Chem Quiz 3 Material
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
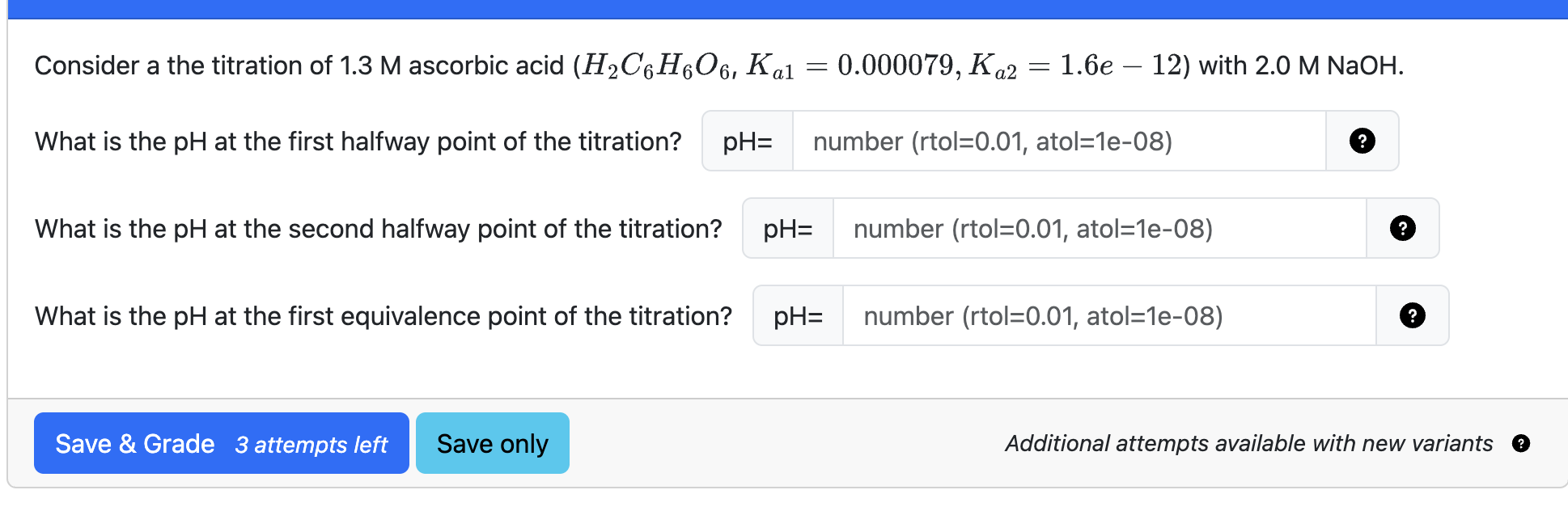
In strong base and weak acid titrations, what is the pH at the 0.5 equivalence point? Is it a buffer?
pH = pKA. Yes, its a buffer
Describe the components of a weak acid/strong base titration curves
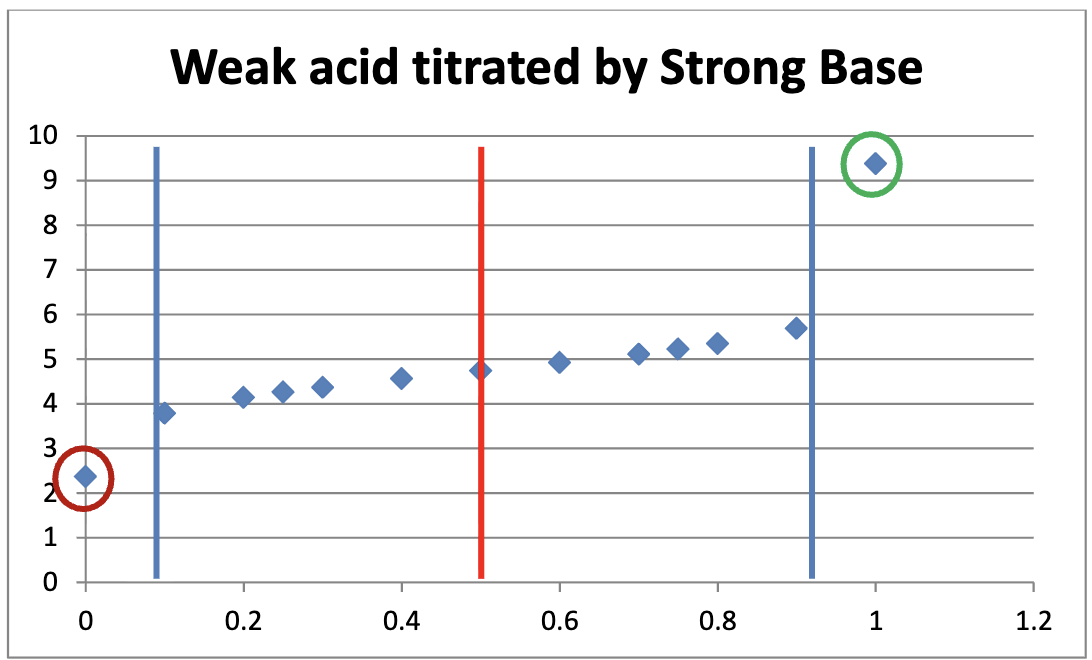

What is a titration curve?
A titration curve is a plot of some solution property versus the amount of added titrant. For acid-base titrations, solution pH is a useful property to monitor because it varies predictably with the solution composition and, therefore, may be used to monitor the titration’s progress and detect its end point.
What is the main difference between strong acids and strong bases vs weak acids?
Strong acids and strong bases have complete dissociation, while weak acids must factor in equilibrium
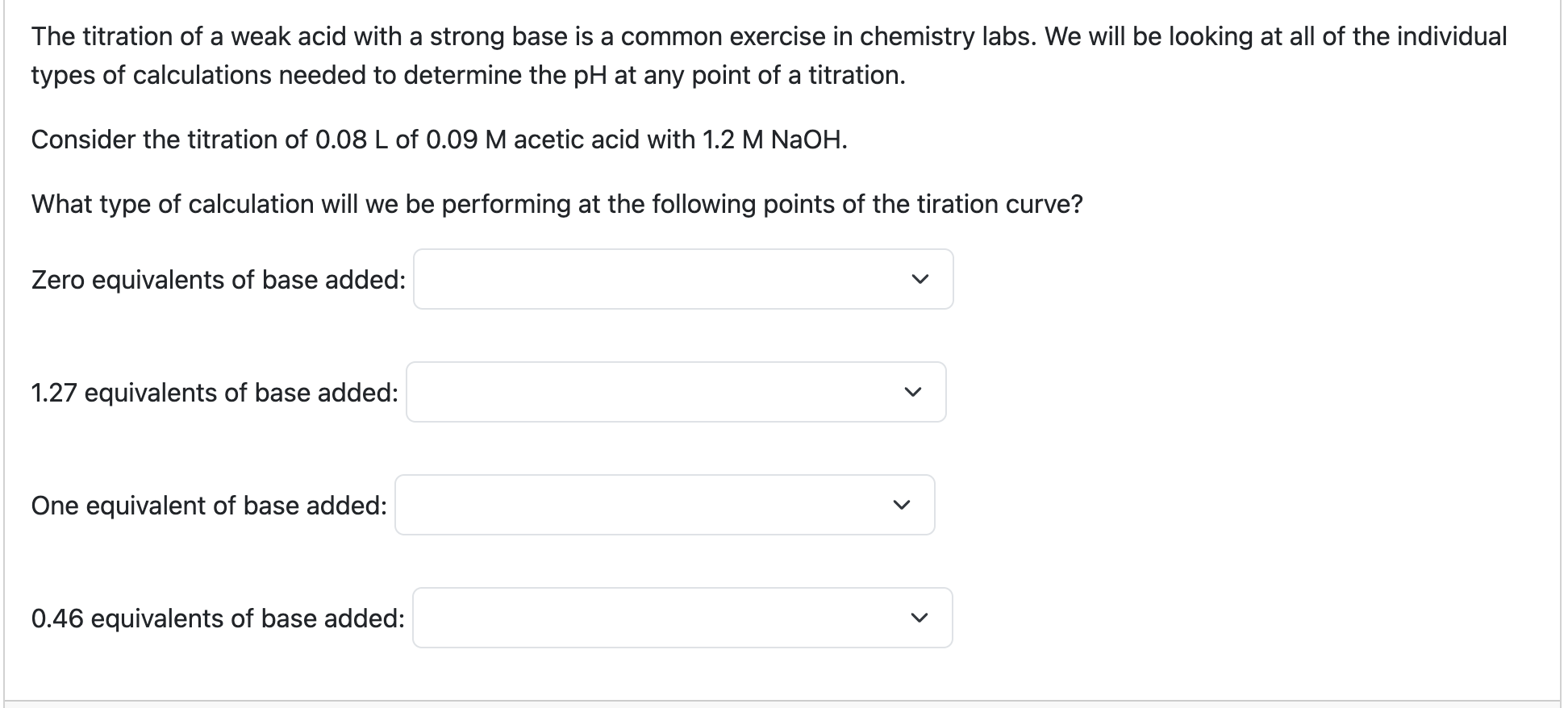
What are the general steps for solving for weak acids/strong bases?
Figure out what 1 equivalence is equal to (equal moles of acid + base)
Figure out pH before we’ve added any base (weak acid calculation)
What happens after we add base (BCA table)
After we’ve made the buffered solution, we can use the Henderson-hasselbach equation. We must find the concentration to do this
If the ratio is = 1, what happens to the log X [A-/HA] component of henderson hasselbach?
It becomes 0
When comparing titration curves, the strongest acid will have the highest or lowest pka?
Lowest
Will more base increase or lower pH?
Increase
What are the general steps for ranking titrations in order of increasing pH at the equivalence point of the titration (top=lowest pH and bottom = highest pH)


Describe the components of a polyprotic titrations curve
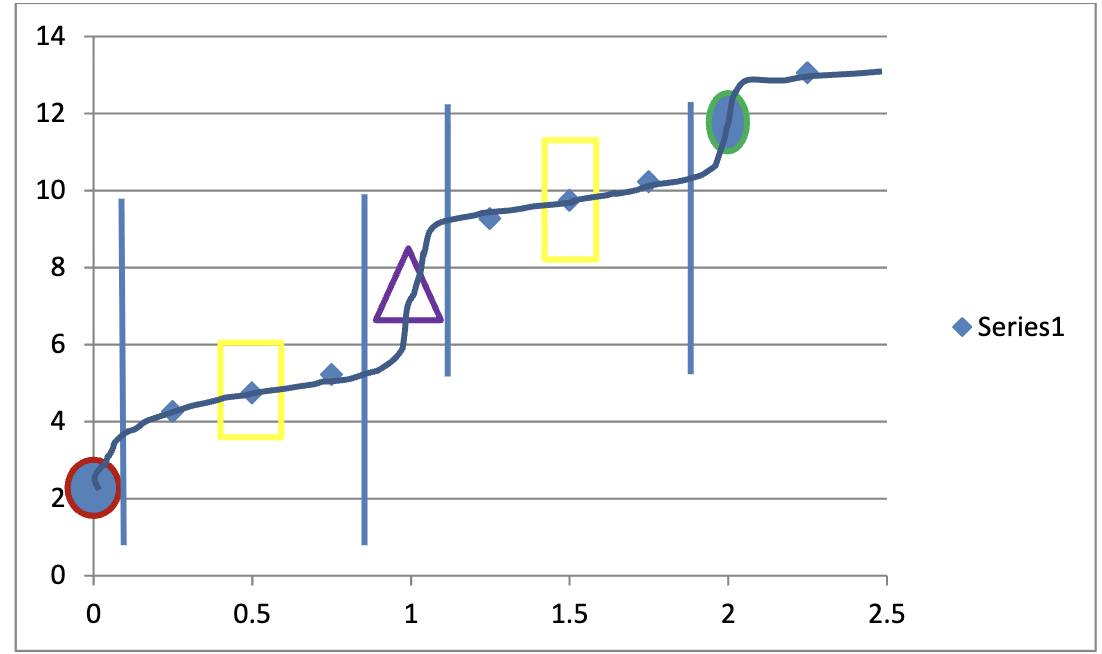

At equivalence of 1,2, or 3 on a polyprotic titration curve, what is the pH?
The average of pKA1 and pKA2
Where can you use Henderson Hassleback on polyprotic titration graph?
Between 0 and 1, and 1 and 2 equivalence (both halfway points)
How can we get the inital or end pH for polyprotic acids?
The inital is a weak acid equation, but the end can be found through plotting on the pH line and using ka values
In polyprotic acids, when Ka’s get smaller, what 2 important things does that mean
There is smaller amounts of dissociation, and you can treat each dissociation as seperate
How do you know how many equivilance of bases there are?
Depends on how many acidic protons
On a graph, will you usually have flat lines or curves at halfway points? Why?
Flat lines because they represent buffers
When you have questions like this: What do you do?
What happens to the charge at the equivalance and halfway points?
Equiv: Drop by 1
Half: Drop by 0.5
Define protanated?
Transfer of a proton, gaining a positively charged hydrogen ion
At ½ what is pH = to?
pKa
Is a lower pKa acidic or basic?
Acidic
Which proton will be removed first?
The acidic one
What is an equivalent?
Amount of base needed to completely remove H+, anytime pH is below pka, its in the protenated form. Above is deprotenated
When going from A to B drawings, what changes?
You’re just removing the most acidic proton
In amino acids and peptides, how do you know how many equivalence there are?
Based on how many are needed to remove both protons
What does isoelectric mean?
Not charged
How do you know if something is in its acidic or basic form?
If the pH>pKa (by 2 or more units) the base form will dominate. If pH < pKa, the acid does
What will OH- always interact with?
The best acid
How do you know what one equivalent is equal to?
The moles
What is A- and HA in the henderson hasslebach?
A- is the base and HA is the acid
What is the halfway point pH equal to?
pKA
Anytime that a weak acid is titrated with a strong base, will pH (at equivalence) be greater or less than 7?
Greater
At equivalence, its equal ___ of acid and base
Moles
At the equivalence point, what is equal?
Acid = base
What is 1 equivalent = to?
Moles of acid/ base in original solution
At the halfway point, what is ph = to?
pka
If you’re comparing endpoint pH’s, what do you do?
At endpoint only the conjugate is left, so you can rank based onka/kb to see which has the highest/lowest pH. If its being titrated with strong acid it will be Ka, strong base will be Kb
How do you know how many equivalence are needed?
Depends on how many pkas are given in the problem
WIll there be OH- or H3O+ at the third equivalence point?
No, you’ve used all the strong acid and base by that point
How do you decide which pka to use?
Look back at the titration curve
How do you know when to stop using a bca table and start using an ice table
When the strong acid or base has run out
What is enthalpy? What is sponteneity?
The heat of a reaction at constant pressure
Sponteneity: The natural tendency of a process to occur without a continuous input of external energy
What is entropy?
Disorder, randomness, chaos. Better used to explain microstates: and
What is entropy?
Disorder, randomness, chaos
Better used to explain Microstates: Any particular arrangement at a particular time of a particular substance (snapshots)
Does the universe favor going to microstates?
Yes, increasing entropy
What does the letter S signify?
entropy
Do solids have high S?
No, they have low entropy. Then its liquids, then gas
How do we determine what has more or less entropy?
Change in entropy for a reaction (ΔS) = sum (mol products times the entropy of the products) - sum (mol reactants times entropy of reactants)
State vs path function
State functions depend only on the initial and final conditions of a system, not the path taken, while path functions depend on the specific route or process used to move between states
Is enthalpy a state or path function
State
What is hess’s law
Hess's Law states that the total change in enthalpy for a chemical reaction is the same, regardless of the path or number of steps taken
What is the 3rd law of thermodynamics?
The entropy of a perfect crystal (a perfect crystal is a hypothetical, idealized substance where all atoms are arranged in a flawless, ordered, repetitive lattice without any defects, impurities, or thermal vibrations) at 0 kelvin = 0
What is the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
In any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases
What does the ΔS of the universe =?
ΔS universe = ΔS system + ΔS surr
What does ΔS surr =?
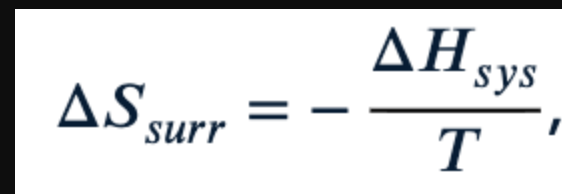
Do systems tend towards conditions that have more possible microstates?
Yes
When you’re trying to determine entropy, which state of matter do you look at first?
The gas, view the change in moles. Increasing moles is increasing entropy, and the other way around
When you have equal moles of gases, what do you look at?
The table that details the standard entropies for each gas (use equation for ΔSrxn
When ΔS of the universe is positive, negative, or 0. is it spontaneous?
Positive = Yes
Negative = Spontaneous in reverse direction
0 = Equilibrium
In terms of -ΔH/T (which = -q/t), in a combustion reaction, what increases?
Entropy of the system. We give off heat, - value for delta H. Increase entropy of surroundings
Why is ΔS important?
Can understand spontaneity
Does lower temperature have lower molecular motion?
Yes
How do you know if something exists in the predominately ionic form (charged)?

What is Gibbs Free Energy denoted by?
G or delta G
What is the equation for Gibbs Free Energy?
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
If ΔG is negative, is it spontaneous or non?
It is spontaneous. Positive is still spontaneous but in the reverse direction
0=equilibrium
In ΔG = ΔH - TΔS, what does ΔH - TΔS mean?
ΔH represents enthalpy, while - TΔS represents entropy.
When ΔH is negative, do you favor ΔG?
Yes
What does entropy favor?
-ΔG when ΔS (entropy) is positive
What is the other equation for ΔG?

How can you solve for temperature for processes at equilibrium for standard state using ΔG = ΔH - TΔS?

When ΔG is negative, positive, or 0, what is it?

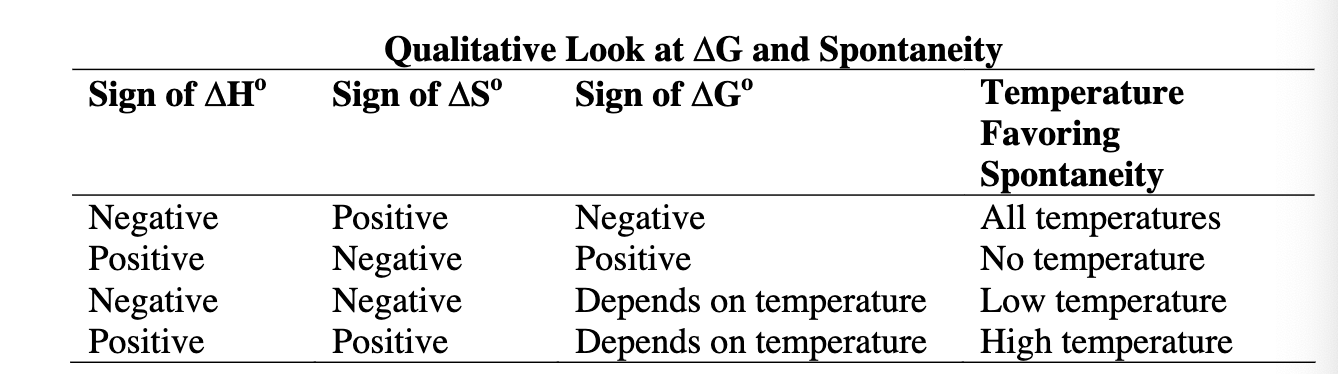
Given the sign of ΔS or ΔH or ΔG, what is the temperature favoring spontaneity?
Is Gibbs free energy a state functions?
Yes
What does -ΔG/T=?
-ΔH/T + ΔS, or ΔSsur + ΔS universe
What does ΔS universe equal?
-ΔG/T
How can you determine spontaneity using symbols of ΔG and ΔSuniv? Whats the limitation?
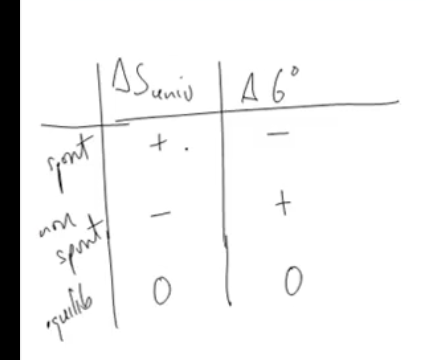
Only works at constant T and P
Which symbol represents the maximum energy we can get out after expansion work? What does it favor?
ΔH, favors - ΔG
What represents the maximum energy we will lose to entropy (disorder)?
-TΔS, +ΔS favors -ΔG
How does ΔG represent free?
It represents maximum energy “free” to do non expansion work
List the table you can use for temp that favors spont.

How do you know if entropy increases?
Entropy ↑ when the number of gas molecules ↑ or when species dissociate into more particles (solid to liquid or liquid to gas)
Do systems tend to macrostates with the greatest microstates?
Yes
What does standard formation actually mean?
1 mol of a species from its elemental form
A perfect cystal at 0 kelvin has 0 entropy because what?
There is only 1 microstate, so iyt has 0 kelvin, 0 motion
If a reaction is spontaneous, does it need to have an increase in ΔSrxn?
Yes
What are standard conditions?
All gases at 1atm, pure solid, pure liquid, and solutions all at 1 M
What is the equation for Gibbs Free Energy? What does each stand for?
ΔG standard = ΔH standard - TΔS standard
ΔG is the energy thats free to do work
ΔH is the maximum energy stored in bonds
T is temperature
Δs is the minimum energy lost to heat and particles spreading out
What does ΔS universe and ΔG rxn need to be to be spontaneous, nonspontaneous, and at equilibrium?
Spontaneous: ΔS universe +, ΔGrxn -
Nonspontaneous: ΔS universe -, ΔGxn +
Equilibrium: 0 and 0
How an you determine spontaneity using Gibbs?
High temp: ΔH + | ΔS + | ΔG ?
Low temp: ΔH - | ΔS - | ΔG ?
All temp: ΔH - | ΔS +| ΔG -
No temp: ΔH + | ΔS - | ΔG +
In what units do components of Gibbs free equation need to be in?
ΔH = Kj
ΔS = J
T in Kelvin
CONVERT EVERYTHING TO KJ