Chapter 12 Synovial Fluid
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
where is synovial fluid formed
Synovial fluid is produced as an ultrafiltrate of blood plasma
what is synovial fluid primarily composed of
hyaluronan, lubricin, proteinase, collagenases, and prostaglandins
what are the functions of synovial fluid
•Moistens and lubricates joints
•Reduces friction between bones during joint movement
•Provides nutrients to articular cartilage
•Lessons shock of joint compression
what are the lab findings for Group I Noninflammatory joint disorders
clear yellow fluid
good viscosity
WBCs <1000 uL
neutrophils <30%
similar to blood glucose
ex) ganglion cysts
what are the lab findings for Group II inflammatory joint disorders of immunologic origin
cloudy, yellow fluid
poor viscosity
WBCs 2000-75,000 uL
neutrophils >50%
decreased glucose level
possible antibodies present
ex) lupus
what are the lab findings for Group II inflammatory joint disorders of crystal-induced origin
cloudy or milky fluid
low viscosity
WBCs up to 100,000 uL
neutrophils < 70%
decreased glucose level
crystals present
what are the lab findings for Group III inflammatory joint disorders of septic origin
cloudy yellow-green fluid
variable viscosity
WBCs 50,000-100,000 uL HIGHEST WBC
neutrophils >75%
decreased glucose level
positive culture & gram stain
what are the lab findings for Group IV inflammatory joint disorders of hemorrhagic origin
cloudy red fluid
low viscosity
WBCs equal to blood
neutrophils equal to blood
normal glucose level
neutrophils in synovial fluid indicate____?
bacterial sepsis, crystal-induced inflammation
lymphocytes in synovial fluid indicate____?
nonseptic inflammation
macrophages in synovial fluid indicate____?
normal fluid or viral infection
synovial lining cells in synovial fluid indicate____?
normal fluid or disruption from arthrocentesis
LE cells in synovial fluid indicate____?
lupus erythematosus
Reiter cells in synovial fluid indicate____?
reactive arthritis (infection in another part of the body)
RA cell (ragocyte) in synovial fluid indicate____?
rheumatoid arthritis immunologic inflammation
cartilage cells in synovial fluid indicate____?
osteoarthritis
rice bodies in synovial fluid indicate____?
tuberculosis
septic and rheumatoid arthritis
fat droplets in synovial fluid indicate____?
traumatic injury or chronic inflammation
hemosiderin in synovial fluid indicate____?
pigmented villonodular synovitis
what are the most common crystals found in synovial fluid
monosodium uric acid (MSU) and calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD)
MSU crystals in synovial fluid indicate____?
gout
CPPD crystals in synovial fluid indicate____?
pseudo gout
how many tubes are used for synovial fluid specimens
three tubes
red stopper tube
green or lavender stopper tube
green or yellow stopper tube
what is the red stopper tube for synovial fluid used for
1st 4-5mL of synovial fluid
no coagulants or preservatives added
observed for clotting
chemical/immunologic analysis
must be centrifuged
what is the green stopper tube for synovial fluid used for
2nd 4-5 mL of synovial fluid OR 3rd 4-5mL
sodium heparin
cell count, differential count, crystal identification
what is the lavender stopper tube for synovial fluid used for
2nd 4-5mL of synovial fluid
EDTA
cell count, differential count, crystal identification
what is the yellow stopper tube for synovial fluid used for
3rd 4-5 mL of synovial fluid
sodium polyanethol sulfonate
microbiological studies
should powdered or liquid anticoagulants be used
liquid; powdered can interfere with crystal anaylsis
what does normal synovial fluid viscosity (String test) look like
jelly-like; should form 4-6 cm long strings from pipette during string test

what does abnormal synovial fluid viscosity (String test) look like
low viscosity; indicates inflammation
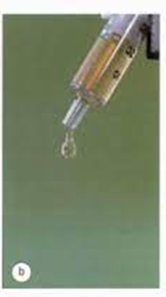
what does a normal Rope’s test look like
after addition of acetic acid, a solid or soft ropey mucin clot forms
what does an abnormal Rope’s test look like
after addition of acetic acid, friable (breakable) clot forms OR no clot at all
what does normal synovial fluid look like
colorless and clear, maybe a yellow tinge
what does red, brown, or xanthochromic synovial fluid indicate
hemorrhage into joint
what does yellow/clear synovial fluid indicate
noninflammatory effusion
what does yellow cloudy synovial fluid indicate
inflammation
what does white cloudy synovial fluid indicate
crystals
what do rice bodies in synovial fluid indicate

rheumatoid arthritis or synovium enriched with fibrin
what do free-floating black-colored inclusions that appear similar to ground pepper in synovial fluid indicate

Ochronotic shards
debris from joint prosthesis
describe what a LE (lupus eryhematosus) cell looks like in synovial fluid
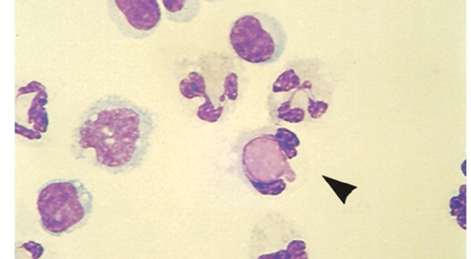
neutrophils that have engulfed a nucleus of a lymphocyte
describe what a Reiter cell looks like in synovial fluid
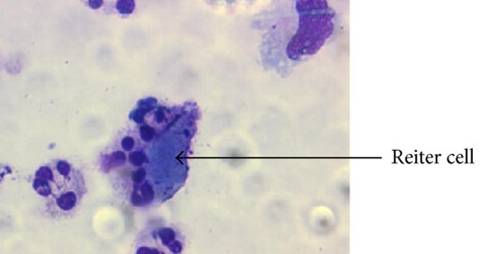
macrophage containing ingested nuclei of a neutrophil
describe what a RA cell looks like in synovial fluid
isn't a single distinct cell type, but rather refers to neutrophils, which are the predominant inflammatory cells found in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fluid
what crystal is this and name characteristics/what it signifies
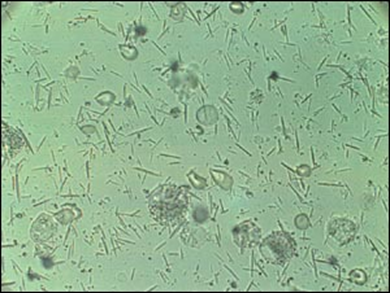
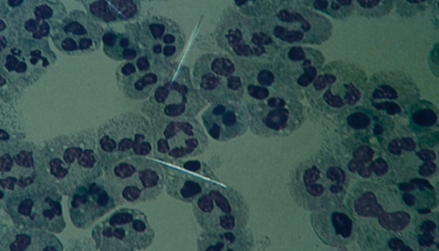
Monosodium urate (MSU)
needle shaped
negative birefringence
appear yellow when oriented parallel to the compensator's slow axis
gout
what crystal is this and name characteristics/what it signifies
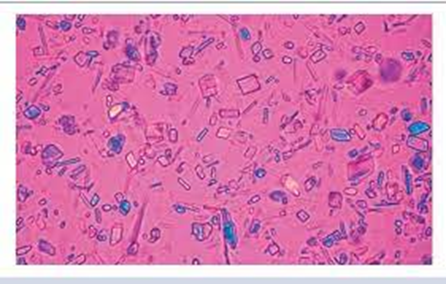
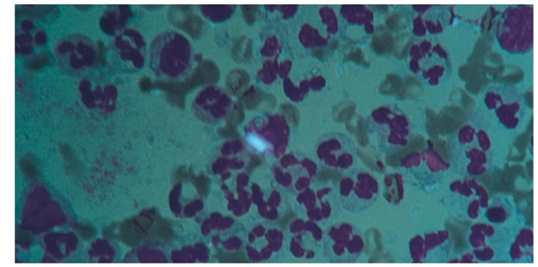
Calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate crystals (CPPD)
rhomboid, square, rods
positive birefringence
appear blue when parallel to the slow axis
pseudogout
what crystal is this and name characteristics/what it signifies
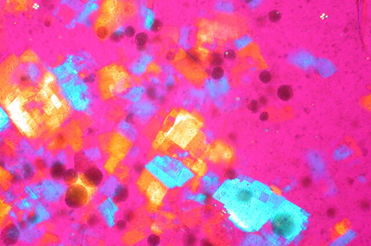
cholesterol crystals
notched, rhomboid plates
negative birefringence
chronic inflammation from patients with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis
what crystal is this and name characteristics/what it signifies
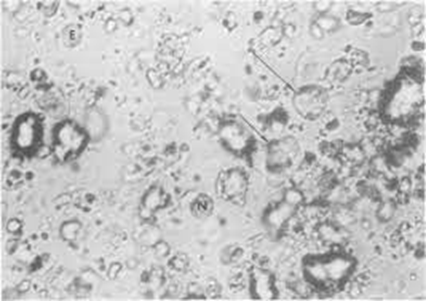

corticosteroid crystals
flat, variable-shaped plates
positive and negative birefringence
present after intra-articular injections
what crystal is this and name characteristics/what it signifies

calcium oxalate crystals
envelope shaped
negative birefringence
seen in patients on renal dialysis
what crystal is this and name characteristics/what it signifies
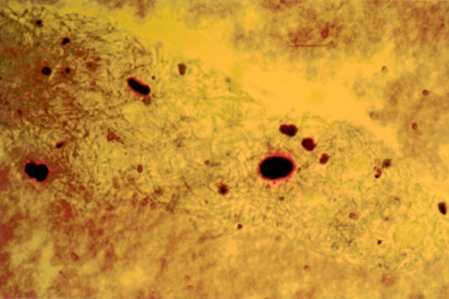
apatite crystals
small particles (require electron microscopy)
no birefringence
osteoarthritis or calcified cartilage degeneration
if synovial glucose is < 10 mg/dL than serum glucose levels, this is considered ____ and indicates _____.
normal
if synovial glucose is 10-20 mg/dL less than serum glucose levels, this is considered ____ and indicates _____.
abnormal; osteoarthritis, pigmented villonodular synovitis, trauma
if synovial glucose is 0-40 mg/dL less than serum glucose levels, this is considered ____ and indicates _____.
abnormal; inflammatory disorders
if synovial glucose is 20-100 mg/dL less than serum glucose levels, this is considered ____ and indicates _____.
abnormal; infections and crystal-induced
elevated lactate levels above 9 mmol/L (81 mg/dL) indicate _____?
bacterial arthritis
GPC or GNB
List four genera of bacteria found most frequently in synovial fluid.
•Staphylococcus
•Streptococcus
•Haemophilus
•N. gonorrhoeae
list 4 microorganisms in synovial fluid that require PCR testing for detection
Borrelia burgdorferi (tick bite)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Chlamydia trachomatis
N. gonorrhoeae
Describe the relationship of serological serum testing to joint disorders
serological testing plays an important role in the diagnosis of joint disorders.
•Most of these tests are performed on serum, synovial fluid is a confirmatory measure