amino acids and phospholipids
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
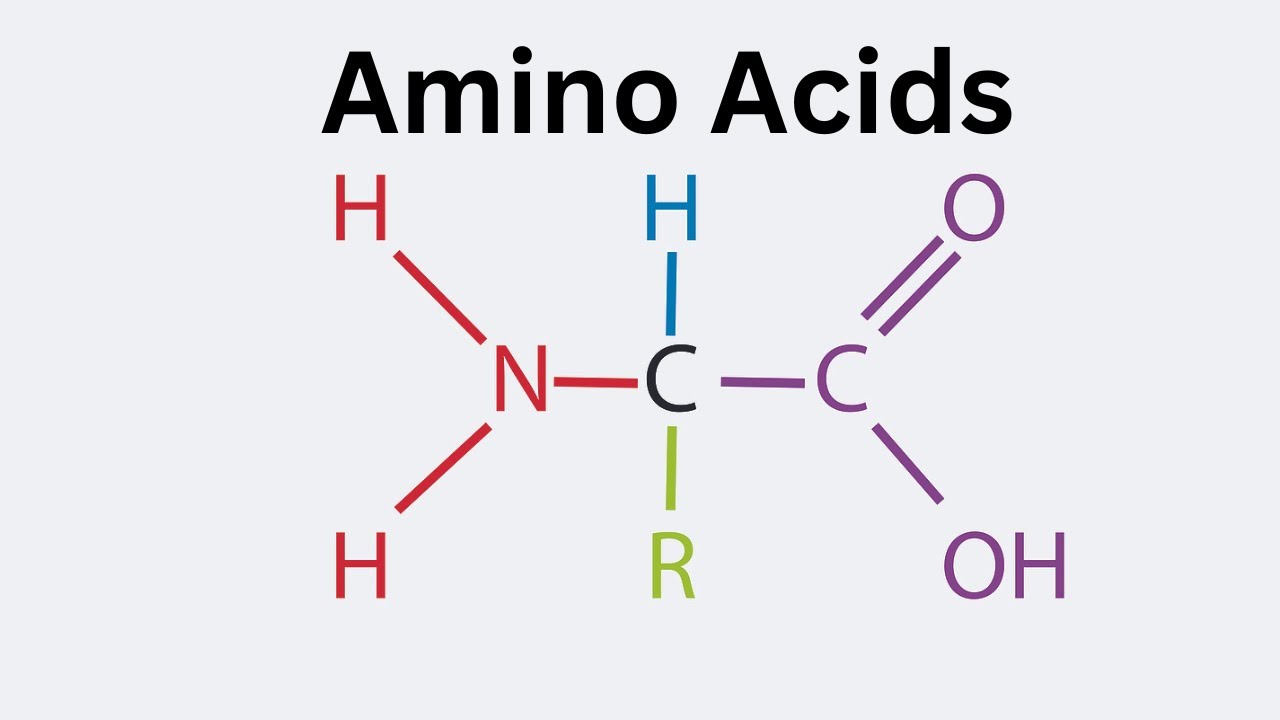
what is the structure of an amino acid
amine group
carboxyl group
r group
what type of bonds do amino acids form?
peptide bond, condensation reaction, the reaction takes place in the ribosome
what enzyme catalyses the reaction of amino acids?
protease enzyme
what is primary structure?
the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide
determined by the DNA sequence of the gene which codes for that polypeptide
what is the secondary structure?
the shape of the chain caused by hydrogen bonds e.g alpha helix or the beta pleated sheet
what is the tertiary structure?
further folding of the secondary structure - active site
what is the quaternary structure?
how individual polypeptide subunits (chains) are arranged with each other to form a larger 3D molecule e.g haemoglobin
what is a prosthetic group?
non-protein molecules forming part of the structure
proteins with a prosthetic group are called conjugated proteins
what are non polar amino acids?
non polar amino acids have uncharged R groups. they are not attracted to water and are called hydrophobic
what are disulfide bonds?
the covalent bonds between two sulfur molecules, these are relatively strong
what are globular proteins?
globular proteins tend to have a spherical shape
they are soluble in water → they have hydrophilic amino acids on their surface
some roles include enzymes, hormones and oxygen carrying proteins
what are fibrous proteins?
often play a structural role e.g bones or tendons
form long rope like molecules
large proportion of amino acids with hydrophobic R groups → insoluble in water
what is the structure of haemoglobin?
globular protein with 4 polypeptide subunits
two are called alpha and two are called beta subunits
each subunit contains the prosthetic group haem which is an Fe2+ (conjugated protein)
this is where the oxygen binds, so one haemoglobin molecule can bind to four oxygen molecules
when one molecule of oxygen joins the quaternary structure changes slightly which makes it more easier for more oxygen to attach
what is the structure of collagen?
found in skin, tendons and ligaments
polypeptide chains wrap tightly together to form a triple helix
every third amino acid is glycine - the R group of glycine is hydrogen - the smallest R group of any amino acid
the polypeptides can wrap very tightly around each other
hydrogen bonds form between the polypeptide chains
polypeptides also joined by strong crosslinks
large number of polypeptide helixes join together to form microfibrils and fibrils
the molecules are staggered so there are no weak spots
what is the structure of keratin?
found in hair and fingernails
insoluble in water
consists of long stranded molecules
high proportion of the amino acid cysteine
cysteine is used to form disulfide bonds
what is the structure of elastin?
long strands containing hydrophobic regions
found in skin and arteries
describe the structure of a phospholipid
glycerol bonded to two fatty acids and a phosphate
the phosphate head is negatively charged and is polar (hydrophilic)
the tails are non polar and hydrophobic
the tails are joined to the phospholipid via ester bonds
the phosphate is joined via phosphoester bonds
describe the structure of cholesterol
hydrophilic hydroxyl group
rest is hydrophobic
what is the role of cholesterol?
controls membrane fluidity
contributes to stability