2.1.2 Mapping Brain Function HBS PLTW Human Body Systems WCHS Mr. Alasti
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Why are animal dissections so important?
Animals can be used as models to study the function of major organs and to gain insight into systems and can shed light on unique human behaviors, potential drug therapies for neurological conditions, and understanding how our brain changes as we age
Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum, also known as gray matter
Olfactory Nerve (cranial nerve 1)
Relays information about the sense of smell
Optic Nerve (cranial nerve 2)
Relays information about the sense of sight
What do most neurological exams provide?
The ability to identify signs of disorders that affect your brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Function of the parietal lobe
Responsible for sensory perception and integration. It interprets input from other areas of the body such as taste, hearing, sight, touch, and smell
Function of the occipital lobe
Responsible for perceiving, processing, and remembering visual stimuli. It allows you to see color, size, distance, depth, and recognize faces and objects
Function of the cerebellum
Involved in motor control as well as select cognitive activities. It contains most of the neurons in the brain but only represents about 10% of the brain’s overall weight
Function of the brain stem
Involved in vision, hearing, motor control, alertness, temperature regulation, breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure
Function of the temporal lobe
Helps with processing pain and auditory stimuli, emotions, and memories. It also allows you to understand what you hear, retain visual memories, and process and remember emotions
Function of the frontal lobe
Controls voluntary movement, expression and language, cognition, planning, and is the control center for personality, behavior, and emotion
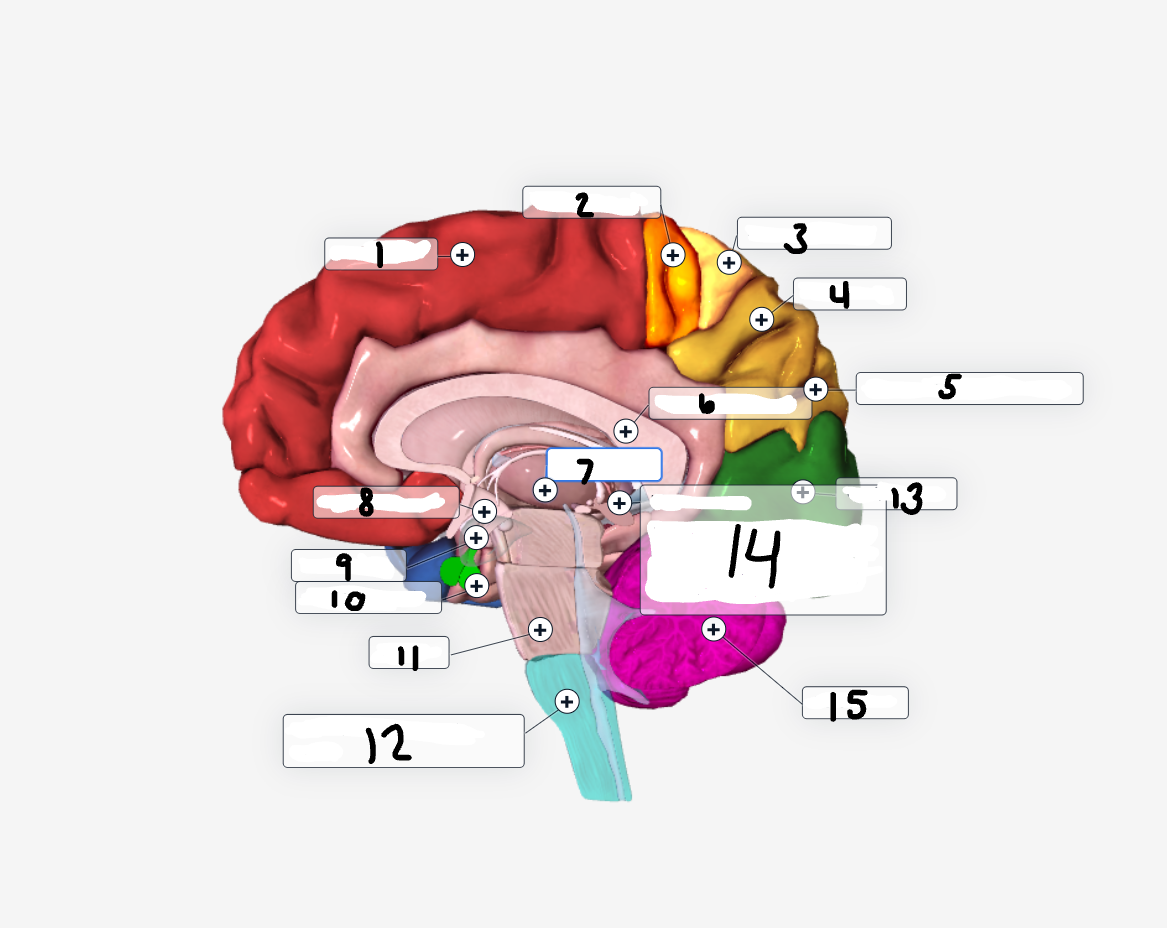
Label the image
Frontal Lobe
Motor Cortex
Sensory Cortex
Parietal Lobe
Right Superior Parietal LobuleParietal
Corpus Collosum
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Amugdala
Pituitary Gland
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
Occipital Lobe
Hippocampus
Cerebellum