P1: Conservation and dissipation of energy
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
System
An object or group of objects
What happens when a system changes?
Changes in the way energy is stored
Law of conservation of energy
Energy can’t be created or destroyed
Only transferred usefully, stored or dissipated
Kinetic energy
Energy stored in moving objects
How much KE does a stationary object have?
0
Kinetic energy equation

How can energy be transferred?
Heating
Waves
Electric current
Force when it moves an object
Energy transfers for a car moving at a constant speed
Chemical energy store (in petrol) → KE store (when car moves)
What does the energy in a KE store depend on?
Its mass
Its speed
What happens when a spring is stretched?
Work is done
As applying a force to change the length of the spring
What is put in to stretch a spring?
Energy
So stretched spring stores EPE
Elastic potential energy
Energy stored in an elastic object when work is done on the object
Energy stored in a stretched spring
Extension (e)
Amount by which a spring’s length increases when a force is applied (compared to og length)
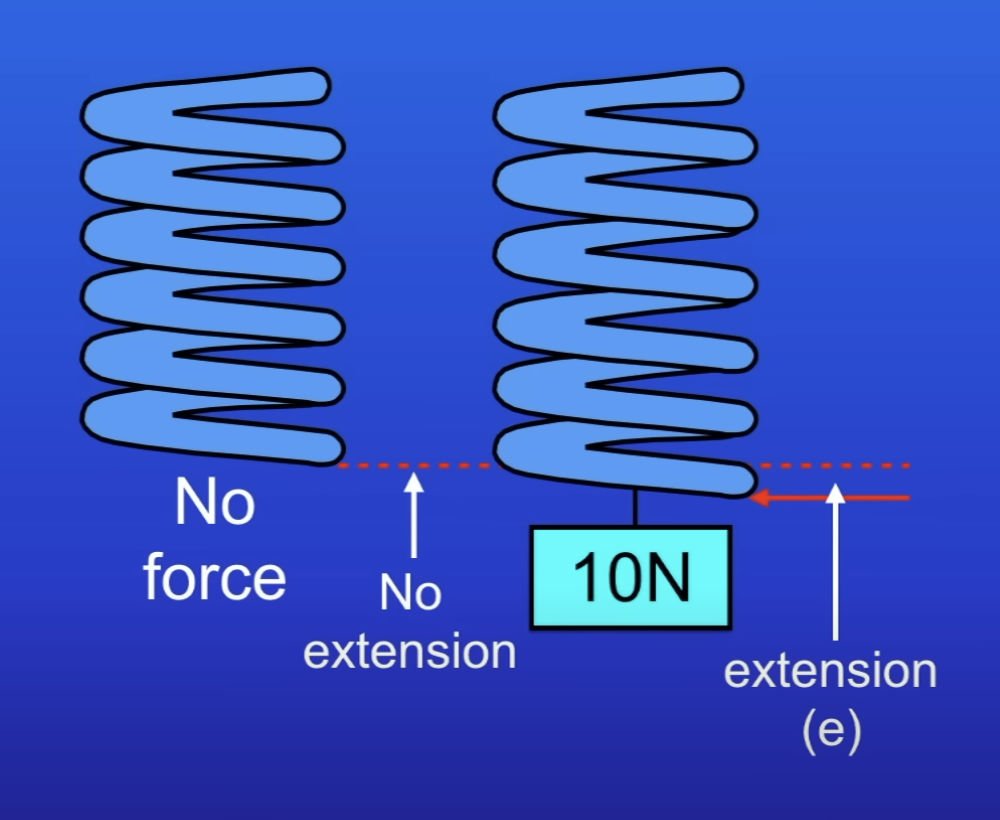
Spring constant
Force per unit extension of a spring
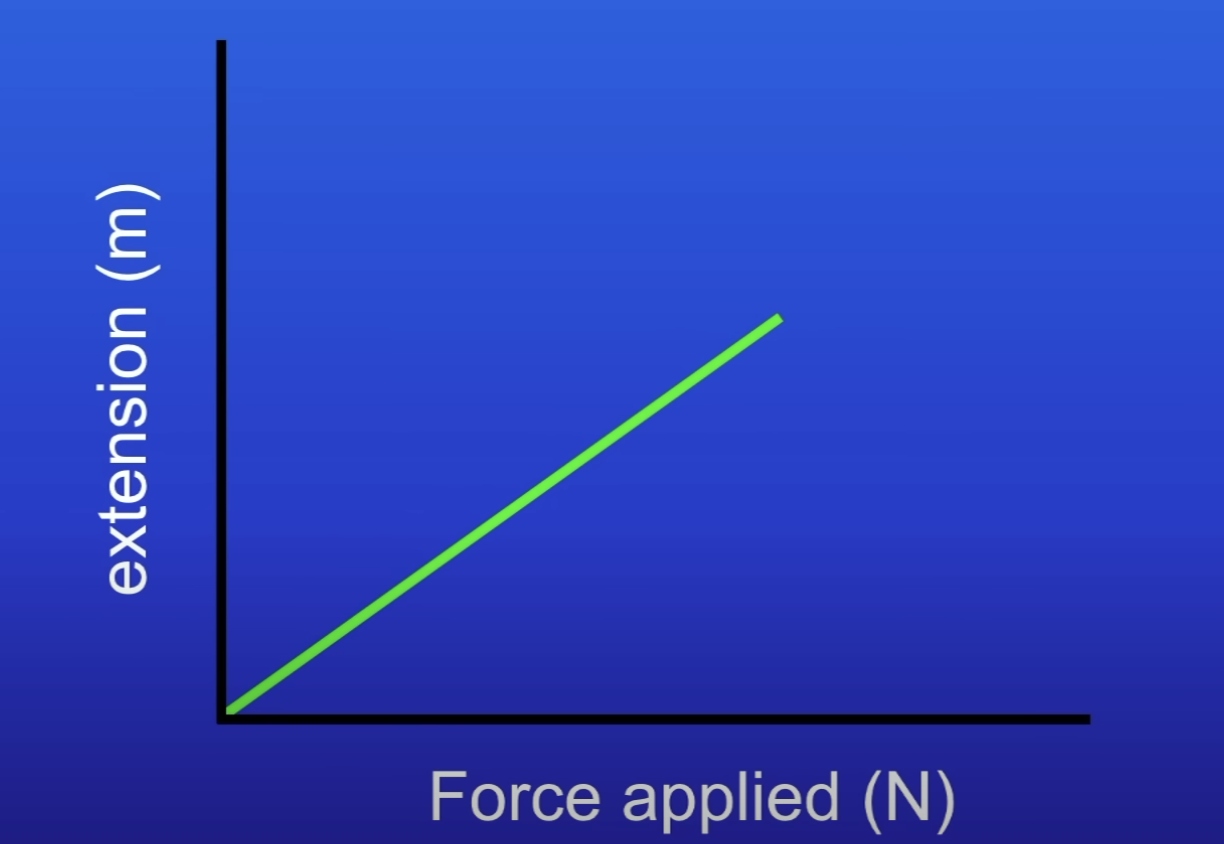
What is the extension of a spring directly proportional to (within limit of proportionality)
Force (N)
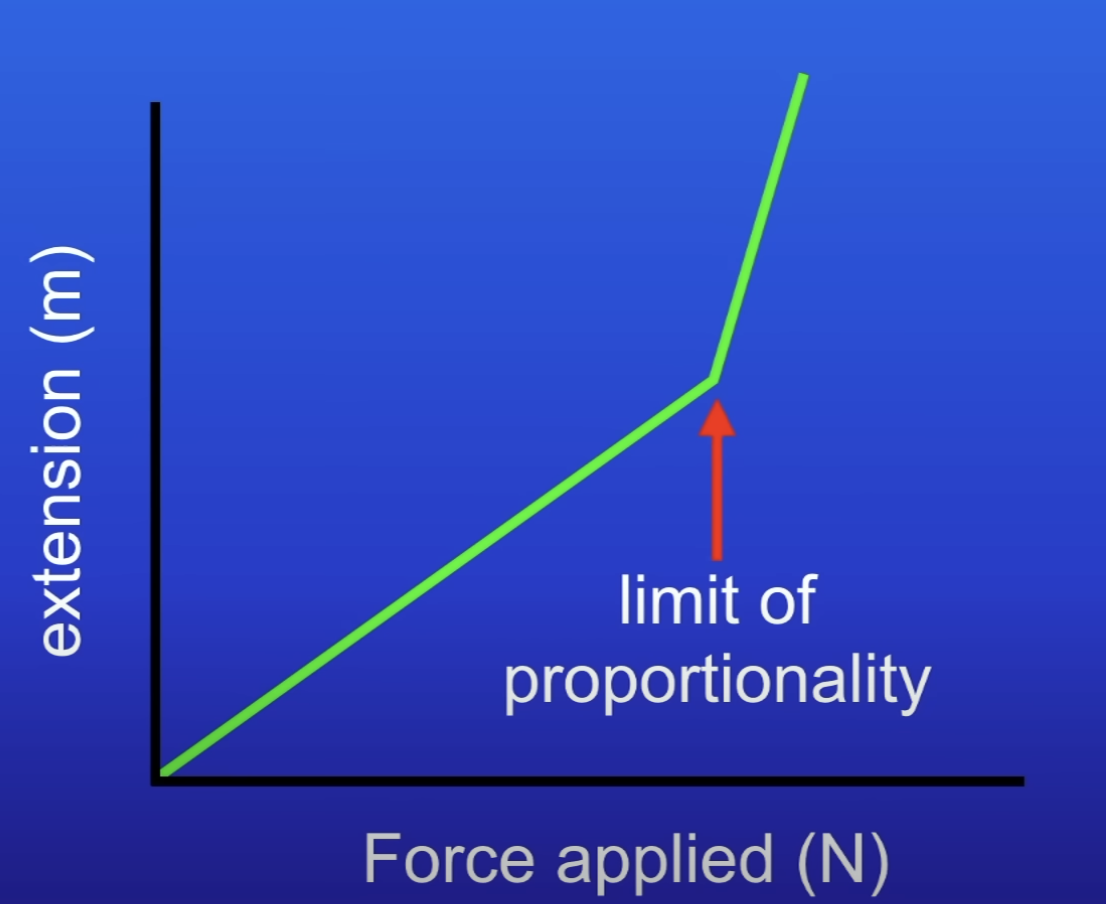
Limit of proportionality (recheck definition)
Max point an elastic object will stretch + return to its og shape?
Graph of force against extension when a spring has passed its limit of proportionality
Elastic potential energy equation

Gravitational potential energy
Energy stored in an object due to its position above the Earth’s surface
What causes GPE?
Force of gravity acting on an object
When does the GPE store of an object increase?
When it moves up
Why does the GPE store of an object increase when you move it up?
Chemical energy stored in muscles- used to lift object
CE of muscles → GPE in ball
Why does the GPE store of an object increase when it is lifted?
Work is done on it to overcome the gravitational force
When does the GPE store of an object decrease?
When it moves down
Why does a balls GPE store decrease when it falls from a shelf to the ground?
GPE → TE + KE
So ball has no GPE
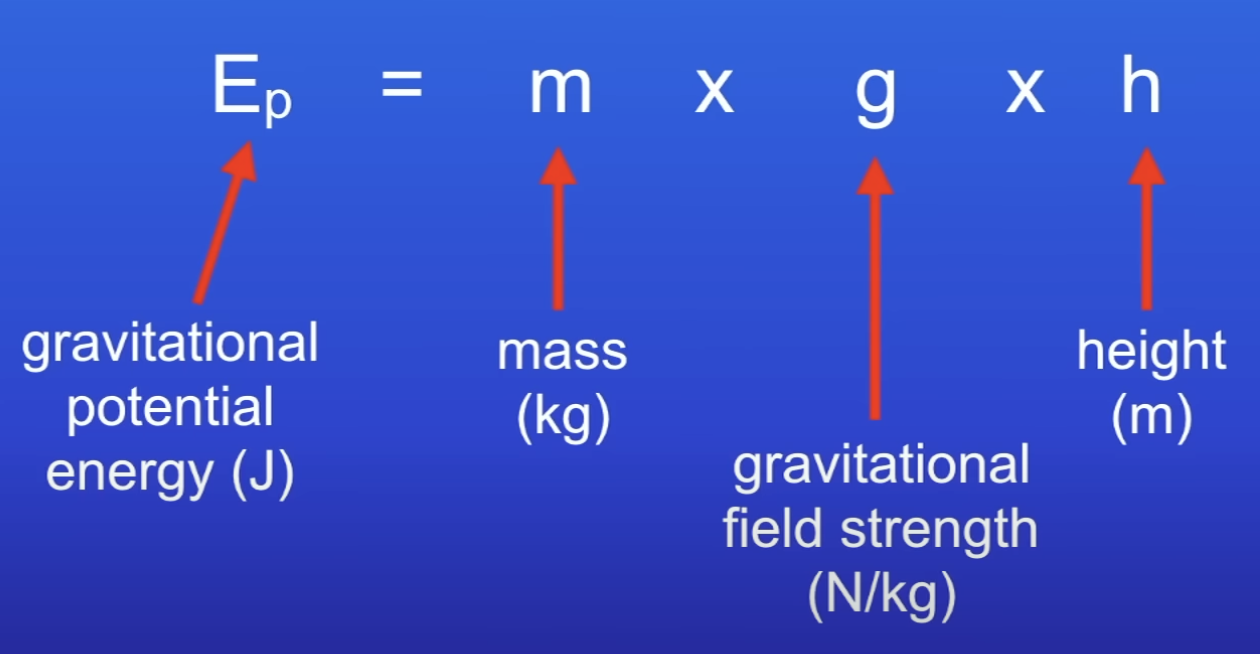
Gravitational potential energy equation
Gravitational field strength
Measure of the force of gravity
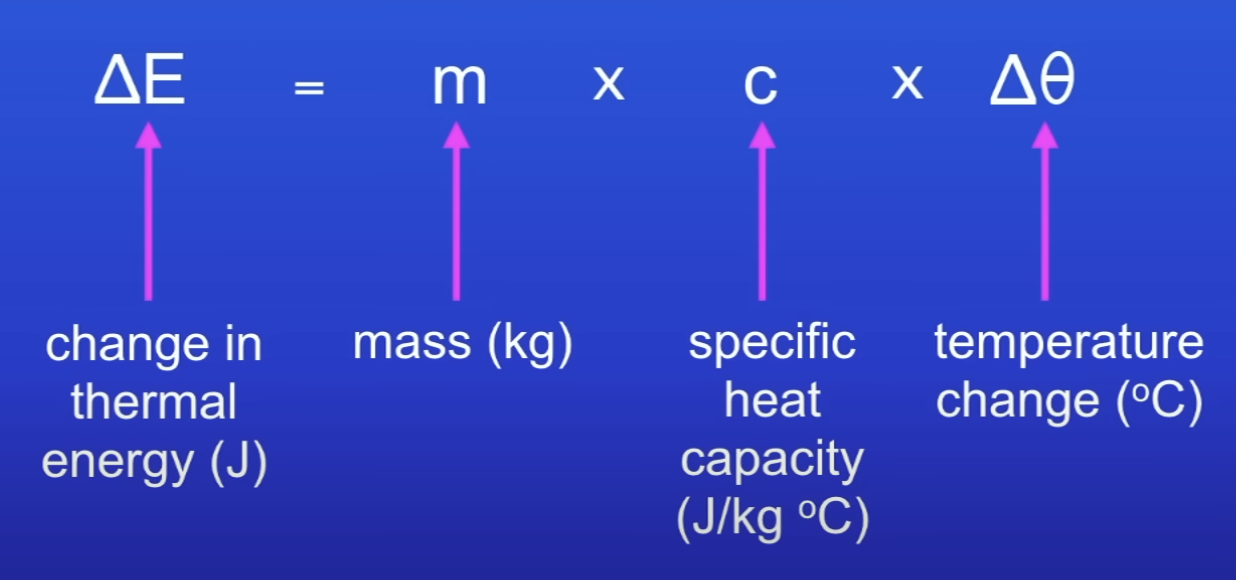
Specific heat capacity
Amt of energy needed to raise the temp of 1 kg of the substance by 1°C
Specific heat capacity equation
Equation to calc the amt of energy stored in / released from a system as its temp changes
If an object has more mass, will it have more or less KE?
More
More mass, more KE
Closed system
No energy can enter or leave
So no net change to the total energy
What happens when a person stretched an elastic band?
CE store in muscles decreases → ET to EPE store of elastic band (increases)
Work done
When energy is transferred from 1 store to another
2 types of work
Mechanical- using a force to move an object
Electrical- current transferring energy
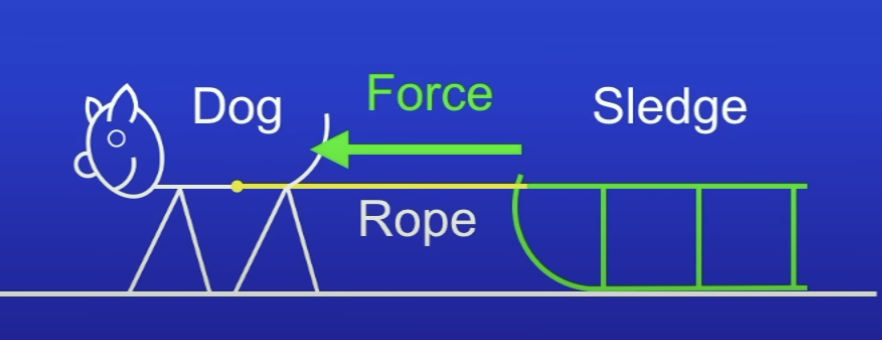
Energy transfers in this diagram:
Dog applies force to sledge → force causes sledge to move
CE in dog → KE in moving sledge → TE in sledge + ground (due to friction)
So work is done
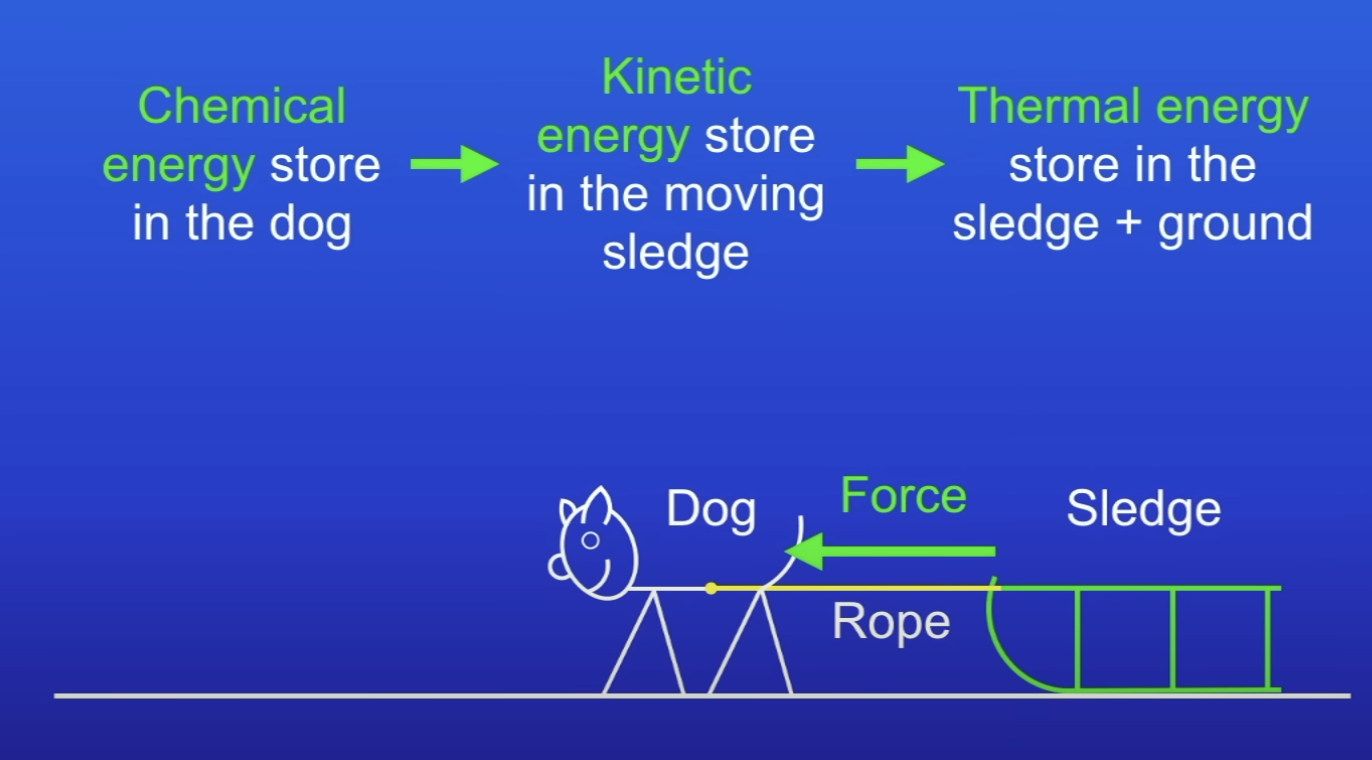
How do you know work is done?
ET betw diff stores
How do you know work is done when a force moves an object?
ET to object
Work done equation

Power
Rate at which energy is transferred
Or rate at which work is done
Power equation
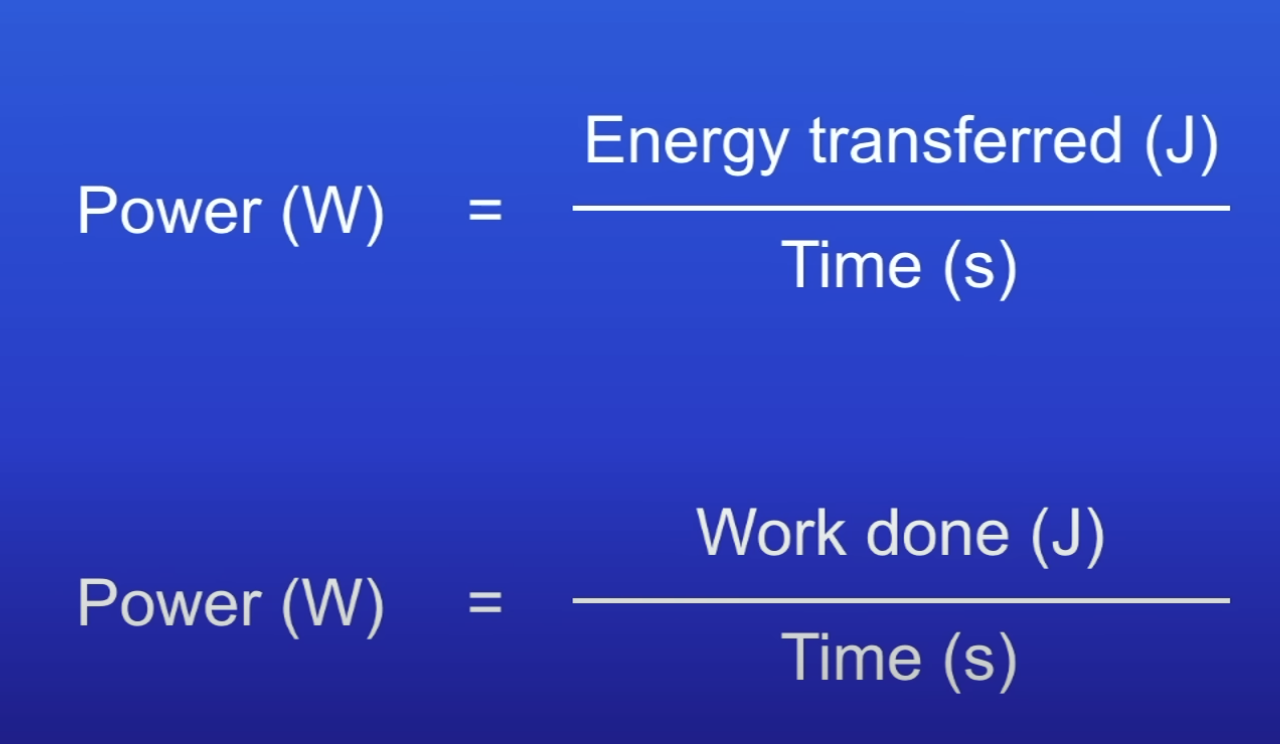
1 W =
Energy transfer (or work done) of 1 J per second
The higher the power of an appliance…
The faster the rate of energy transfer is
1 kW =
1000 W
Example of comparing power
2 electric motors that both lift the same weight to same height but 1 does it faster than the other
Friction
Force that opposes the motion of 2 surfaces in contact w each other
Work done to overcome friction is mainly transferred to?
Thermal energy stores by heating
What happens when an elastic object is stretched / squashed?
WD on it is stored as EPE
Elastic object
Regains its og shape after being stretched / squashed
Efficiency
What fraction of input energy is transferred to useful forms of energy
Efficiency equation

Input energy
Energy supplied to a machine
Useful output energy
Energy transferred usefully by a machine
Input energy equation
IE = useful output energy + energy wasted
Efficiency can’t be greater than?
100%
Can’t create energy
The more efficient a machine…
The less energy wasted
How do machines waste energy?
Friction betw moving parts
Air resistance
Electrical resistance
Noise
Principle on how to increase the efficiency of an energy transfer?
Reduce energy they waste
How to increase efficiency of a machine by reducing:
Friction betw moving parts
Air resistance
Electrical resistance
Lubrication
Make shape of vehicles more streamlined
Use copper wires
What do machines do?
Transfer energy for a purpose
Wasted energy
Energy not transferred usefully
What eventually happens to wasted energy?
Transferred to surroundings → surroundings become warmer
Dissipates
Spreads out
What happens to the usefullness of energy as it dissipates?
Becomes less useful
Electrical appliances should be designed to?
Waste as little energy as possible → increases efficiency
Uses of everyday electrical appliances?
Heating
Lighting
Making objects move (using an electrical motor)
Producing sound
Producing visual images
Describe all changes involved in the way energy is stored when a system changes:
An object projected upwards
Moving object hitting an obstacle
Object accelerated by a constant force
A vehicle slowing down
Bringing water to a boil in an electric kettle
What causes energy changes as a result of changing a system?
Heating
Work done by forces
Work done when a current flows
What happens when energy dissapates?
Stored in less useful ways
Wasted energy
Chemical energy