
Exam 2A-13
Which structural changes are caused by cAMP binding activate protein kinase A?
a. removal of the consensus phosphorylation sequence of the R subunit from thecatalytic site of the C subunit
b. removal of the pseudosubstrate sequence of the R subunit from the catalytic site of the C subunit
c. rotation of the R subunit to free the catalytic site of the C subunit
d. rotation of the pseudosubstrate sequence outward of the catalytic site of the R subunit
e. rotation of the C subunit to free the catalytic site
b. removal of the pseudosubstrate sequence of the R subunit from the catalytic site of the C subunit
Exam 2A-14
For the enzyme ATCase, PALA (N-(phosphonacetyl)-l-aspartate) would serve as a:
a. positive homotropic effector.
b. positive heterotropic effector
c. negative homotropic effector.
d. negative heterotropic effector.
e. competitive inhibitor
e. competitive inhibitor
Exam 2A-15
The curve of the reaction rate versus substrate concentration is sigmoidal for allosteric enzymes like ATCase because:
a. regulatory subunits act cooperatively upon binding substrate molecules.
b. allosteric and catalytic subunits act together.
c. a single allosteric enzyme is able to bind multiple substrates.
d. a catalytic subunit is able to bind a phosphate.
e. catalytic subunits act cooperatively upon binding substrate molecules
e. catalytic subunits act cooperatively upon binding substrate molecules
Exam 2A-16
Which of the following statements regarding isozymes such as lactatedehydrogenase is FALSE?
a. isozymes are encoded by different genes
b. isozymes can be expressed in different tissues
c. isozymes have different amino acid sequences
d. isozymes demonstrate the same Km
e. isozymes can vary during developmental stages
d. isozymes demonstrate the same Km
Exam 2A-17
If protein kinase A recognizes the consensus sequence Arg-Arg-X-Ser-Z, then which of the following amino acids would be the most likely candidate for X?
a. tryptophan
b. histidine
c. glutamate
d. alanine
e. phenylalanine
d. alanine
Exam 2A-18
Phosphorylation of proteins is an effective means to regulate target proteins because:
a. the free energy of phosphorylation is small
b. the phosphoryl group can add 3+ hydrogen bonds
c. phosphorylation adds two positive charges to the target protein
d. phosphorylation can be used to limit signals
e. phosphorylation limits the Km of the reaction making more efficient
b. the phosphoryl group can add 3+ hydrogen bonds
Exam 2A-19
Once the initial cleavage of chymotrypsinogen takes place between Arg15 and Ile16, the next step is:
a. Ile 16 forms a covalent bond with Asp 194
b. Ile 16 forms a covalent bond with Gly 195
c. Ile 16 forms an ionic bond with Asp 194
d. Ile 16 forms an ionic bond with Gly 195
e. Ile16 forms a covalent bond with Ser195 in the substrate pocket
c. Ile 16 forms an ionic bond with Asp 194
Exam 2A-20
The clotting pathway that is triggered by the release of tissues factors upon trauma to the body would be the pathway.
a. extrinsic
b. intrinsic
c. proteolytic
d. allosteric
a. extrinsic
Exam 2A-21
Calcium ions bind to the _____ domain of the prothrombin polypeptide.
a. kringle
b. gla
c. serine protease
d. fibrin
e. transglutaminase
b. gla
Exam 2A-22
Which molecule is required for the proper synthesis of prothrombin?
a. Factor Xa
b. Factor Va
c. Tissue factor
d. fibrin
e. Vitamin K
e. Vitamin K
Exam 2A-23
Which of the following limits the degree of blood clotting in a vessel?
a. Inactivation by trypsin inhibitors
b. concentrating the clotting factors in the spleen
c. instability of the clotting factors in the blood
d. inactivation by Factor Xa
e. activation of coagulation by heparin
c. instability of the clotting factors in the blood
Exam 2A-24
The polymerization of fibrin monomers into a soft clot is catalyzed by the enzyme:
a. trypsin
b. chymotrypsin
c. transglutaminase
d. elastase
e. carboxypeptidase
c. transglutaminase
Exam 2A-25
The allosteric coefficient of an enzyme (L) would increase if:
a. the T state of the enzyme decreases and R state remains the same
b. the T state of the enzyme increases and the R state remains the same
c. the R state decreases and the T state decreases
d. the R state increases and the T state remains the same
e. the R state increases and the T state decreases
b. the T state of the enzyme increases and the R state remains the same
Exam 2A-26
In bacterial mRNA, the initiating AUG codon is preceded several nucleotides awayby a purine-rich sequence called the _____, which base-pairs with a complementary sequence in an rRNA.
a. consensus sequence
b. Pribnow box
c. Shine-Delgarno sequence
d. Hogness box
e. reading frame
c. Shine-Delgarno sequence
Exam 2A-27
The interactions that allow Watson-Crick base pairing in the double helix are due to:
a. covalent bonds
b. hydrogen bonds
c. van der Waals interactions
d. the hydrophobic effect
e. ionic bonds
b. hydrogen bonds
Exam 2A-28
A means to generate different forms of the same antibody protein so that one isoform is membrane bound while another is secretory is through:
a. exon shuffling
b. degeneracy of the genetic code
c. recombination
d. alternative splicing
e. degenerative splicing
d. alternative splicing
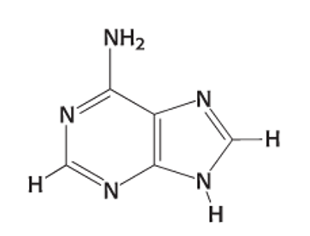
Exam 2A-29
Which nitrogenous base is shown below?
(
a. uracil
b. adenine
c. guanine
d. thymidine
e. cytosine
b. adenine
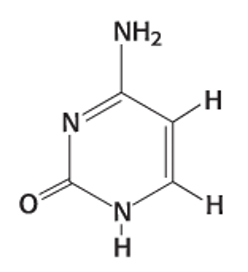
Exam 2A-30
Which nitrogenous base is shown below?
a. uracil
b. adenine
c. guanine
d. thymidine
e. cytosine
e. cytosine
Exam 2A-31
The formation of the double helix which results in a left-hand helix is called:
a. A-DNA
b. B-DNA
c. Z-DNA
d. RNA
e. stem loop
c. Z-DNA
Exam 2A-32
The following are all modifications of eukaryotic mRNA except for:
a. 5' methyl-guanosine cap
b. removal of introns
c. 5' poly-A tail
d. ligation of exons
e. 3' poly-A tail
c. 5' poly-A tail
Exam 2A-33
A spliceosome consists of proteins and:
a. snRNA
b. tRNA
c. mRNA
d. siRNA
e. rRNA
a. snRNA
Exam 2A-34
Elongation of a newly synthesized DNA strand involves:
a. 5'-OH makes a nucleophilic attack on the innermost phosphoryl group on the incoming nucleoside triphosphate
b. 3'-OH makes a nucleophilic attack on the innermost phosphoryl group on the incoming nucleoside triphosphate
c. 5'-OH makes an electrophilic attack on the innermost phosphoryl group on the incoming nucleoside triphosphate
d. 3'-OH makes an electrophilic attack on the innermost phosphoryl group on the incoming nucleoside triphosphate
b. 3'-OH makes a nucleophilic attack on the innermost phosphoryl group on the incoming nucleoside triphosphate
Exam 2A-35
The temperature at which half the DNA double helix is dissociated is called:
a. Teq
b. Tm
c. Td
d. Ta
e. Ti
b. Tm
Exam 2A-36
Codons that specify the same amino acid are referred to as:
a. degenerate codons.
b. consensus codons.
c. synonyms.
d. universal codons.
e. antisense codons
c. synonyms.
Exam 2A-37
Matt Meselson and Frank Stahl demonstrated in their DNA replication experiment that:
a. after one round of replication, all of the DNA was a N14/N15 hybrid
b. after one round of replication, two bands formed in the centrifuge tube, representing all N14/N14 or N15/N15
c. after three rounds of replication, all of the DNA was a N14/N15 hybrid
d. after ten rounds of replication, all of the DNA was a N14/N15 hybrid
a. after one round of replication, all of the DNA was a N14/N15 hybrid
Exam 2A-38
Retroviruses such as HIV-1 have a ____ genome.
a. double-stranded DNA
b. single-stranded DNA
c. double-stranded RNA
d. single-stranded RNA
e. hybrid RNA-DNA double stranded
d. single-stranded RNA
Exam 2A-39
The correct sequence of events in polymerase chain reaction is:
a. DNA strand separation at 72°C, primer attachment at 54°C, elongation at 95°C
b. DNA strand separation at 95°C, primer attachment at 54°C, elongation at 72°C
c. DNA strand separation at 54°C, primer attachment, at 95°C, elongation at 72°C
d. DNA strand separation at 95°C, primer attachment, at 72°C, elongation at 54°C
e. DNA strand separation at 95°C, elongation at 72°C, primer attachment, at 54°C
b. DNA strand separation at 95°C, primer attachment at 54°C, elongation at 72°C
Exam 2A-40
If the DNA you want to insert into a plasmid does not contain the same restrictionenzyme sites as the plasmid, what can be done to allow insertion of the foreign DNA?
a. use the same restriction enzyme
b. use T4 ligase to attach the ends
c. add linker bases to the foreign DNA
d. digest the insert DNA with a different restriction enzyme
e. give up and go home
c. add linker bases to the foreign DNA
Exam 2A-41
What is the difference between lytic and lysogenic pathways that λ phage uses for multiplying?
a. In the lysogenic pathway, λ phage enters the cell, while in the lytic pathway, λ phage destroys the cell.
b. In the lysogenic pathway, new virion copies lead to lysis of the host cell. In the lyticpathway, new virion copies leave the host cell through budding.
c. In the lysogenic pathway, λ phage destroys three specific nucleotide sequences, while in the lytic pathway, λ phage destroys five specific nucleotide sequences.
d. In the lysogenic pathway, viral DNA is transferred in the cell inside the phage, while in the lytic pathway, viral DNA is transferred in the cell and the phage stays outside the cell.
e. In the lysogenic pathway, viral DNA is integrated in the E. coli genome, while in the lytic pathway, phage DNA multiplies without insertion
e. In the lysogenic pathway, viral DNA is integrated in the E. coli genome, while in the lytic pathway, phage DNA multiplies without insertion
Exam 2A-42
The RNA interference technique employs which of the following to create small interfering RNA's?
a. reverse transcriptase
b. RNA polymerase
c. Dicer
d. Cas9
e. T4 ligase
c. Dicer
Exam 2A-43
Which of the following tool is the least useful for incorporating foreign DNA into eukaryotic cells?
a. introduction of a pUC plasmid with b-galactosidase as a marker
b. microinjection of GFP-labelled foreign DNA into a mouse egg
c. electroporation of foreign DNA into plant cells that have had their cell walls stripped away
d. gene gun loaded with tungsten pellets containing foreign DNA to be "shot" at a target group of cells in a dish
e. infection of human cells with an adenovirus carrying recombinant DNA
a. introduction of a pUC plasmid with b-galactosidase as a marker
Exam 2A-44
Which of the following next generation sequencing techniques relies upon adding each dNTP and analyzing if the incorporated nucleotide carries out a "flash" light reaction?
a. Sanger dideoxy sequencing
b. reversible terminator sequencing
c. pyrosequencing
d. ion semiconductor sequencing
c. pyrosequencing
Exam 2A-45
The blotting technique that would allow the researcher to identify a specific RNA after transferring the separated bands from the original agarose gel is:
a. Western Blotting
b. Southern Blotting
c. Northern Blotting
d. Eastern Blotting
c. Northern Blotting
Exam 2A-46
The 2',3'-dideoxy analog is a useful tool in the Sanger sequencing method because:
a. it possesses modified nitrogenous bases
b. it lacks a hydroxyl group on the 3' terminus of the sugar group
c. it has a hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon
d. it blocks polymerization because it possesses only two phosphoryl groups instead of three
e. it can be added in excess quantities and compete with the usual deoxynucleoside trisphosphates
b. it lacks a hydroxyl group on the 3' terminus of the sugar group
Exam 2A-47
A DNA microarray can be employed to examine all of the following except:
a. overexpression of a cancer-related gene
b. underexpression of a gene critical in the aging process
c. the transcriptome of liver versus brain cells
d. point mutations in a pseudogene
d. point mutations in a pseudogene
Exam 2A-48
If you target a specific gene on chromosome #5 for gene knockout by substituting a complete mutated DNA segment in place of the normal gene, then you are performing:
a. site-directed mutagenesis
b. homologous recombination
c. nonhomologous end-joining recombination
d. homology directed repair
b. homologous recombination
Exam 2A-49
In the CRISPR-Cas9 system, the duplex formed by the target DNA and the signal guide RNA is recognized and bound by the:
a. CRISPR
b. sgRNA
c. REC lobe of the Cas9
d. NUC lobe of the Cas9
e. PAM
c. REC lobe of the Cas9
Exam 2A-50
The advantage of a cDNA library over a genomic library is:
a. the cDNA library uses viral vectors to carry the fragment of interest, which the genomic library uses plasmid vectors
b. the cDNA library restricts the DNA used to only the noncoding regions while genomic libraries use only coding regions
c. the cDNA library is generated from all of the RNA found in the cell rather than the genomic library which is generated from all of the genomic DNA
d. the cDNA library is generated from the mRNA's expressed by a cell while thegenomic library is generated from all of the RNA'S produced by the cell
e. the cDNA is generated from the mRNA's expressed by a cell while the genomic library is generated from the DNA found in the nucleus of a cell
e. the cDNA is generated from the mRNA's expressed by a cell while the genomic library is generated from the DNA found in the nucleus of a cell