Amino Acids & Peptides
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 4 and part of 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
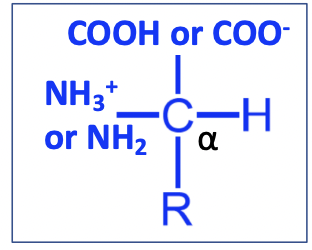
General structure of Amino Acid
Amino group: NH3+ / NH2
pKa = 9.5
Carboxyl group: COOG / COO-
pKa = 2.0
R = side chain
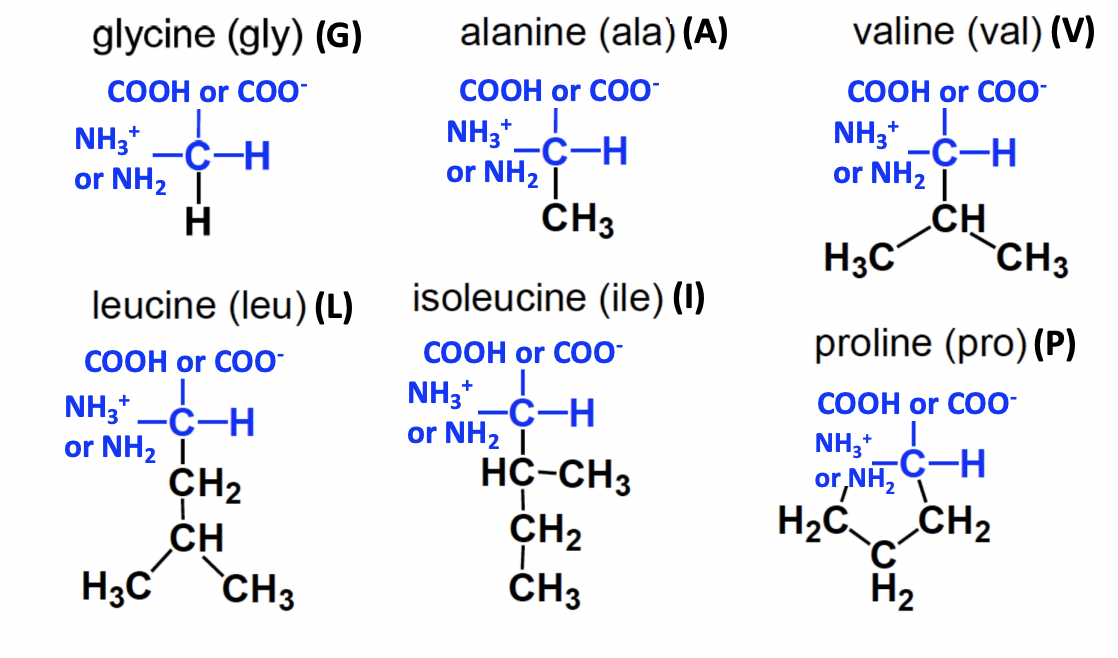
Neutral non-polar amino acids
= aliphatic
GAVLIP
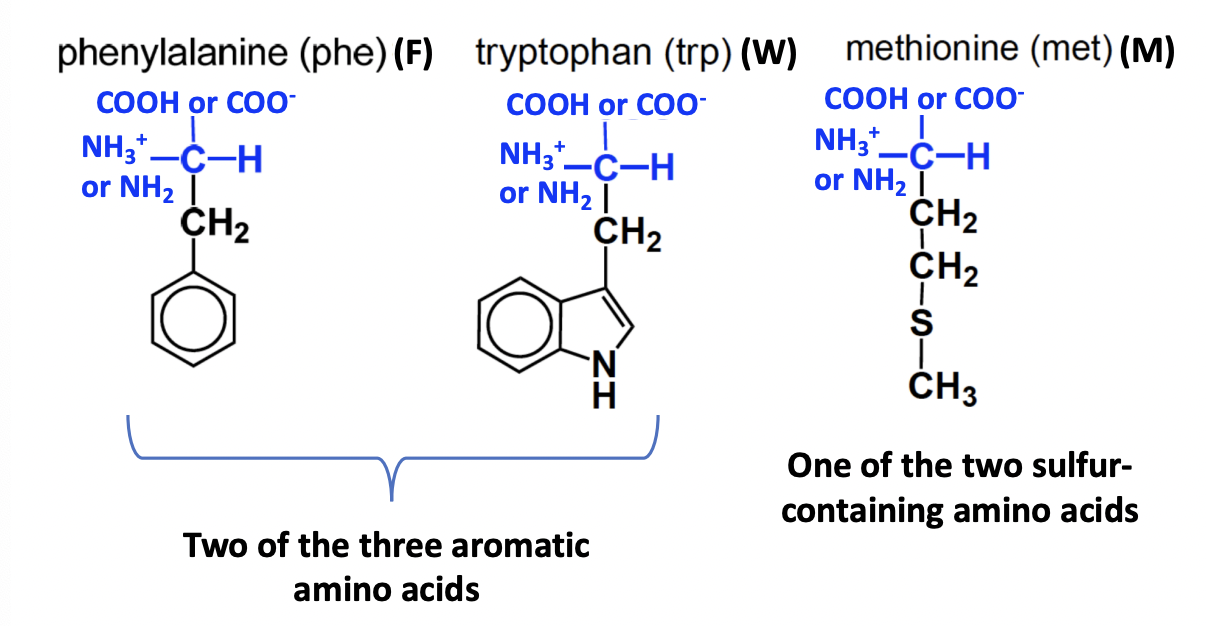
Neutral non-polar amino acids (cont.)
FWM
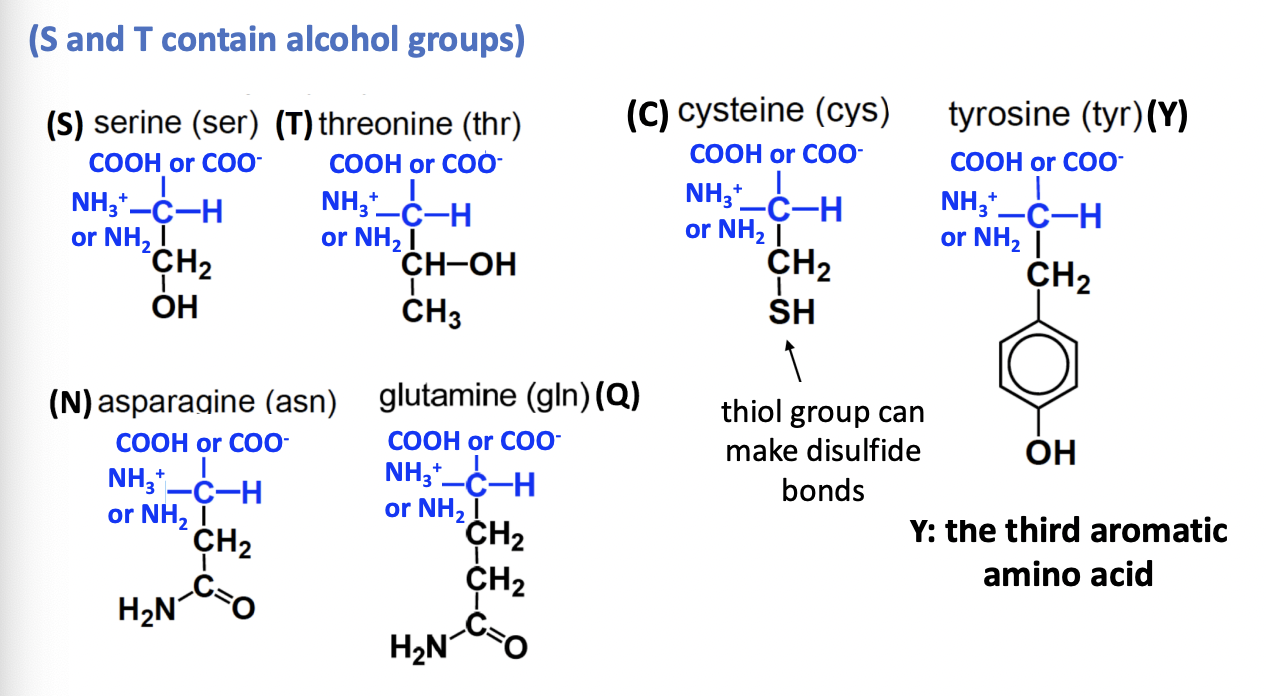
Neutral polar amino acids
STCYNQ
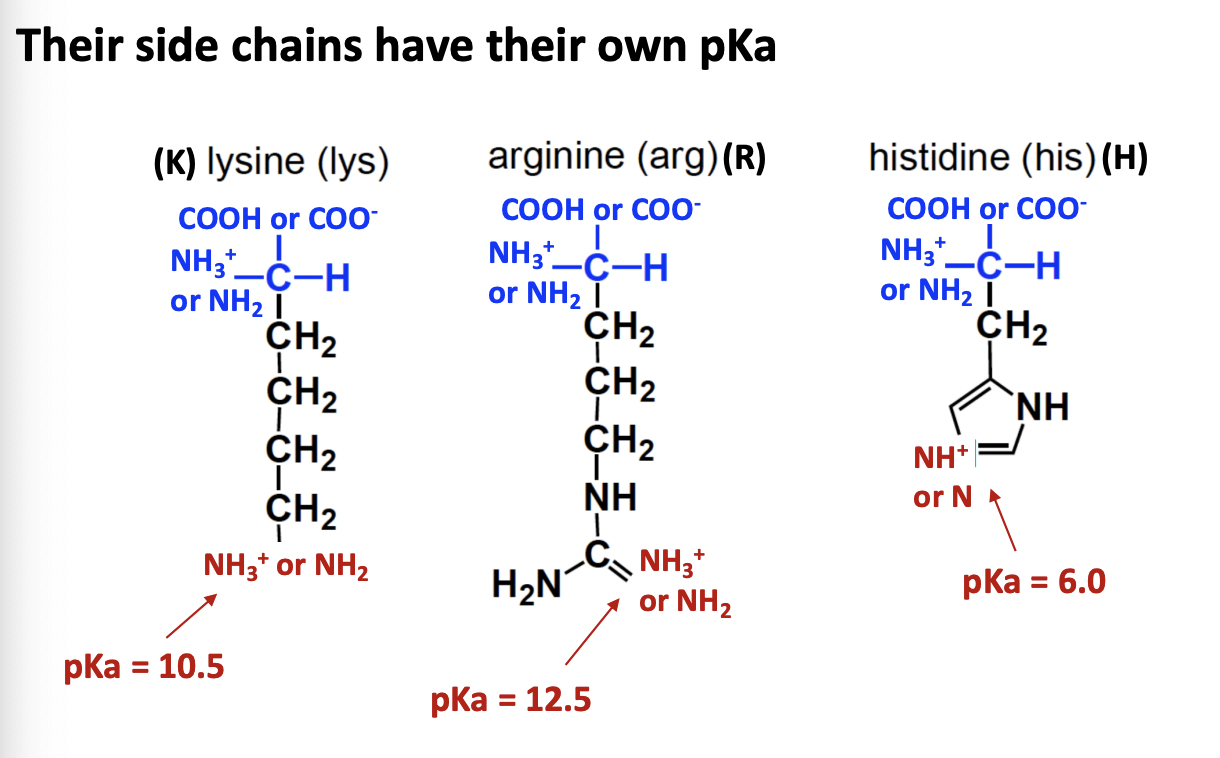
Positively charged basic amino acids
KRH
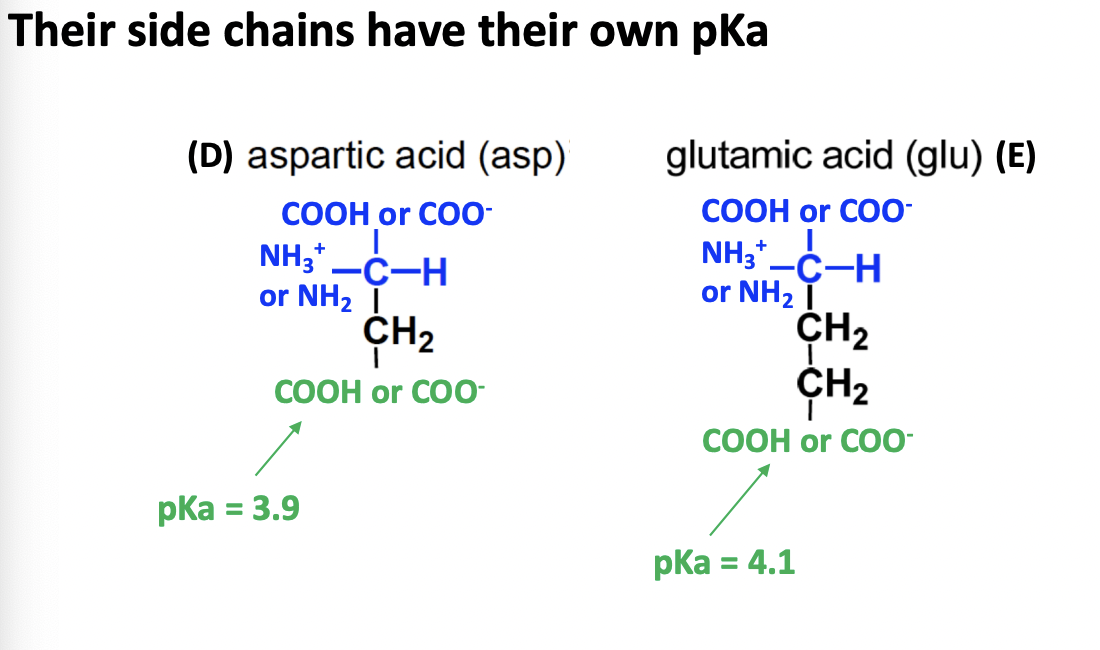
Negatively charged acid amino acids
DE
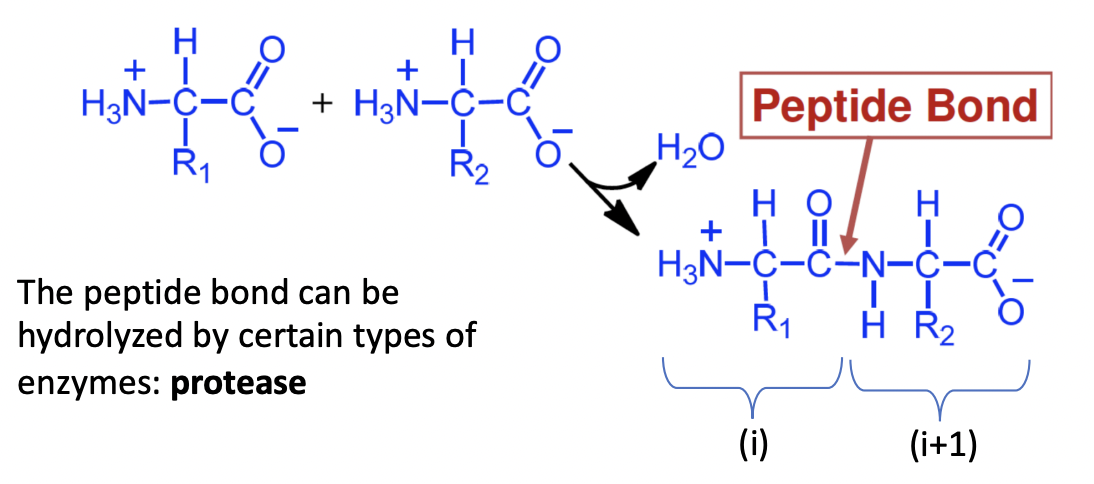
Bond between 2 amino acids in a protein
amide bond
formed between carboxylic group of amino acid (i) and the amino group of amino acid
Direction of protein sequence
N-term to C-term
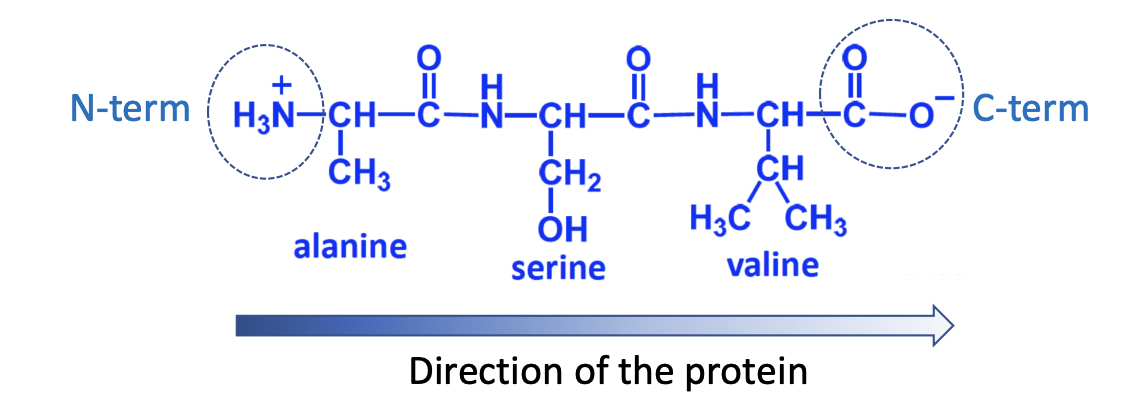
Peptide nomenclature
# amino acids < 10 = peptide
# amino acids from 10-100 = polypeptide
# amino acids > 100 = protein
A
Ala
Alanine
R
Arg
Arginine
D
Asp
Aspartic Acid
N
Asn
Asparagine
C
Cys
Cysteine
E
Glu
Glutamic Acid
Q
Gln
Glutamine
G
Gly
Glycine
H
His
Histidine
I
Ile
Isoleucine
L
Leu
Leucine
K
Lys
Lysine
M
Met
Methionine
F
Phe
Phenylalanine
P
Pro
Proline
S
Ser
Serine
T
Thr
Threonine
W
Trp
Tryptophan
Y
Tyr
Tyrosine
V
Val
Valine
K, R, and H
basic
NH3+ / NH2 side chain
D, E
acidic
COOH / COO- side chain
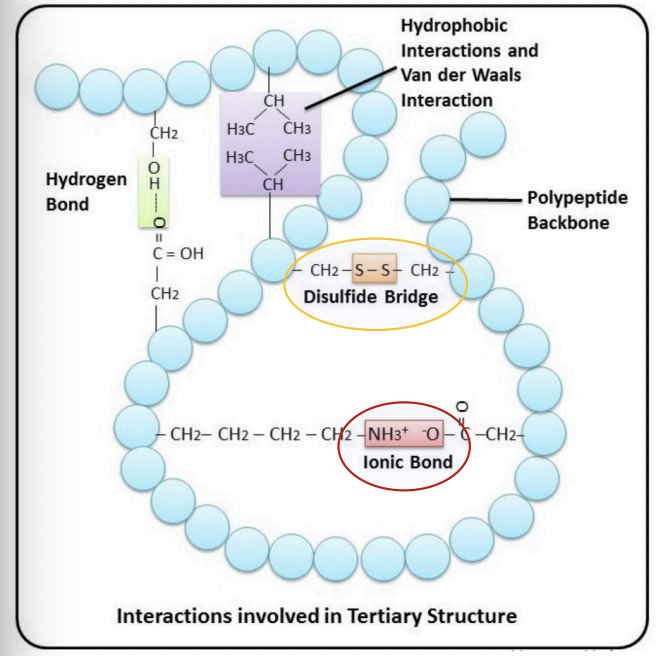
Hydrophobic interactions
= interactions between non-polar amino acids
(Ala, Val, Ile, Leu, Trp, Phe)
Hydrophobic aa: clustered in the core of he protein away from water
Hydrophilic aa: exposed at the surface
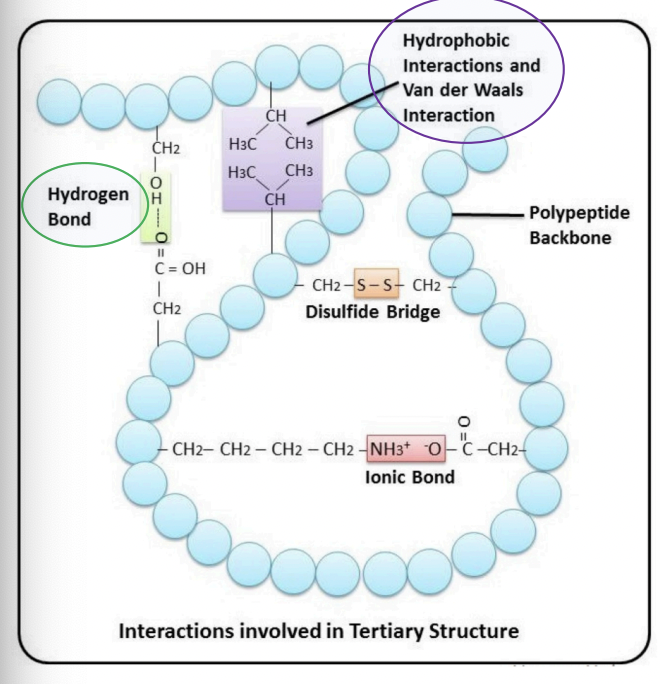
Hydrogen bonds
Between the amide groups of the protein backbone
Between side chains
(Ser, Asp)
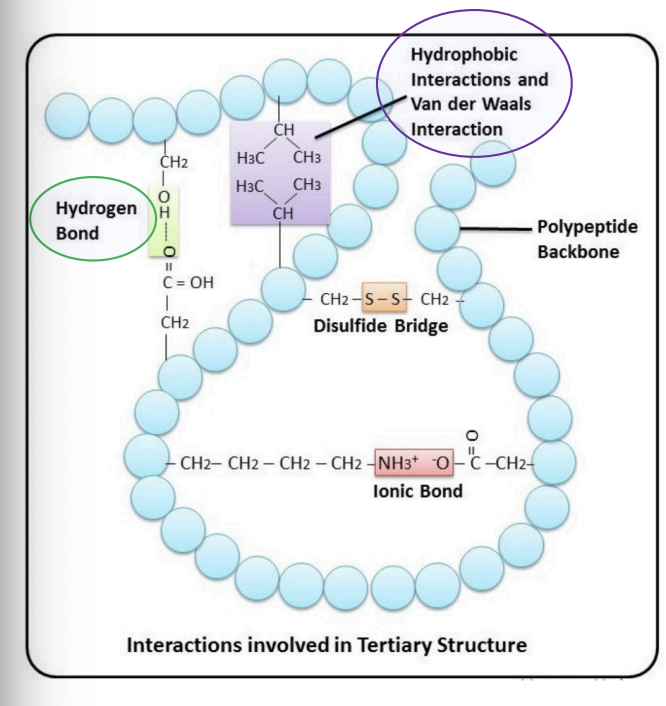
Ionic bonds
= interactions between positively charged amino acids (Lys, Arg) & negatively charged amino acids (Asp, Glu)
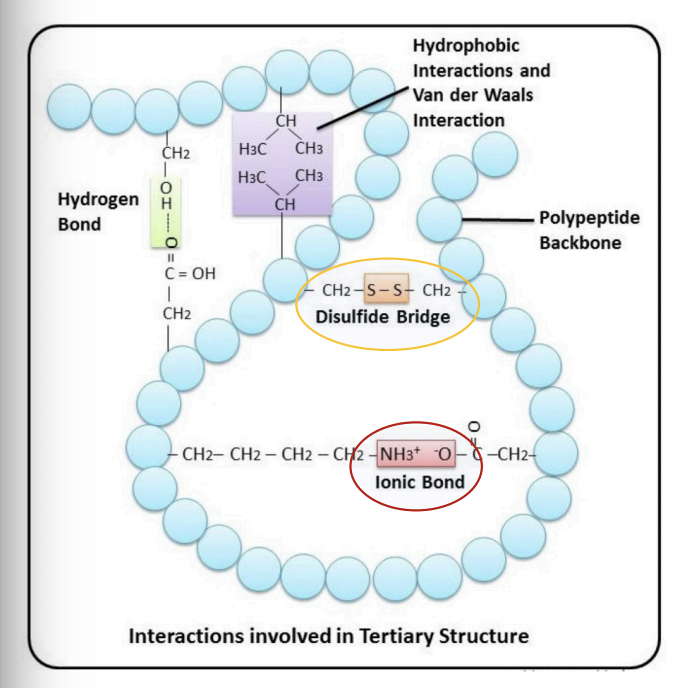
Disulfide bridges
= covalent bond between two cysteines
(oxidation of their thiol groups)