Chapter 17, 18, and 19 Test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Last updated 2:17 PM on 3/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
gene expression
the process by which DNS directs protein synthesis which includes transcription and translation
2
New cards
alkaptonuria
hereditary disease in which enzyme is missing to break down alkapton- turns urine black
3
New cards
primary transcript
initial RNA transcript from any gene pior to processing
4
New cards
central dogma
DNA→ RNA → PROTEIN
5
New cards
Pre-mRNA
RNA before splicing
6
New cards
exon
part of DNA expressed
7
New cards
intron
Part of DNA cut out
8
New cards
RNA Polymerase
catalyzes RNA synthesis which pries DNA apart and joins together RnA nucleotides
9
New cards
Initiation
RNA Polymerase finds and bonds to the promoter
10
New cards
Elongation
adds on corresponding RNA transcript
11
New cards
Termination
End signal adn RNA transcript is disconnected
12
New cards
Promoter
where RNA Polymerase attaches
13
New cards
Transcription Unit
Stratch of DNA that is transcribed
14
New cards
Transcription factors
mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the iniation of transcription
15
New cards
TATA Box
promoter that is crucial to the initiation complex
16
New cards
Modification of Pre-mRNA
5’ recieves a 5’ cap
3’ end gets a poly A tail w/ 50-250 adenines
3’ end gets a poly A tail w/ 50-250 adenines
17
New cards
RNA splicing
removes introns adn joins exons creating an mRNA molecule
18
New cards
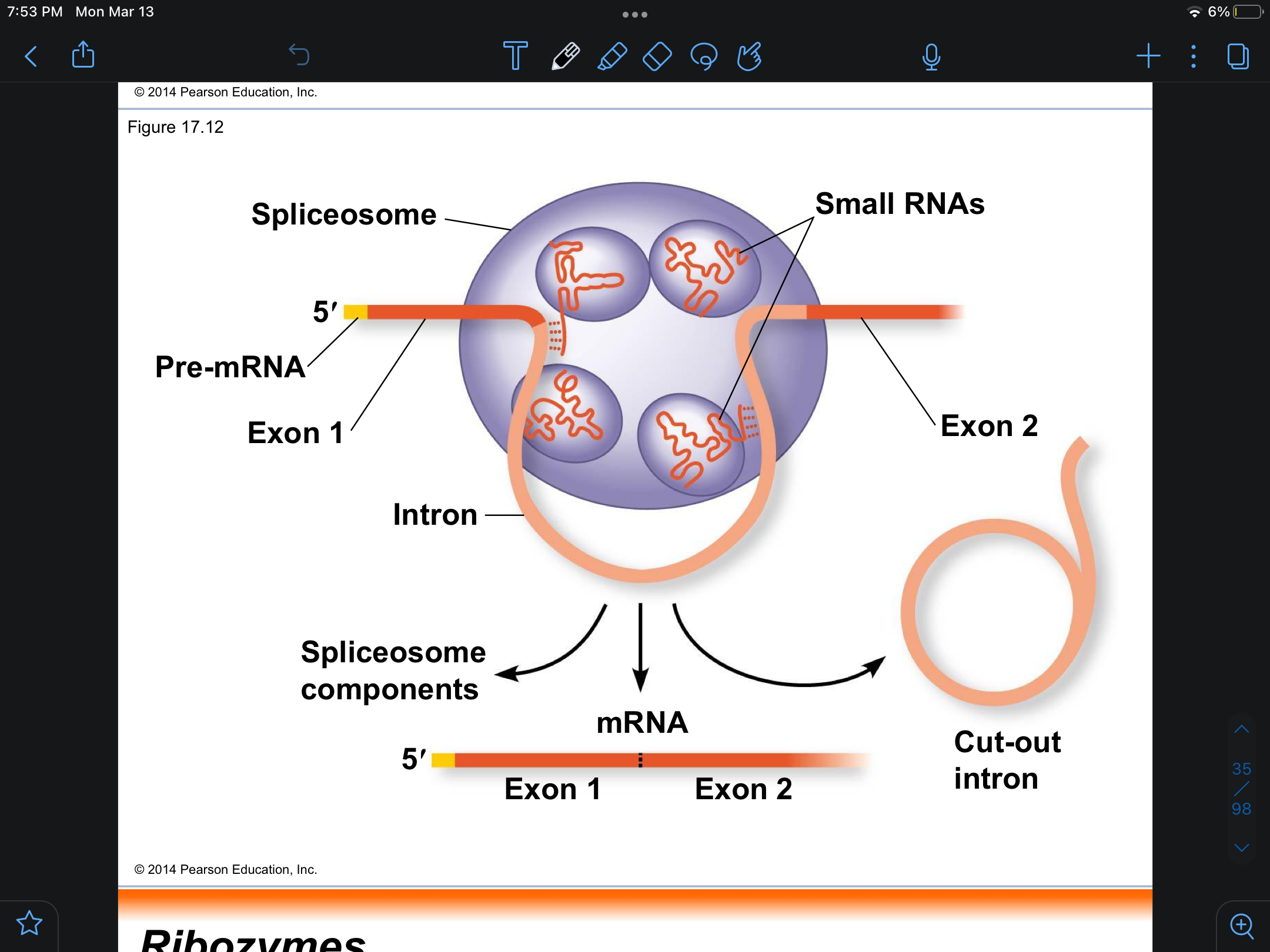
spliceosome
variety of protein and snRNPs that recognize the splice sites
19
New cards
Ribozymes
catalytic RNA molecules that function as enzymes and can splice RNA
20
New cards
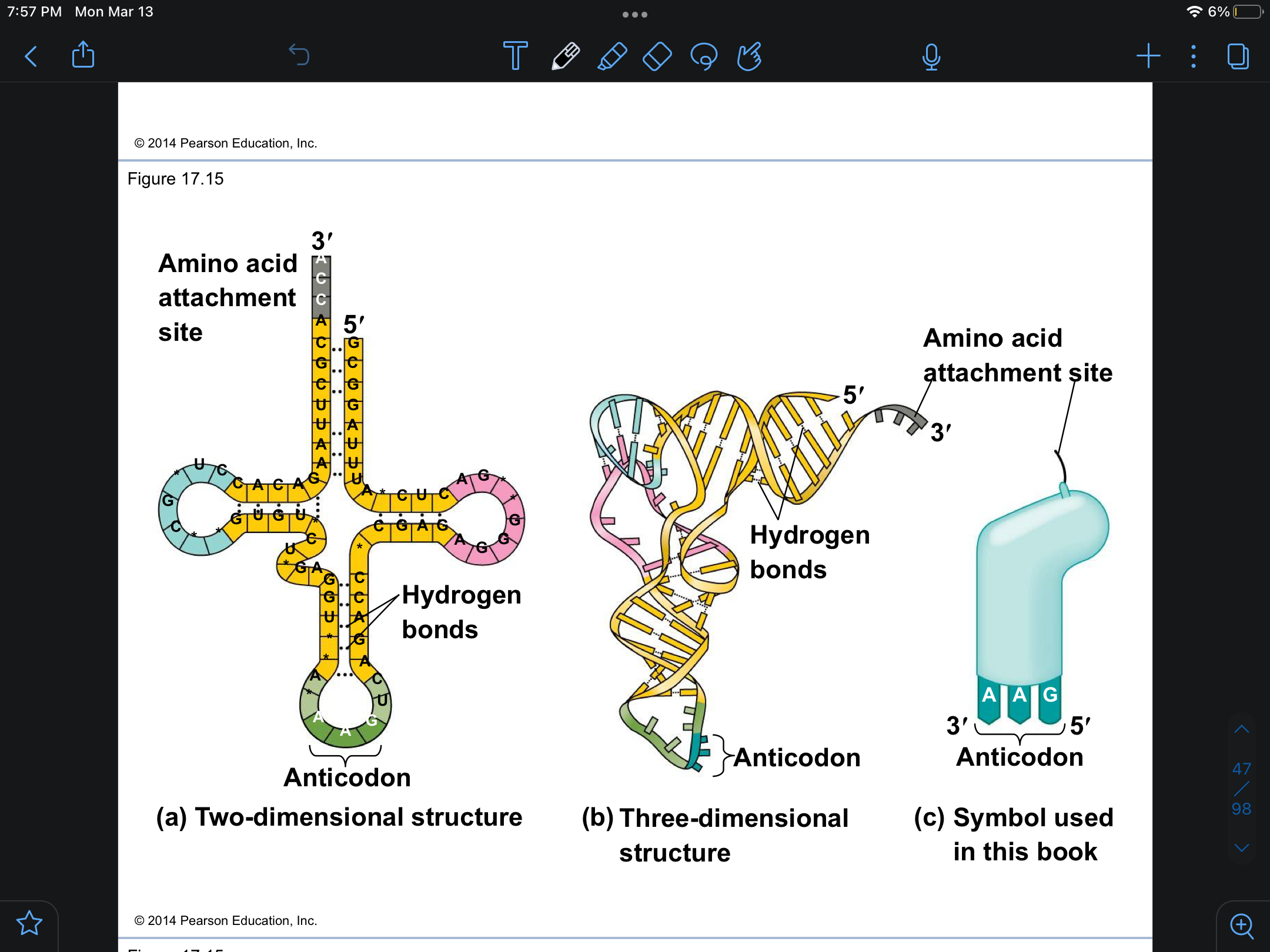
tRNA
translates the mRNA into protein with the help of this; brings mRNA to the ribosome
21
New cards
anticodon
codes for a codon which codes for specific amino acid
22
New cards
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
enzyme that attaches tRNA and an amino acid
23
New cards
wobble
explains how multiple anticodons can code for the same codon due to the flexible base pairing in the third base
24
New cards
rRNA
makes up ribosomal subunits
25
New cards
P site
holds the tRNA that carries the growing polypeptide
26
New cards
A Site
holds the tRNA that carries the next amino acid to be added to the chain
27
New cards
E site
discharged tRNA leave the ribosome
28
New cards
signal-recognition particle (SRP)
particle bound to the ER that ribosomes bind to when transporting polypeptide chain
29
New cards
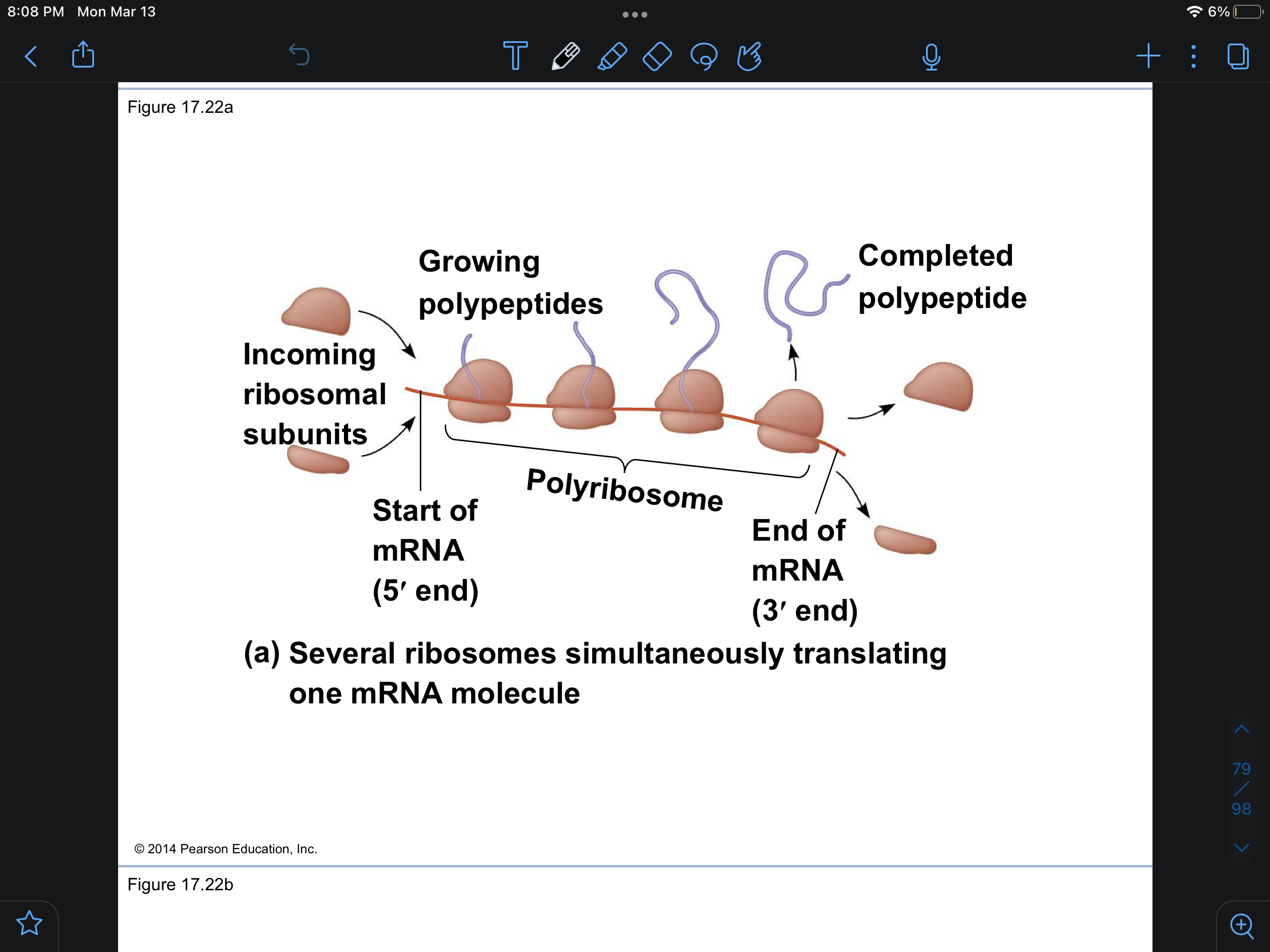
Polyribosome
multiple ribosomes translating a single mRNA simultaniously
30
New cards
point mutation
chemical changes in just one base pair of a gene
31
New cards
silent mutation
no effect in the amino acid produced
32
New cards
missense mutation
still code for an amino acid but no the correct one
33
New cards
Nonsense mutation
change in amino acid codon into a stop codon leading to a nonfunctional protein
34
New cards
insertion/deletion
additon and deletion of nuclotide pairs
35
New cards
frameshift mutation
shift of the reading frame changing all the amino acids produced off of the mRNA chain
36
New cards
mutagen
physical or chemical agents that can cause mutations
37
New cards
operator
the “switch” positioned usually in the promoter of DNA
38
New cards
operon
the entire stretch of DNA that includes the promoter operator and gene
39
New cards
repressor
prevents gene transcription by binding to the operator and blocking RNA polymerase
40
New cards
corepressor
a molecule that cooperates with a repressor protein the switch off and operon
41
New cards
inducible operon
one that is usually off and the inducer in activates the repressor and turns on transcription (lac)
42
New cards
inducer
inactivates the repressor to turn the operon on
43
New cards
differential gene expression
the expression of different genes by cells with the same genome
44
New cards
histone acetylation
acetyl groups are attached to positively charged lysine in histone tails; loosens chromatin and promotes transcription
45
New cards
DNA methylation
the addition of methyl groups to certain bases in DNA; associated with reduced transcription in some species
46
New cards
virus
infectious particle consisting of genes packaged in a protein coat
47
New cards
capsid
protein shell that encloses the viral genome
48
New cards
capsomeres
monomer of capsid
49
New cards
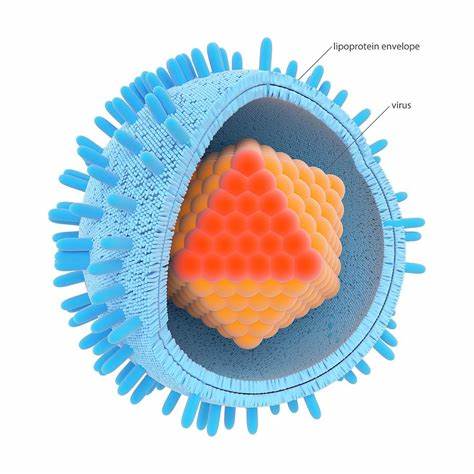
viral envelopes
surround the capsids of influenza viruses and many other viruses found in animals
50
New cards
bacteriophages
viruses that infect bacteria
51
New cards
obligate intracellular parasites
meaning that viruses can only reproduce in a host cell
52
New cards
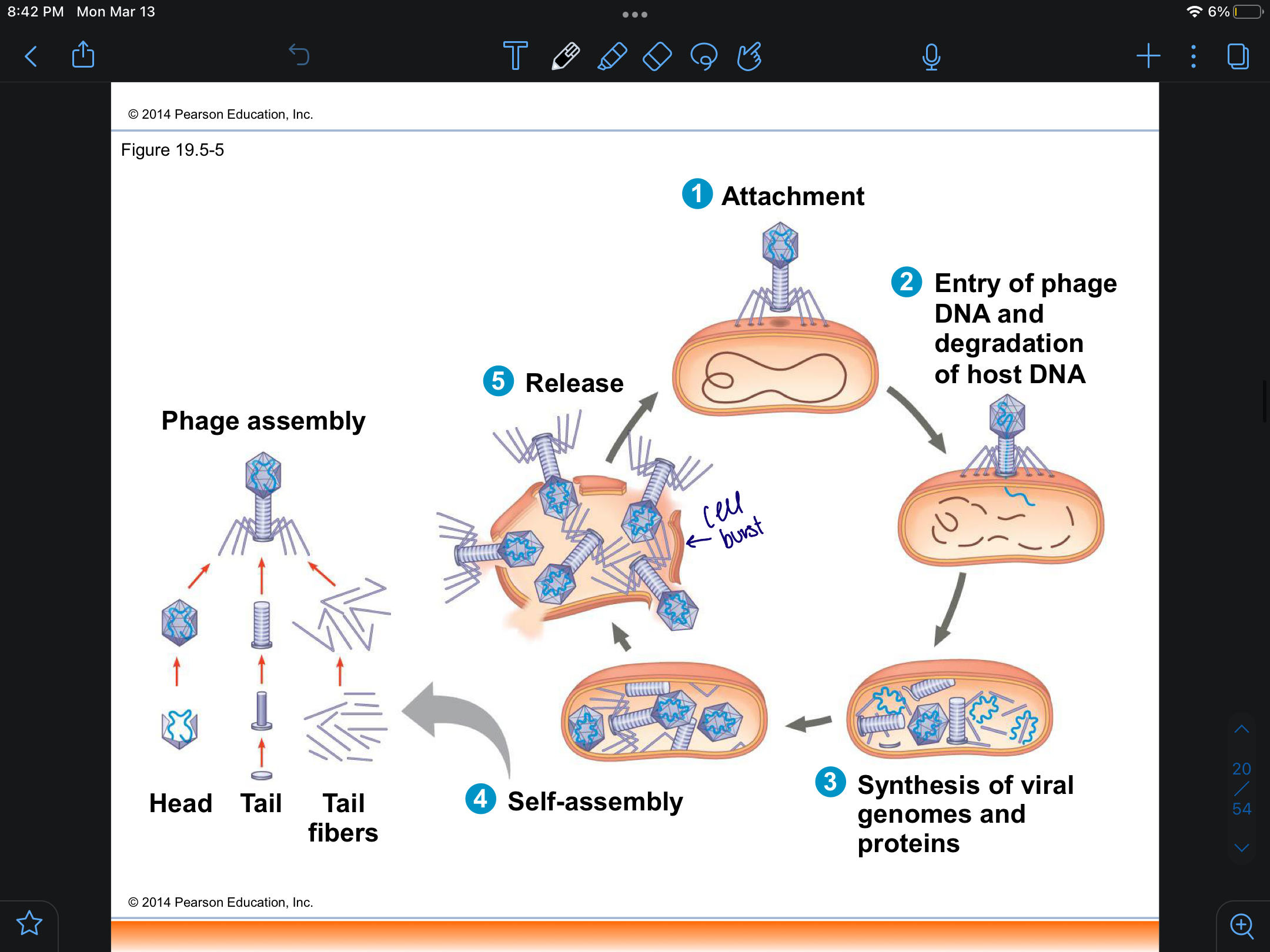
lytic cycle
produces new phages and the lyses the cell releasing more of the phages
53
New cards
lysogenic
when the viral DNA is incorporated into the host cell’s chromosome
54
New cards
prophage
integrated viral DNA
55
New cards
temperate phages
phages that use the lytic and lysogenic cycle
56
New cards
retroviruses
use reverse transcriptase to copy their RNA genome into DnA
57
New cards
provirus
viral DNA that is integrates into the host genome
58
New cards
vaccines
harmless derivates of pathogenic microbes that stimulate the immune system to mount defenses against the harmful pathogen
59
New cards
horizontal transmission
plant viruses entering through damaged cell walls
60
New cards
vertical transmission
inheriting the virus from a parent
61
New cards
viroids
small circular RNA molecules that infect plants and disrupt their growth
62
New cards
prions
slow-acting virtually indestructible infectious proteins that cause brain diseases in mammals