Magnets fission fusion
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Define magnet:
an object that produces a magnetic field, it has a north and South Pole
What are soft vs hard magnets?
Soft magnets -> easy to magnetize and temporary, lose magnetism easily (e.g. induced)
Hard magnets -> harder to magnetize, more likely to be magnetized permanently, easy not to lose magnetism

What are magnetic field lines?
Imaginary lines that show the direction and strength of a magnetic field
What are the 3 rules for drawing magnetic field lines?
Magnetic field lines always point from north to south (need arrows)
The closer together the lines, the stronger the magnet is
Each magnetic field line must start and end at the magnet (its 3D too in all areas)
What’s a magnetic MATERIAL
Any object that can be influenced by magnetic fields, and has the potential to become a magnet
What are some common magnetic elements?
Nickel, Cobalt, Iron, Steel (not magnets, can be induced)
What is a permanent magnet?
A magnetic that produces their own magnetic field ALL THE TIME
What is an induced / temporary magnet?
Objects that only have magnetic field TEMPORARILY
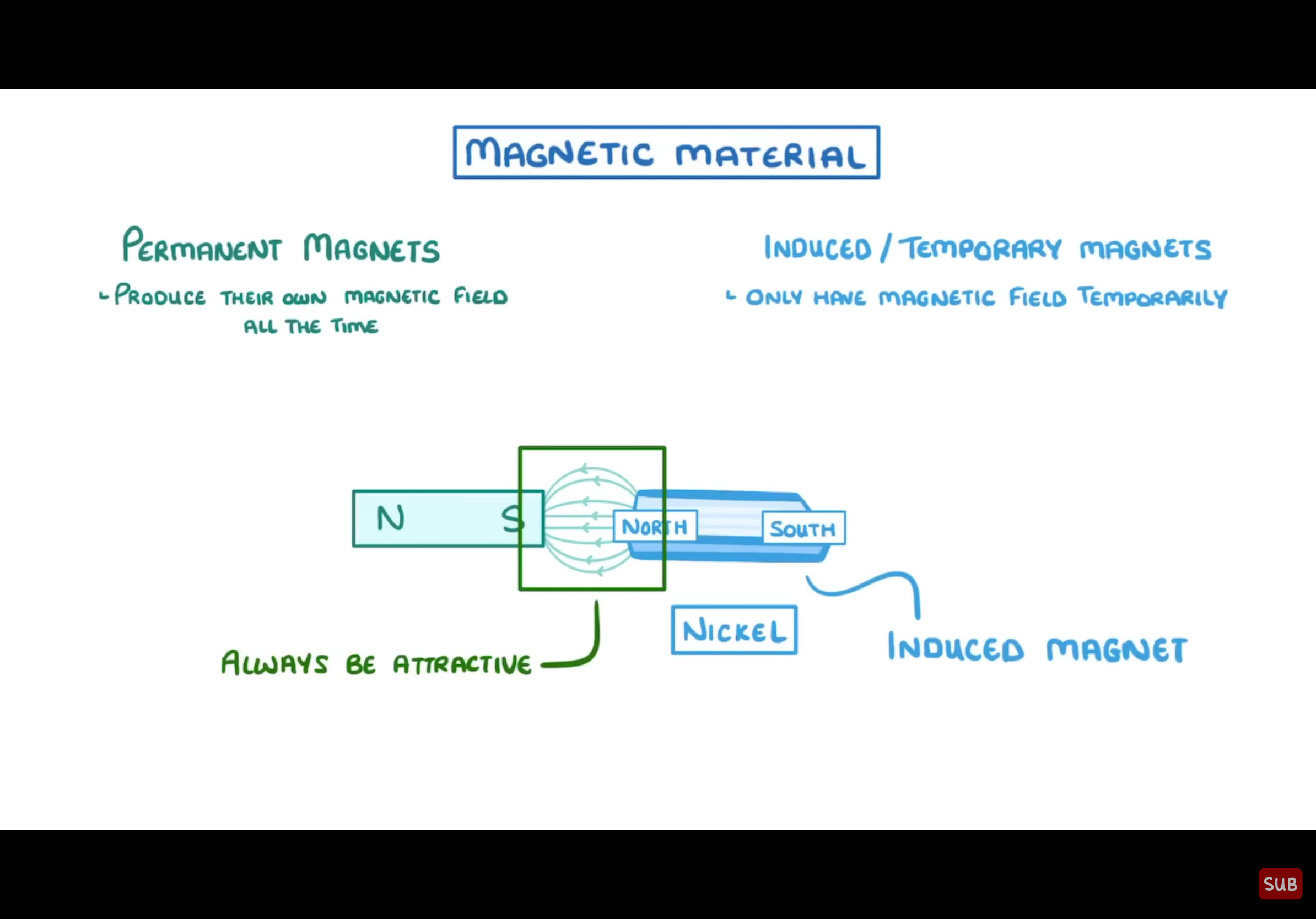
What happens when nickel is put near a bar magnet?
It will have a temporary magnetic field at the ATTRACTING side to the bar magnet
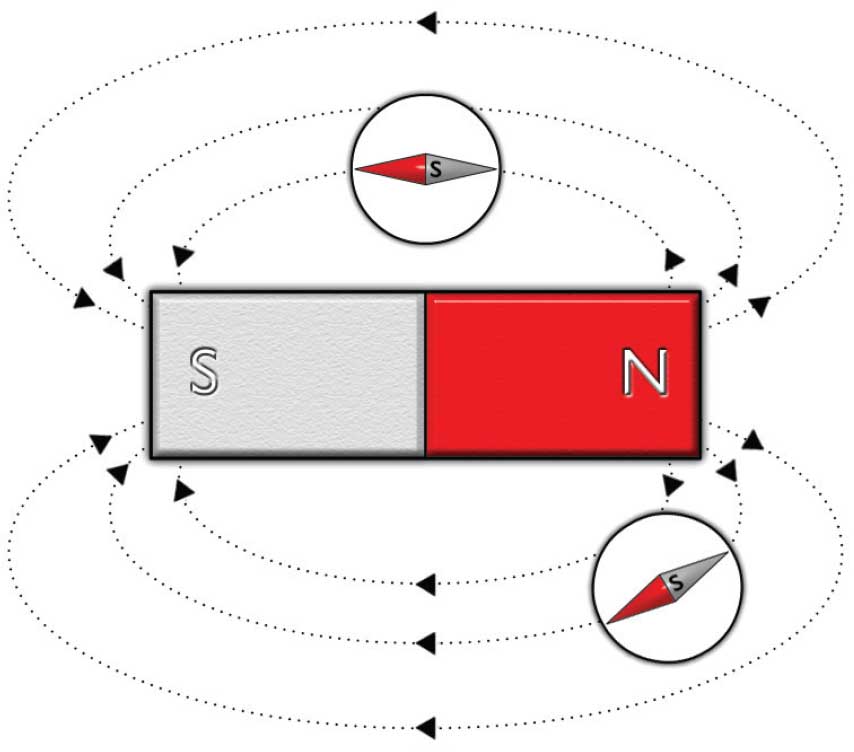
How do you find magnetic field lines?
Take compasses and move them around the magnet, putting dots where their needle points to
The needles will point to the south?? Pole and all of the lines will create magnetic field lines when joined up
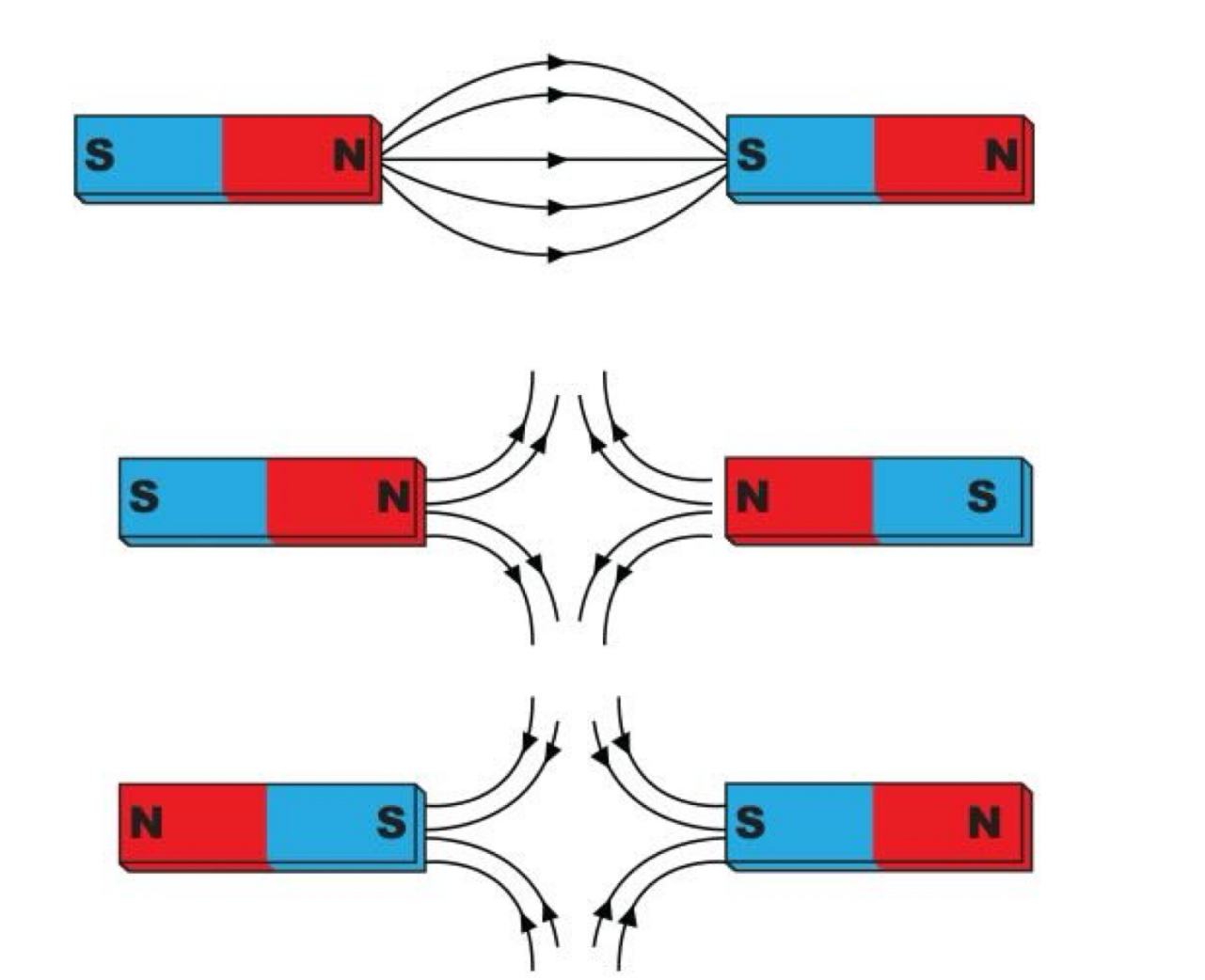
What happens when: S-N :: N-S , N-S :: S-N , S-N :: S-N
Image
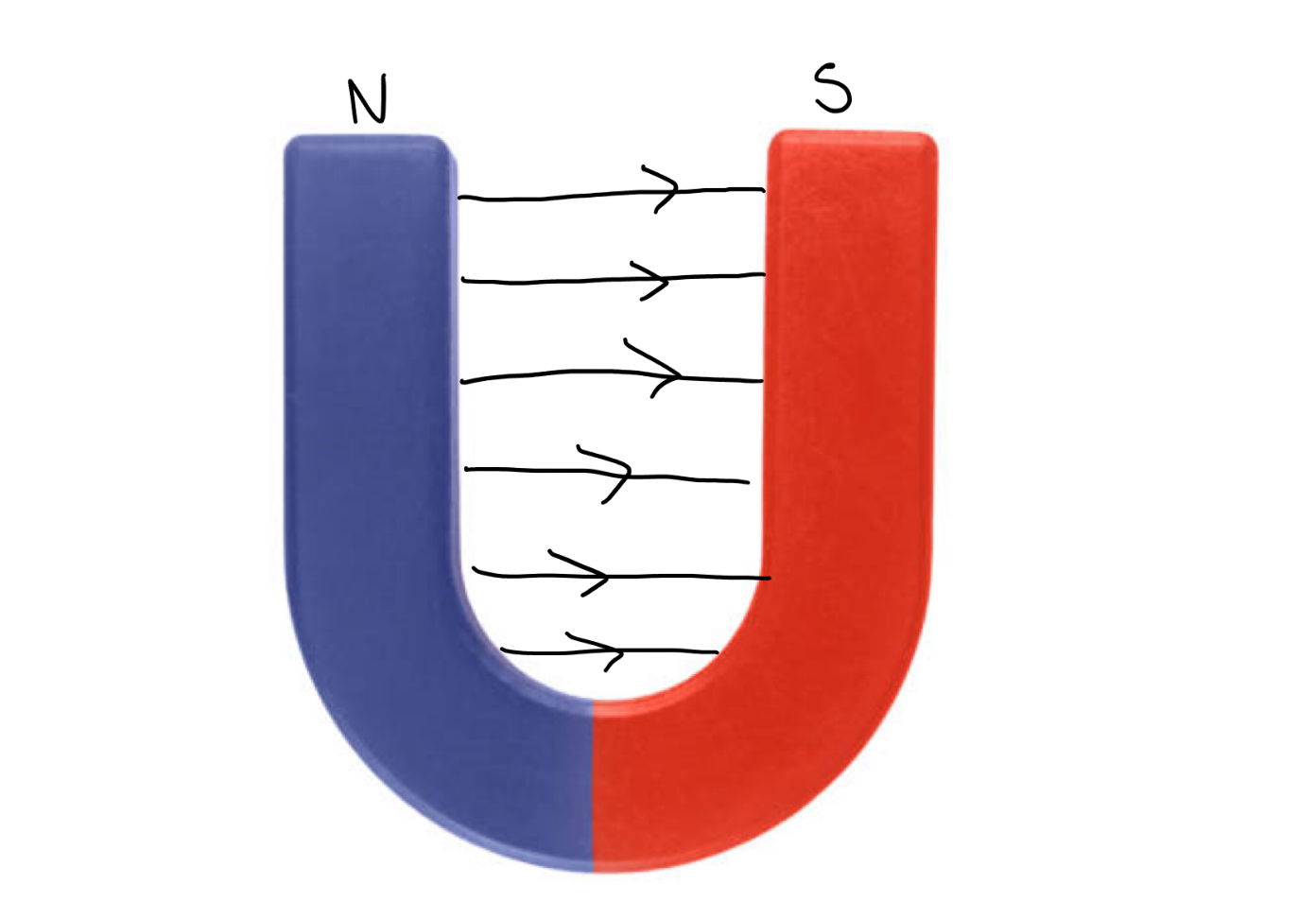
How can two permanent magnets create uniform magnetic field lines?
Opposite poles are placed very close together so magnetic field lines will be parallel and evenly space resulting in a consistent field strength and direction
An ___________ in a conductor produces a magnetic field around it (electromagnetism)
Electric current in a conductor
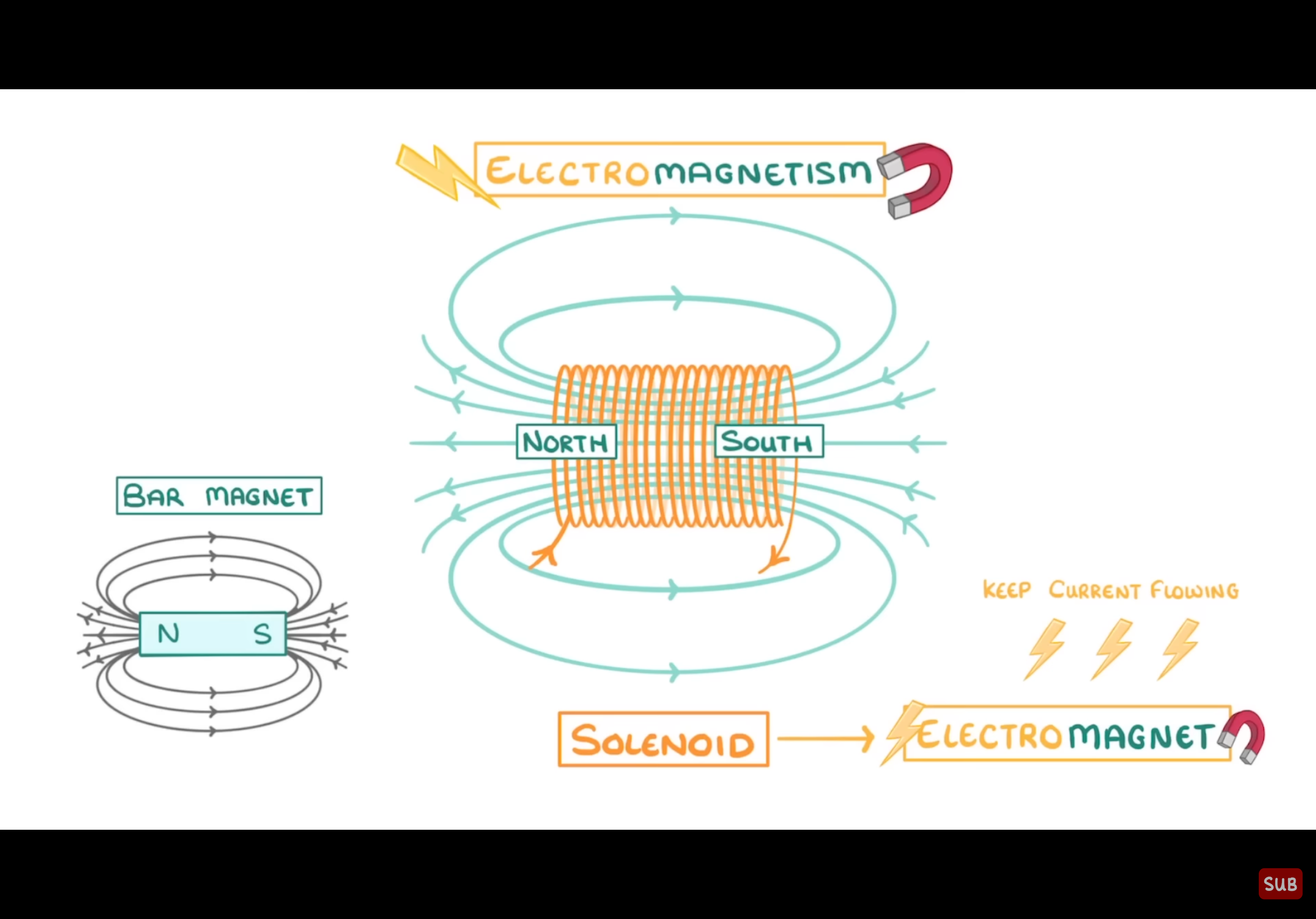
How are electromagnets formed?
Wrapping a coil of wire around a magnetic core (like iron) so that when current turns on, the magnetic field is created
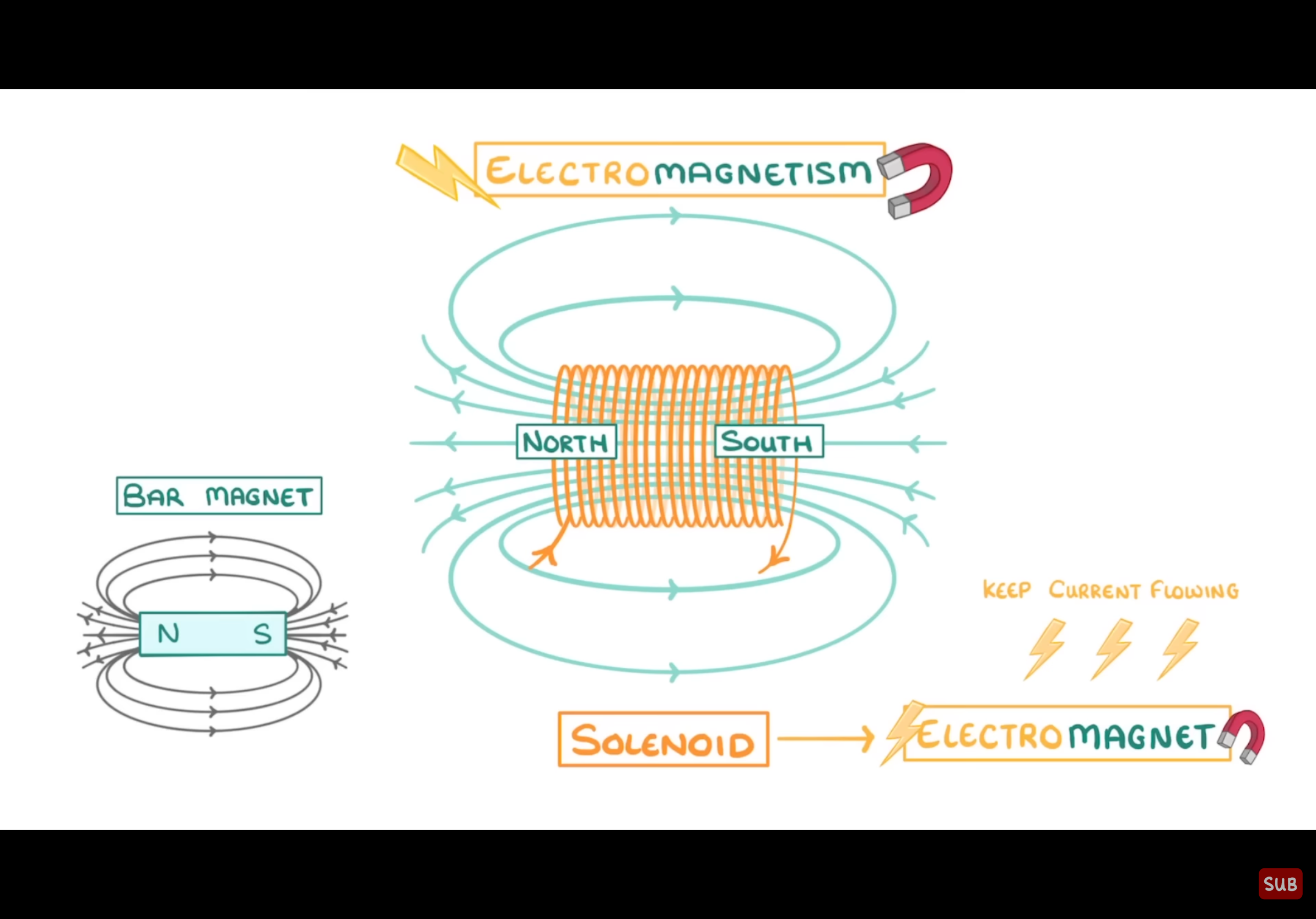
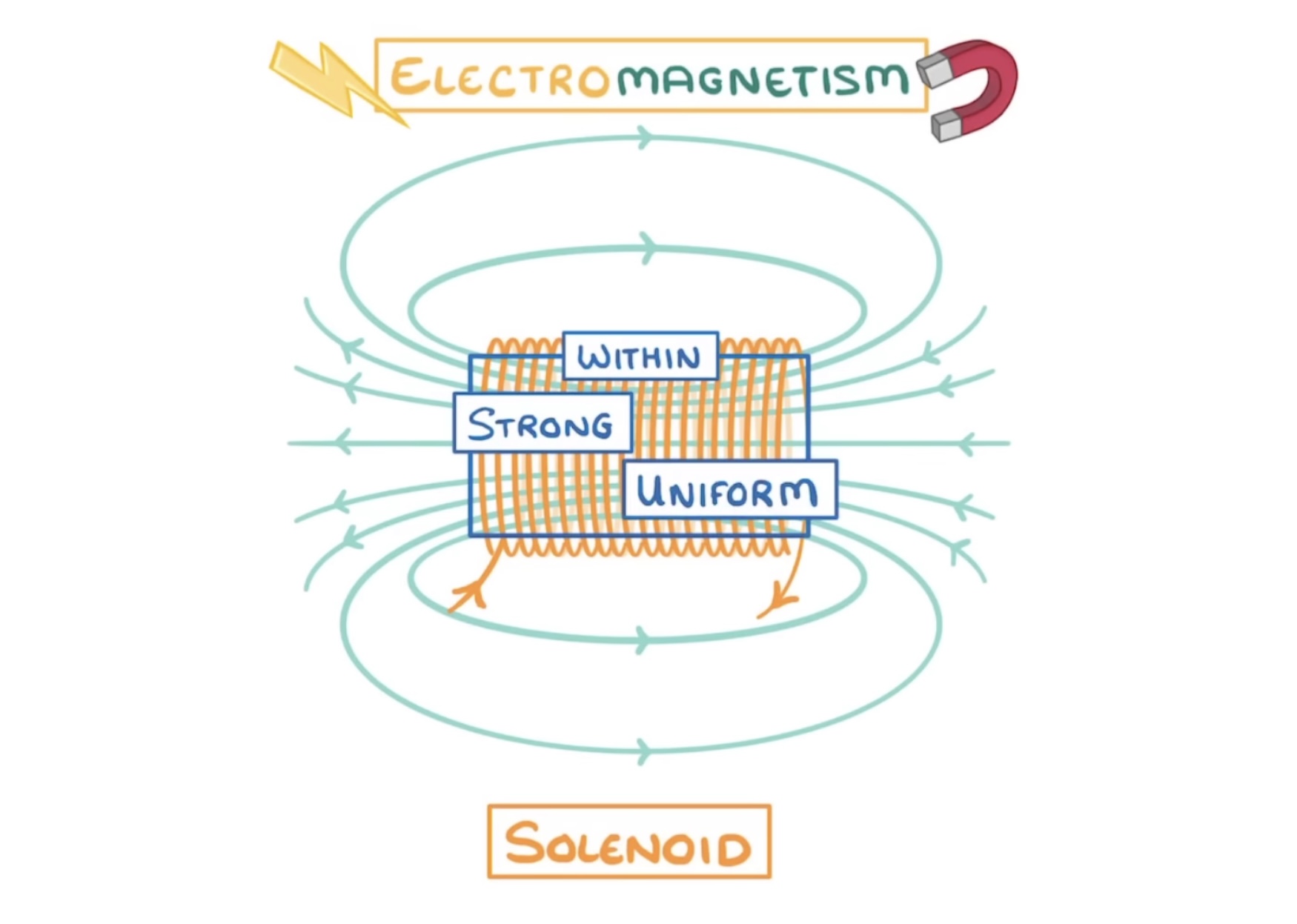
What is a solenoid?
A coil of wire that acts as a temporary magnetic when an electric current passes through it
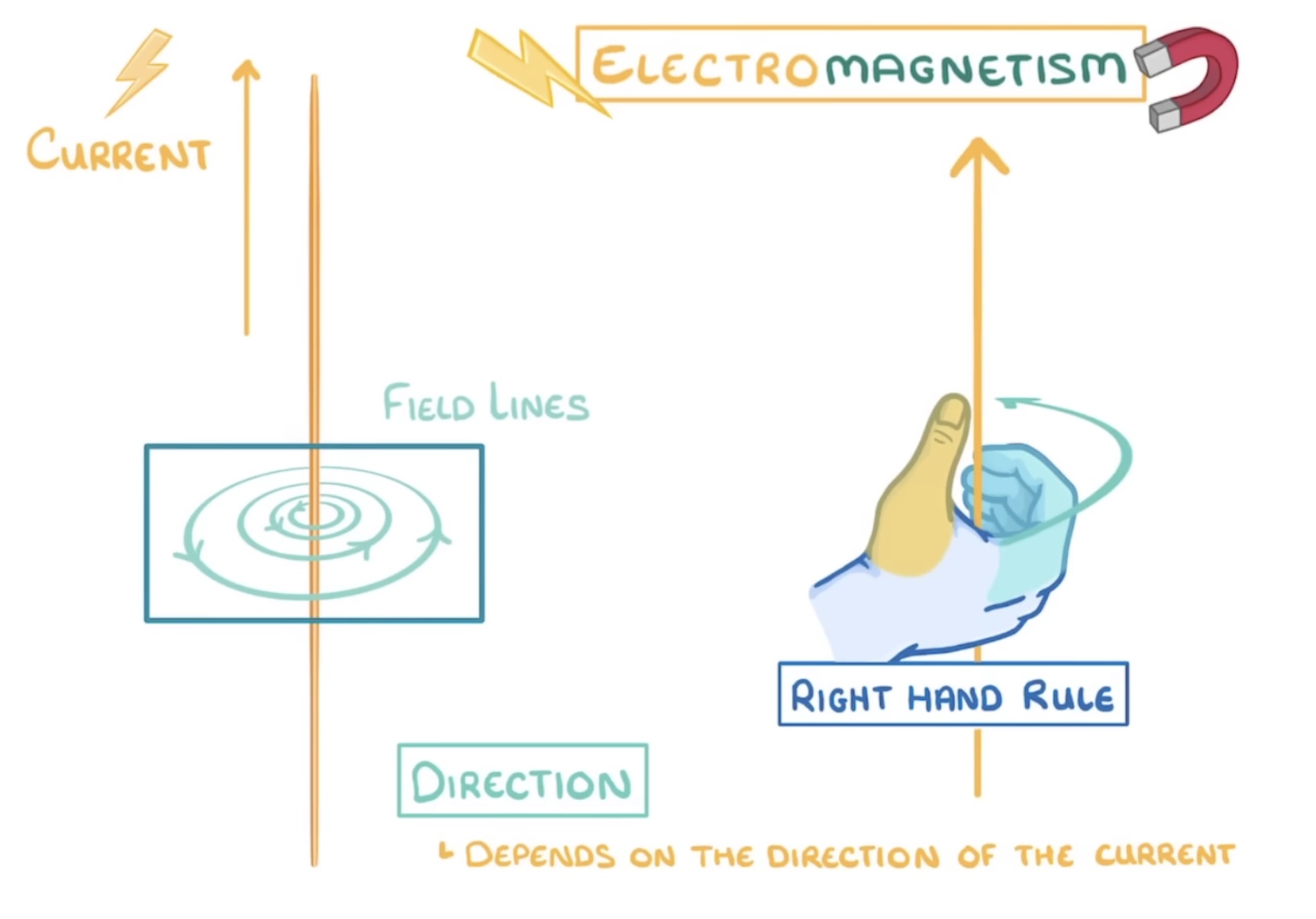
What is the right hand rule?
Thumbs up in direction of current whichever way your 4 fingers curl is the field direction (straight wire)
What do the magnetic field lines look like on a flat circular coil? (Electromagnet)
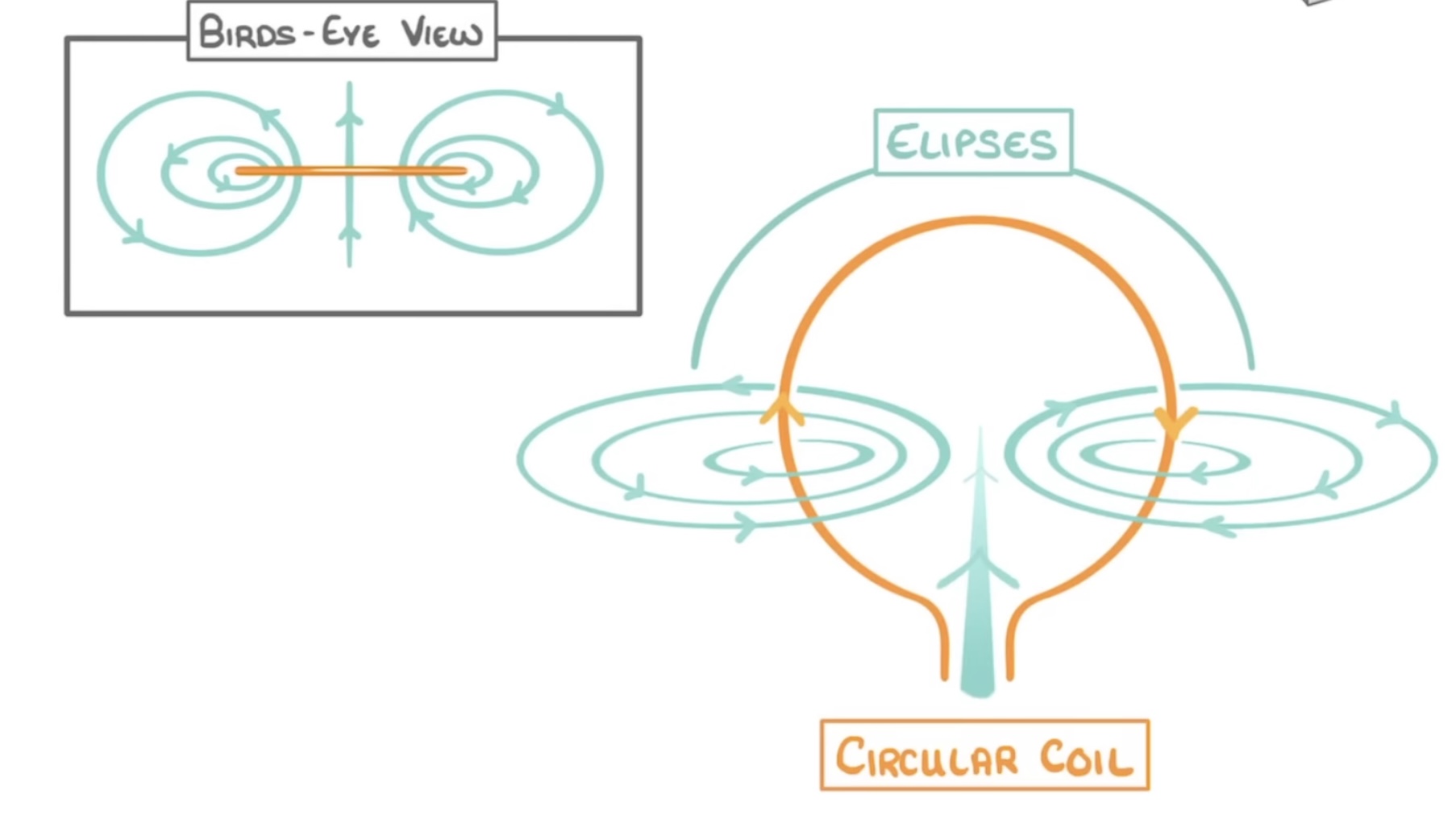
Difference between drawing bar magnet field lines and solenoid field lines?
Draw which way the current is going
Current passes THROUGH the inside
Current can be switched along with field lines
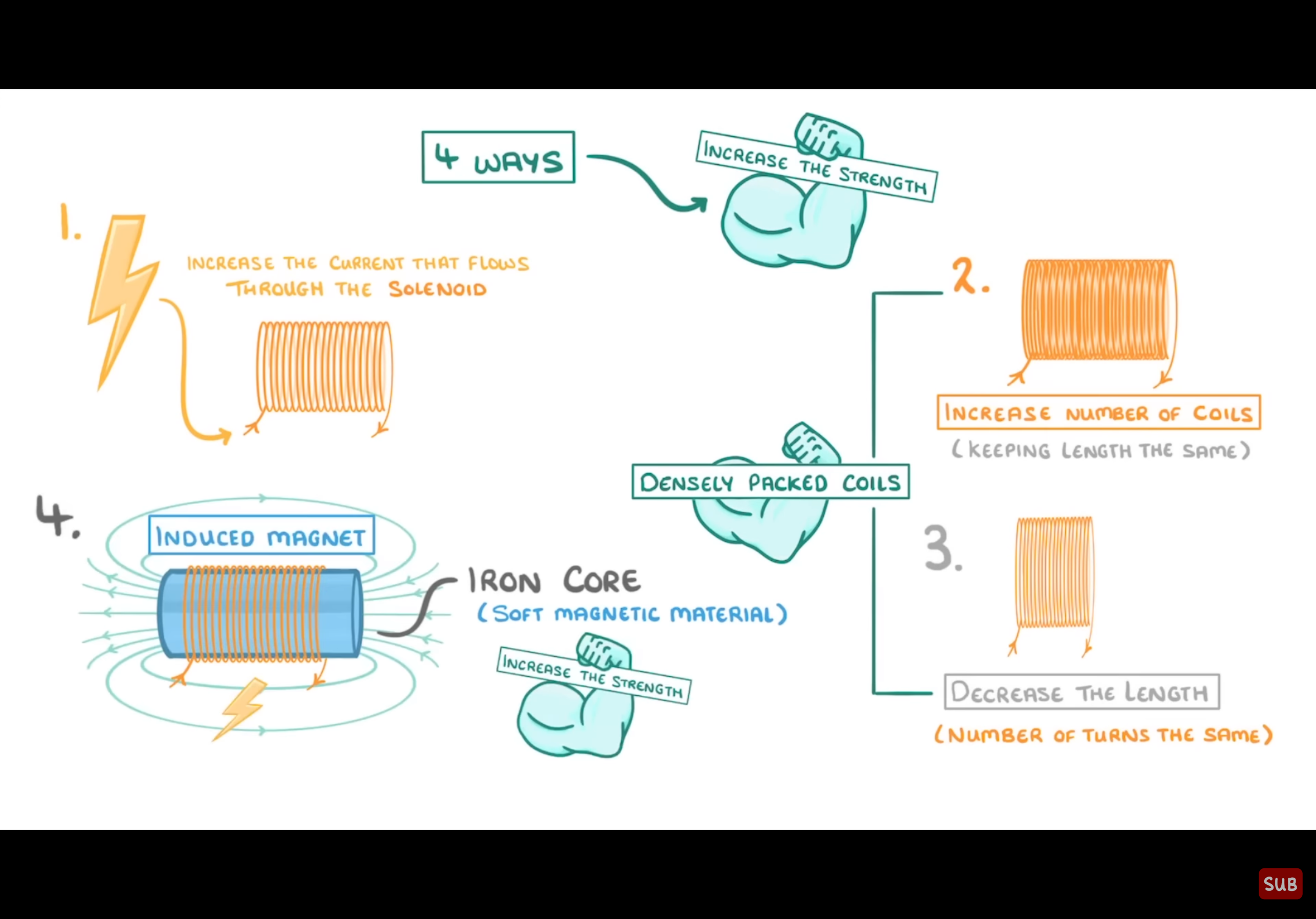
What are the 4 ways an electromagnet in a solenoid can be made stronger?
Increasing the current
Increasing the number of coils with same length
Decreasing the length while keeping number of turns the same
Add an iron core to the inside to increase magnetic strength
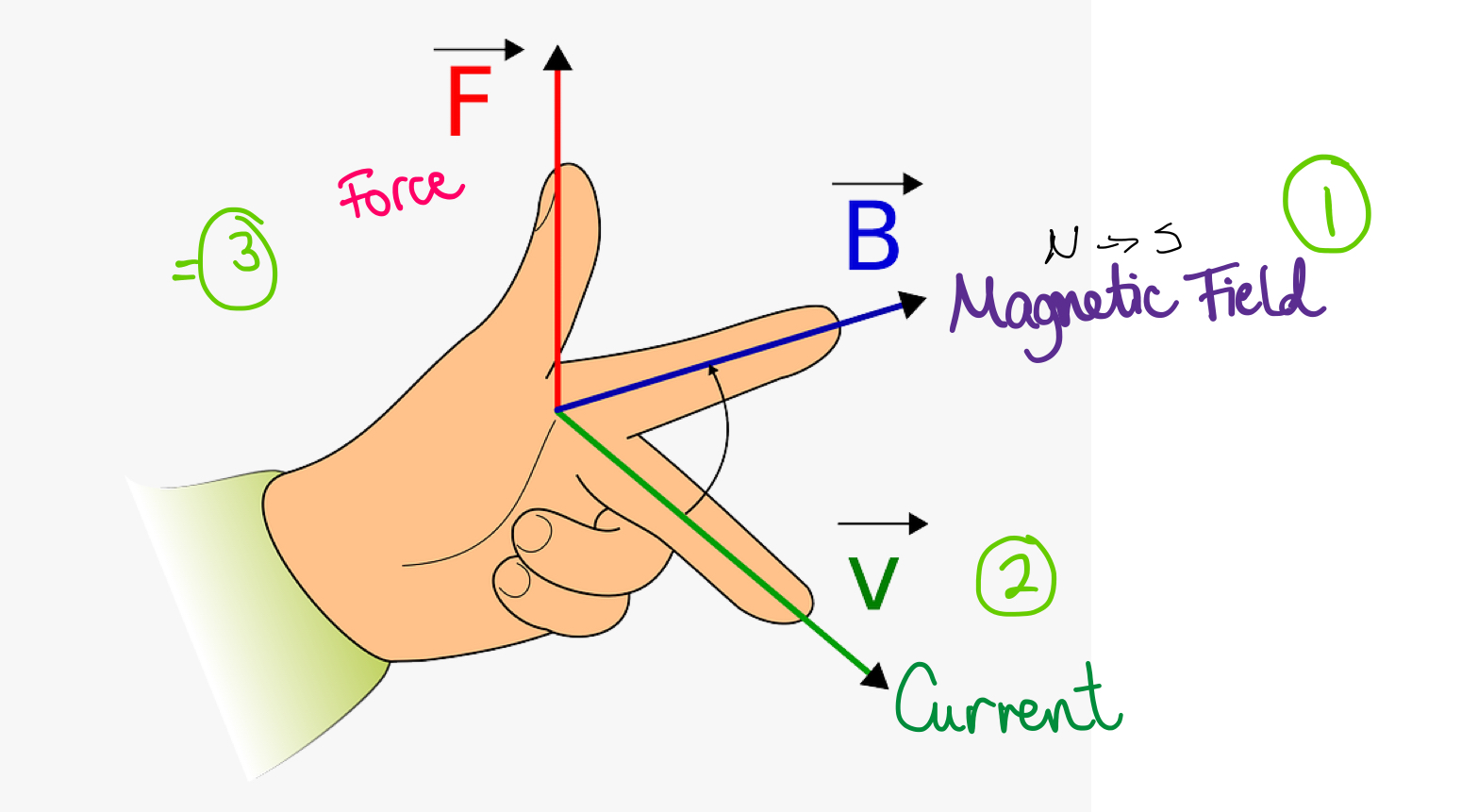
What’s the left hand rule?
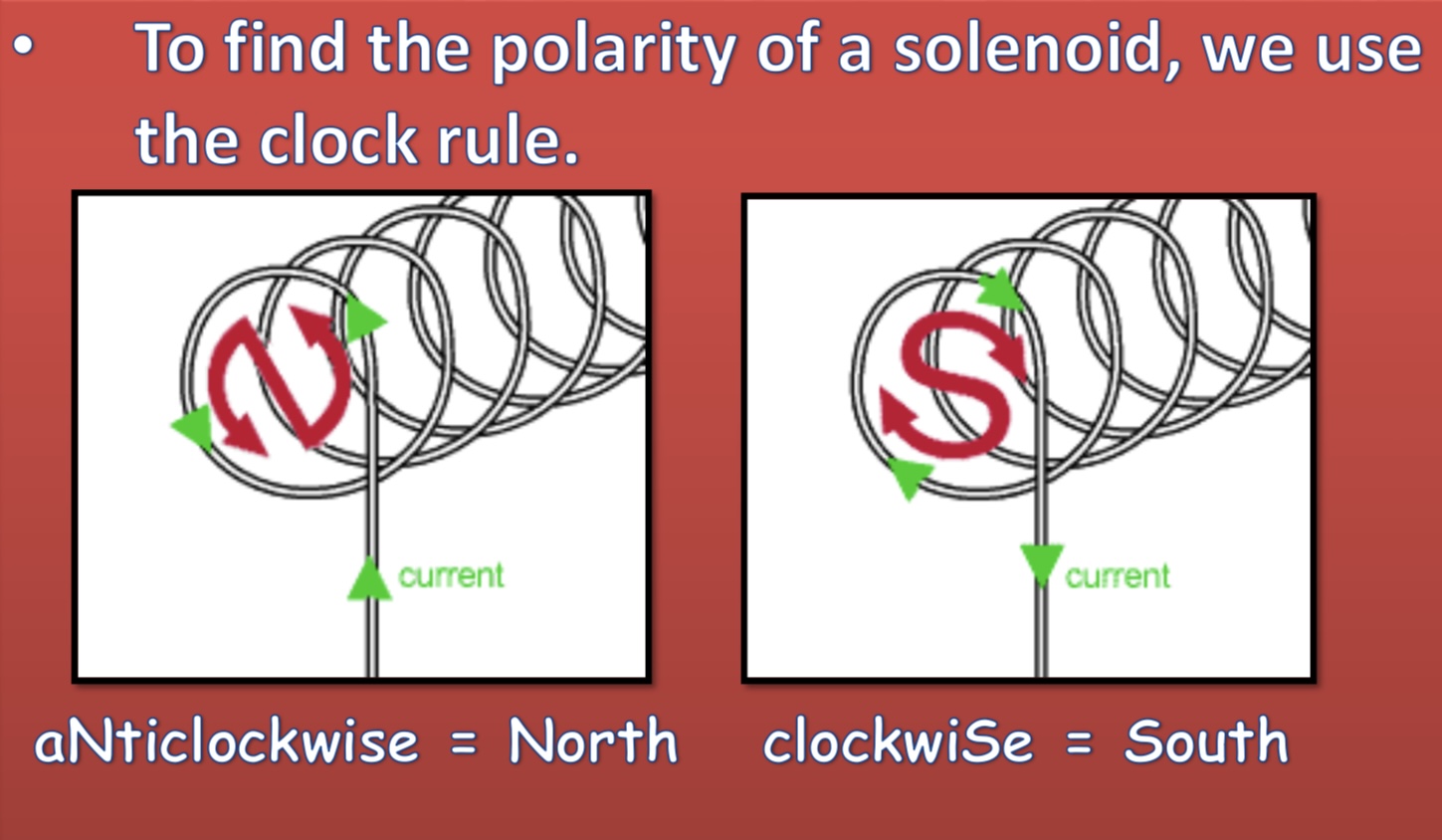
How do you find the polarity of a solenoid?
Clock rule
If a charged current carrying wire is put in a magnetic field Between 2 poles what happens?
The current of the poles will bend around the current carrying wire, repelled away.
EXCEPT FOR IF IT’S MOVING PARALLEL TO THE POLES
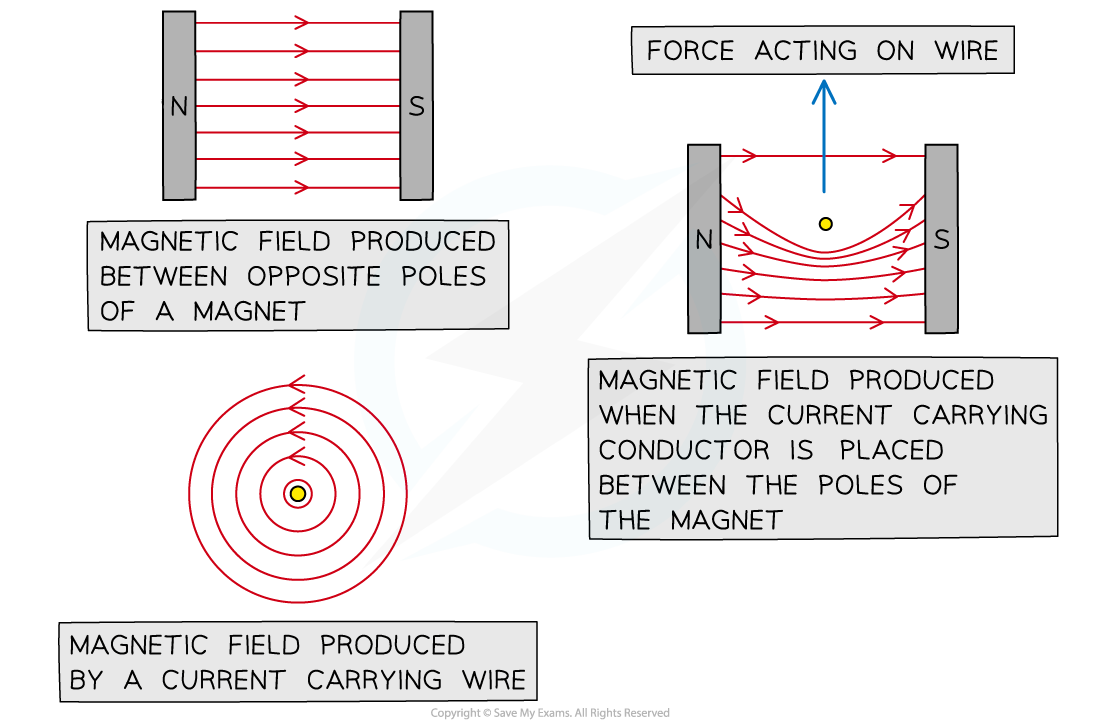
What is the motor effect and how does it work?
Current flows in the wire/coil.
This creates a magnetic field around the wire/coil.
This magnetic field interacts with the field from the permanent magnet.
This produces a force on the wire/coil which moves the wire/coil.
The split-ring commutator changes the direction of the current every half turn as it spins. This reverses the direction of the forces, allowing the coil to continue spinning
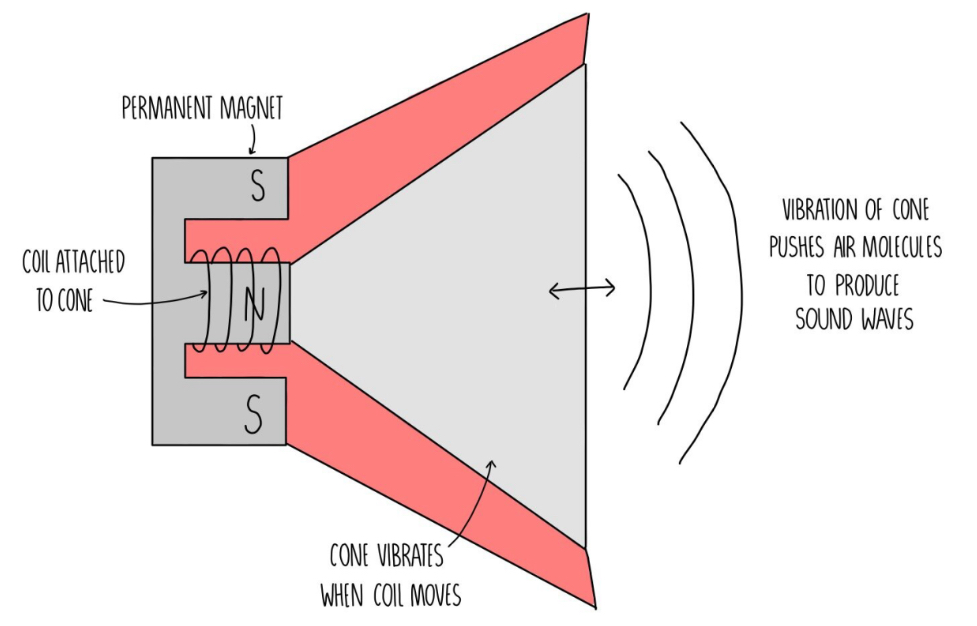
How does a loudspeaker work?
Current passes around the wire wrapped around a magnet core, causes a force due to the motor effect
The force causes the wire to move + makes a magnetic field
Changing the direction of the current (A.C) causes the force to reverse constantly so the coil vibrates back and forth
This causes the diaphragm / coil to vibrate in and out so sound waves are created
It moves the cone and thats how it works :D
<<Doesn’t work if it’s DC because no vibrations are made>>
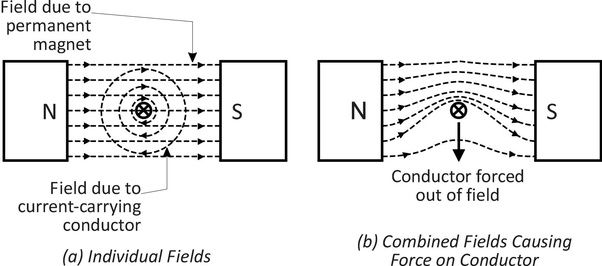
What happens if you increase the magnitude / change the direction of a current-carrying-wire in between two poles?
If you increase the magnitude of the current through a wire or the size of the magnet being used, you increase the force on the wire.
If you change the direction of the current or reverse the poles of the magnet, you change the direction of the force on the wire
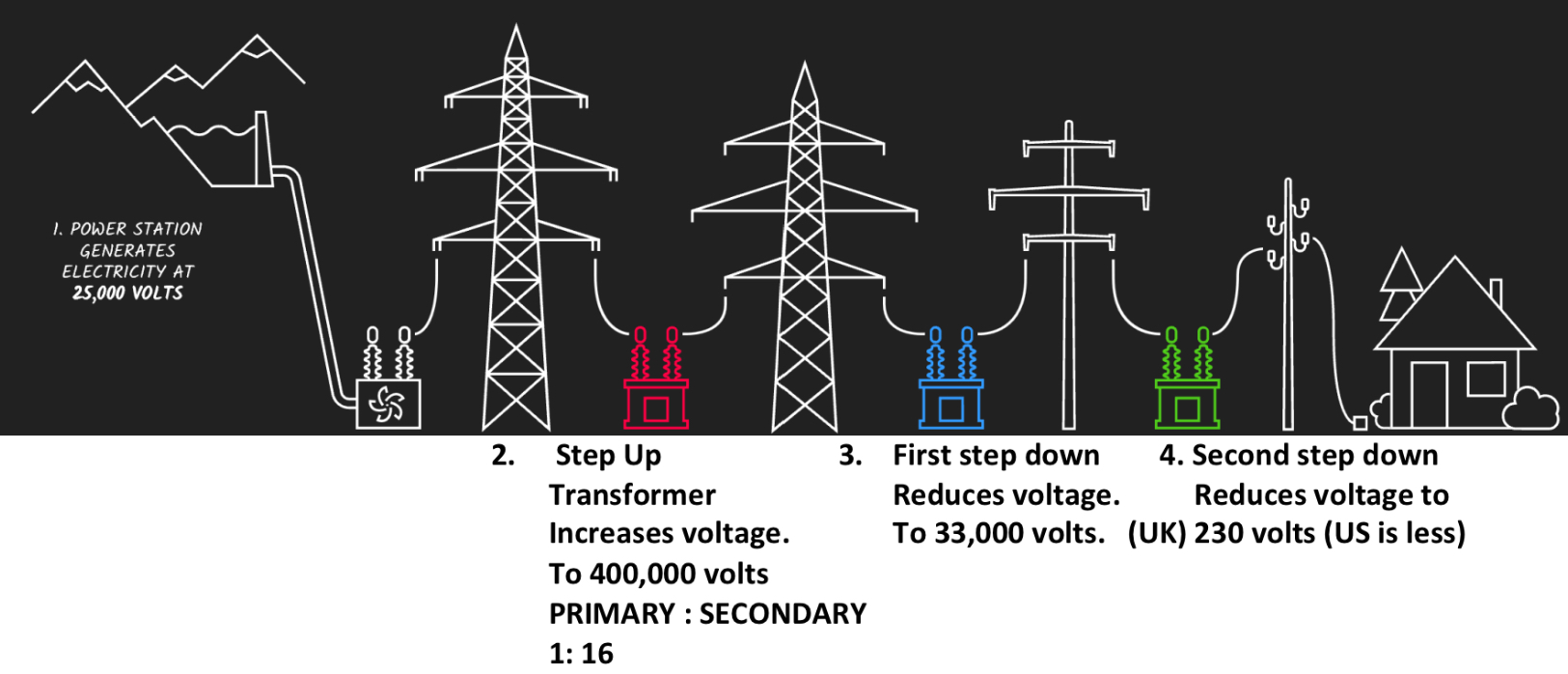
Step Up vs Step Down Transformer
Step up transformers increase the voltage (more turns on the secondary coil than primary coil)
Step down transformers decrease the voltage (more turns on the primary coil than on the secondary coil)
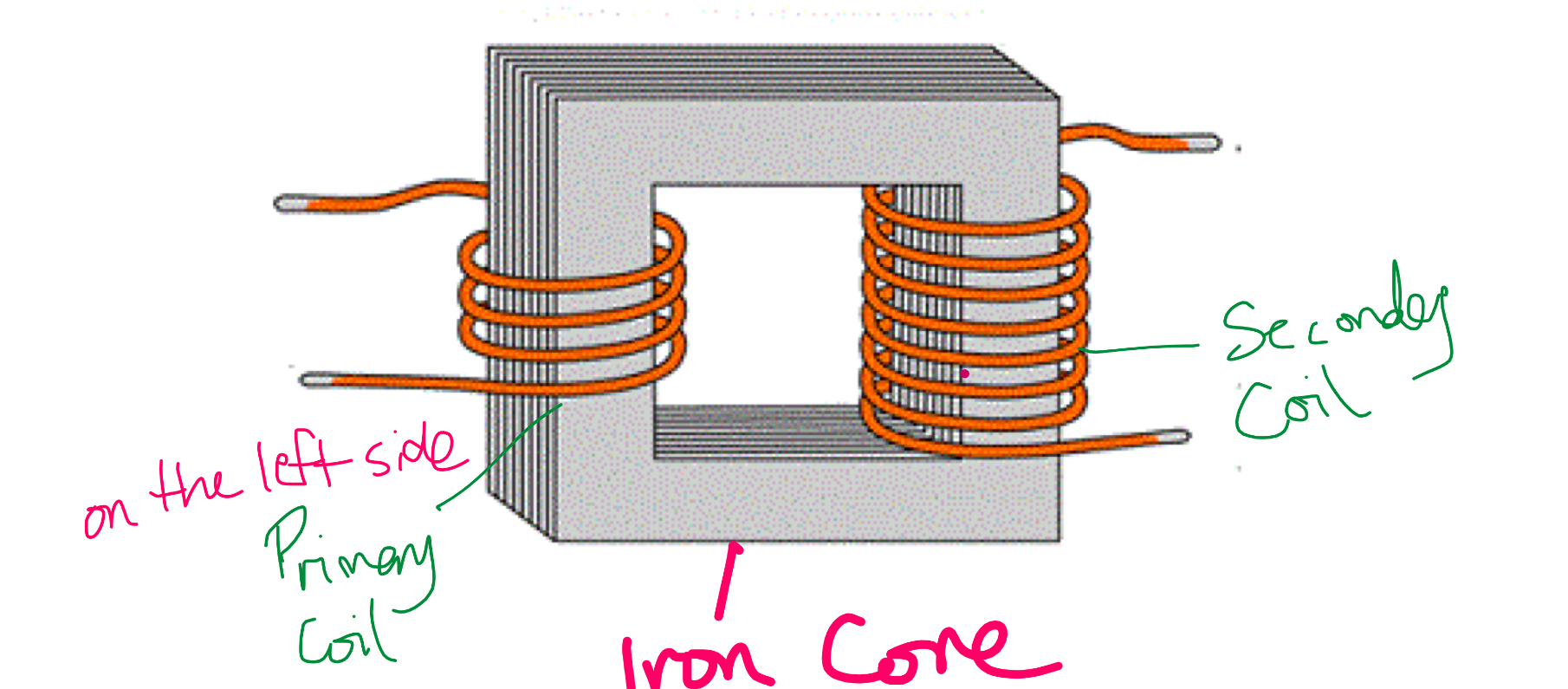
What is a transformer? (Definition and ratio)
A device that changes the voltage of an alternating current as it changes the magnetic field around the iron core. Transformers can increase or decrease the voltage in a circuit. Turns primary: turns secondary same ratio as Voltage primary: Voltage secondary
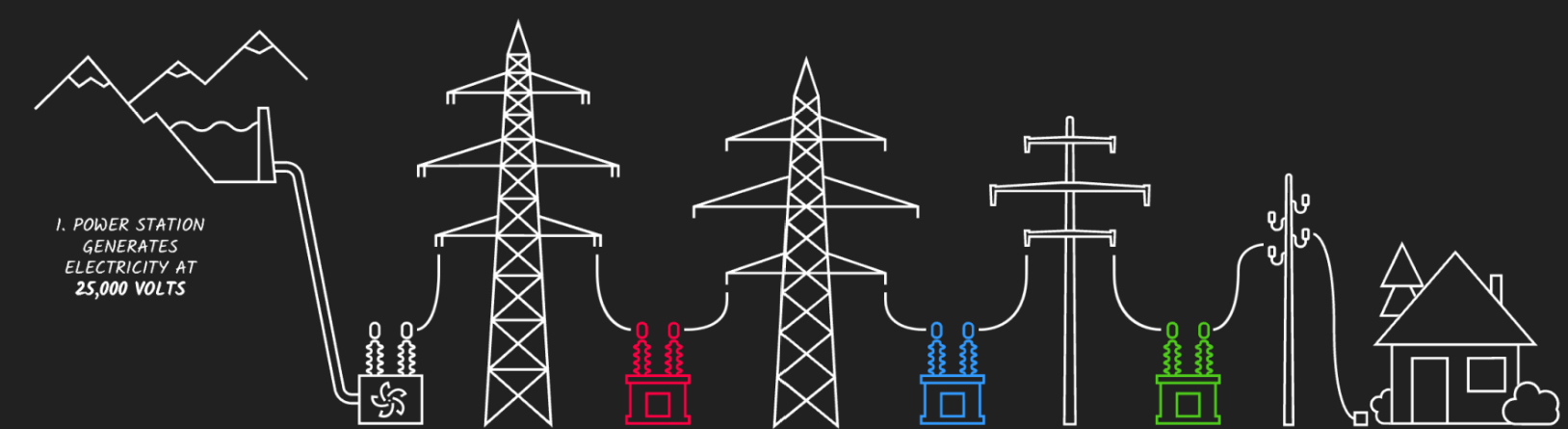
Are transformers red, blue and green step up or down?
Red → step up from power station 1:16 up to 400,000 volts
Blue → step down to 33,000 volts
Green → second step down to 230 volts (UK) for house
When does nuclear fission occur?
When one large UNSTABLE nucleus is split into two smaller, more stable nuclei. Large amounts of energy are released
How is radioactive decay a source of energy?
It emits ionizing radiation
Why are step up and down transformers used?
Power stations generate electricity at 25,000 Volts approximately. This is too low for an efficient transfer of power and low voltages lead to high currents, which waste lots of energy as heat. A series of step-up and step-down transformers are used to maximize the efficiency of energy transfer through and electrical grid.
What happens when a conductor experiences a changing magnetic field? (+ variables that change it)
When a conductor experiences a changing magnetic field a potential difference / voltage is induced in it. The strength of the potential difference depends on the strength of the magnetic field, how fast it changes i.e. how fast the coil is spinning, and how much of the conductor is exposed to the field i.e. how many turns in the coil.