Biochemistry final exam
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
What is needed to complete the mutagenesis process after DNA damage?
A. Formation of a tumor
B. Increase in pigmentation
C. A round of replication
D. Formation of a thymine dimer
E. UV light absorption
C. A round of replication
Andy is a homeless kid, 9 y.o., that sleeps during the day and begs during the nights in Rio, Brazil. He is covered with freckles and has a couple of open skin rashes on his face. Most of his body look OK. You examine him and find out that one of the rashes is cancerous. None of his homeless friends show this condition. His older brother 20 y.o. died of cancer, but all of the rest of his 4 siblings are OK. This is consistent with:
A. Allergy
B. Lupus
C. Xeroderma Pigmentosa
D. Lica
E. Chemical irritation
C. Xeroderma pigmentosa
In Dam- mutants of E. coli what % of mismatches would be fixed correctly?
a. Less than 10%
b. About 33%
c. About 50%
d. About 75%
e. Over 90%
c. About 50%
Which substance would make a DNA molecule longer?
a. 2-Aminopurine
b. 5-Bromouracil
c. Ethidium bromide
d. Dimethyl sulfate
e. Sodium nitrite
c. Ethidium bromide
Which substance will damage DNA without making nor breaking covalent bonds?
a. 2-Aminopurine
b. 5-Bromouracil
c. Ethidium bromide
d. Dimethyl sulfate
e. Sodium nitrite
c. Ethidium bromide
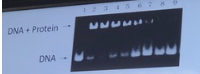
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is due to faulty DNA repair. DNA from CRC patients (2-8) and cancer free controls (1 and 9), was mixed with a protein, and run in an agarose gel. The slowing down of the DNA band is due to a complex formed between the DNA and the protein. Which protein could that be?
a. protein X
b. MutS
c. P53
d. Rad51
e. DNA Pol III
b. MutS
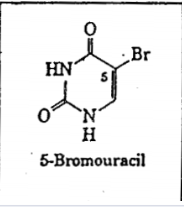
This substance is mutagenic and carcinogenic. What is the mode of action?
a. DNA polymerase inhibitor
b. Weakness the mRNA
c. Mimics a pyrimidine
d. Intercalates in the DNA
e. Cross links the DNA strands
c. Mimics a pyrimidine
In principle, what could reduce the reactivity of the molecule?
a. Drinking more water
b. Ionizing radiation
c. Belly fat
d. Antioxidants
e. Sun light
d. Antioxidants
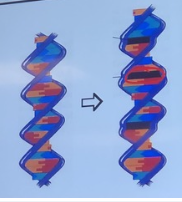
What substance can induce this change in the DNA?
a. 2-Aminopurine
b. Ethidium Bromide
c. Dimethyl sulphate
d. Nitrogen mustard
e. N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine
b. Ethidium Bromide
Heritability is the proportion of the phenotypic variance in a population explained by genetic susceptibility. What type of study would you use to measure heritability?
a. Family studies
b. Adoption studies
c. Twin studies
a. Family studies
Among car drivers, melanomas and other skin cancers are far more common on the left arm. Why do you think this is so?
a. Left arm is used much less than the right arm
b. This arm is more exposed to toxic chemicals from the road
c. This arm is less oxygenated than the right arm
d. Drivers seek medical help for the right hand, not so much for the left
e. This arm receives more sunlight than the right
e. This arm receives more sunlight than the right
Melanomas and other forms of skin cancers are far more common on the right arm among UK drivers. Why do you think this is so?
a. Vehicles are much smaller in the UK
b. Diesel is the preferred fuel in the UK, as opposed to gasoline
c. The steering wheel of cars is located at the right, as opposed to
the left as in the US
d. The UK has less regulations for air quality
e. The UK is more humid than the US
c. The steering wheel of cars is located at the right, as opposed
to the left as in the US
Chemotherapeutic drugs, like alkylating agent cisplatin, are mutagenic. Why are cancer cells (CC) more susceptible than normal cells to these mutagens?
a. The CC has lower DNA repair
b. These agents interfere with DNA replication
c. These agents modify all types of RNAs
d. Normal cells have mechanisms to exclude these substances
e. Normal cells can metabolize these substances to less toxic compounds
b. These agents interfere with DNA replication
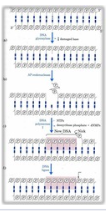
The absence of which enzyme would increase the number of AP sites of a person's DNA?
a. AP endonucleases
b. DNA glycosidase
c. DNA polymerase I
d. DNA polymerase III
e. DNA lygase
a. AP endonucleases
Why are mutagenicity experiments with UV light done in the dark?
a. Visible light can cancel UV light
b. Nonspecific angle illumination will hinder mutagens
c. So you know the exact dose of UV light given
d. Light will activate a type of DNA repair
e. Eliminate interference from blue component light
d. Light will activate a type of DNA repair
Richard Peto of the University of Oxford, UK, in the 1970s, noted that, in general, there is little relationship between cancer rates and the body size or age of animals. This is known as the Peto paradox, because large animals should have more mutations due to more mitosis.
Why do you think elephants are protected against cancer?
a. They have 20 copies of the tumor suppressor gene p53
b. They live in unpolluted natural environment
c. They are vegetarians
d. They have larger livers and thus detox better
e. Their immune response is larger
a. They have 20 copies of the tumor suppressor gene p53
The DNA repair that does not require ligase is:
a. Mismatch
b. Base-excision
c. Nucleotide-excision
d. Direct repair
e. SOS response
d. Direct repair
Which of the following mutations in the exon of a gene has the highest chances of producing a functional enzyme?
a. A deletion of 1 base pair
b. A deletion of 2 bp
c. A deletion of 3 bp
d. An insertion of a bp
e. An insertion of 14 bp
c. A deletion of 3 bp
Do you approve laws that require that all citizens have their DNA sequence in data banks, so that fighting crime becomes easier?
a. Yes
b. No
c. Don't know
d. Only certain felons
b. No
(Wow to this question lol, I guess its more opinion based to get
you thinking)
Which of the following chromosomal disorders causes the largest number of spontaneous abortions?
a. Klinefelter Syndrome 47 XXY
b. Turner Syndrome 45 X
c. Trisomy 18
d. Trisomy 13
e. Wolf Hirschhorn Syndrome 4p-
b. Turner Syndrome 45 X
The most common trisomy found in spontaneous abortions is:
a. Trisomy 2
b. Trisomy 19
c. Trisomy 9
d. Trisomy 16
e. Trisomy 21
d. Trisomy 16
________ also known as 5P- (deletion of terminal chromosome 5p), this disorder is characterized by unique facial features, growth retardation, and microcephaly. Patients have an unusual catlike cry. Most patients have major organ anomalies and significant intellectual disability.
a. Wolf Hirschhorn syndrome
b. Williams Syndrome
c. Cri du Chat
d. Smith-Magenis Syndrome
c. Cri du Chat
A 25-year-old male underwent genetic testing to diagnose what appeared to be a feminizing disorder. He was tall with sparse facial hair, small testes, and gynecomastia. He also had poor coordination and language and reading difficulties. Which of the following best describes the reason for his abnormal karyotype?
a. Patau syndrome; trinucleotide repeat
b. Klinefleter syndrome: Nondisjunction
c. Angelman: UBE1A gene translocation
d. Alagille: translocation
b. Klinefelter syndrome: Nondisjunction
Which of the following is not a form of trisomy?
a. Trisomy 21
b. Edwards syndrome
c. Patau syndrome
d. 69 XXX
e. Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome
F. D & E
F. D & E
69 xxx -
Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) is a genetic disorder caused by a deletion on the short arm of chromosome 4
The life expectancy is longer for the following type of trisomy:
a. Trisomy 21
b. Trisomy 18
c. Trisomy 13
d. 69 XXX
a. Trisomy 21
The following laboratory findings would NOT indicate Turner Syndrome:
a. Hypogonadism confirmed in girls who have high serum levels
of FSH and LH
b. A blood karyotype showing 45, XO
c. GH and IGF-1 levels are normal
d. A blood karyotype showing 47, XXY
d. A blood karyotype showing 47, XXY
Genetic testing can be done on several sample types. Which of the following sample types would you prefer to utilize?
a. Cultured nail cells
b. Blood
c. Buccal cells
d. Tissue biopsy
b. Blood
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of single gene disorders:
a. Are caused by individual mutant genes found in one chromo-
some or both
b. Includes mitochondrial disorders
c. Includes in live births is 0.36%
d. Rarely due to the same mutation in unrelated individuals
d. Rarely due to the same mutation in unrelated individuals
The characteristics of _______ in humans can be summarized as follows: (1) A horizontal pattern occurs in the pedigree, with a single generation affected. (2) Males and females are affected with equal frequency and severity. (3) Two-thirds of all clinically unaffected offspring are carriers.
a. Autosomal dominant inheritance
b. Autosomal recessive inheritance
c. Sex linked inheritance
b. Autosomal recessive inheritance
A compound heterozygote is:
a. An individual with mutation in two different genes
b. An individual with no mutant alleles
c. An individual with two different mutant alleles at the same locus
d. An individual with mutant alleles at eh same locus
c. An individual with two different mutant alleles at the same locus
The following are characteristics of Retinitis Pigmentosa except:
a. General term for a disparate group of rod-cone dystrophies
b. Characterized by progewssive night blindness
c. Visual field constriction with a ring scotoma
d. Allelic heterogeneity
e. Loci Heterogeneity
d. Allelic heterogeneity
An 18-month-old boy is exhibiting failure to thrive despite a healthy appetite, a foul-smelling and frequent stools. A sweat test for the presence of chloride ions was positive. The sweat electrolyte measurements is used as cardinal diagnostic tests for what disease?
a. Hypocholermia
b. Hypokalemia
c. Cystic fibrosis
d. Metabolic alkalosis
c. Cystic fibrosis
The sweat electrolyte measurements is used as cardinal diagnostic tests CF. What other tests could be performed?
a. Pulmonary function test
b. Sputum test
c. Panels that identify on the order of 20-140 CFTR variants
d. For difficult cases, complete CFTR exonic sequencing together with analysis of splice junctions and key regulatory elements can be obtained
e. All of the above
e. All of the above
The clinical manifestations for Marfan syndrome include:
a. Characterized by joint hypermobility and skin that is velvety in texture, hyperextensible, and easily scarred
b. A connective tissue disorder characterized by vascular features in addition to a variety of skeletal and cutaneous features.
c. Tall, thin, scoliosis, pectus, long fingers, myopia, dislocated lenses, aortic dilation, dissections, aneurysms, mitral valve prolapse
c. Tall, thin, scoliosis, pectus, long fingers, myopia, dislocated lenses, aortic dilation, dissections, aneurysms, mitral valve prolapse
A 12-year-old Russian girl immigrated to the United States with her parents. She was slow in her mental milestones, displayed arm and leg tremors, along with periods of hyperactivity. A blood test indicated elevated levels of phenylpyruvate. A potential defective enzyme in this child is which one of the following?
a. Tyrosinase
b. Homogentisic acid, 1,20dioxygenase
c. Branched-chain alpha keto acid dehydrogenase
d. Monoamine oxidase
e. Phenylalanine hydroxylase
e. Phenylalanine hydroxylase
A 14-year-old female is referred to you due to lack of secondary sexual characteristics. You diagnose her with Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome. This disorder can have which of the following features:
A. Elevated or occasionally normal serum testosterone for a male, with an elevated serum LH
B. Affects at least 1 in 100,000 46,XY individuals
C. Androgen receptor gene mutation (Xp11-q12).
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
100% of the following two mutant individuals express the phenotype:
mutations in the LDLR, APOB, or PCSK9 gene; Point mutation in
FGFR3
This very rare genetically heterogeneous disorder is characterized by mental retardation, renal abnormalities, obesity, and hexadactyly, brachydactyly, or syndactyly. Central diabetes insipidus may or may not be associated. GnRH deficiency occurs in 75% of males and half of affected females. Retinal degeneration begins in early childhood, and most patients are blind by age 30.
Bardet-Biedl syndrome
Which statement is CORRECT about the globin genes?
a. Globin genes are not highly conserved across species
b. Alpha and beta globin are encoded by the same locus
c. Genes expressed in adults are located in 5' of those expressed
in the fetus
d. Hemoglobin alpha-2-beta-2 is encoded by 2 alpha-globin genes
and 1 beta-globin gene
d. Hemoglobin alpha-2-beta-2 is encoded by 2 alpha-globin genes
and 1 beta-globin gene
Which disease is properly linked to the mutation/issue causing this
condition?
a. Alpha thalassemia- Homologous pairing and unequal crossover
b. Beta thalassemia-duplication of beta-globin genene
c. Sickle cell disease- Glu to Ala
Persistence of HbF - inability to switch from delta to beta globin
synthesis
a. Alpha thalassemia- Homologous pairing and unequal crossover
The key feature of OI is a severe decrease in bone mass that makes bones brittle. The disorder is associated with blue sclerae, dental abnormalities, progressive hearing loss, and a family history. Most patients have mutations:
a. Substitution Gly227Asp in COL1A1 gene
b. Substitution Gly476Arg in COL1A1 gene
c. Duplication Ala675dup in COL1A1 gene
d. Deletion of COL1A1 gene/diminished collagen production
d. Deletion of COL1A1 gene/diminished collagen production
For a person with Osteogenesis imperfecta: missense mutation COL1A1, what proportion of the collagen molecules (triple helix)
formed would be normal? Abnormal?
a. 25% normal: 75% abnormal
b. 50% normal: 50% abnormal
c. 75% normal: 25% abnormal
d. 100% abnormal
e. 100% normal
a. 25% normal: 75% abnormal
Which of the following CFTR mutations is a missense mutation:
a. Arg117His
b. Glu112del
c. Ser1255Pro
d. DNA TTC to TTT (silent mutation bc there was no change to the
amino acid)
e. DNA TAC to TAA (nonsense)
A. Arg117His and C. Ser1255Pro
Which of the following classes of CFTR mutations is least likely to lead to cystic fibrosis?
a. Absent protein, normal mRNA abundance
b. Defective regulation
c. Reduced numbers of transcript
d. Protein with residual activity
d. Protein with residual activity
Plasma amino acid analysis shows increased phenylalanine without increased tyrosine. What enzyme analysis should you consider performing first?
a. Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH)
b. Pterin carbinolamine-4-alpha-dehydratase (PCD)
c. Dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR)
d. 6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin synthase (PTPS)
e. All of the above
a. Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH)
PAH activity is normal. What genetic testing should be performed?
a. Pterin carbinolamine-alpha-dehydratase (PCD)
b. Dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR)
c. 6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin synthase (PTPS)
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
Programmed cell death is termed as:
Apoptosis
In cells, mutagenesis of tumor suppressor genes can occur:
A. due to formation of cyclobutene pyrimidine dimers by UV radiation
B. by excess formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
C. as a result of reduced endogenous antioxidant capacity
D. due to aberrant DNA repair capacity
E. All of the above
E. All of the above
What could be coded by a tumor-suppressor gene?
A protein that helps prevent progression through cell cycle
Proto-oncogenes cannot be transformed to oncogenes by this mechanism
Complete deletion of the proto-oncogene
What property of p53 enables it to prevent the development of cancer?
It prevents replication of cells with damaged DNA
What genetic change IS NOT a common hallmark of cancer cells?
elevated expression of tumor suppressor gene
How does Ras oncogene contribute to cancers?
It codes for a GTPase switch protein, which in its mutated form
cannot be switched off
What would convert Ras into an oncogene:
mutations that impair Ras' GTPase activity
CpG islands in the promoter regions of genes can play significant
roles everywhere, EXCEPT:
The region where silencing occurs by carboxylation
Dr. Chris P Bacon is a research oncologist working at medical research institution near your residence. He discovered a novel compound that uncoupled the reaction of RAS, an oncogene product. In the presence of this compound, Ras does not bind to cell membrane. What event is most likely affected by this compound?
Farnesylation
Migration of cancerous cells from the site of origin to other part of the body forming secondary tumors is called
Metastasis
The characteristic of malignant other than benign tumor is:
Undergoes metastasis
What is a hallmark of hereditary cancers?
multiple primary tumors
A 12-year-old girl from Egypt shows up to the hospital with various
cutaneous 'lesions' on her torso. Physical examination reveals multiple raised, firm, pink-to-flesh-colored keratotic papules and plaques, some of which demonstrates ulcerations on the arms, torso and legs. Her neck, face, and hands are multiple flat, firm, pale cutaneous lesions that appear translucent, shiny, and waxy. The patient has a younger brother who is similarly affected. Based on the history, what is the most likely consequence of the mutations you expect to see in this patient?
Incapacity to properly repair DNA damage
The immune system is a system of many biological structures and
processes within an organism that protects against disease. The
immune system can be divided into:
Adaptive and innate immunity
The lymphoid cells that serve as the foundation of our humoral
immune system are the:
B lymphocytes (B cells)
What cells of the body defenses have as their major function the
production of antibodies?
plasma cells
Cell mediated immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies, but rather involves that activation of lymphocytes. The cell-mediated immune system specializes in eliminating:
all pathogens
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is the locus of genes that encode for proteins on the surface of cells that are responsible for regulation of the immune system. What is TRUE about HLA Class 1 proteins?
Encoded by 26 genes, has a heavy chain, HLA A & B are relevant to MHC
________ results in failure to pass meconium by newborns, followed by constipation. If only a very short segment of intestine is involved, built-up pressure may cause diarrhea.
a. IBS
b. Retentive constipation
c. Hirschprung's disease
Hirschsprung's disease
Which of the following statements best describe in the inheritance of Hirschsprung's disease?
a. Chromosome abnormalities associated with HSCR
b. Mutations in these genes account for only about 50% of the known cases of HSCR
c. Inheritance of Hirschsprung disease is complex, often on Mendelian and characterized by variable penetrance
d. All of the above
all of the above
This is a general term for a disparate groups of rod-cone dystrophies characterized by progressive night blindness, visual field constriction with a ring scotoma, loss acuity, and an abnormal electroretinogram (ERG).
a. Macular Degeneration
b. Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
c. Retinitis Pigmentosa
d. Melanoma
Retinitis Pigmentosa
Inheritance of digenic retinitis pigmentosa is best describes as:
a. Autosomal recessive
b. Autosomal dominant peripherin/RDS mutation
c. Autosomal dominant rhodopsin mutation
d. Mutations at the unlinked peripherin/RDS and ROM1 loci
d. Mutations at the unlinked peripherin/RDS and ROM1 loci
A study found: During 1,294,7999 person of years of follow-up,
3,844 incident cases of diabetes were documented. Compared
with whites, the age-adjusted relative risks (RRs) were 1.43 for
Asians, 1.76 for Hispanics and 2.18 for blacks. What is the group
with the highest disease risk:
Low number: Protected (Asians)
High number: more at risk (Blacks)
Which of the following relatives are the least genetically similar?
a. Fraternal twins
b. Sisters born 20 years apart
c. Cousins from identical twin mothers
d. Cousins from identical twin mothers and fathers
c. Cousins from identical twin mothers
Alpha thalassemia follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. If both parent are carriers, what is the probability that a child will also be a carrier? Have the disease?
50% carrier;
25% affected
25% unaffected
You are looking at a section of a biopsied tissue from a skin lesion on the forehead of a 50 year old European farmer. You can identify the following histological features in the tissue section: raised pearly borders (this is a basal cell skin CA) surrounded by fine telangiectasias, cellular nuclei arranged in palisades, island of tumor cells. Which of the following do you think most likely caused the mutation that led to the formation of the tumor in this patient?
a. DNA polymerase replication errors
b. Formation of 8-oxo-deoxyguanosine
c. Formation of cyclobutane rings
d. Chronic tissue inflammation
e. Diminished DNA repair capacity
c. Formation of cyclobutane rings
A 67 yo man with a hx of prostate CA presents for fu after surgical management. He has been having back pain for the past two months, a pain that does not respond to ibuprofen. On XR, a significant lesion is found in the L12 vertebra (hallmark6). Which of the following traits of the original neoplasm is most directly responsible for this observation?
a. N Cadherin down regulation
b. Collagenase overexpression
c. P16 hypermethylation
d. Loss of function Rb mutation
e. Mutation of Ras in Glycine 12
b. Collagenase overexpression
Remember Hallmark#6 is epithelial-mesenchymal transition
A 50 yo man comes to the physician with weight loss, fatigue, night sweats, easy bruising, and nosebleeds chronic (myelogenous leukemia). He also pain in his first metatarsophalangeal joint in his left foot. PE shows hepatosplenomegaly. Labs show preponderance of WBCs (>50,000/mm3) and a full spectrum of myeloid cells in a peripheral blood smear. On genetic analysis, a translocation of chromosomes 9 and 22 is found and thus the patient is initiated in the imatinib as a first line treatment which of the following cancer hallmarks will be most directly activated by this t(9:22) translocation?
a. Self sufficiency of mitogenic signals
b. Insensitivity to anti growth signals
c. Evasion of apoptosis
d. Activation of angiogenesis
a. Self sufficiency of mitogenic signals
A 67 yo chinese immigrant with hx of alcohol abuse and chronic Hepatitis B virus infection has been experiencing fatigue, weight loss, and vague abdominal pain for several months. PE reveals a palpable mass in the liver. Before the mass can be surgically resected, the patient dies of respiratory failure. Which of the following can be said about the primary tumor of this patient?
a. It originated in the lungs
b. It underwent epithelial to mesenchymal transition
c. It is stage as T2N0M0
d. It shows clear, smooth and regular margins
e. It likely originated because of germline mutation
b. It underwent epithelial to mesenchymal transition
A 17 yo boy presents to his pediatrician with pain in his right leg. Biopsy reveals a malignancy in the distal femur. He has a fmhx of "eye cancer" in a younger sister. Which of the following most directly describes the molecular defect you would find in cells obtained from this boy's tumor?
a. An incapacity to induce p 21 in response to DNA damage
b. Overactive expression of c Myc
c. Ras incapacity to hydrolize GTP
d. Unrestricted Abl kinase activity
e. Increased E2F dependent transcription
e. increased E2F dependent transcription
An asymptomatic 30 yo woman presents to her physician's office for a routine health maintenance examination. Papanicolau smear indicates high grade dysplasia (i.e., an abnormal growth). What is the mechanism by which the responsible agent causes disease?
a. Arrest of blood vessel growth
b. Cell cycle continuation after DNA damage
c. Inhibition of DNA replication
d. Inhibition of mitogenic signal transduction
e. Inhibition of RNA dependent DNA polymerization
b. Cell cycle continuation after DNA damage
A 6 yo boy presents to his pediatrician with skin lesions all over his body. For several yrs he has been suffering from photosensitivity. Neither the boy's parents nor his siblings have the same skin lesions or sun sensitivity. Biopsies of several of the boy's lesions reveal squamous cell CA. Which mutation would you expect to be abundant in this patient's DNA?
a. Hyper methylation of genes
b. Missense mutations of genes
c. Nonsense mutation in the middle of genes
d. Point mutations within promoter regions
e. Thymidine dimers
e. Thymidine dimers
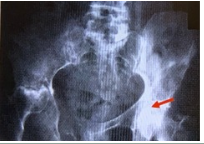
A 68 yo man presents to his physician's office with diffuse pelvic pain. XR of the abdomen for this patient is shown right. Which of the following would help to diagnose the primary tumor most commonly responsible for these radiologic findings?
a. Digital rectal examination
b. Palpation of the abdomen
c. Palpation of costovertebral angle
d. Palpation of the neck
e. Skin examination
a. Digital rectal examination
A woman whose mother had CA in both breasts develops breast CA at age 26. The patient's identical twin sister decides to undergo genetic testing to determine her chances of developing breast CA. What mechanism causes the genes (BRCA) that are most tested for breast CA to become tumorigenic?
a. Chromosomal rearrangement
b. Dominant negative effect
c. Gain of function
d. Loss of function
e. Viral infection
d. Loss of function
As a pathologist , you receive breast CA tumor biopsies from 10 patients, and based on your analysis you need to make a recommendation as to which of these patients will respond to Trastuzumab therapy, which is based on blocking the activation of EGFR by its ligand. What molecular signature or biomarker would you test in these biopsies as the most adequate and convenient indicator of a positive therapy response?
a. Aberrant transcriptional profile of cell adhesion genes
b. Gene amplifications or copy number variations (CNV)
c. A specific phosphorylation signature in Rb
d. Chromosomal reciprocal translocations
e. Global changes in gene methylation patterns
b. Gene amplifications or copy number variations (CNV)
Mr jones has been ignoring a persistent cough for almost a month, until he had to be rushed to an ER when he started suffering dyspnea, sharp chest pain exacerbated by breathing, and coughing of blood. A chest radiograph showed a mass in the left lung and the doctor decided to perform a bronchoscopy guided needle biopsy, which was sent for analysis to the pathology lab. A dx of non-small lung carcinoma was made. CT imaging combined with 4.2 cm in size, with invasion into the phrenic nerve and mediastinal pleura. Genetic Testing of the tumor showed an exon 21 mutation (l585R) in the gene coding for the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGFR). In addition to palliative care to alleviate symptoms, the patient was treated with Erlotinib, which decreased tumor size by 70% in four months, after which the patient entered remission for an additional eleven months. Unfortunately, the tumor recurred after remission, and the patient died four months after recurrence. Which of the following can be considered a clinically useful biomarker in this case?
a. Mass detected by the chest radiograph
b. PET scan revealing tumor size
c. The EGFR mutational status
d. Dyspnea together with a sharp chest pain
c. The EGFR mutational status
Mr jones has been ignoring a persistent cough for almost a month,
until he had to be rushed to an ER when he started suffering dyspnea, sharp chest pain exacerbated by breathing, and coughing of blood. A chest radiograph showed a mass in the left lung and the doctor decided to perform a bronchoscopy guided needle biopsy, which was sent for analysis to the pathology lab. A dx of non-small lung carcinoma was made. CT imaging combined with 4.2 cm in size, with invasion into the phrenic nerve and mediastinal pleura. Genetic Testing of the tumor showed an exon 21 mutation (l585R) in the gene coding for the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGFR). In addition to palliative care to alleviate symptoms, the patient was treated with Erlotinib, which decreased tumor size by 70% in four months, after which the patient entered remission for an additional eleven months. Unfortunately, the tumor recurred after remission, and the patient died four months after recurrence. Which of the following can be predicted or assessed based on the biomarker?
a. Histological subtype
b. Overall survival
c. Probability of recurrence of resistance
d. Good response to targeted therapy
d. Good response to targeted therapy
Mr jones has been ignoring a persistent cough for almost a month, until he had to be rushed to an ER when he started suffering dyspnea, sharp chest pain exacerbated by breathing, and coughing of blood. A chest radiograph showed a mass in the left lung and the doctor decided to perform a bronchoscopy guided needle biopsy, which was sent for analysis to the pathology lab. A dx of non-small lung carcinoma was made. CT imaging combined with 4.2 cm in size, with invasion into the phrenic nerve and mediastinal pleura. Genetic Testing of the tumor showed an exon 21 mutation (l585R) in the gene coding for the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGFR). In addition to palliative care to alleviate symptoms, the patient was treated with Erlotinib, which decreased tumor size by 70% in four months, after which the patient entered remission for an additional eleven months. Unfortunately, the tumor recurred after remission, and the patient died four months after recurrence.
What do you think is Erlotinib's mechanism of action?
a. It is a DNA alkylating agent
b. Also called Bevasizumab, and is an anti Vascular Endothelial
Growth Factor (VEGF) antibody
c. Also trastuzumab, an anti EGFR antibody
d. It is an ATP competitor
e. It blocks GLUT transporters
d. It is an ATP competitor
As a pathologist, which of the following biomarkers, when detected by immunohistochemistry, will be particularly indicative for you that the patient will have a very poor prognosis related to a high probability for metastasis?
a. Elevated PCNA or Ki67
b. Elevated p53
c. Abundant cytokeratin expression
d. High collagen content in the tissue
e. Low staining for E-cadherin
e. Low staining for E-cadherin
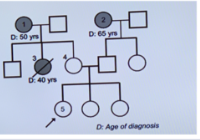
This pedigree depicts a family in which several women developed
breast CA. The proband wants to know if she is a carrier of a mutation for hereditary breast CA. Which family member should receive genetic testing first?
a. #1
b. #2
c. #3
d. #4
e. #5
a. #1
What changes in the retinoblastoma (Rb) gene are required for the formation of bilateral retinoblastomas in a young child?
a. Somatic occurrence of a single mutation in one Rb allele in an otherwise genetically normal cells
b. Somatic occurrence of mutations in both Rb alleles in an otherwise genetically normal cell;
c. Amplification of both copies of Rb in an otherwise genetically normal cell
d. Loss of function of one copy of the Rb gene due to an inherited mutation
e. Loss of function of both copies of the RB gene due to inherited and somatic mutationsRe
e. Loss of function of both copies of the RB gene due to inherited and somatic mutations
Remember the fact that they telling us its the bilateral form means it is most likely the hereditary form of retinoblastoma vs the sporadic form. Also, remember this answer choice refers to the Two-Hit Hypothesis
A 44 yo woman has a small number of cancerous polyps along the
proximal side of the colon. Her mother was dx with these types of tumors and another sibling has developed gastric CA. all were identified with CA in their mid 40s. Analysis of the tumors revealed microsatellite instability, the presence of numerous additional alleles not present in noncancerous cells. Which of the following syndromes best describes this family?
a. Xeroderma Pigmentosum
b. Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
c. HBOC
d. Li-Fraumeni syndrome
e. Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC-Lynch)
e. Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC-Lynch)
Which of the following is the strongest indication that a patient suffers from hereditary cancer rather than a sporadic cancer?
a. A brother with colon cancer at 70 years of age
b. A family history of cardiovascular disease
c. A bilateral breast cancer at 30 years of age
d. A unilateral breast cancer
e. A first-degree relatives with lung cancer
c. A bilateral breast cancer at 30 years of age
A patient is referred to a cancer genetic clinic for consultation. You find out that he developed colon cancer at 42 years of age and that his father also had colon cancer at an early age. The tumor from the patient showed microsatellite instability. No family history of polyps. Which of the following genes would you recommend for genetic testing?
a. P53
b. BRCA1 and BRCA2
c. APC
d. MLH1, MSH2, MSH6
e. XPC
d. MLH1, MSH2, MSH6
The human immune system can be divided into:
a. Adaptive and innate immunity
b. Cellular and innate immunity
c. Humoral and adaptive immunity
d. Lymphocyte and neutropenic immunity
e. Eosinophilic and basophilic immunity
a. Adaptive and innate immunity
The innate immune system includes all the following except?
a. macrophage
b. Natural killer cell
c. Neutrophil
d. APC
e. Plasma cells
e. Plasma cells
Our immune system can combat which of the following:
a. Bacteria
b. Parasites
c. Viruses
d. Cancer cells
d. All pathogens
d. All pathogens
(When working properly of course)
Which of the following cells are not matched with the correct function?
a. T cell recognize antigens that originate within other cells (presented on MHC molecule)
b. B cells programmed to encode a surface receptor specific for antigen
c. NK cells recognize and lyse virus infected cells and tumor cells
d. Macrophage cells produce immunoglobulins
d. Macrophage cells produce immunoglobulins
Macrophages are a type of WBC that phagocytose pathogens
All of the following are characteristics of the MHC locus, except
a. Contains 3 HLA class types
b. Are located on chromosome 3
c. For HLA Class I, DR + DQ + DP are the most relevant to MHC
compatibility
d. For HLA
b. Are located on chromosome 3

The Ig class shown below is: (pentamer)
a. IgA
b. IgE
c. IgD
d. IgM
e. IgA
d. IgM
Ig class___ is the most abundant Ab in blood plasma.
a. IgG
b. IgE
c. IgD
d. IgM
e. IgA
a. IgG
Ig class ___ is found in body secretions as a dimer
a. IgG
b. IgE
c. IgD
d. IgM
e. IgA
e. IgA
The enzyme that cleaves off the sialic acid from degrading glycoproteins are directed to the lysosomes by which signal?
A. Pro-Pro-Lys-Lys-Lys-Arg-Lys-Val-
B. Extended block of hydrophobic amino acids
C. The KDEL sequence
D. Ser-Lys-LeU
E. Mannose-6-phosphate
E. Mannose-6-phosphate