Bloop Vessels
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
tunica externa
connective tissue, collagen fibers
tunica media
smooth tissue, elastic tissue, contracts, controls blood pressure
tunica interna
epithelial tissue, elastic tissue, simple squamous
lumen
thing in middle of vessel
veins
small walls, big lumen, contain valves, return blood to heart
arteries
big walls, smaller lumen, pushes blood away from heart
cappilaries
just tunica interna, where materials leave/enter blood
things that impact blood pressure
stress, salt, fats, exercise, sleep
cardiac output
how much blood leaves the heart in one minute, heart rate x stroke volume
resistance
force against bloodflow, generates blood pressure
barorecptor
pressure receptor in vessel, tells brain blood pressure is going up
brain response to baroreceptor
can tell artery to dilate or heart to slow down
adrenaline affect on blood pressure
increases
most important for long term blood pressure
kidney
why kidney is most important
high sodium → body retains water → higher blood volume → higher blood pressure
sphygomomanometer
measures blood pressure
korotkot sounds
sounds arteries make while taking blood pressure
hypertension
high blood pressure, 140/90
hypotension
low blood pressure, 100/60
pulse
wave of high presssure
blood pressure
force blood pushes into the arteries
diastolic pressure
low number in blood pressure
systolic pressure
high number in blood pressure
steps of using sphygmomanometer
place cuff centered on brachial artery
2. place stethoscope on brachial artery
3. inflate to 180 mmHg
4. let pressure fall 2-3 mmHg/sec
5. 1st sound is systolic pressure
6. when the sound stops is diastolic pressure
atheroscelerosis
accumulation of plaque in artery walls
coronary artery disease
plaque built up in coronary arteries (heart)
ischemia
lack of oxygen
angina pectoris
chest pain
congestive heart failure
heart wears out
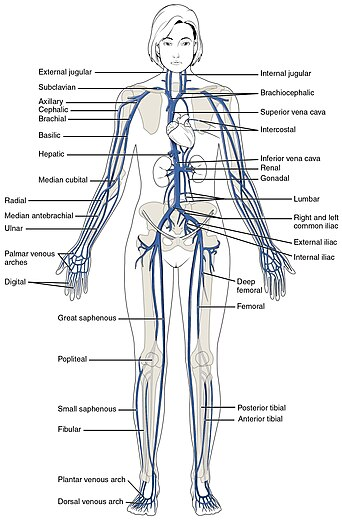
veins
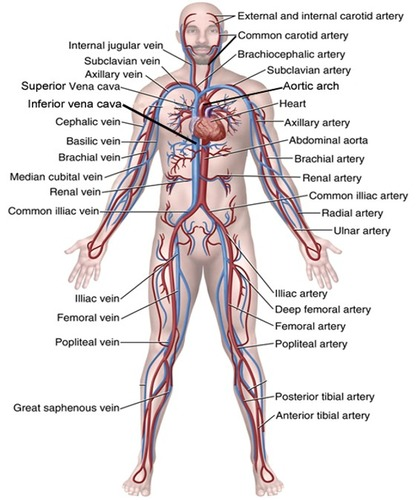
arteries
double-loop circuit
a circulatory system where blood passes through the heart twice and has two separate circuits, one for oxygenated blood and one for deoxygenated blood
pulmonary circulation
function to exchange blood and other tissue fluids between the heart, the lungs, and back
systemic circulation
provides the functional blood supply to all body tissue
Artery pressure compared to veins
higher
vein pressure compared to arteries
lower
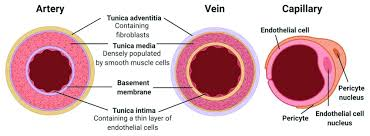
structures