physics tougher or stupid questions that you have got wrong
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
232 Terms
2025 42 m/j
After 30 minutes, the temperature of the water in container A remains constant. State, in terms of energy transfers, why the temperature remains constant.
rate of transfer of energy from the container is equal to rate of transfer of energy to the container
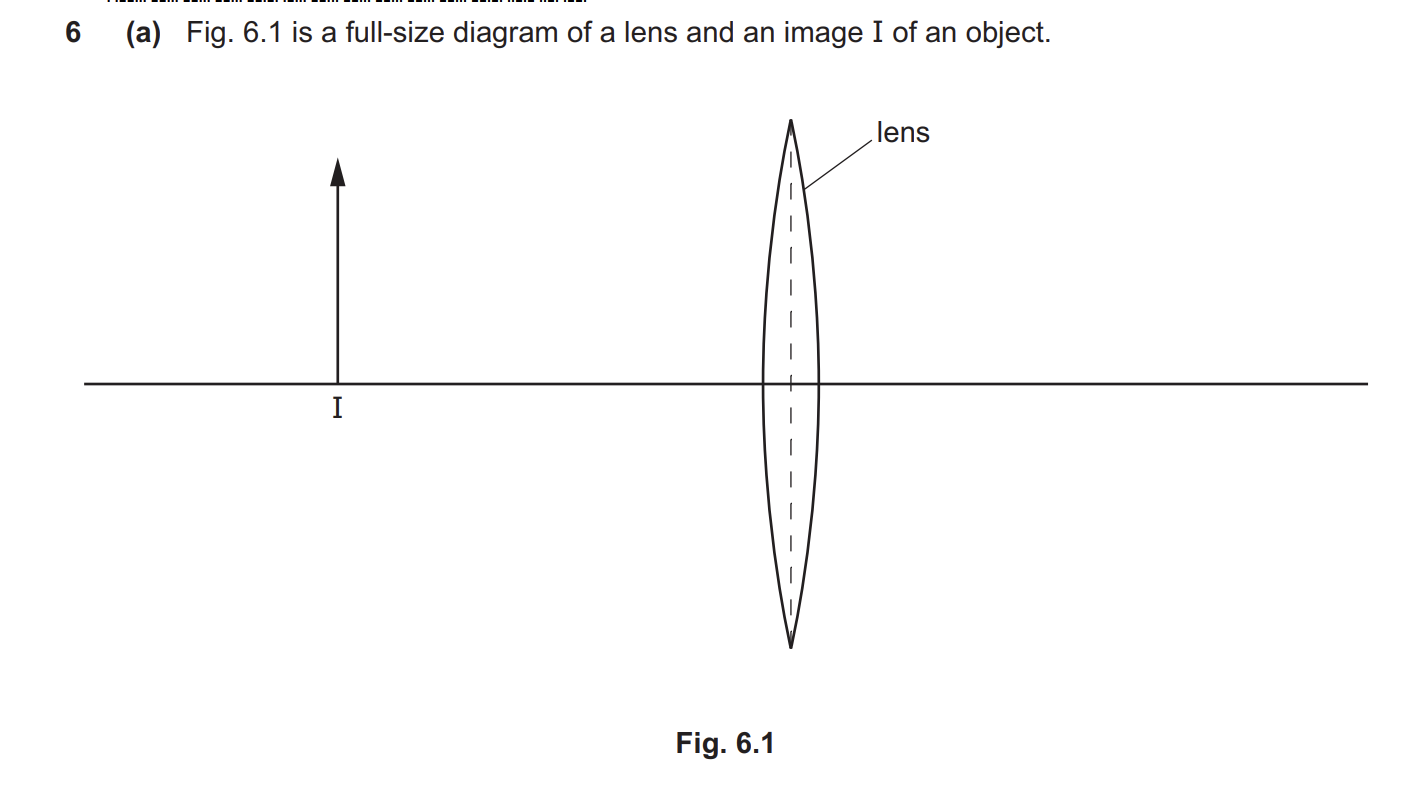
draw two lines from the top of I to find the position of the object
long-sigthedness
can only see long distances, lines are made past the retina, use convex lens to fix (converging lens)
The negatively charged plastic rod is suspended by an insulating thread. Another negatively charged plastic rod is brought close to the suspended rod. State what happens to the suspended plastic rod.
moves away
Define the kilowatt-hour (kWh) in words
energy transferred in one hour at a rate of transfer of 1 kW
Explain why an electromotive force (e.m.f.) is only induced when the coil is turning.
coil cuts magnetic field
State one possible change that causes a larger e.m.f. to be induced.
• increase strength of magnetic field • increase speed of rotation of coil • increase number of turns (of coil)
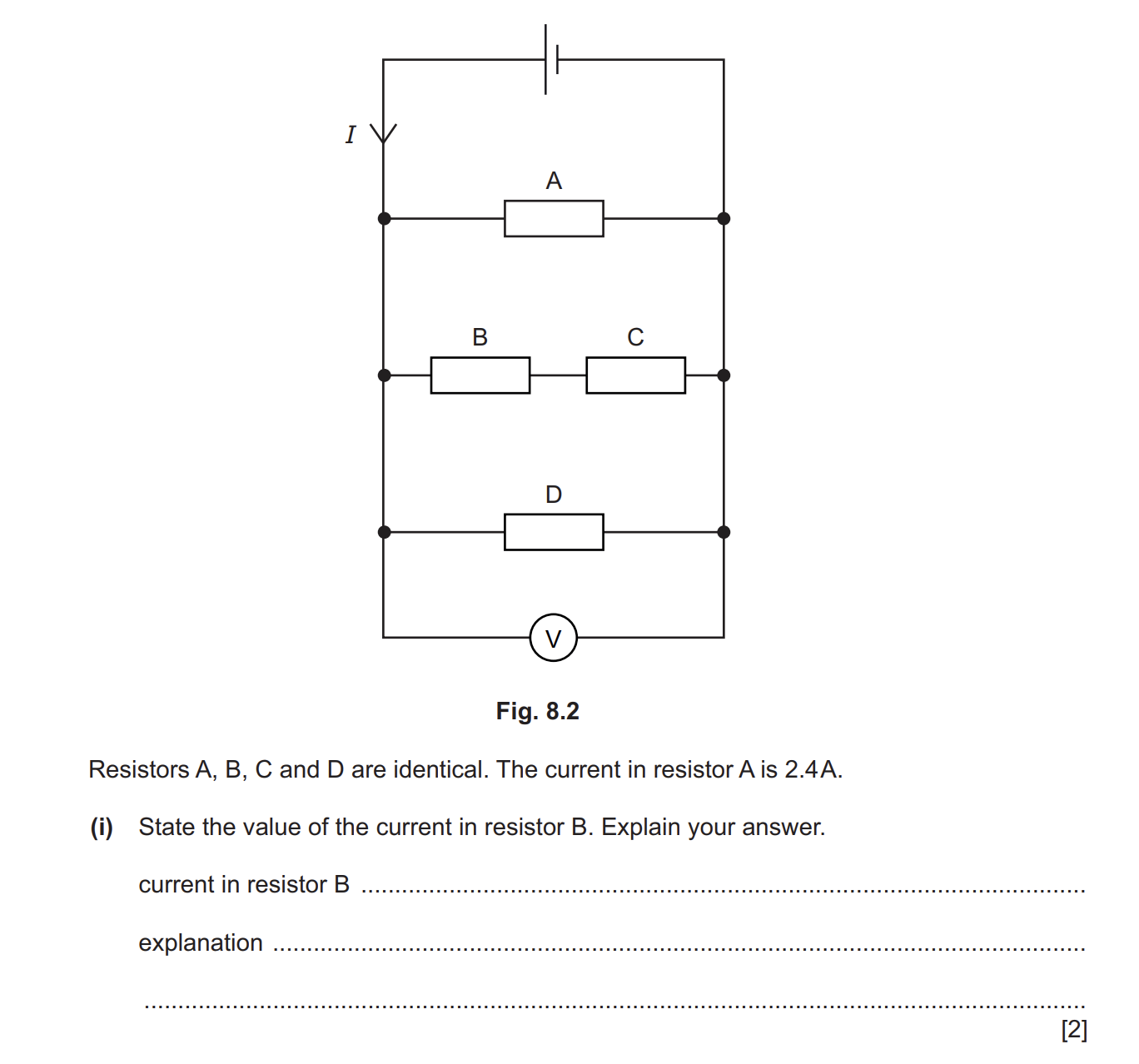
answer
1,2 AND the resistance of two resistors in series is added
State what is meant by background radiation
radiation (always) present in the environment OR radiation from natural sources
Radium-223 is injected into the body to treat a specific organ. Explain why the source must be inside the body.
alpha (particles) would be absorbed / stopped by the skin owtte
An isotope of technetium is injected into the body to detect cancer in one of the organs. The half-life of this isotope is 6 hours and it decays by emitting gamma (γ) radiation. The radiation is detected outside the body. (i) Explain why a source of gamma radiation is used
gamma / radiation needs to pass out of the body (to detector)
Explain why a source with a short half-life must be used.
after a few days / some time, little radiation is emitted owtte
An object falls through a height of 2m on each of the planets in Table 10.1. State and explain on which planet the object falls 2m in the shortest time. Ignore any effect due to the atmosphere.
the planet in which gravitational field strength is highest so acceleration (due to gravity) is greater OR gravitational field strength is highest so greater (downward) force on the object
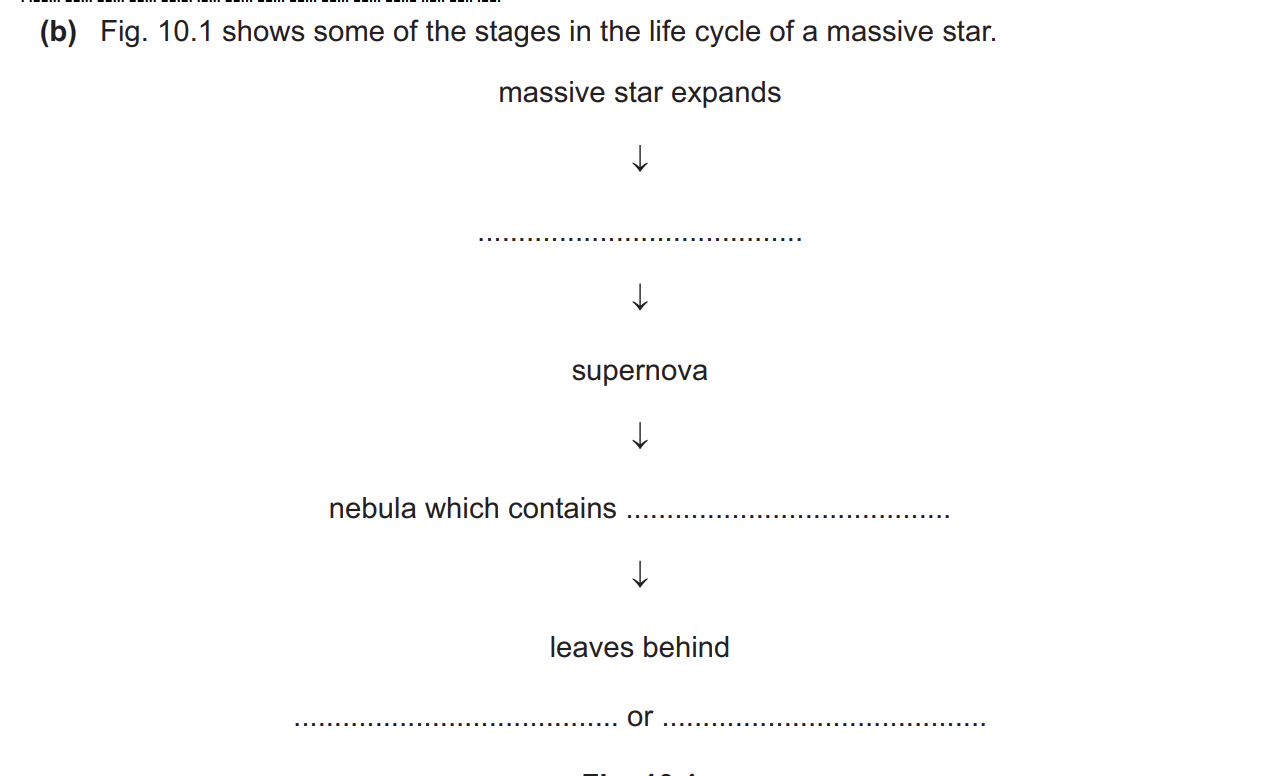
answer
red supergiant, heavier elements OR hydrogen, any two from: • neutron star • black hole • new stars (with orbiting planets)
State the quantity that the brightness of a supernova in a galaxy can be used to determine.
distance (from Earth) to galaxy
2025 41 m/j
State one other way that forces may change a stationary object.
• (change) size • (change) shape
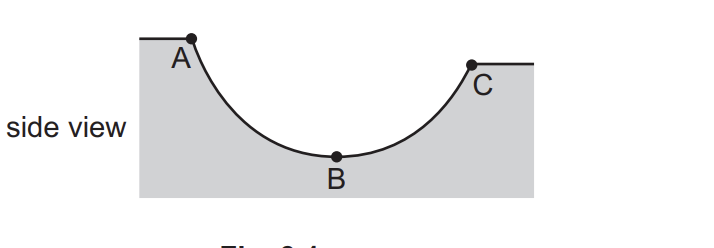
describe the energy transfers from point A to C
gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy to gravitational potential to thermal store of surroundings
4aii
warm air rises OR less dense air rises B1,, warm air is less dense (than cool air) ORA,,any one from: • cold air replaces warm air • cold air falls and the process repeats owtte • there is a convection current owtte
wavelength of 680nm in m
680 × 10^-9
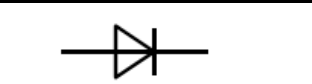
symbol for diode
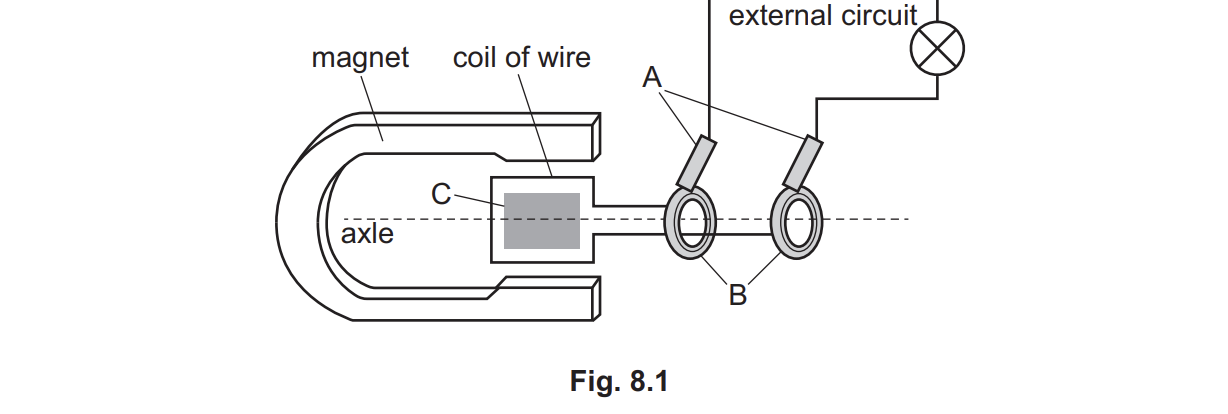
C is made of soft iron. Describe the effect of this component on the generator
strengthens magnetic field
Suggest how the nucleus of a stable isotope of strontium differs from a nucleus of strontium-90 (radioactive). Explain your answer.
(stable isotope) has fewer neutrons AND radioactive isotopes (usually) have an excess of neutrons
(stable isotope) has fewer neutrons AND radioactive isotopes are too heavy
Explain why scientists limit the amount of time they are exposed to radioactive strontium.
ionising radiation is harmful (to humans) OR beta particles are ionising and harmful (to humans)
Define gravitational field strength
force per unit mass
State one factor which causes the difference between the gravitational field strength at the surface of Jupiter and the gravitational field strength at the surface of the Earth.
mass
State and explain the difference between the orbital speed of Jupiter and the orbital speed of the Earth.
Jupiter is slower,,Jupiter is further from the Sun ORA OR orbital speeds of planets decrease as distance from the Sun increases,, gravitational field (strength) of Sun decreases with distance (from Sun)
2025 42 f/m
A light-dependent resistor (LDR) has a ___ resistance in ___ light intensity and a ___ resistance in the dark.
low, high, high
you should know all the electrical symbols - but light-dependent resistor———
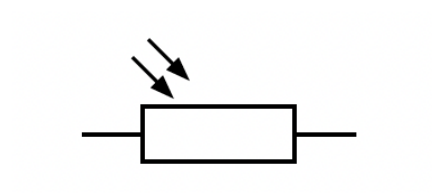
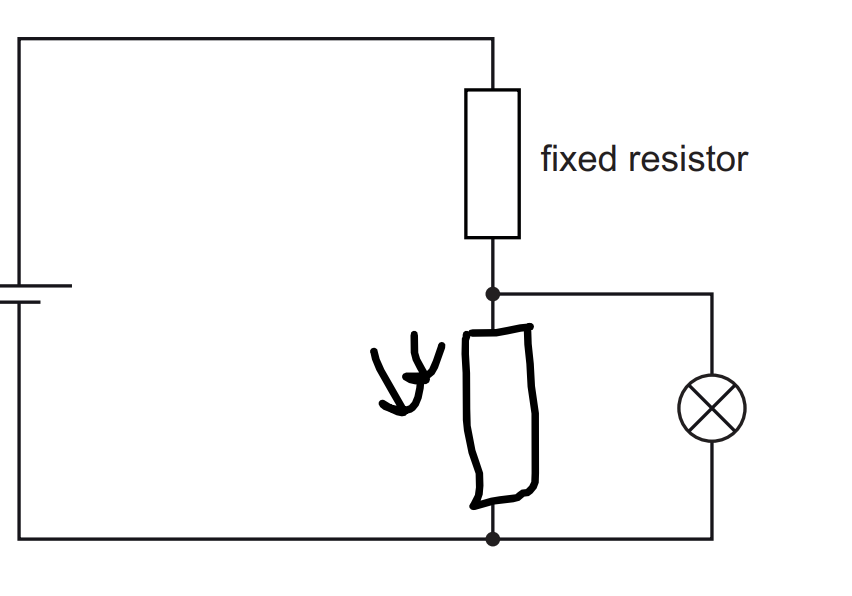
Explain why the lamp is off in the light and the lamp is on in the dark. Use ideas about potential difference (p.d.) in your answer. (mentioned in Q that has in high light intensity, resistance is low in LDR)
(for two marks)- in the dark, VLDR is a bigger proportion of e.m.f OR when RLDR is high VLDR is a bigger proportion of e.m.f. OR when VLDR is high VLDR is a bigger proportion of e.m.f………… (for one marks)- emf shared (between fixed resistor and LDR) OR emf is constant - VLDR = VLAMP OR p.d. is the same across components in parallel
functions of —(J carbon brushes),(K coil),(L axle),(M split ring commutator)
J- • connect cell / circuit to coil / wire / split ring(s) / commutator • maintains (continuous) connection • prevent wires from tangling (as motor rotates),,,,,,,,,,,,, (K coil) Any one from: • rotates / turns • conducts / has a current in it,,,,,,,,,,,,(L axle) Any one from: • allows the coil to rotate / turn • allows motor to turn / spin,,,,,,,,,(M split ring commutator) Any one from: • keeps motor turning in the same direction owtte • reverses the connections to the coil (every half-turn) owtte • prevents wires from tangling (as the motor rotates),,,,,
One metal sheet is 0.75mm thick. Suggest why strontium-90(emitting beta particles) is a suitable radioactive source to measure the thickness of the metal sheets.
(there is a) different count rate with different thicknesses of metal OR number of -particles detected varies with thickness
The strontium-90 source is replaced with a new source after 15 years. Using Fig. 9.1, suggest why a strontium-90 source that is more than 15 years old needs to be replaced with a new source.
• count rate / activity (too) low (to detect differences in thickness) owtte • detector needs high activity (to detect differences in thickness) owtte • count rate / activity too close to background owtte • less difference in activity for different thicknesses owtte

bi and bii
F, H
Define ‘limit of proportionality’
maximum load that can be applied when the extension is proportional to load
uses of optical fibres
• internet transmission / (highspeed) broadband • telephone networks • cable TV OR telecommunications • endoscope • lasers in surgery • microscopy • military aircraft wiring • imaging (cameras) in industry • inspection of pipes or other hard to reach places B2 OR telecommunications
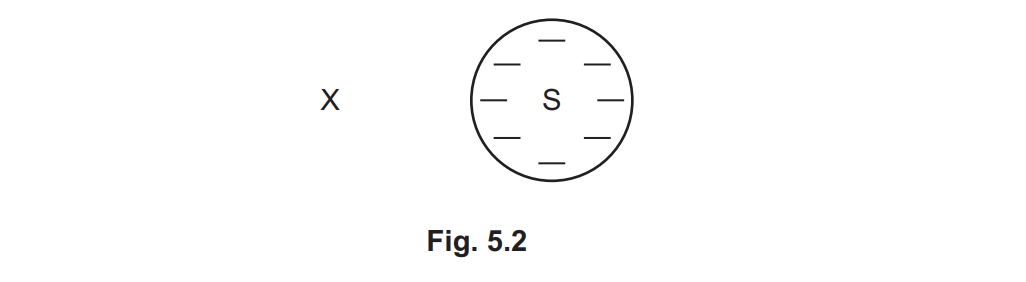
the negatively charged particle at X is released from rest. Describe the motion of the small negatively charged particle due to the electric field around sphere S.
accelerates away from the sphere
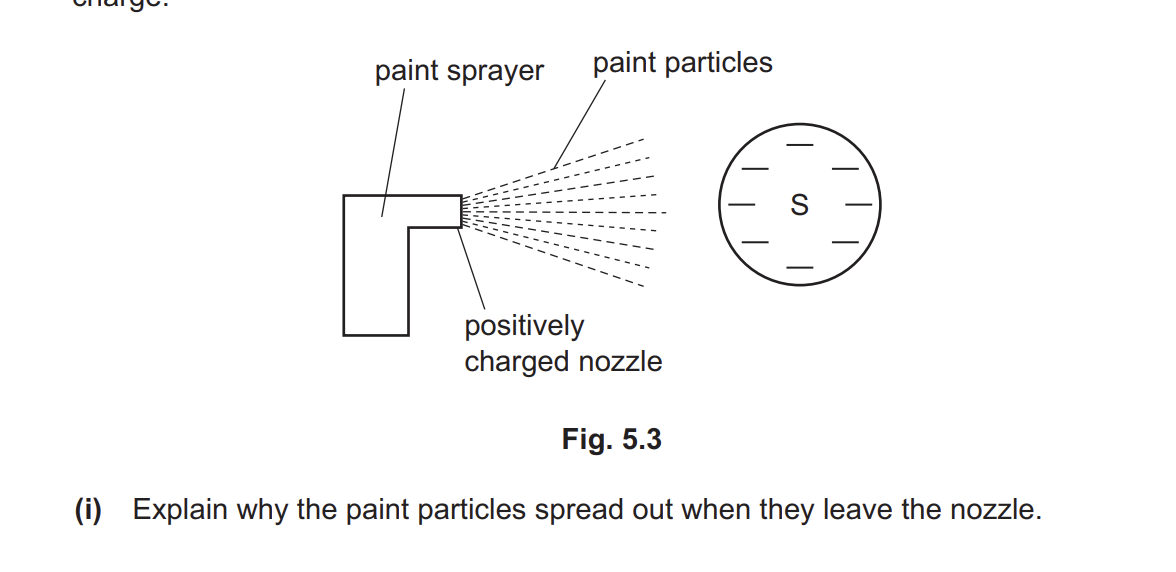
Explain why the paint particles spread out when they leave the nozzle
like charges repel
The alpha‑particles destroy the cancer cells. Suggest and explain one reason why alpha particles are more suitable than gamma radiation for use in this treatment of brain cancer.
alpha is less penetrating / has shorter range (than gamma),,,,,,,alpha more easily absorbed / stopped by cancer / tumour cells or won’t travel beyond cancer cells or so won’t damage other / healthy cells OR alpha highly ionising (than gamma) (B1) will destroy / damage cancer cells more easily
increase distance between source and _______
living tissue
galaxies further away (are receding) with higher speed OR galaxies further away have greater redshift
stars more massive than the Sun can eventually form black holes. Describe how a black hole can be formed from a more massive star
• (most of the) hydrogen has been converted to helium or hydrogen begins to run out • (star expands and) forms a red supergiant • (red supergiant) explodes as a supernova (forming a nebula)…………………core (of red supergiant collapses and) forms black hole OR a black hole forms at the centre (of the supernova/nebula)
2024 o/n/ 42
Define, in words, the term weight.
(weight is) the gravitational force on a mass / an object (with mass) OR (weight is) the effect of a gravitational field on a mass
Rockets are used to launch satellites into space. When the satellite is released, the rocket returns to the Earth. Explain in terms of forces why the rocket reaches terminal velocity as it travels through the atmosphere back to the Earth.
resistive force / air resistance / drag increases as velocity increases B1 until gravitational force is balanced by air resistance (at terminal velocity) OR until resultant / net force is zero (at terminal velocity)
On a sunny day, the temperatures of a black tarmac road and the air above the road increase. (a) Explain why the surface temperature of the tarmac increases.
(tarmac / it) absorbs infrared radiation (emitted from the Sun)
Explain why the surface temperature of the tarmac is higher than the surrounding air temperature.
1 black / tarmac is a better absorber (of radiation) than air 2 tarmac is a poor emitter (at low / this temperature) 3 thin layer of tarmac / very large volume / column of air above road
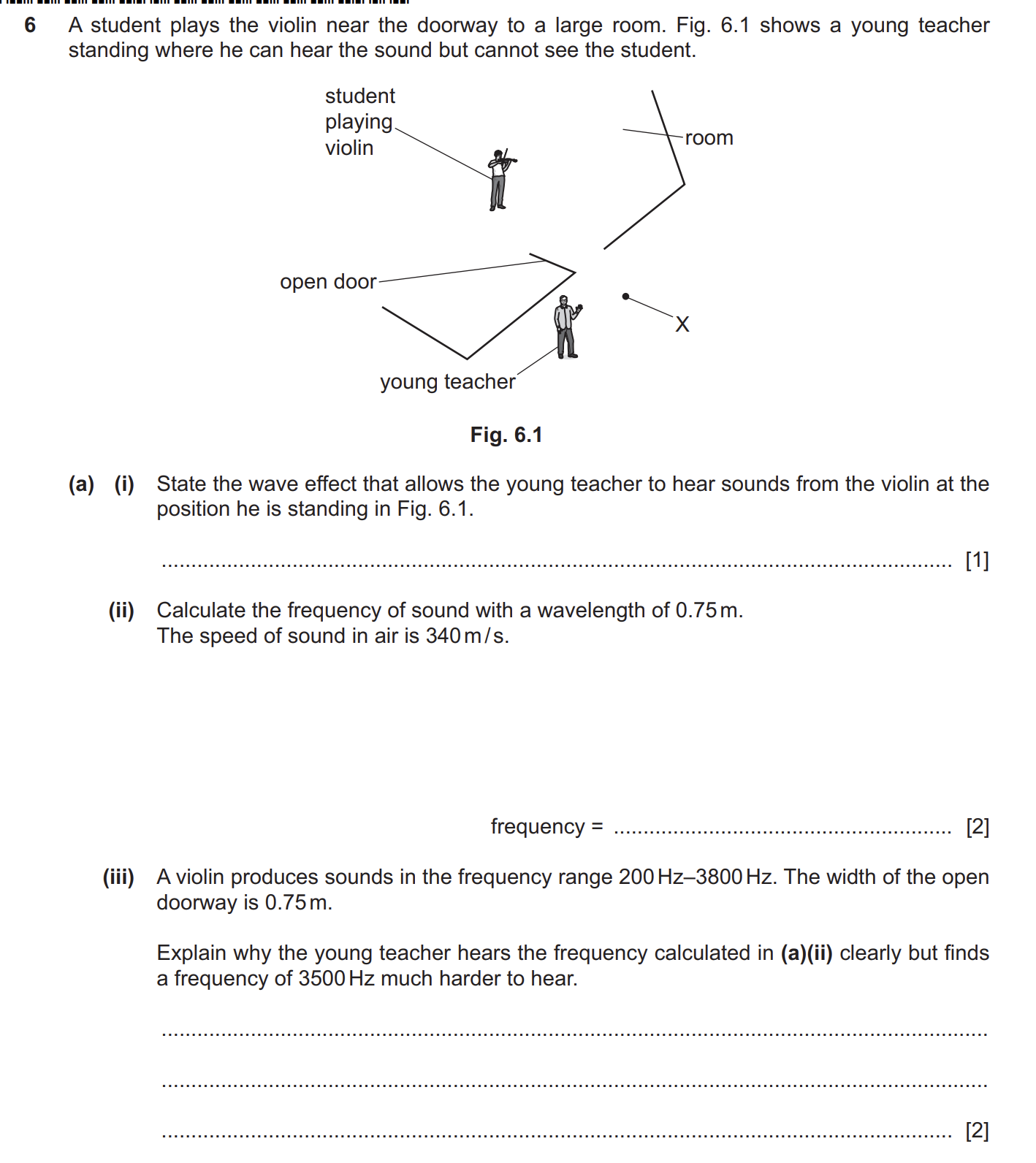
iii
large diffraction when gap size / doorway is similar to wavelength B1 high frequency / 3500 Hz has (much) shorter wavelength AND there is less diffraction (with shorter wavelengths)
Pointers for proving what total current is equal to
Sum of currents into a junction = sum of currents out of junction OR total current is sum of the current in the branches
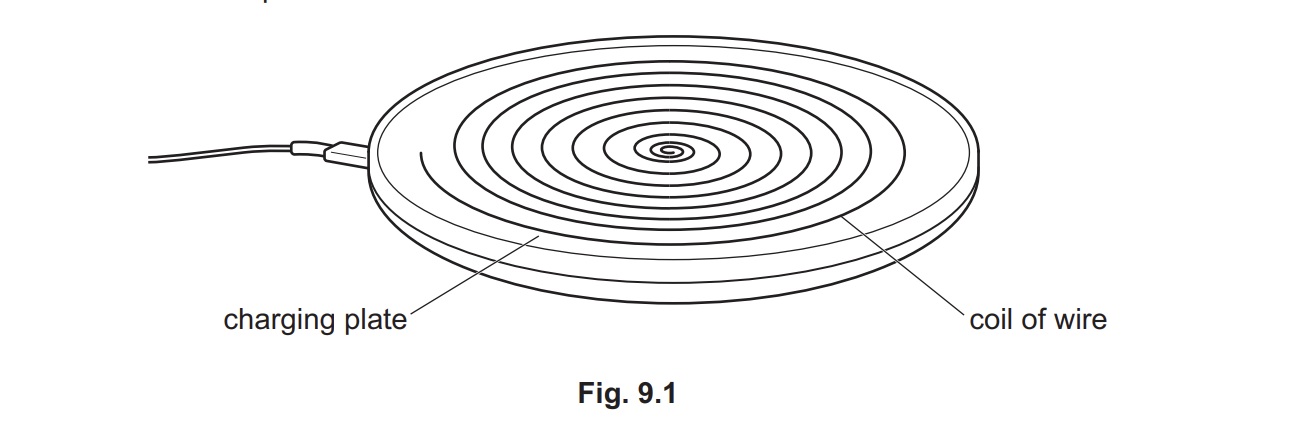
The charging plate is connected to an a.c. power supply. The power supply is turned on. (a) Describe the magnetic field around the charging plate in terms of its magnitude and direction.
1 (magnitude is) constantly changing owtte 2 (magnetic field is) stronger closer to the coil of wire ORA 3 (the magnetic field is) perpendicular to the a.c. current (producing it) 4 (the magnetic field) changes direction owtte
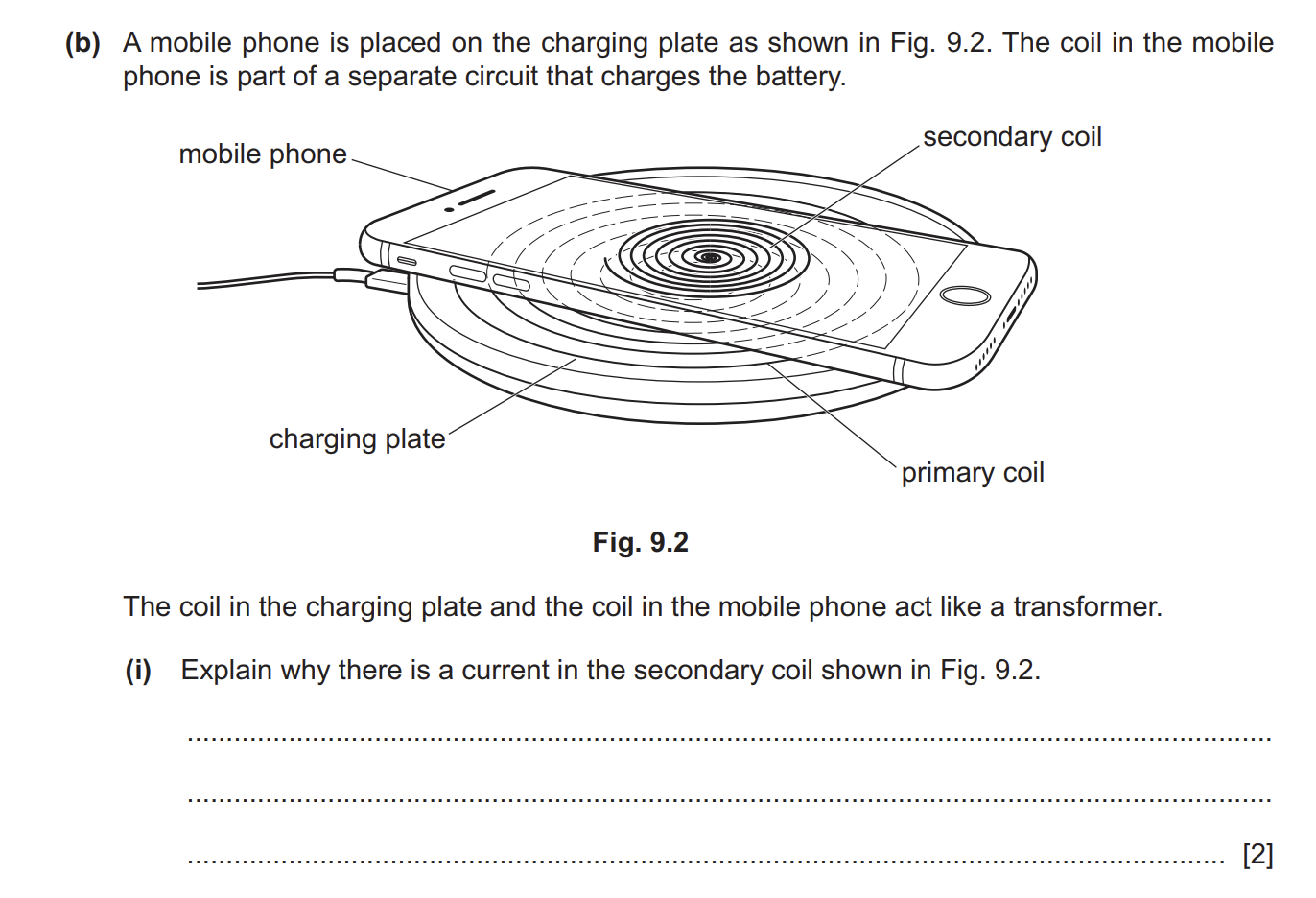
Explain why there is a current in the secondary coil shown in Fig. 9.2.
any one from: • secondary coil is in changing / varying magnetic field • secondary coil is in the magnetic field of primary coil OR voltage is induced (in the secondary coil)
Suggest why the transformer made from the charging plate and mobile phone is not 100% efficient. (from previous question)
• There is no iron core (to strengthen field) • transformer usually has an iron core to connect the two coils • some energy transferred to thermal energy (in phone / surroundings)
isotopes have different half-lives. Suggest a use of a radioactive isotope with a half-life of one hour. Explain why a short half-life is suitable for this use.
use- medical tracers OR medical imaging OR medical diagnosis, explanation- • keep dose low • doesn’t stay in body too long • less damage (to body) OR less harmful (to humans)
comets are balls of ice and dust. Some comets orbit the Sun. State how the speed of a comet changes as it orbits the Sun. Explain your answer using ideas about the conservation of energy. You may include a labelled diagram in your answer.
any one from: • comet has an elliptical orbit • speed of comet is faster when it closer to the Sun • speed of comet is slower when it is further away from the Sun…….any one from: • (conservation of energy requires that) transfers between kinetic and gravitational stores (as comet changes speed) • total energy remains constant • energy cannot be created or destroyed…….as radius of orbit decreases, gravitational energy decreases and kinetic energy increases ORA (3 marks total)
2024 o/n 41
the deceleration of the car is not constant.
gradient is changing OR line / graph / it is a curve / curved
The block shown in Fig. 3.1 is in equilibrium. State the two different conditions that apply when an object is in equilibrium.
resultant force = 0 OR (all) forces cancel out owtte,,,,resultant moment = 0 OR moments balance owtte,,,
Describe an experiment to determine the specific heat capacity of aluminium. You may draw a diagram. Include in your answer: • the measurements made • any equations needed.
1 Any one method to transfer measurable amount of thermal energy for ∆: (a) to aluminium block (with electrical heater) (b) from aluminium block to known liquid (c) from known liquid to insulated aluminium (calorimeter) (d) to known liquid and aluminium (calorimeter) B1 2 Determination of energy transferred for ∆, to match workable method in 1: (a) Use of E = Pt OR E= IVt (b) Use of E = mc with s.h.c. of known liquid (c) Use of E = mc with s.h.c. of known liquid (d) Use of E = Pt OR E = IVt AND E = mc (with known s.h.c. of liquid) B1 3 Any one measurement from: • initial and final temperature / temperature change • time (of heating) • mass of aluminium B1 4 c = E / m OR (c =) E / m
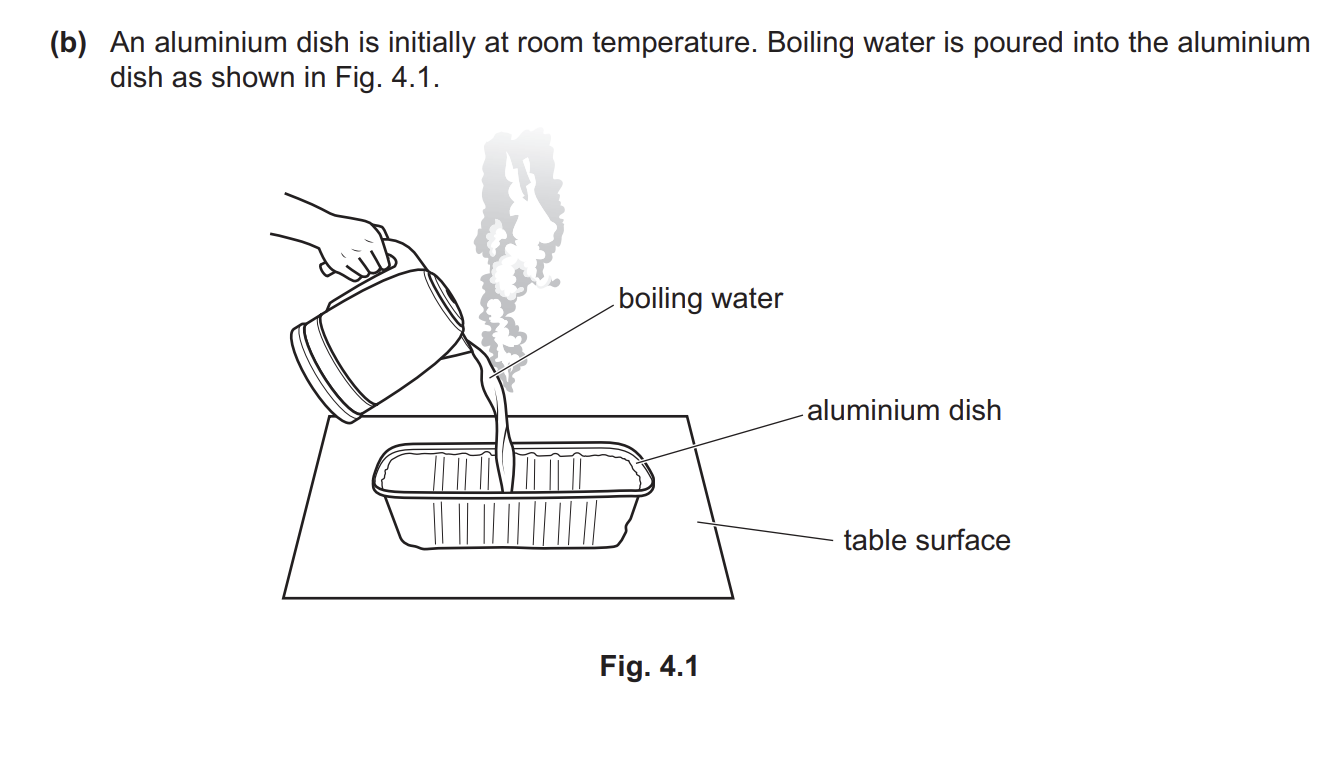
Explain why, after a short time, the dish and the water are the same temperature
Any three from: 1 (net) transfer of energy from higher temperature to lower temperature OR (net) transfer of energy from water / to dish 2 (energy transfer) by conduction OR aluminium is a good conductor (of thermal energy) 3 temperature of water decreases AND temperature of dish increases 4 no (net) transfer of energy when temperature of dish = temperature of water
Define potential difference (p.d.)
work done by a unit charge passing through a component
c) The resistance of the LDR decreases and the resistance of the thermistor increases. (i) State what has happened to the light intensity incident on the LDR and the temperature of the thermistor….. intensity of incident light on LDR: ________………temperature of thermistor______
(intensity of light on LDR) increased AND (temperature of thermistor) decreased
The resistance of the variable resistor increases. Explain what happens to the magnetic field surrounding the bar and state how the pattern of field lines that represents the field changes.
current (in the coil) decreases B1 (current decreases so magnetic field) strength decreases B1 (field strength decreases so) fewer field lines (in same area) OR (field strength decreases so) field lines further apart
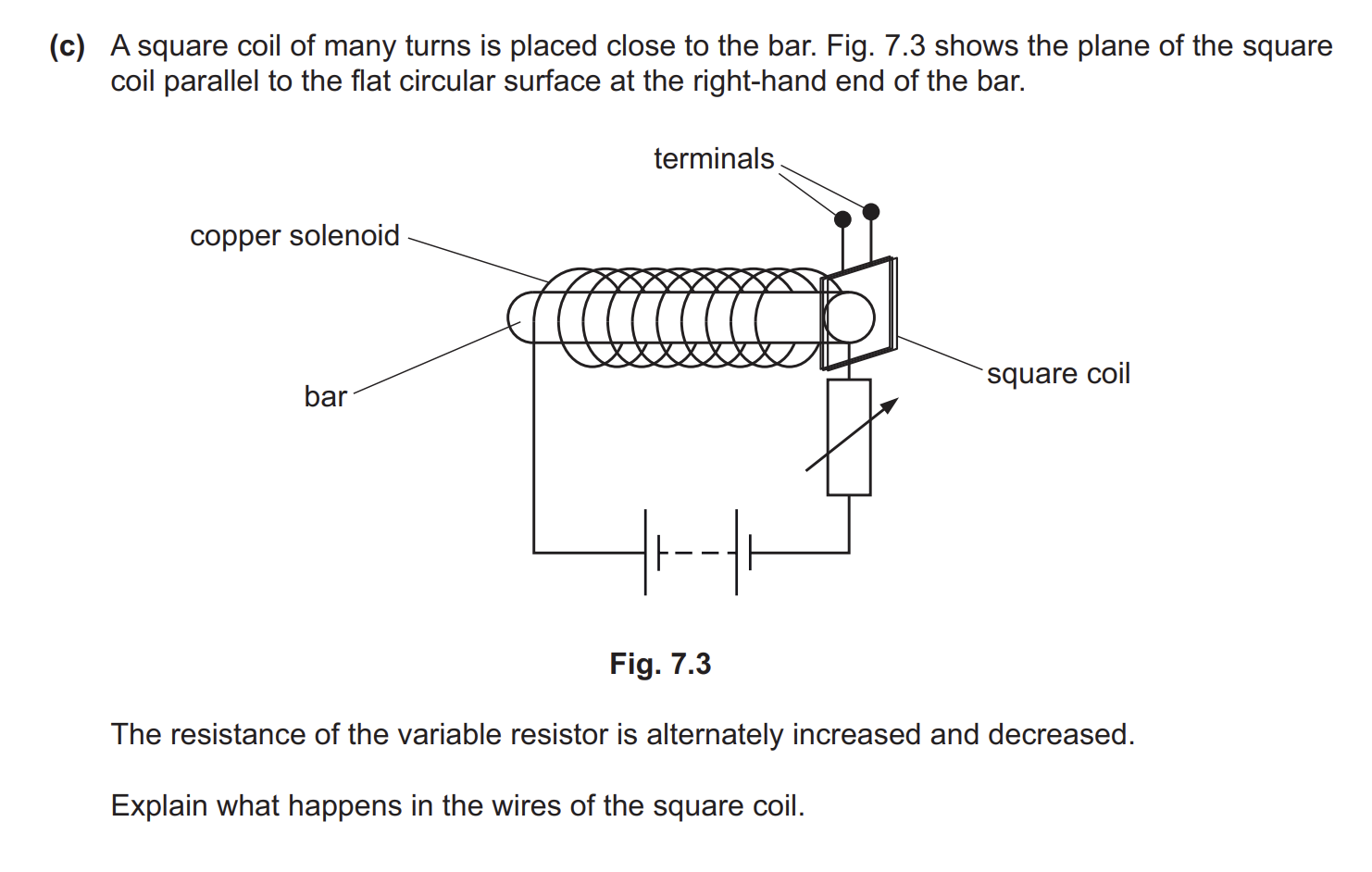
Any two from: 1 (changing resistance causes) changing current (through solenoid) 2 (changing current causes) changing magnetic field (around solenoid) 3 (square) coil cuts (changing) magnetic field OR coil in changing magnetic field B2 e.m.f. induced (between terminals)
Describe how the composition of a neutral atom of carbon-14 is different from the composition of a neutral atom of nitrogen-14 (14 7 N).
(carbon) has one more neutron OR nitrogen has one fewer neutron B1 (carbon) has one fewer proton / electron OR nitrogen has one more proton / electron
Describe the change that takes place in carbon-14 as a beta-particle is emitted.
a neutron changes into a proton (and electron)
State what a galaxy is
group / collection of (billions of) stars
State how the speeds of galaxies and their distances from the Earth are related.
(their) speeds are (directly) proportional to distances (from Earth) OR H0= v / d
define gravitational field strength
force per unit mass
Describe the energy transfer in the solar cell
(electromagnetic) radiation / light (from the Sun) B1 (produces) electrical (work done)
State the meaning of the term kilowatt-hour (kWh)
the amount of (electrical) energy transferred by a 1 kW appliance in 1 hour owtte OR energy transferred in one hour at a rate of transfer of 1 kW
) Energy is produced by each solar cell for an average of 6 hours per day. A household uses approximately 7400kWh of electrical energy per year. Calculate the number of solar cells needed to produce energy for one household. Give your answer as a whole number of solar cells. (one cell is 540 W)
7
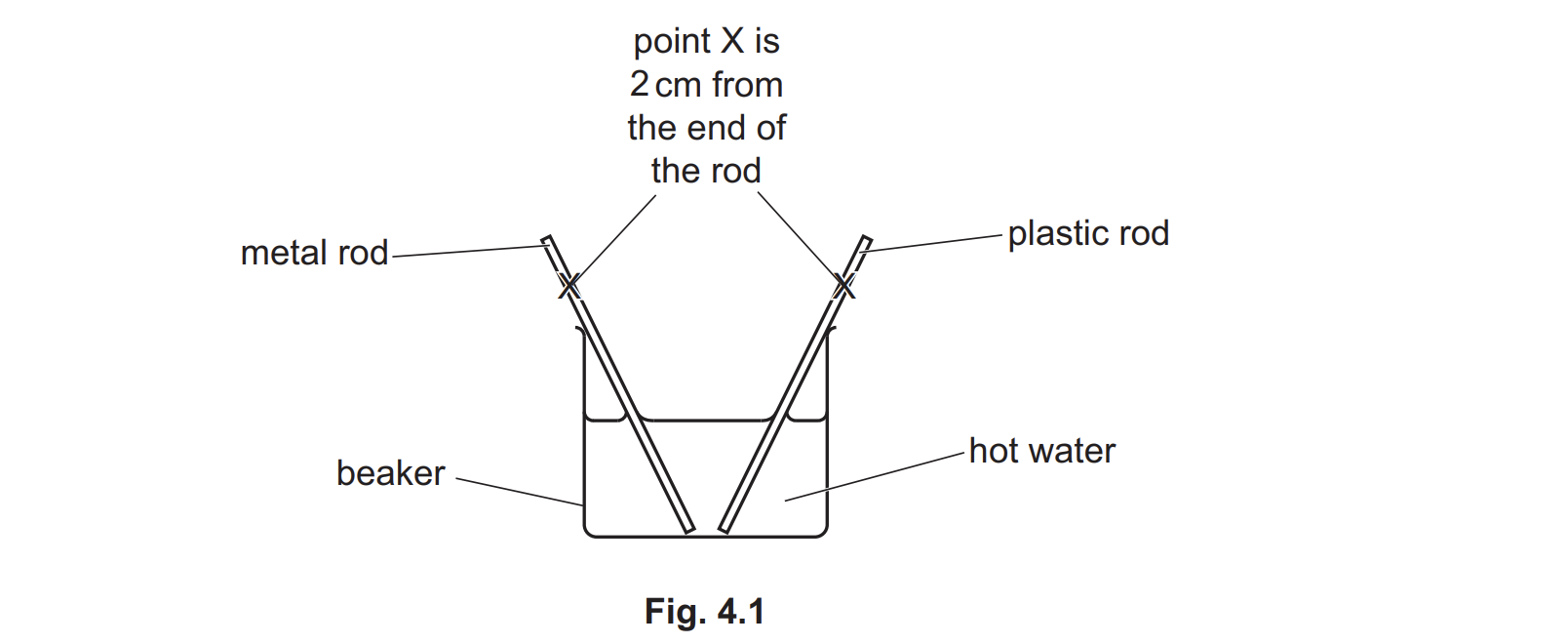
Describe how the temperature of point X on each rod changes after the rods are placed in the beaker. Explain your answer.
(temperature of point X) on metal rod increases faster ORA…………..thermal energy is transferred) by conduction…………….metal rod (transfers thermal energy through movement of) delocalised / free electrons. ORA
The sound waves travel .................................................. to the direction of the vibrations.
parallel
State two advantages of using optical fibres in high-speed data transmission compared to electrical signals sent on copper wires.
• high rates (of data transmission) / faster (data transmission) • carry large amounts (of data / information) • secure • Little data / signal loss • glass is transparent to (some) infrared
State the meaning of critical angle
angle of incidence (of light) at which the angle of refraction is (exactly) 90°
Determine the reading on the ammeter. Show your working
Current in lower branch is 0.16(0) A B1 ammeter reading is sum of currents in each branch M1 (ammeter reading =) 0.24 A
Explain in terms of work done and potential difference why there is a larger heating effect in R3 than in R1
potential difference (p.d.)(across R3) is larger (than p.d. across R1) B1 more work done (passing charge through R3)
solenoid doesnt gain magnetism
it becomes a magnet
Describe what happens to a star when most of the fuel in its centre has been converted to helium
• (the star) expands B1 Any one from: • (smaller star) forms a red giant • (more massive star) forms a red supergiant
comets have an elliptical ________
orbit
2025 o/n 42-
energy is a ________ quantity
scalar
The engine of the truck provides the forward force on the truck. State two forces acting on the truck in the opposite direction to the forward force.
air resistance OR drag B1 friction (between tyres and road)
slides off the track at point P. State two possible reasons that cause the car to slide off the track.
• car has higher speed • less friction (between car and track) OR not enough friction • larger mass
State and explain one advantage of using black solar panels.
more electricity generated OR makes solar panels more efficient B1 black is a good absorber OR black is a poor reflector owtte
State the difference between alternating current and direct current
alternating current reverses direction OR direct current is only in one direction
explain, in terms of particles, why gases can be compressed but liquids cannot.
distance between gas particles is much larger (than distance between liquid particles) OR particles in liquid are touching AND particles in gas are far apart owtte
State two conditions that are necessary for total internal reflection to occur.
speed of light in first region is less than speed of light in second region owtte B1 angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle
State two advantages of using optical fibres for transmitting high speed broadband.
• high rates of data (transmission) • carry large amounts of data / information • secure • little data / signal loss • glass is transparent to visible light and (some) infrared
State what is meant by a magnetic field
region in which a (magnetic) pole experiences a force
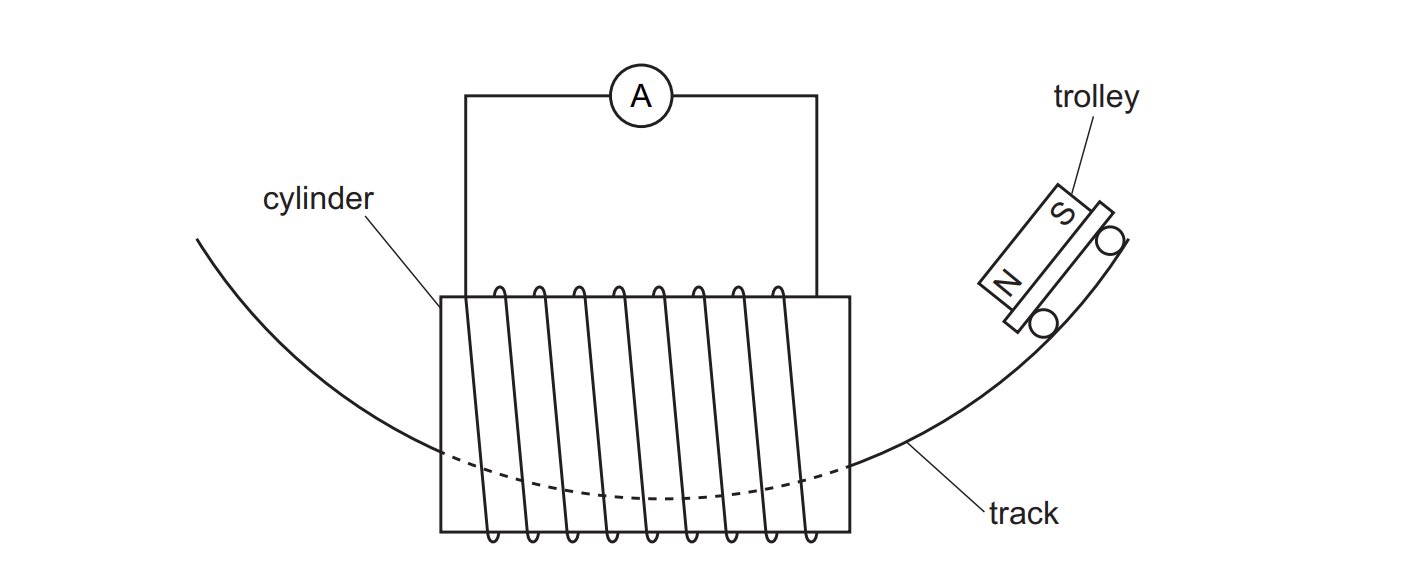
The trolley is released from the position shown in Fig. 8.1. It travels through the coil from right to left. The trolley travels back from left to right. It has a lower maximum speed when it travels from left to right. The plastic cylinder does not affect any magnetic field. A magnet is fixed to the trolley. (i) State why there is a lower maximum speed when the trolley travels back from left to right.
friction between trolley and track OR the (induced) current produces a magnetic field which opposes the (magnetic) field that causes the (induced) current
As the trolley enters the coil moving from right to left, the ammeter needle deflects to the left and then returns to zero. State and explain any changes to the deflection on the ammeter as the trolley enters the coil when moving back from left to right. (smaller speed)
• direction will (still) be left OR there is no change of direction • induced current / emf / voltage does not change direction • smaller deflection • smaller (rate of) change of magnetic field • smaller current / emf / voltage induced (in coil)
maybe redo question 8 of o/n 42 2025 cuz it was hard
Define half‑life of a radioactive isotope
time taken for half the nuclei of a sample to decay
The radiation detector is used to measure the thickness of the aluminium sheets and control the gap between the rollers. State the most suitable radioactive source in Table 9.1 for the machine in Fig. 9.2. Explain why this radioactive source is the most suitable and why the other sources are unsuitable. most suitable source ......................................................................................................... explanation
R B1 half-life not too short OR half-life is suitable so that source does not need to be replaced often B1 so count rate changes with thickness B1 γ- rays would not be stopped at all AND α-particles would be absorbed by any thickness of aluminium
All the planets were formed when a cloud of gas and dust collapsed due to ..............................................................................
gravitational force
2024 43 m/j
Define deceleration
decrease in velocity per unit time OR rate of decrease in velocity OR negative rate of change of velocity