#1 Chem Quiz
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
blackbody
perfect black obj that does not refect any light but emits light if you increase the temperature
frequency (f)
the number of cycles per time, units s-1 , Hz
wavelength (λ)
the length of a wave, units m
wave equation
(f)(λ) = c
speed of light constant ( c )
3.00 × 108
quantum
specific landa
what are the 3 types of atomic spectrums?
visible spectrum
emission spectrum/bright line spectra
Absorption spectra/darkline spectra
what is a continous spectrum/visible spectrum?
spectrum where a prisim can be used to split up white light into all of its colours
how is a continous spectrum/visible spectrum produced?
white light → prisim/spectrophotometer → spectrum
what is a bright line/emission spectrum?
spectrum where each element emits a certain wavelength of light when heated
how is a bright line/emission spectrum produced?
heated up element → spectrophotometer → line spectrum
what is a absoprtion spectra/darkline spectra?
spectrum where a cold element gas absorbs a certain wavelength of light, done when placed in front of white light
how is a absorption spectra/darkline spectra produced?
white light → cold element → spectrophotometer → absorption spectrum
photoelectric effect
light energy (EM) can give electrons enough energy to leave a substance
Classic theory
as light gets brighter (more energy waves), electrons absorb more energy and are more likely to be emitted from the substance
classic theory was wrong
more intense light did not change the amount of energy liberated
what did max plank propose?
Max Plank proposed that light travels as a quantum of energy waves
minimum amount of energy needed/certain wavelength to give enoguh electrons to leave a substance
what is the visible light spectrum range?
700nm - 400nm
what is the visible light spectrum colours?
ROYGBV
list the waves from longest wavelength to shortest wavelength.
radiowaves
microwaves
infared
visible
UV
x-rays
gamma rays
what is the menomic to memorize the electromagnetic spectrum from longest wavelength to shortest wavelength (lowest energy & frequency, to highest energy and frequency)?
Raging martians invaded venus using x-ray guns
what is plank equation? (energy of photon)
E = hf
what is the h constant?
6.63 × 10-34
using the absorption spectra and emission spectra for the same element, what did bohr conclude?
an atom of an element can only absorb and emit certain wavelengths of energy
stationary state
electrons do not emit energy but they constantly orbit the nucleus
excited state
the farther away the orbit, the higher the energy level. electrons can absorb energy waves to jump to higher energy orbitals
what did balmer do?
he calculated the amount of photon energy released when electrons jumped back to a certain ground state for hydrogen
What is the balmer series?
6th, 5th, 4th, 3rd to 2nd shell
400-700 nm
visible spectrum
What is the lynmann series?
6th, 5th, 4th, 3rd, 2nd, to 1st shell
UV light
Paschen series
6th, 5th, 4th to 3rd shell
Infared light
Energy of an electron in a shell formula
E=\frac{-2.18x10^{-18}}{n^2}
Energy released
E=E_{h}-E_{l}
h = higher shell
l = lower shell
What are quantum numbers?
advances in the quantum mechanical model was made to explain new observations of atomic spectra
principal quantum number (n)
n represents the energy level of a orbital
EX n=1 → 1st shell
n² = # of orientations
2n² = # of electrons in that shell
secondary quantum number (ℓ) & scientist
ℓ represents the type of subshell orbital
Sommerfeld noticed that if you looked closer at a bright line spectra some lines were actually made up of 2 or more lines packed together
ℓ = 0
s orbital
ℓ = 1
p orbital
ℓ = 2
d orbital
ℓ = 3
f orbital
magnetic quantum number (mℓ) & scientist
m_{\ell} represents the # of different orientations of each subshell
Zeeman noticed that when a strong magnetic field was put near an element its bright line spectrum lines split
proposed that each type of subshell orbital had different orientations in space
how do you calculate mℓ ?
-ℓ to +ℓ (possible values)
magnetic spin (ms)
ms represents the electron spin in each orbital
2 electron per orbital
one electron spins clockwise, other spins counter-clockwise
what does ms = +1/2 mean?
unpaired electron
what does ms = -1/2 mean?
paired electron
Louis de Broglie
theorized that electrons do not move in circular orbits but in a wave
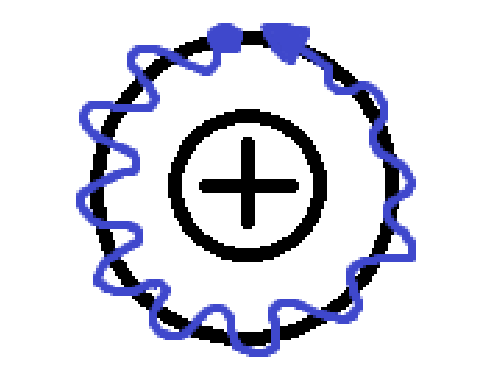
what does the formula \lambda=\frac{h}{mv} tell you?
wavelength of electron depends on mass and velocity
Werner Heisenberg
came up with the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
impossible to know the exact position and speed of a electron at the same time
probability of location of a electron is 90-95% accuracy
Schrodinger
invented wave equations (quantum mechanics) to determine the electron probability density (orbitals)
What did the bohr and quantum mechanical model have in common?
protons and neutrons in the nucleus
quantum mechanical model
translational movement around the nucleus in an energy level in a space called an orbital
different shapes of orbitals
2 energy levels
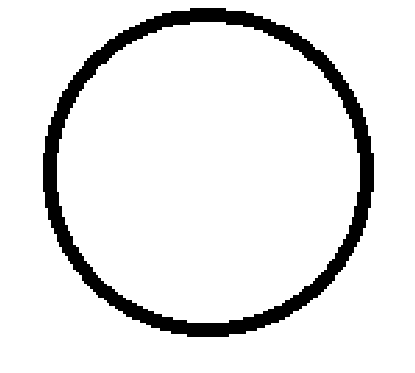
s orbital
1 orientation
2 electrons max
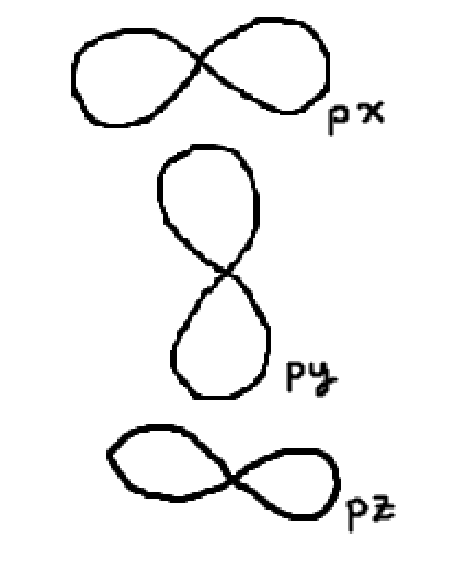
p orbital
3 orientations
6 electrons max
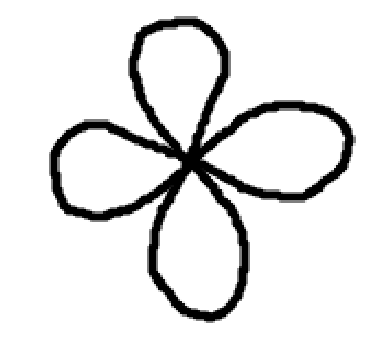
d orbital
5 orientations
10 electrons max

f orbital
7 orientations
14 electrons max
Aufbau principle
electrons must fill orbitals in order of lowest to highest energy
Pauli exclusion principle
max of 2 electrons per orbital
Hunds rule
orbitals must be half filled first in an energy level before paring up
What is the exeption when an electron will jump?
jump from an s to a d orbital so it is half filled or fullly filled, only applies to d4 and d9
Strength of ferromagnetisim
strongly magnetic
Strength of paramagnetism
weakly magnetic
which is found in nature, ferro or para?
ferro
give 3 examples of ferromagnetic metals that are found naturally?
iron, cobalt, nickel
Why are ferromagnetic metals stronger?
lots of atoms work together — their tiny magnetic fields all line up in the same direction, creating strong regions called magnetic domains.
why are paramagnetic metals weaker?
each atom with unpaired electrons makes a tiny magnetic field, but they don’t all line up together, so the effect stays weak
unpaired electrons spin and partially align with the external magnetic field
Persistence for ferromagnetisim
Magnetism can remain even after the external magnetic field is removed
Persistence for paramagnetisim
Magnetism disappears when the external magnetic field is removed
Dalton
each atom of the same element are exactly the same
atoms are the smallest unit of matter and are indivsible
Law of Definite Proportions/Constant composition
elements of a specific compound have constant portions by mass
Law of multiple proportions
transition metals that are mutlivalent (multiple charges) can form different compounds
Law of conservation of mass
the total mass of reactants has to equal the total mass of products
Arrhenius and Faraday
proposed the idea of atoms that have charges —> ions
Crookes
placed an iron cross in a cathode ray tube & observed the shadow of the cross
proved that electrons were particles and not energy
Thomson
proposed the idea of subatomic particles (electrons and protons)
atoms contained equal amount of electrons and protons
placed a positive and negative plate around the cathode ray tube & observed the beam was attracted to the positive plate
Rutherford
shot alpha rays at gold foil
proposed the idea of a nucleus where protons are surrounded by a cloud of negative electrons because some of the rays deflected back
Chadwick
proposed the idea of a neutron in the nucleus to account for the mass when compared to protons
found atoms of same element & diff mass called isotopes
all elements are relative to c-12
Radioactive
an element that emits radiation
Alpha decay
emits gamma radiation and helium
Beta decay
emits gamma radiation and electron
Gamma
emits gamma radiation
when are elements radioactive when looking at the neutron proton ration?
when n/p = 1.5 element is radiactive
intermolecular forces
bonds between atoms
what is a cation
metal loses valence electron to become stable —> positive ion (+)
what is a anion
non-metals gian electrons to be stable —> negative ion
when is covalent bonding found?
mollecular compounds (non-metal + non-metal)
what is covalent bonding?
non-metals share valence electrons in order to have a full shell to be stable
what are the 2 exeptions to the octect rule?
If the center atom has 3 energy levels (3rd row) or lower, they may have more than 8 electrons
Certain atoms in the center such as B, Be can have less than 8 electrons (not full)
Why can the center atom on the 3rd energy level or lower have more than 8 electrons?
it has available d orbitals that are empty which allows for it to have more electrons.
What does a molecule with (-) mean?
add electron
What does a molecule with (+) mean?
remove electron
what does resonance mean?
delocalized electrons in pi bonds moving positions
structures that contain a double bond can have multiple ways of drawing
EX CO3²- has 3 resonance
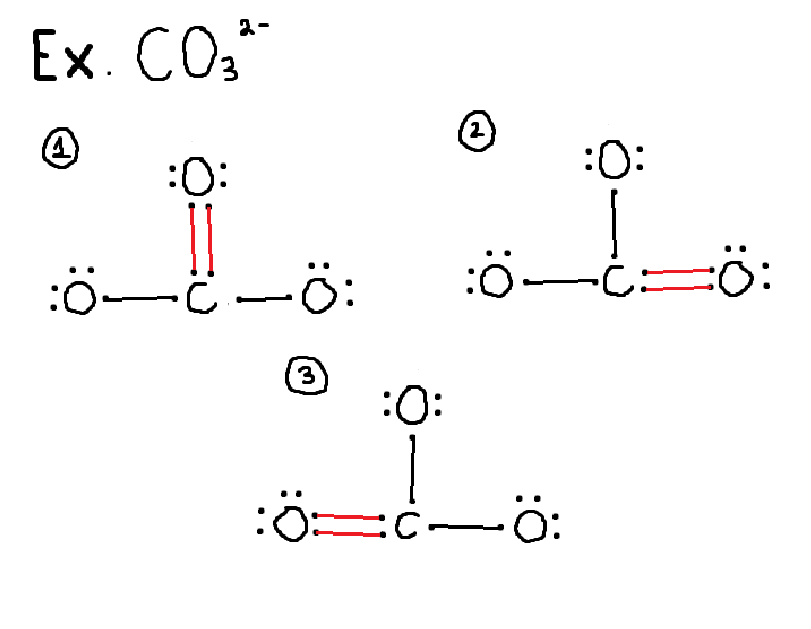
How is a pi bond created?
unhybridized p-orbitals that are vertical to the bond axis overlap
what is bond length?
distance between the 2 nuclei of the atoms involved in the bond
what does a longer bond length mean in terms of strength?
longer bond = weaker bond strength
what does a shorter bond length mean in terms of strength?
shorter bond = stronger bond strength
what is bond strength?
the amount of energy needed to break a bond
pi bonds < sigma bonds
multiple bonds > single bonds
why was hybridization developed?
to explain the bonding and shape of molecular structures
how do you calculate electron domain?
sigma bonds + lone pairs of electrons
from what orbitals do you remove electrons?
s & p orbitals
Who created VSPER theory?
Nyholm and Gillespe
why was VSPER theory created?
it was created to theorize why molecules have the shape they do
What does VSPER stand for?
Valence Shell Pair Electron Repulsion