Levers
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
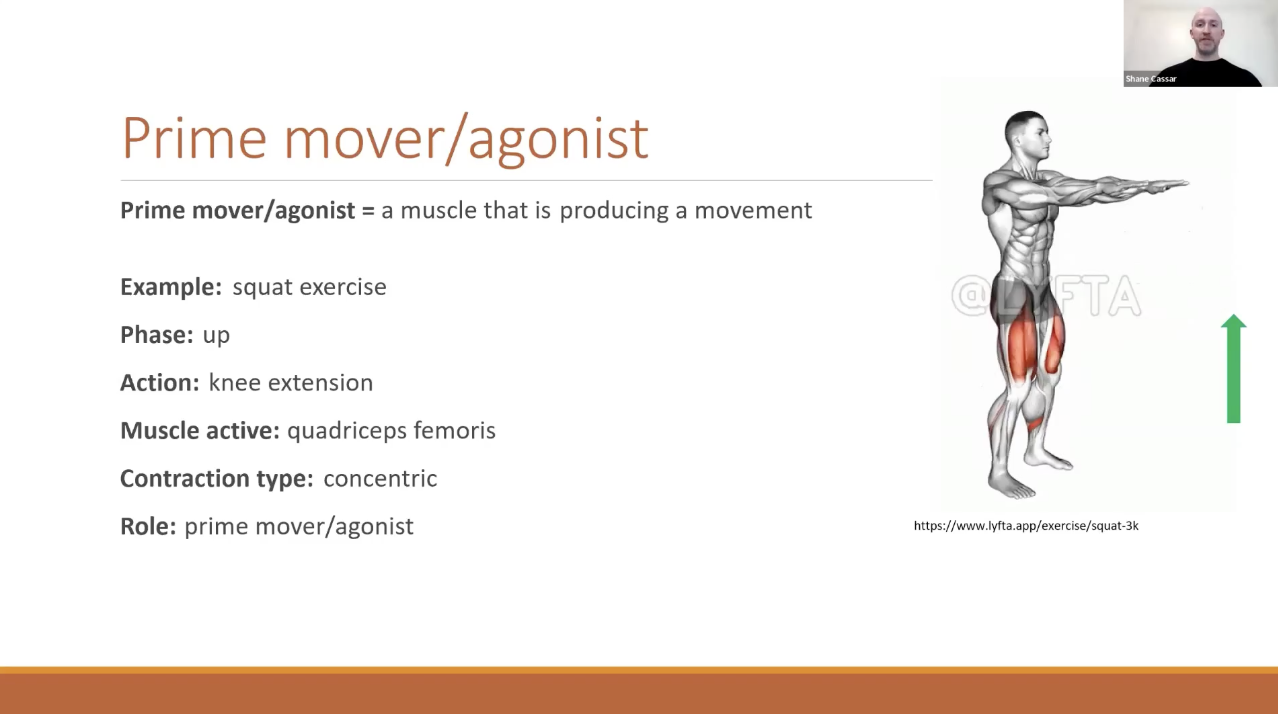
Agonist muscle/Primer movers
Concentrically contracting muscles are ALWAYS agonists
Gravity can also be a prime mover, when the muscle is moving downward
Antagonist muscle

Fixator muscle

Synergist muscles

Isotonic Contractions
Iso - Same
Tonic - Tension
Tension in the muscle remains constant.
Length of the muscle changes.
Two types:
Concentric contraction (Shortens)
Eccentric contraction (Lengthens)
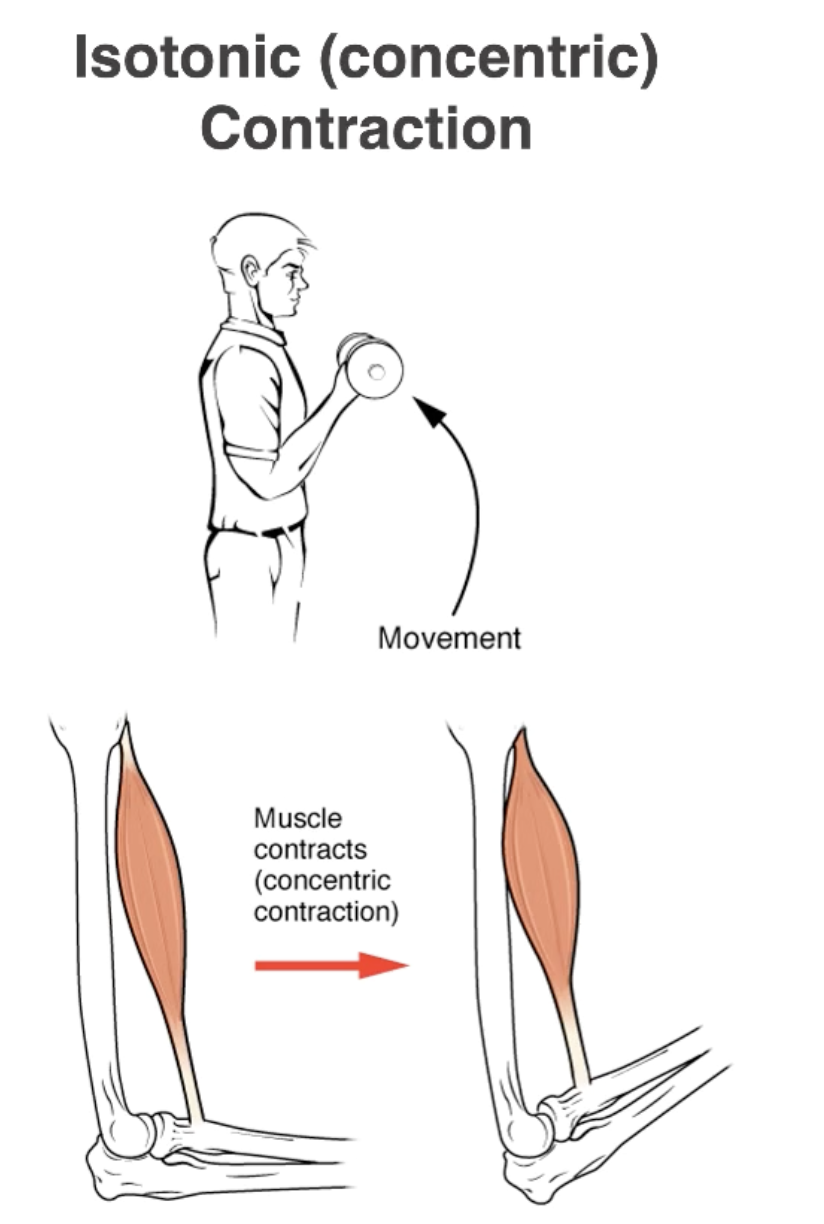
Isotonic Contractions:
Concentric Contraction
Muscle Shortens
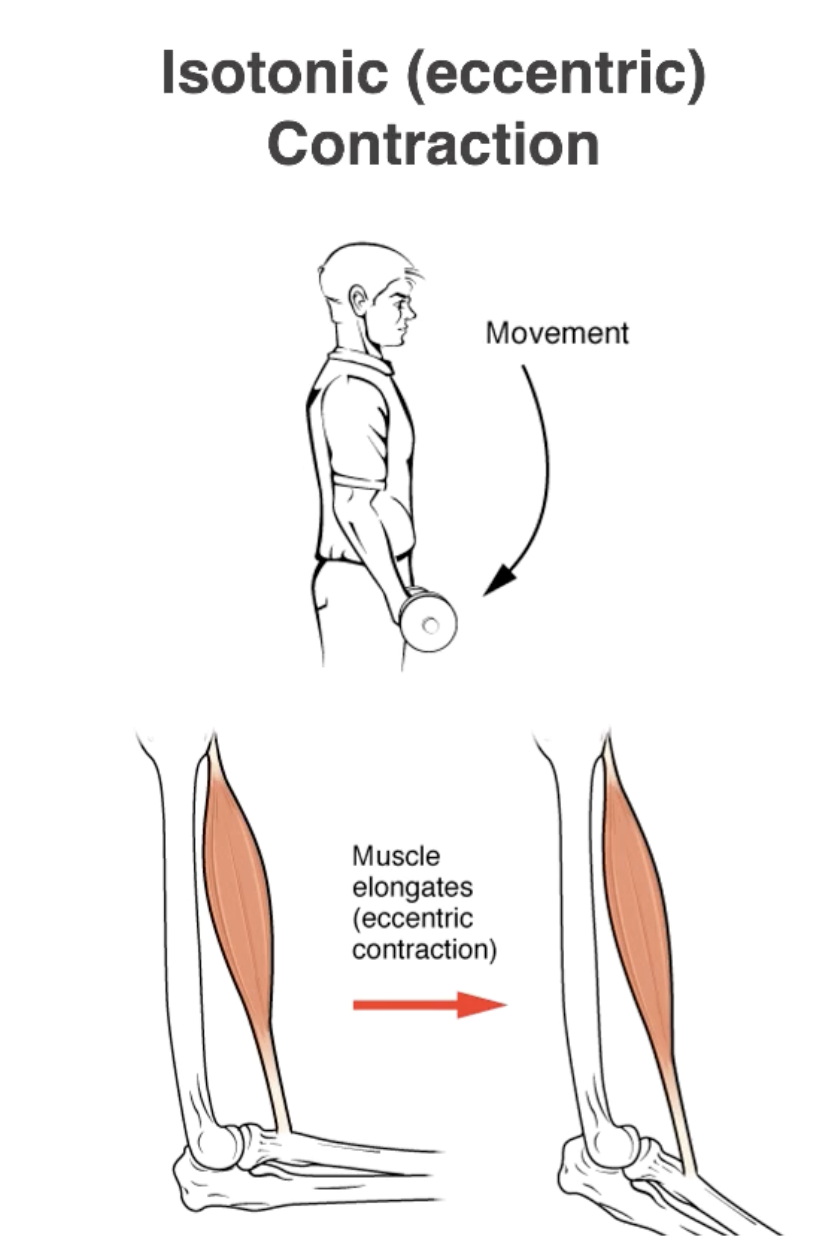
Isotonic Contractions:
Eccentric Contraction
Muscle Lengthens
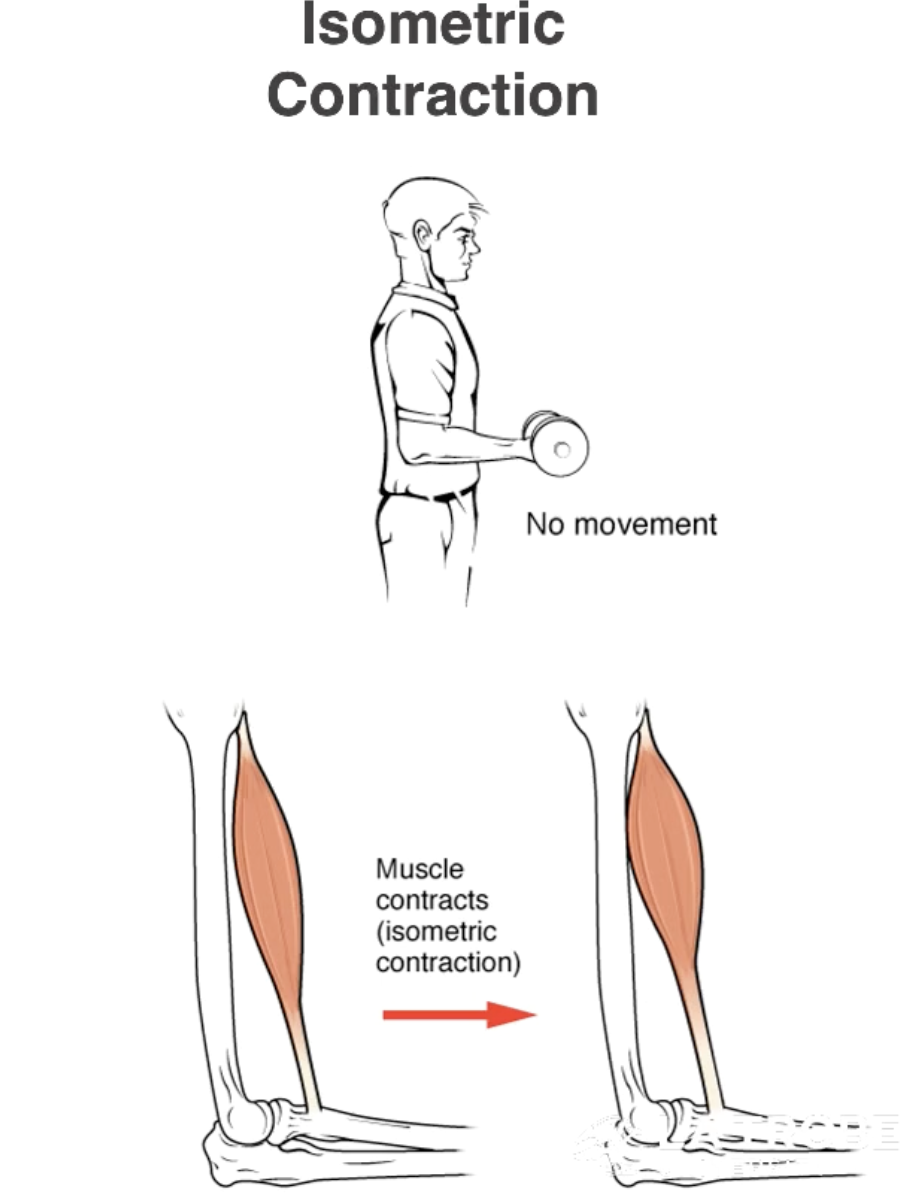
Isometric Contractions
Iso - Same
Metric - Length
Tension in the muscle remains constant.
Length of the muscle remains constant.
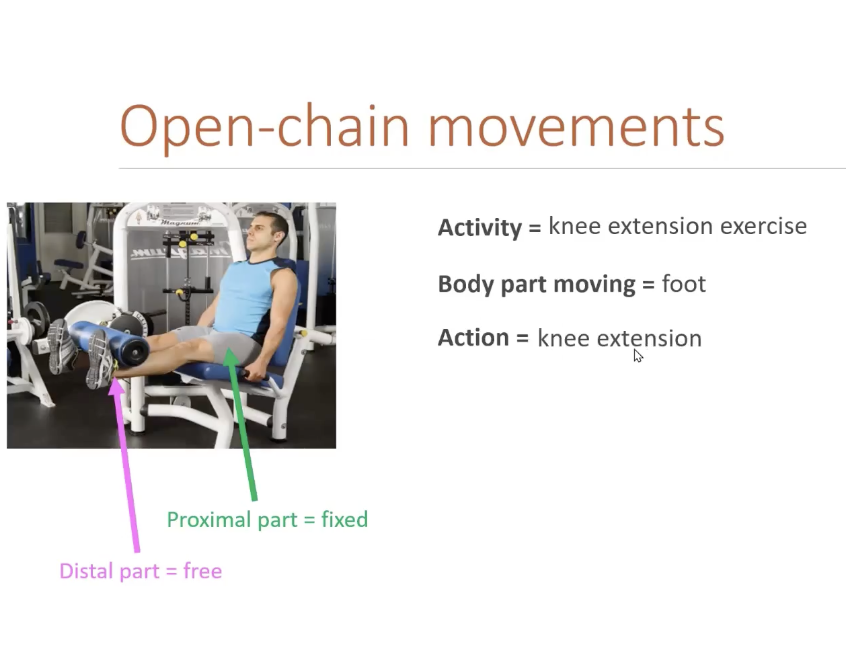
Open-Chain movements
Not touching the ground
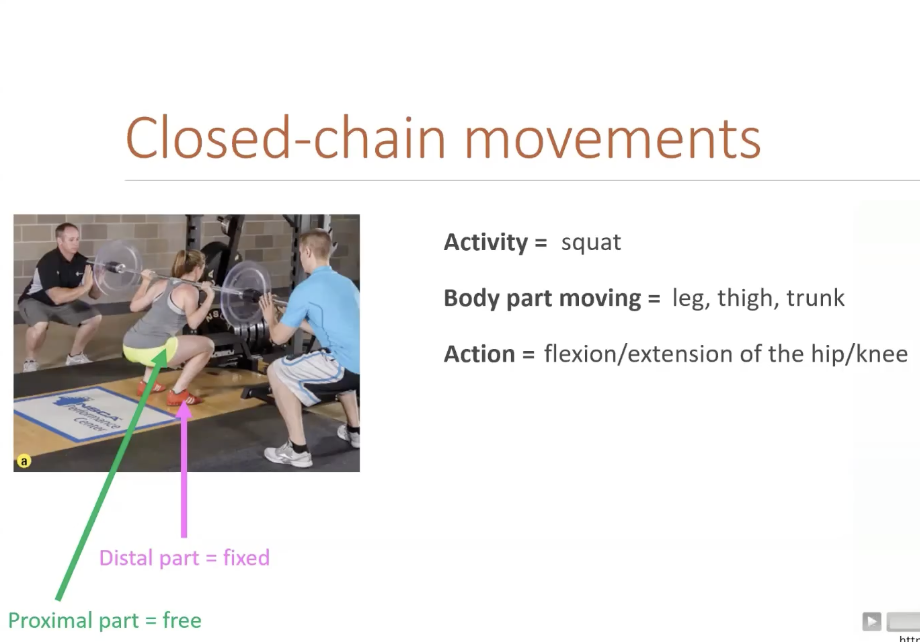
Close-Chain movements
Touching the ground
Levers
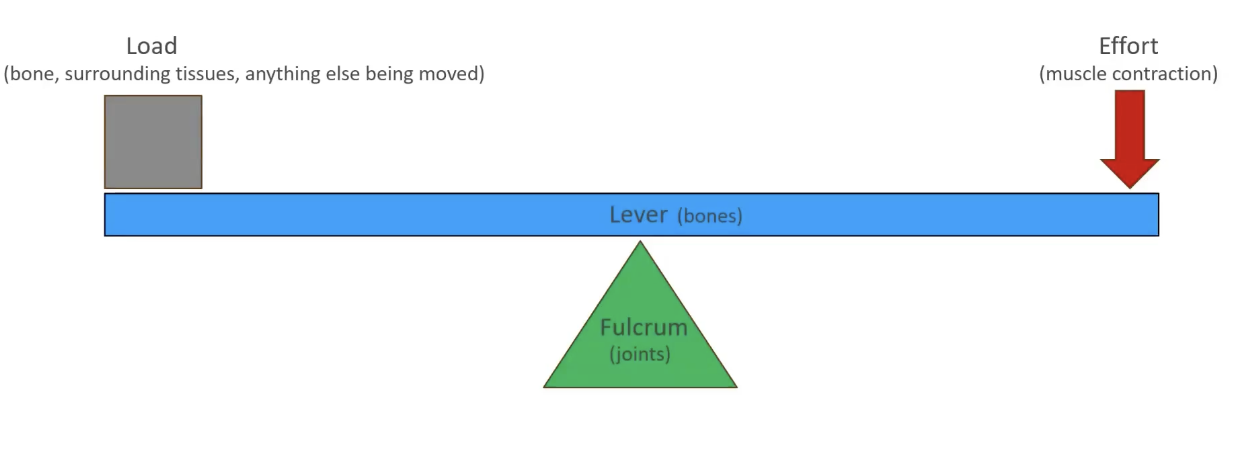
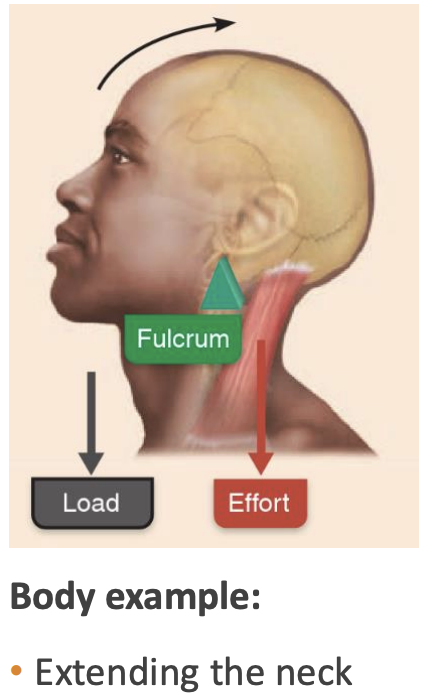
First-class lever
A lever where load (resistance) and effort (force) are on opposing sides of the fulcrum (axis).
(e.g see-saw (body example: neck))
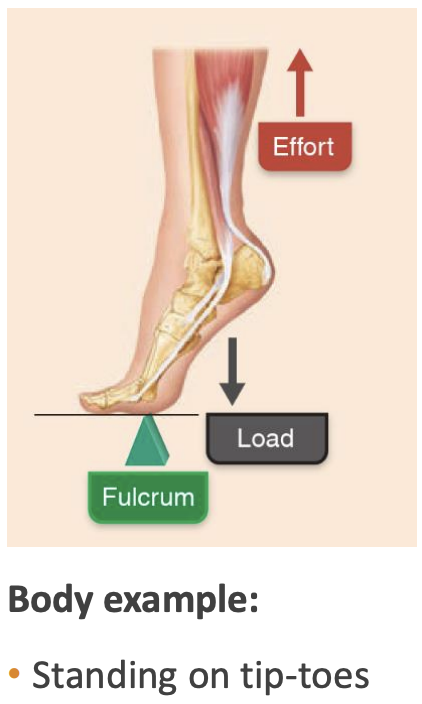
Second-class lever
Lever where, from the fulcrum (axis), the effort (force) is applied further than the load (resistance). Amplifies force production.
(e.g wheelbarrow (body example: tip-toeing))
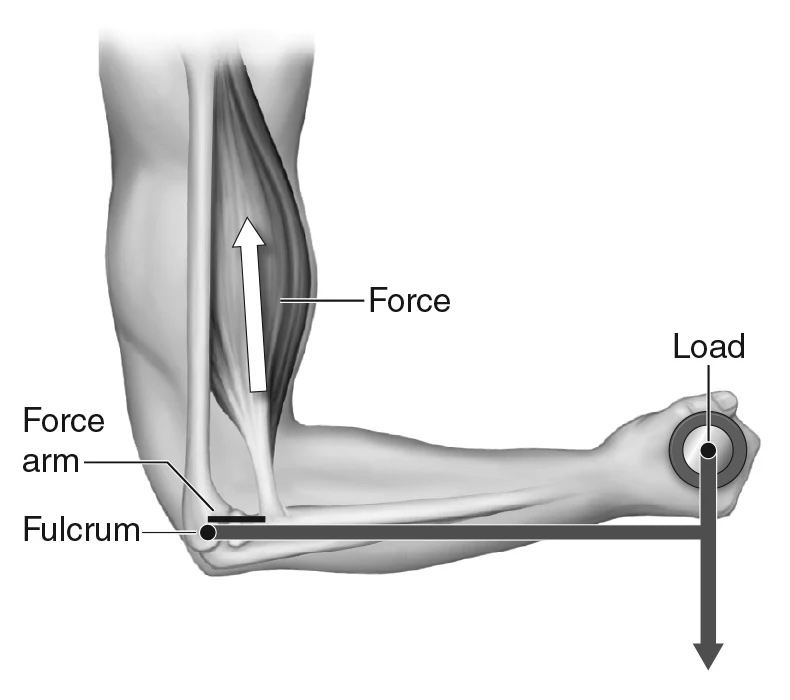
Third-class lever
Lever where, from the fulcrum (axis), the load (resistance) is applied further than the effort (force). Amplifies speed production.
(e.g fishing pole (body example: swinging tennis racket))
Most levers in the body are third-class.
Effort in levers
Located where athlete touches the equipment
Load in levers
Usually comes from an outer object (e.g tennis ball hitting racket)
Mechanical advantage
The amount by which the lever amplifies the force (effort).
Mechanical advantage = force arm/resistance arm = effort arm/load arm
>1 in second-class levers
<1 in third-class levers